ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. Blue Polemonium (Polemonium cаeruleum L.) is the only representative of the Lilac family, which is allowed for use in medical practice. Blue polemonium rhizomes with roots are used as an expectorant and sedative and are included in the State Pharmacopoeia XIV edition. The herb of the plant is used as a biologically active additive of sedative action, however, regulatory documentation for this type of raw material has not been developed so far.
Aim. Description of anatomical features required in the development of draft pharmacopoeial article for the formation of the section "Microscopy" and assessing the authenticity of plant raw materials "Polemonium cаeruleum herba".
Materials and methods. Several samples of blue polemonium, which were collected independently from cultivated plants (Polemonium cаeruleum L.) in 2022 and 2023 during the period of mass flowering on the territory of the Botanical Garden named after B. M. Kozo-Polyansky VSU (Voronezh), were used in this work. Microscopic analysis was performed in accordance with the requirements of the current regulatory documentation.
Results and discussion. It was found that epidermal cells of leaf, calyx and corolla of blue polemonium are twisted, elongated on peduncles. Trichomes are of two types. There are papillae-like outgrowths of epidermis along the leaf margin and on sepals. Mesophyll is represented by spongy tissue. The conducting system is predominantly of spiral thickening type. Stomata are of anomocytic type. Stem is rounded or with weakly expressed edges. Primary cortex of the stem is represented by collenchyma, storage parenchyma without inclusions, endoderm with Caspari girdles. The stem is of tubeless structure. Cambium consists of continuous rows of small cells. Phloem is represented by small cells, sieve tubes with satellite cells. Secondary xylem lacks heart-shaped rays, radially arranged vessels have thick walls. The medulla is represented by parenchyma cells with oil droplets. The petiole is triangular in outline with a deep notch at the top and long marginal outgrowths, where there is one small conducting bundle each. The central bundle is arc-shaped with inwardly curved edges with parenchyma lining. Conclusion. In the framework of the present study, anatomo-diagnostic features of blue polemonium herb were studied with the help of various methods of microscopic analysis. The obtained data will be used in the development of the draft pharmacopoeial article "Polemonium cаeruleum herb", namely for the formation of the section "Microscopy".
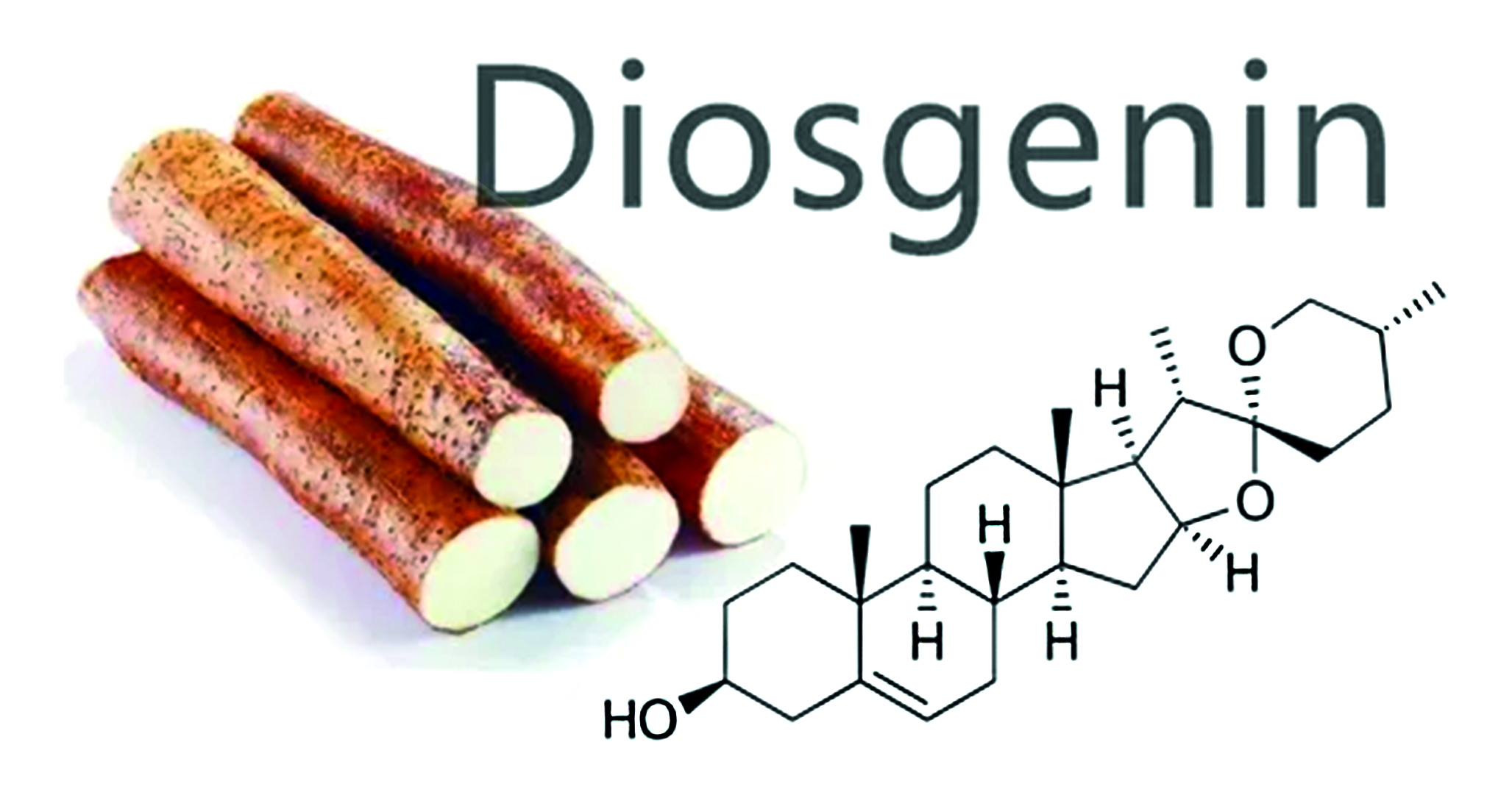
Introduction. The original article presents the results of an experimental study conducted using the method of high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) on plant samples – rhizomes with roots of Dioscorea caucasica Lipsky and Dioscorea nipponika Makino. These species of Dioscorea are used in various fields of medicine as fungicides, antimicrobials, and anti-sclerotic agents. The HPTLC method is used at the screening stage of plant samples for preliminary identification and densitometric quantitative determination of diosgenin in plant extracts.
Aim. Development of a HPTLC methodology for quantitative assessment of diosgenin content after acid hydrolysis of extracts in air-dried raw materials – rhizomes with roots of Dioscorea caucasica Lipsky and Dioscorea nipponika Makino.
Materials and methods. The extracts were obtained by preliminary degreasing and depigmentation of air-dried rhizomes with roots of the studied Dioscorea species using high-purity dichloromethane, followed by double extraction. The first extraction was carried out in a 50 % aqueous solution of isopropanol with ultrasonication, followed by acid hydrolysis of O-glycosidic bonds and evaporation. The second extraction was carried out by redissolving the dry residue in methanol; it was purified from suspended particles by filtration through syringe filters with a perforation diameter of 20 μm. HPTLC was performed on a «CAMAG» (Switzerland) apparatus using HPTLC Aluminum sheets Silica gel 60 F254 20 × 20 cm, which were cut to a size of 20 × 10 cm.
Results and discussion. After performing scanning densitometry at 366 and 542 nm, it was established that the chromatography of methanol extracts in a toluene-chloroform-acetone solvent system (2 : 8 : 2 v/v) allows for satisfactory separation and subsequent densitometric quantitative determination of diosgenin. The tracks of plant extracts from the rhizomes and roots of Dioscorea caucasica Lipsky and Dioscorea nipponika Makino were compared with a standard sample of diosgenin.
Conclusion. The study found that the content of the steroid sapogenin diosgenin in air-dried Dioscorea nipponica Makino raw material (286,4–296,3 μg/g) slightly exceeds its content in Dioscorea caucasica Lipsky raw material (257–277,1 μg/g). The quantitative values obtained, calculated separately for peak height and area, show good convergence, confirming the correctness of the method. The developed method of high-performance thin-layer chromatography with densitometric detection of diosgenin can be recommended for routine quantitative analysis of this compound in plant raw materials.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
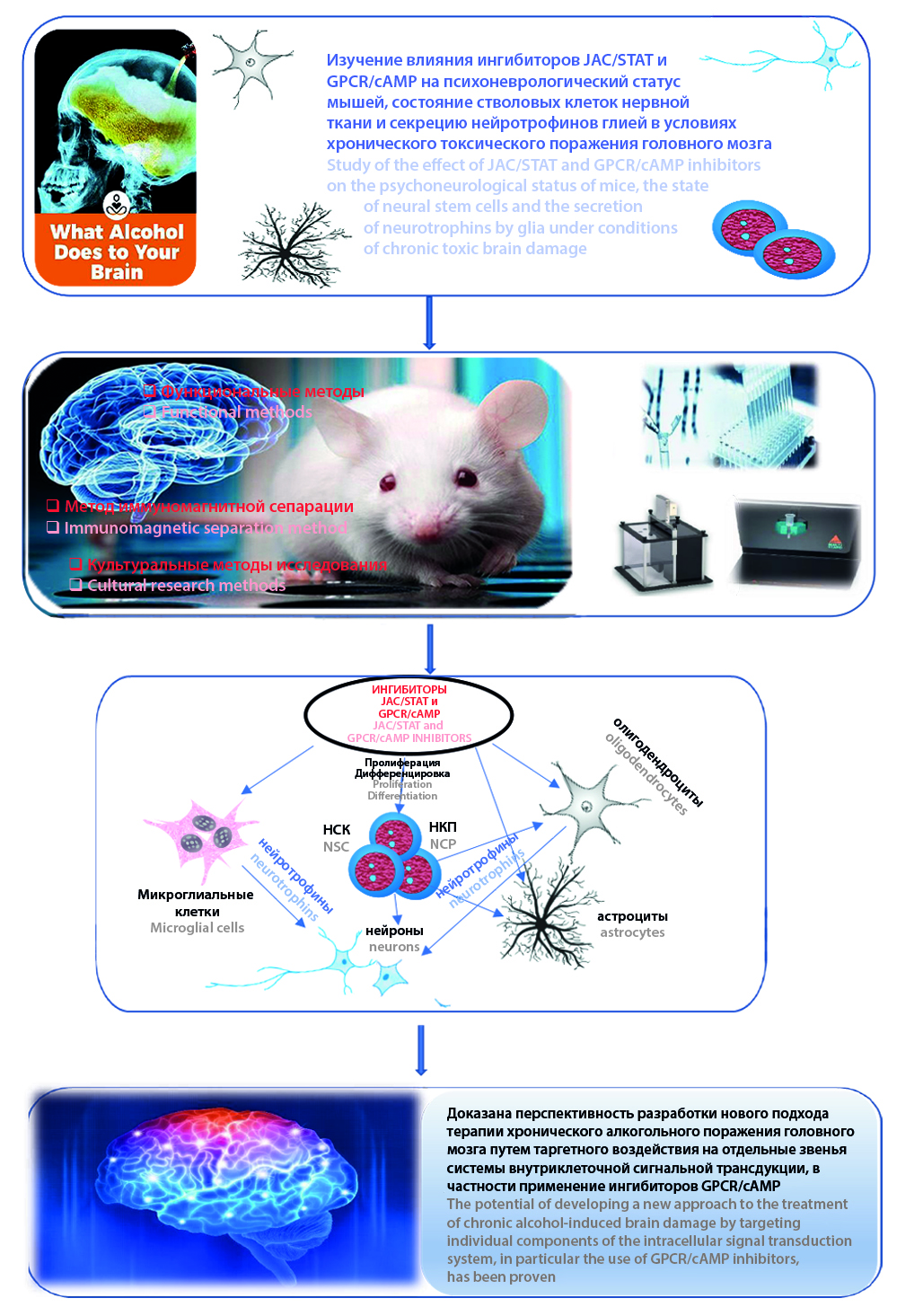
Introduction. Impaired central nervous system function resulting from chronic ethanol consumption is often associated with suppressed neurogenesis. The GPCR/cAMP-dependent pathway and JAK/STAT signaling are considered to be among the key signaling cascades involved in regulating the proliferation and differentiation of neural and neuronal stem cells. Clearly, the search for fundamentally new approaches to treating ethanol-induced neurodegeneration by targeting intracellular signaling molecules is highly relevant and in demand in practical medicine.
Aim. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of JAC/STAT and GPCR/cAMP inhibitors on the psychoneurological status of mice, the state of neural stem cells, and the secretion of neurotrophins by glia under conditions of chronic toxic brain injury.
Material and methods. The studies were conducted on 90 C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol-induced neurodegeneration was modeled by per os administration of 30 % C2H5OH solution at a dose of 3 g/kg/day for 8 weeks. JAC/STAT and GPCR/cAMP inhibitors were administered subcutaneously once a day for 7 days at a dose of 15 and 10 μg/kg, respectively. The psychopharmacological effects of the blockers were assessed in the open field test and by the degree of preservation of the conditioned passive avoidance reflex. The content of neural stem cells and committed neuronal precursors in the subventricular zone of the brain, their proliferative activity and maturation intensity were studied using cultural methods; the production of neurotrophic factors by glial cells was investigated.
Results and discussion. The introduction of JAC/STAT and GPCR/cAMP inhibitors corrected the functional signs of alcoholic brain pathology (changes in exploratory behavior were abolished). At the same time, the course use of a GPCR/cAMP inhibitor leveled out, and the introduction of a JAC/STAT blocker aggravated the decrease in the level of reproduction of the conditioned passive avoidance reflex in alcoholized mice. In the groups of animals receiving JAC/STAT and GPCR/cAMP inhibitors, an increase in the number of neural stem cells and committed neuronal precursors was observed, accompanied by an increase in their mitotic activity and intensity of specialization. The introduction of a GPCR/cAMP inhibitor after modeling ethanol-induced brain damage was accompanied by an increase in the secretion of neurotrophins by astrocytes and microglia.
Conclusion. The obtained results indicate the prospects of developing a new approach to the treatment of chronic alcohol-induced brain damage by targeting individual links in the intracellular signal transduction system, in particular, the use of GPCR/cAMP inhibitors.
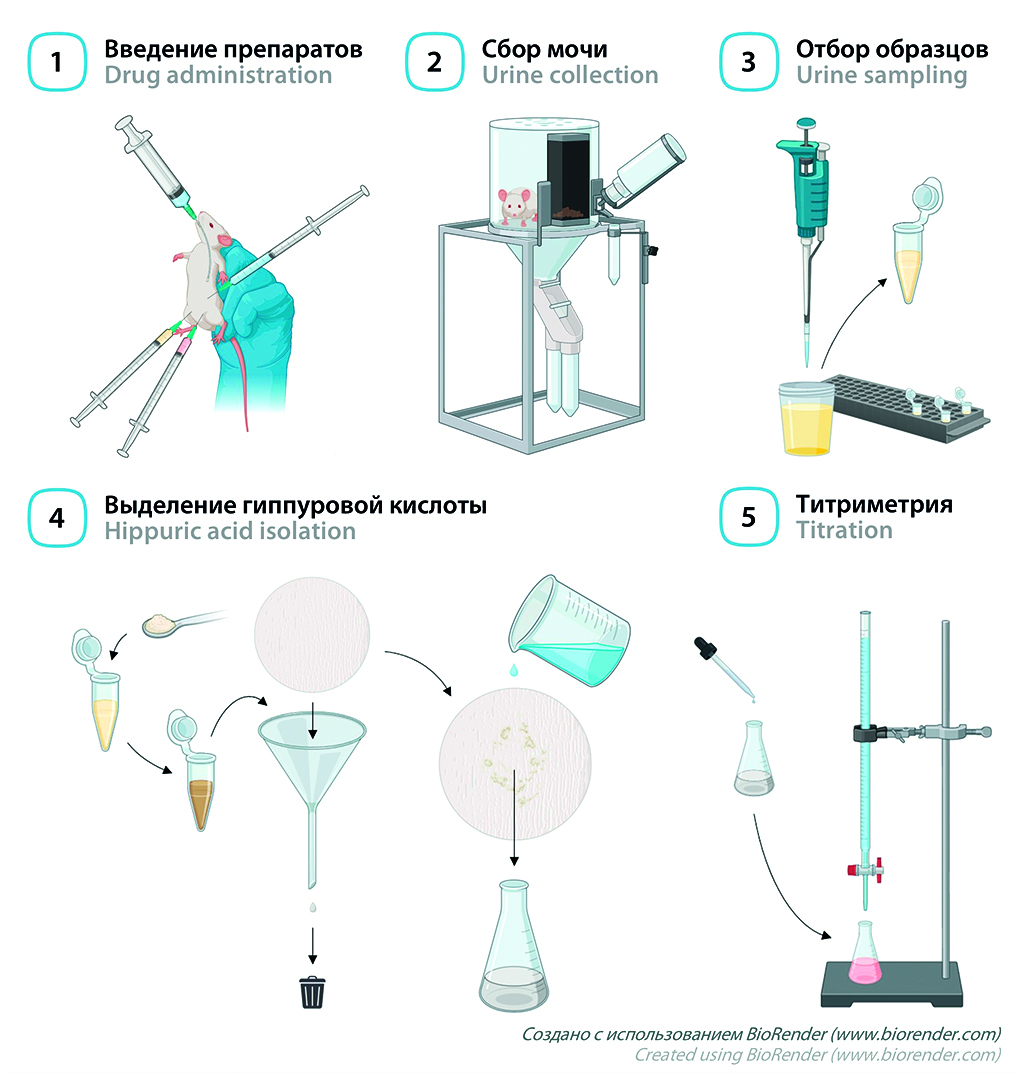
Introduction. Functional liver tests are a relevant group of methods for liver function screening, that can be used in a laboratory setting as well as in clinical practice. This group includes, among others, the Quick – Pytel test, which is based on the enzymatic formation of hippuric acid from glycine and benzoate in the liver. This test is minimally invasive and comparatively ease to perform, yet as of now, there is no detailed protocol to carry it out in small laboratory animals.
Aim. The objective of this work was to develop a protocol of the Quick – Pytel test to assess liver antitoxic function in small laboratory animals.
Materials and methods. Loading doses of sodium benzoate and glycine at an equimolar ratio (504 mg/kg and 264 mg/kg, respectively) were administered intraperitoneally to white outbred male mice (n = 10), after which urine samples were collected over 18 h in metabolic cages. Following sample preparation, the newly formed hippuric acid was titrated by 0.01 N potassium hydroxide in the presence of 1 % phenolphthalein. In 1 week, the mice were injected with carbon tetrachloride (1 mL/kg) to induce acute toxic hepatitis, and the test was repeated. Liver injury was confirmed morphologically with haematoxylin and eosin staining.
Results and discussion. Following carbon tetrachloride administration, urinary concentrations of hippuric acid decreased significantly (p < 0.01) by over 50 % from baseline. Liver samples exhibited characteristic features of acute toxic hepatitis.
Сonclusion. We have developed a protocol of the Quick – Pytel test in mice and confirmed its applicability to assess liver antitoxic function under acute injury conditions. The method we describe is simple and straightforward, is relatively low-cost, and can be used in routine practice to assess liver function in small laboratory animals.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
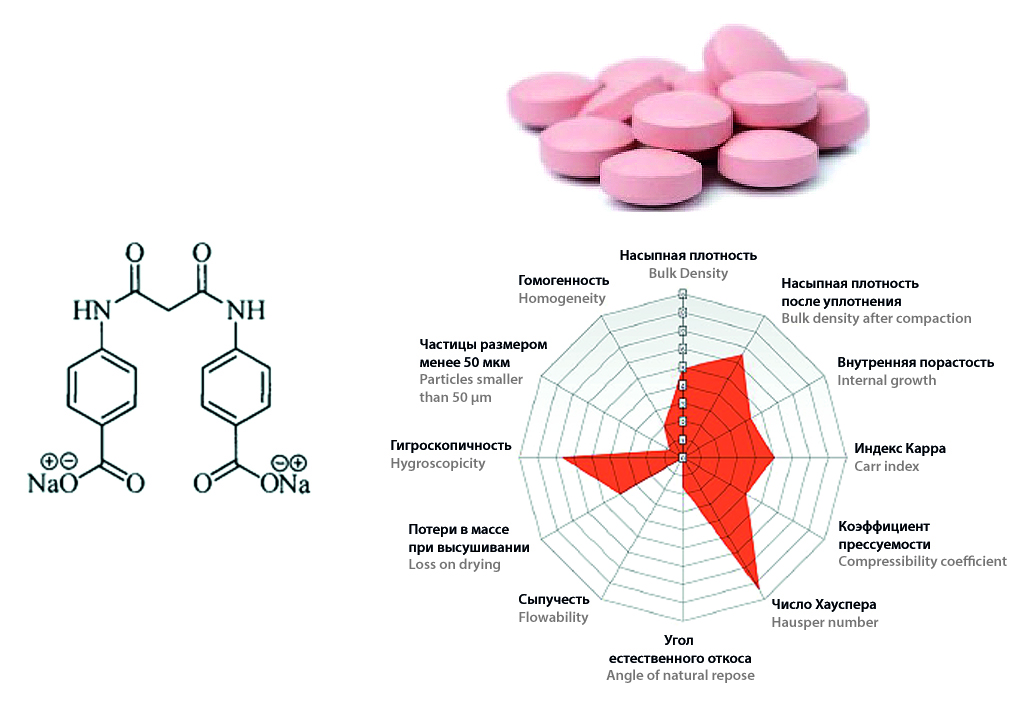
Introduction. Pharmaceutical development is a complex work, the main goal of which is to achieve the quality target product profile (QTPP). QTPP is formulated on the basis of a whole set of requirements for the drug, including pharmacopoeial, consumer, pharmacological, etc. The traditional empirical approach to the development of the composition and technology of the dosage form in this case seems to be labor and resource-intensive, while it does not fully achieve an understanding of all processes both from the point of view of technology and from the point of view of further stages of the life cycle of the drug. The Quality by Design (QbD) approach allows you to assess the impact of factors on processes, which, in turn, contributes to proactive risk management and the creation of robust technologies.
Aim. Demonstrate the comprehensive use of QbD tools, including expert systems (Sediment Delivery Model, SeDeM), experimental planning (Design of Experiment, DoE) and risk analysis, using the example of the development of prolonged-release tablets based on sodium 4,4’-(propanediamido)dibenzoate.
Materials and methods. The paper uses the original active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) – sodium 4,4’-(propanediamido) dibenzoate, modern excipients and polymers that provide prolonged release (ethylcellulose, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, etc.). At the first stage, the SeDeM method was used to design the compositions. In the second step, screening DoE was used to optimize the release profile
Results and discussion. The SeDeM method made it possible to quantify and neutralize the risks associated with the unsatisfactory technological properties of the API. Compositions with satisfactory technological properties were designed and experimentally confirmed. As a result of DoE, it was found that HPMC provides the most complete and uniform release (more than 80% in 12 hours), close to zero-order release kinetics.
Conclusion. The comprehensive use of QbD tools made it possible to effectively and reasonably develop a robust composition of prolonged-release tablets based on sodium 4,4’-(propanediamido) dibenzoate, providing both the required technological properties and the required release profile.
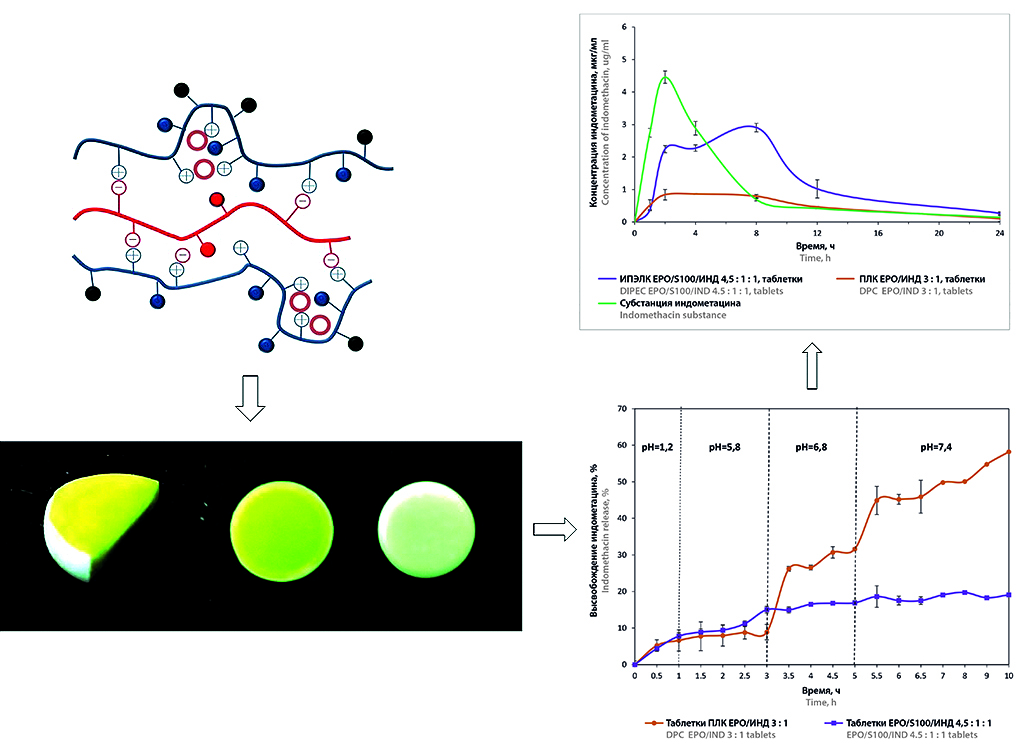
Introduction. Interpolyelectrolyte complexes (IPEC) are promising carriers for controlled drug delivery systems. The introduction of ionic API into delivery systems can lead to the formation of bonds with polyelectrolytes, which affects the release of the drug from the dosage form. Previously, a drug-polymer complex (DPC) based on Eudragit® EPO with indomethacin, as well as an drug-interpolyelectrolyte complex (DIPEC) with the participation of copolymers of Eudragit® EPO, Eudragit® S100 and indomethacin were obtained. The physicochemical properties of the optimal samples were assessed and the prospects for their use in controlled delivery systems of indomethacin were shown.
Aim. Comparative biopharmaceutical evaluation of drug-polymer and drug-interpolyelectrolyte complexes as oral controlled delivery systems for indomethacin.
Materials and methods. Drug-polymer complex based on Eudragit® EPO and indomethacin (DPC EPO/IND) and druginterpolyelectrolyte complex based on Eudragit® EPO, Eudragit® S100 and indomethacin (DIPEC EPO/S100/IND) were obtained at the molar ratio of components of 3 : 1 and 4.5 : 1 : 1, respectively. The release of indomethacin from DPC and DIPEC powders and tablets was assessed by apparatus II "Rotating Paddle" using a DT 828 dissolution tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany). The concentration of indomethacin was determined by UV spectrophotometry on a Lambda 25 spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, USA) at a wavelength of 270 nm. Mathematical modeling of indomethacin release was performed using Microsoft Excel Office. Pharmacokinetic studies were performed on Soviet Chinchilla rabbits. The studied samples were administered orally, blood samples were taken from the ear at certain intervals of time after administration. The concentration of indomethacin in blood plasma was determined by HPLC on an LC-20 Prominence chromatograph (Shimadzu, Japan) with UV-detection. The main pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using the Thermo Kinetica® program (Version 5.0, Build 5.00.11; Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA).
Results and discussion. The release profiles of indomethacin from DPC and DIPEC powders are characterized as "intestinal type", where the predominant mechanism is the process of relaxation of polymer chains during the release of the substance. The release of indomethacin from the tablet matrix based on DIPEC differs from the release profile from DIPEC powder and reaches 19 %. The release profile of indomethacin from DPC EPO/IND tablets is similar to the release profile from the powder and reaches 58 %. A hydrogel layer is formed on the surface of DIPEC tablets, which prevents the penetration of the dissolution medium into the matrix. The release of indomethacin from DIPEC EPO/S100/IND samples occurs due to the diffusion of the drug from the matrix. DPC and DIPEC in powder form have a longer mean retention time (MRT) compared to DPC and DIPEC tablets. MRT of DIPEC and DPC in powder form exceeds MRT of indomethacin substance by three and four times, respectively. Maximum concentration of indomethacin in blood plasma of rabbits after oral administration of DIPEC tablets is observed after 8 hours of the experiment.
Conclusion. Indomethacin release from DPC EPO/IND occurs due to the presence of "defective" regions and relaxation of polymer chains, this ensures a slow release of the API and low relative bioavailability, which allows using DPC in indomethacin delivery systems for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the colon. Tablet systems DIPEC EPO/S100/IND allow changing the release profile of indomethacin due to the diffusion processes of the substance through the formed hydrogel layer on the surface of the matrix, ensuring high bioavailability, can be used as matrix systems for delivering the API to the optimal absorption zone.
ANNIVERSARY
OBITUARY
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)