FROM EDITOR
"Center for Pharmaceutical Analytics" received the status award "Industry Leader 2023" and the corresponding certificate from the All-Russian Business Rating.
EVENTS
The Congress "Drug development & registration" will be held in Moscow in a hybrid format on February 27 and 28, 2024. The congress program consists of several sections, where we will talk about the pharmaceutical development of original and generic drugs, non-clinical and clinical studies conducted in accordance with the EAEU rules. Also we will talk about technology transfer as well as drugs' manufacturing technologies and regulatory rules.
Moscow, September 7, 2023, the seminar "Drug development and registration in the EAEU and the Russian Federation – current achievements and a strategic view to the future" was held.
On September 22, the congress “Chemical-pharmaceutical and biological preparations: pharmaceutical and clinical development according to the rules of the EAEU” was held in the building of the congress center of Sechenov University in Moscow. The conference is traditionally organized by the Center for Pharmaceutical Analytics LLC and the journal Drug development & registration. The event was attended by 149 visitors.
The main topics of the business program were approaches to regulating of drug circulation, industry education, interdepartmental interaction, a scientifically based approach to the drug manufacturing, licensing, ensuring compliance with the requirements of GMP rules, pharmaceutical engineering, and typical nonconformities during pharmaceutical inspections.
Representatives of relevant ministries and industry experts discussed the readiness of Russian industry to meet the needs of the healthcare system.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
Introduction. The use of radiopharmaceuticals for targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT), the efficacy of which was established during clinical trials, is safe and effective for various pathological conditions, including cancer. The main feature of therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals (RPs) is the use of β–- and α-emitting radionuclides (RNs) in the finished dosage form (FD). Among the radionuclides used for radionuclide therapy, lutetium-177 is currently one of the most popular in clinical practice because of its chemical and nuclear characteristics. The list of RPs based on lutetium-177 is constantly expanding, and Lutathera® ([177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE) and Pluvicto™ ([177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617) have been approved for clinical use in several countries.
Text. Because of the high activity of RNs in a single dose of therapeutic RPs (up to 8 GBq in a monodose for 177Lu), ionizing radiation of the used RNs leads to a decrease in RPs quality owing to radiolytic degradation of the vector molecule. This leads to a decreased specific accumulation of radioactivity in the foci of pathology, reduced therapeutic effect, and potentially increases the risk of radiotoxicity to non-target organs and tissues. The degree and intensity of radiolytic degradation of the vector molecule and, consequently, the shelf life of RPs depend on many factors, among which the activity concentration of the radionuclide in the preparation, its half-life, and the energy of the emitted particles are the most important. To suppress the effects of radiolysis, various excipients with antioxidant (radioprotective) properties were introduced into the compositions of the finished dosage forms. Among the substances studied, the most popular were gentisic acid, ascorbic acid, and ethanol. In this work, the advantages and disadvantages of various antioxidants and their combinations used in therapeutic RPs were considered in lutetium-177 preparations.
Conclusion. Selection of the optimal composition of the dosage form is an urgent task, as it will ensure high-quality RPs both at the time of preparation and during the shelf life and delivery to the end user, which will greatly facilitate the use and centralized supply of therapeutic RPs. The necessity of creating a unified approach for the selection of antioxidants at the pharmaceutical development stage of radiopharmaceuticals is shown. For this purpose, an approach combining studies of radical reaction kinetics with studies of radiation-chemical yields of radiolysis products under identical or maximally similar conditions with subsequent verification of the stability of RPs dosage form seems to be very promising and has proven to be effective. In contrast, the empirical approach, which implies the selection of radioprotectors based on a direct study of their influence on the preservation of the level of radiochemical purity, is suboptimal because of the high market value of both radionuclides and non-radioactive precursors.
Introduction. Cell cultures spreads widely in different areas of biology, biotechnology and agriculture. Aralia cordata is a perennial herbaceous plant, which has been listed in Red book of the Russian Federation. Pharmaceuticals which are based on raw materials of Aralia ssp. have valuable types of pharmacological activity and are widely used in oriental medicine. A serious obstacle for resumption of the natural populations is the presence of the period of morphophysiological dormancy in the seeds of the plants, which requires a long-time stratification process. Limitation of the natural geographic range and the combination of biological activities useful for humans make Aralia cordata Thunb. prospective object for in vitro introduction.
Aim. The aim of the study is obtaining of the viable cell culture of Aralia cordata Thunb., investigation of the somatic embryogenesis conditions.
Materials and methods. Pieces of the leaves of Aralia cordata intact plant from Komarov Botanical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences were used as a primary explants. Pieces of leaves were sterilized in a 2 % benzalkonium chloride solution for 5 minutes, induction of primary callogenesis was carried out on Murasige – Skoog medium. Nutrient media with different constituents were discovered for choosing one for long-time cultivation of calli. Induction of somatic embryogenesis was carried out on the nutrient media with high auxins content. Ethanol extracts from the intact plant and calli cultures were assayed with HPTLC PRO SYSTEM (CAMAG AG, Switzerland).
Results and discussion. After two weeks of cultivation, the formation of primary callus was observed on the surface of the explants. The Linsmaier – Skoog medium with a reduced amount of sucrose (20 g/l) was recognized as the most suitable medium for long-term maintenance of cultures. Embryoid structures of Aralia cordata have been obtained, now we are continuing to collect analytics data about this process. Qualitative analysis of the extracts showed that callus cultures accumulate triterpene glycosides, their composition is close to that of the intact plant.
Conclusion. A viable strain of callus culture of Aralia cordata Thunb. was obtained, a nutrient medium for long-term cultivation of calli was established. Somatic embryoids have been obtained, and their further development is currently being monitored. A preliminary phytochemical study showed that the composition of the chemical components of calli is close to that of an intact plant.
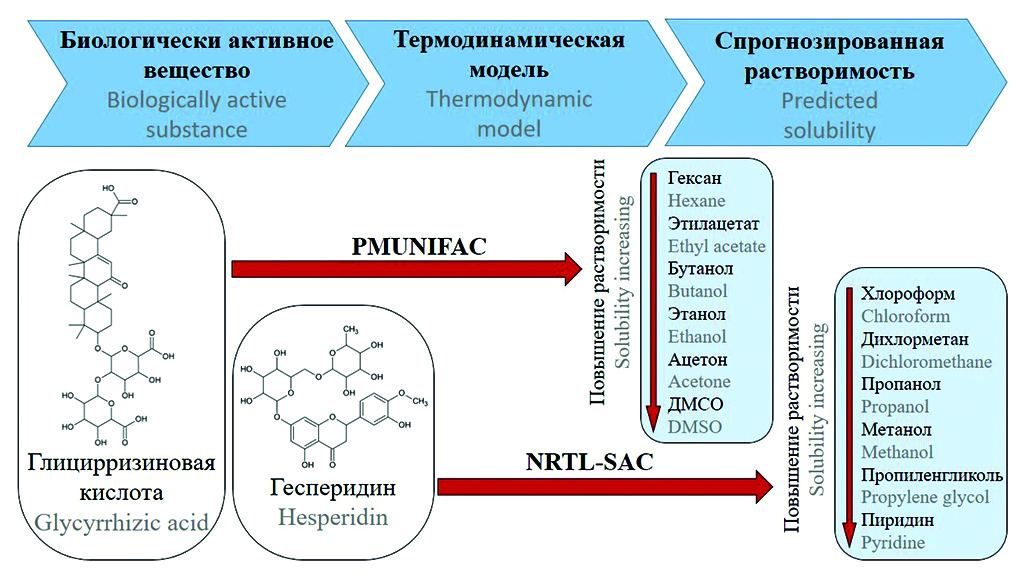
Introduction. The choice of solvents for the processes of extraction of biologically active substances from natural raw materials, the processes of purification of natural and synthesized substances by extraction, crystallization and dissolution methods is an important problem of the modern pharmaceutical industry, because a large number of experiments must be performed to determine the optimal solvent or mixture of solvents. To reduce the cost of developing and optimizing the extraction and purification of substances stages, it is proposed to use thermodynamic models at the stage of preliminary solubility assessment. The article investigates predicting the solubility of pharmaceutical substances issue on the example of the technology for isolating hesperidin and glycyrrhizic acid from plant materials.
Aim. Theoretical determination of the dissolving power of various solvents with respect to hesperidin and glycyrrhizic acid.
Materials and methods. The PMUNIFAC and NRTL-SAC thermodynamic models were used to predict solubility. The solubility calculation for the NRTL-SAC model was performed using Aspen Properties V14 software, and for the PMUNIFAC model using PTC Mathcad Prime V6. To evaluate the results obtained using thermodynamic models, a number of experiments were carried out, the object of which was the peel of an orange (dried flavedo and albedo, the degree of grinding is 0.2–0.5 mm, the moisture content is 8 %). The quantitative content of hesperidin was determined by direct spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 290 nm. Statistical data processing was performed using Minitab v20 software (Minitab Inc., USA), differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results and discussion. On the basis of thermodynamic models, the prediction of the solubility of hesperidin and glycyrrhizic acid was made. It has been shown that the solubility can be assessed both in the presence of solubility data according to the NRTL-SAC model, and in their complete absence according to PMUNIFAC. The correspondence of the theoretically calculated data to the experimental data confirms the correctness of the calculations of thermodynamic models. The results of the calculations are evaluated and solvents are recommended that can be used in the technology of isolating hesperidin and glycyrrhizic for the stages of degreasing, extraction and crystallization with the antisolvent.
Conclusion. Using the NRTL-SAC and PMUNIFAC thermodynamic models, the dissolving power of various solvents with respect to hesperidin and glycyrrhizic acid was determined. From the calculation results, a list of solvents was built, ranked by the solubility of the studied substances in them. The resulting list can be used in the development of an industrial technology for the isolation and purification of hesperidin and glycyrrhizic acid. It is shown that the NRTL-SAC and PMUNIFAC models have good prospects for quantitative prediction of the solubility of active substances.
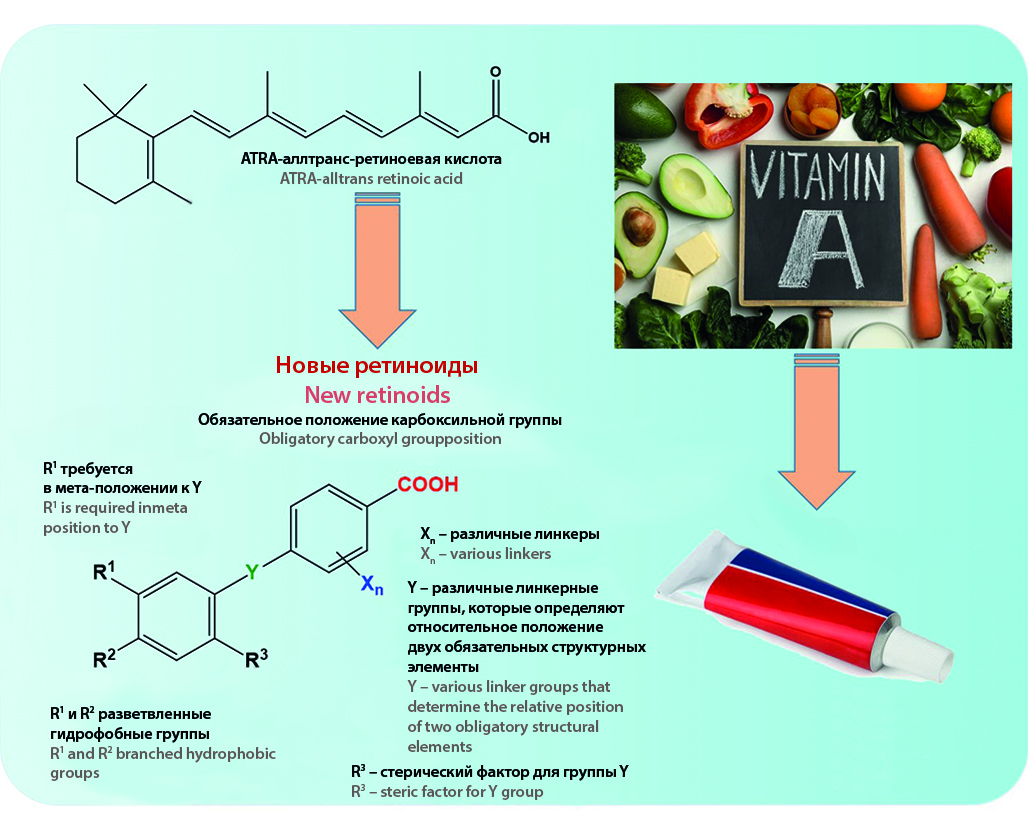
Introduction. Retinoids are a group of endogenous and synthetic substances that regulate numerous important biological processes in normal development. The synthesis and study of the biological activity of new retinoids are a promising area of chemical biology.
Text. The genomic functions of retinoids are mediated by their nuclear receptors RAR(α, β, γ) and RXR(α, β, γ), which regulate gene transcription by recruiting corepressors and coactivators. Retinoids also possess non-genomic functions by acylating proteins and other biomolecules. Regenerative medicine and stem cell biology are advanced areas of research in the biological activity of retinoids. Endogenous and synthetic retinoids are used for the treatment of skin pathologies and in oncology. There is evidence of their potential use in the therapy of lung diseases. The development of retinoids with high selectivity towards specific receptors and tissues may open new approaches to the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and others. Retinoids are necessary for the functioning of the immune system and are powerful immunomodulators. Additionally, retinoids have the potential for the therapy of various proliferative diseases.
Conclusion. Long-term studies of the pharmacological activity of retinoic acid and its structural analogs aim to investigate and establish the precise mechanisms of their actions, as well as their involvement in the pathogenesis of various diseases. The synthesis of retinoids aims to design compounds with high selectivity towards specific receptors, which would exclude the multitarget action of natural regulatory molecules and the associated side effects. Synthetic retinoids devoid of teratogenic and other side effects can find application as therapeutic agents for the treatment of metabolic disorders, various malignancies, as well as kidney, lung, and CNS diseases. Furthermore, the development of prodrugs based on retinoids with controlled release of active molecules is also a promising direction in this field of medicinal chemistry.
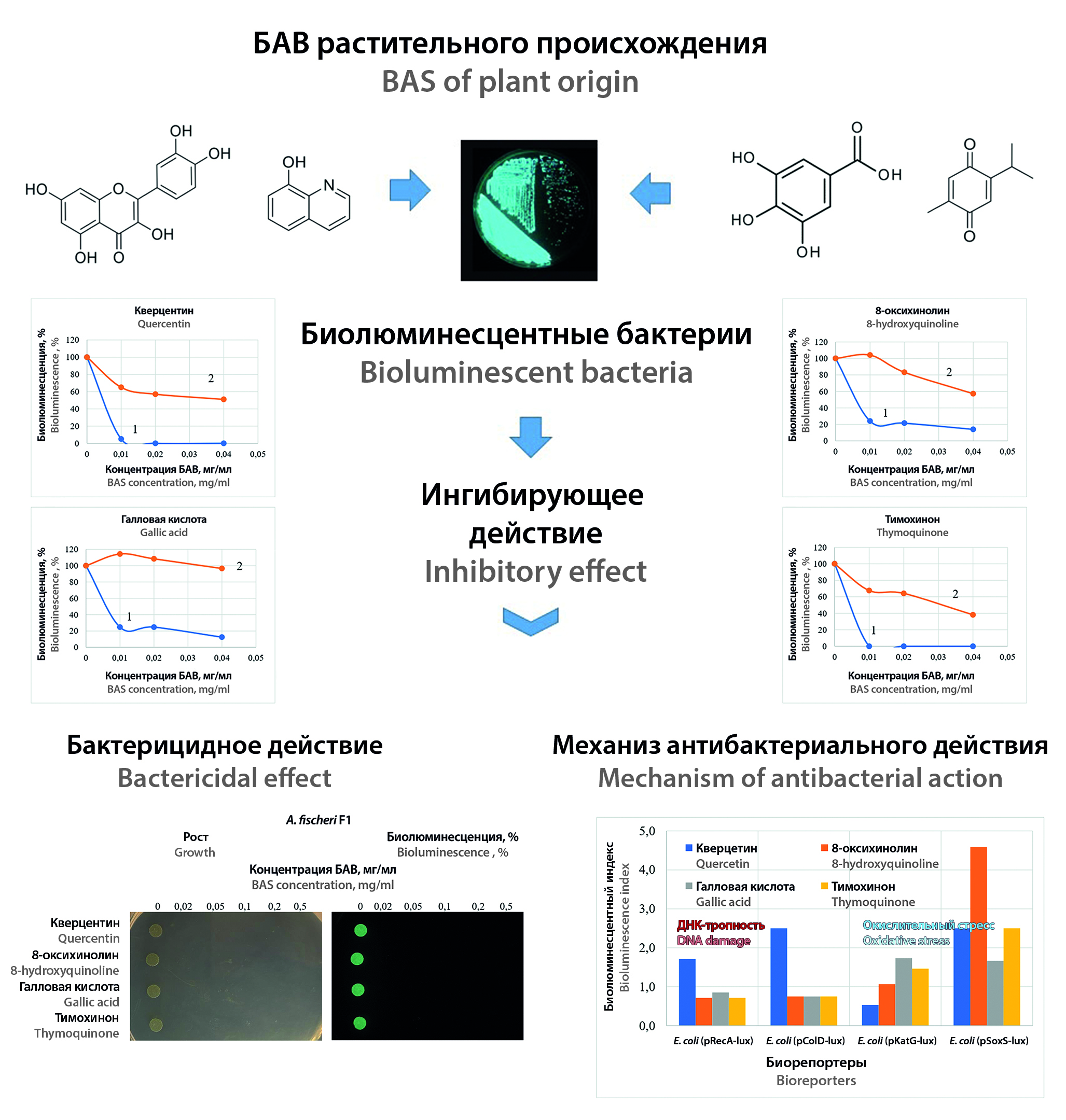
Introduction. Currently, the search for new antibacterial substances is an urgent task due to the growing resistance of pathogens to existing antibiotics. One of the key directions in this area is the expansion of scientific research of medicinal plants, as new sources of therapeutic agents. This article examines the possibility of using highly sensitive bioluminescent test bacteria for these purposes, which can quickly detect non-specific antimicrobial activity and can be adapted to highly effective pharmaceutical screening technologies.
Aim. To study the applicability of bioluminescent bacteria for the analysis of the antibacterial activity of biologically active substances (BAS) of plant origin.
Materials and methods. BAS quercetin, 8-hydroxyquinoline, gallic acid and thymoquinone, which are often found in medicinal plant raw materials and with which its antibacterial properties are associated, were used in the work. Bacteria with constitutive bioluminescence Aliivibrio fischeri F1 and Escherichia coli (pXen7), as well as recombinant bioreporter strains with inducible luminescence were used as test-objects: E. coli (pRecA-lux), E. coli (pColD-lux), reacting to nucleic acid damage; E. coli (pKatG-lux) and E. coli (pSoxS-lux), sensitive to oxidative stress.
Results and discussion. It was found that the nonspecific antimicrobial activity of the studied BAS is manifested in the inhibition of bacterial bioluminescence of test-strains with constitutive glowing. It was noted that the marine test-bacteria A. fischeri F1 have significantly greater sensitivity to the action of BAS, compared with the recombinant strain of E. coli (pXen7). It has been shown that their inhibitory effect begins at concentrations of 2 mcg/ml, and bactericidal activity occurs at concentrations of more than 20 mcg/ml. The results obtained are compared with the data on MIC and MBC of gram(+) and gram(–) pathogens. The study of the induction of bioluminescence of recombinant bioreporter strains showed that the antibacterial effect of the BAS is accompanied by oxidative stress. Also, quercetin caused activation of luminescence in E. coli (pRecA-lux) and E. coli (pColD-lux), which may indicate its participation in damage to nucleic acids. Analysis of the induction factors of bioreporter strains indicates that the revealed mechanisms of antibacterial activity are not major, but may be of a secondary nature.
Conclusion. It has been shown that the intensity of the glow of natural and recombinant bioluminescent bacteria can be an indicator of the antibacterial activity of BAS of natural origin. The high sensitivity of A. fischeri F1 bacteria to the action of substances such as quercetin, 8-hydroxyquinoline, gallic acid and thymoquinone has been shown. Considering that bioluminescence analysis is a quantitative instrumental method, it can be easily adapted for high-throughput pharmaceutical screening. It has been shown that the luminescence intensity of natural and recombinant bioluminescent bacteria can be an indicator of the antibacterial activity of BAS of natural origin. The high sensitivity of A. fischeri F1 to the action of substances such as quercetin, 8-hydroxyquinoline, gallic acid and thymoquinone has been established. Taking in an account that bioluminescent analysis is a quantitative instrumental method, it can be easily adapted for high-throughput pharmaceutical screening.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. Improving the technologies for isolating and purifying biologically active substances from plant materials is an important task for the pharmaceutical, food and cosmetic industries. Technology development often requires changes to the design of existing equipment. During the modernization of equipment for the implementation of new technologies, it is possible to improve its configuration, which makes it possible to significantly increase the yield of active substances at minimal cost. To increase the efficiency of the process of isolating hesperidin from plant materials, we proposed to use a number of technological solutions. In particular, it is proposed to use mixing devices with the configuration of impellers obtained by computational fluid dynamics, when using a Soxhlet extractor to use a heated extraction chamber, by adding an external coil jacket, which makes it possible to regulate the temperature inside the extraction chamber to accelerate the processes of diffusion and mass transfer, and to select the solvent and extractant on the basis of thermodynamic models by calculation.
Aim. Improving the technology for isolating and purifying hesperidin from plant materials using modernized equipment.
Materials and methods. Flow distribution in extraction apparatuses was modeled using computational fluid dynamics methods. To evaluate the results obtained on the basis of modeling, a number of experiments were carried out, the object of which was the peel of an orange (dried flavedo and albedo, grinding degree 0.1–0.2 mm, moisture content 3.5 %). The quantitative content of the flavonoid complex in terms of hesperidin was determined by direct spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 290 nm, the quantitative content of hesperidin was determined gravimetrically. Statistical data processing was performed using Minitab v21 software (Minitab Inc., USA), differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results and discussion. Based on the methods of computational fluid dynamics, to intensify the processes of mixing and dissolution at the stages of preliminary degreasing of raw materials and extraction, a six-bladed impeller was designed, which makes it possible to accelerate these processes by creating axial and radial flows of fluid movement in a capacitive apparatus and maintaining raw materials in suspended state in the volume of liquid at low mixing speeds and energy consumption. Equipping the extraction chamber with a coiled jacket made it possible to significantly increase the solubility of the active substance and extract more of the target component in one extraction cycle. A technology for the isolation and purification of hesperidin was developed, and the parameters of the processes were determined and optimized.
Conclusion. As a result of the study, it was shown that it is possible to intensify the processes of extraction and dissolution of active substances by selecting mixing devices using the method of computational fluid dynamics. To isolate poorly soluble compounds from dense raw materials (roots, bark, etc.), a modification of the Soxhlet apparatus with a heated extraction chamber was proposed. Modernization of typical technological units made it possible to obtain the substance of hesperidin with a yield of up to 95 % and a purity of up to 90 % with a single recrystallization.
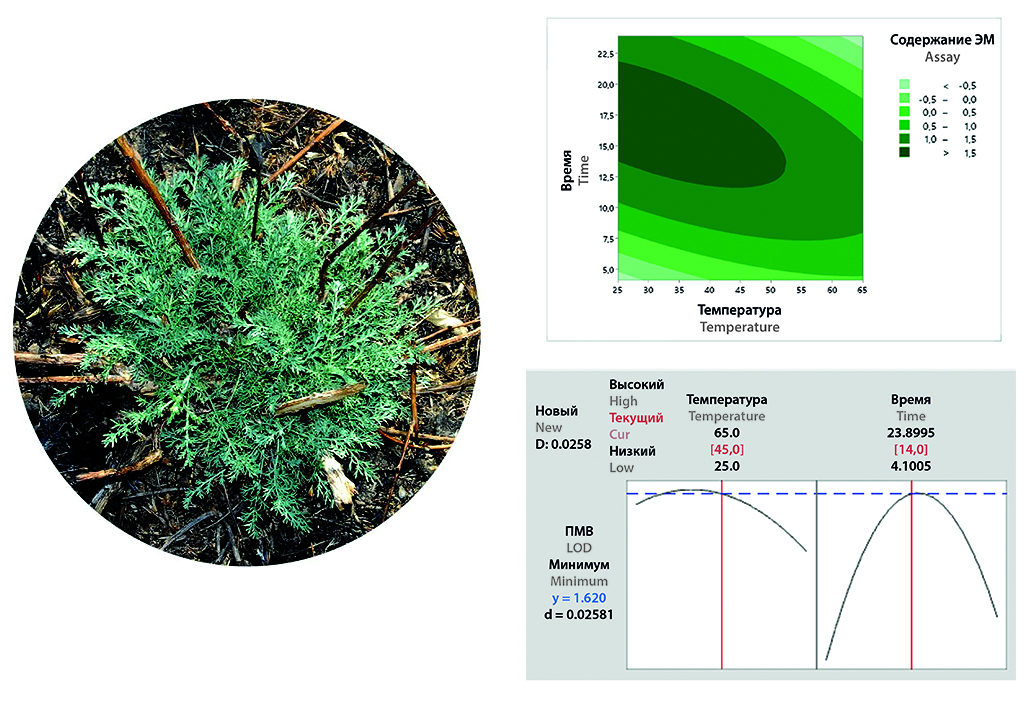
Introduction. Choosing the optimal method for drying medicinal plants is an important aspect of obtaining herbal materials of pharmacopoeial quality. At the site of the pharmaceutical enterprise Fitoleum LLP (Esik, Kazakhstan), a technology for obtaining herbal materials from autumn wormwood (Artemisia serotina Bunge) was developed, within the framework of which the optimal drying method was studied using IR radiation, convective drying and shadow drying in natural conditions. In parallel with the experimental approach, a method for simulating drying conditions was implemented. The development of technology for the obtaining of herbal materials is implemented using the "Quality by Design" concept, one of the principles of which is the modeling of experiments (Design of experiments, DoE). The advantage of modeling when studying the processes is that this technique allows you to simultaneously analyze several input parameters and their impact on quality indicators, while significantly reducing the number of experiments.
Aim. To choose the optimal method for drying autumn wormwood herb for further production of herbal medicine or herbal materials.
Materials and methods. During the experiment, the following equipment was used: a manual harvester for collecting plants, pallets or racks with a mesh bottom, infrared substrates, a convective drying oven, racks with pallets under a canopy in natural conditions, a grass cutter, vibrating sieves. Also, the study was carried out in accordance with the principles of the "Quality by Design" concept using the Minitab Statistical Software 21 program, using a statistical tool – Design of experiments (DoE).
Results and discussion. The results of studies of various drying methods have shown that the most optimal is drying with IR radiation, which allows to maintain the content of essential oils (the main group of biologically active substances) at the optimal level – about 1,7 % with a raw material moisture content of no more than 13 %. The data obtained by simulating the experiment in the Minitab program were comparable to the results of the classical experimental design. The optimal method and technological parameters for drying autumn wormwood have been established – the use of IR radiation, temperature of 35–45 °C and drying time of 14–17 hours. Comparable data on the studied technological parameters of three sequentially produced series were obtained and the validity of the technological process for drying autumn wormwood was confirmed.
Conclusion. Comparative analysis of the methods of drying medicinal plants – IR radiation, convective and shadow drying in natural conditions – of autumn wormwood (Artemisia serotina Bunge) was carried out. It has been established that the maximum content of essential oils (as the main group of biologically active substances) in raw materials is observed when using drying using IR radiation at a temperature of 35–45 °C for 14– 17 hours. At the same time, the residual moisture content of the drug is no higher than 13 %, which corresponds to pharmacopoeial requirements. Conducted studies of predicting optimal drying parameters using the Minitab Statistical Software 21 program showed comparability with the experimental results. Based on the results obtained, an optimal method for drying autumn wormwood herb was proposed for use in production and obtaining pharmacopoeial quality medicinal products.
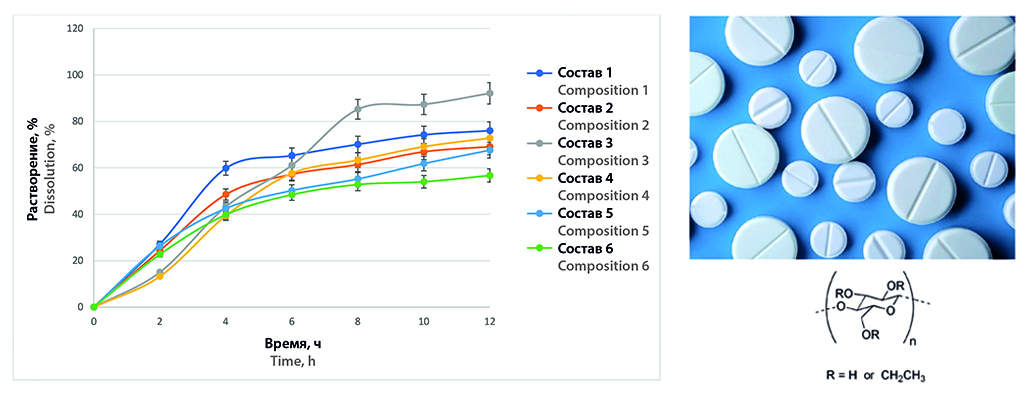
Introduction. Wet granulation technology is a process of directed particle aggregation of powder materials to obtain required properties of tablet masses and, as a consequence, to achieve satisfactory characteristics of tablets. In this addition, as a result of wet granulation technology, if special excipients are used, it becomes possible to control the rate and kinetics of release of active pharmaceutical substances from tablets to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.
Aim. To study the effect of matrix-forming components included in the composition of mixtures for granulation on the rate of release of sodium 4,4'-(propanediamido)dibenzoate from tablets.
Materials and methods. The original substance sodium 4,4'-(propanediamido)dibenzoate, as well as a number of excipients, which included polymers used for prolonged-release dosage forms, lubricant – sodium stearyl fumarate, as well as pore-forming agents – PVP and MCC, were the objects of the study. The key parameters of tablets and dissolution kinetics were studied in accordance with the requirements of State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XIV edition and Pharmacopeia of the Eurasian Economic Union.
Result and discussion. Prolonged release was achieved for all tablets, but more than 90 % of the substance was released after 12 hours in tablets containing ethylcellulose as a matrix-forming polymer. The release of APS from tablets of this formulation was the most prolonged.
Сonclusion. The effect of matrix-forming components included in the composition of mixtures for granulation on the rate of release of 4,4'-(propanediamido)sodium dibenzoate from tablets has been studied. The most uniform and complete release of ASF from tablets in which the matrix-forming polymer is ethylcellulose in the amount of 27.7 %.
Introduction. A comprehensive study of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) molecule is one of the defining criteria for pharmaceutical development according to the Quality by Design (QbD) concept and the ICH Q8 framework. The spatial arrangement of atoms in the molecule often has a significant impact on the physicochemical and technological properties of API, and hence on the method of producing dosage form based on it.
Aim. To study some properties of substances, geometrical isomers of the molecule, which is a derivative of diethylaminoethanol (DEAE), as well as to compare the selected technologies for the preparation of dosage form.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were two substances, spatial isomers of the molecule, a derivative of DEAE, possessing neuroprotective, antiastenic and antioxidant effects. The study of properties of API and the obtained tablets was carried out in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XIV edition, the Pharmacopoeia of the Eurasian Economic Union, as well as the European Pharmacopoeia 9.0 edition. In this research were used substances that have not expired at the time of the study, as well as authorized for medical use.
Results and discussion. The geometrical configuration of the DEAE derivative influences the properties of the API, which has an impact on the stages of pharmaceutical development, especially on the development of the technology and formulation of dosage form. The use of cis-DEAE significantly simplifies the technological process and improves the quality of the resulting drug, and as a consequence, better stability and longer shelf life of dosage form may be achieved.
Conclusion. In the course of the study, some properties of cis-DEAE API were studied and compared with similar properties of trans-DEAE. A comparison of tablet preparation technologies based on the two mentioned configurations of the DEAE derivative molecule has been carried out. It was found that the isomers have different technological properties and also differ significantly in moisture adsorption capacity. This property determines the approach to tablet preparation. The technology of tablets based on cis-DEAE appears to be simpler, and dosage form based on it is more stable.
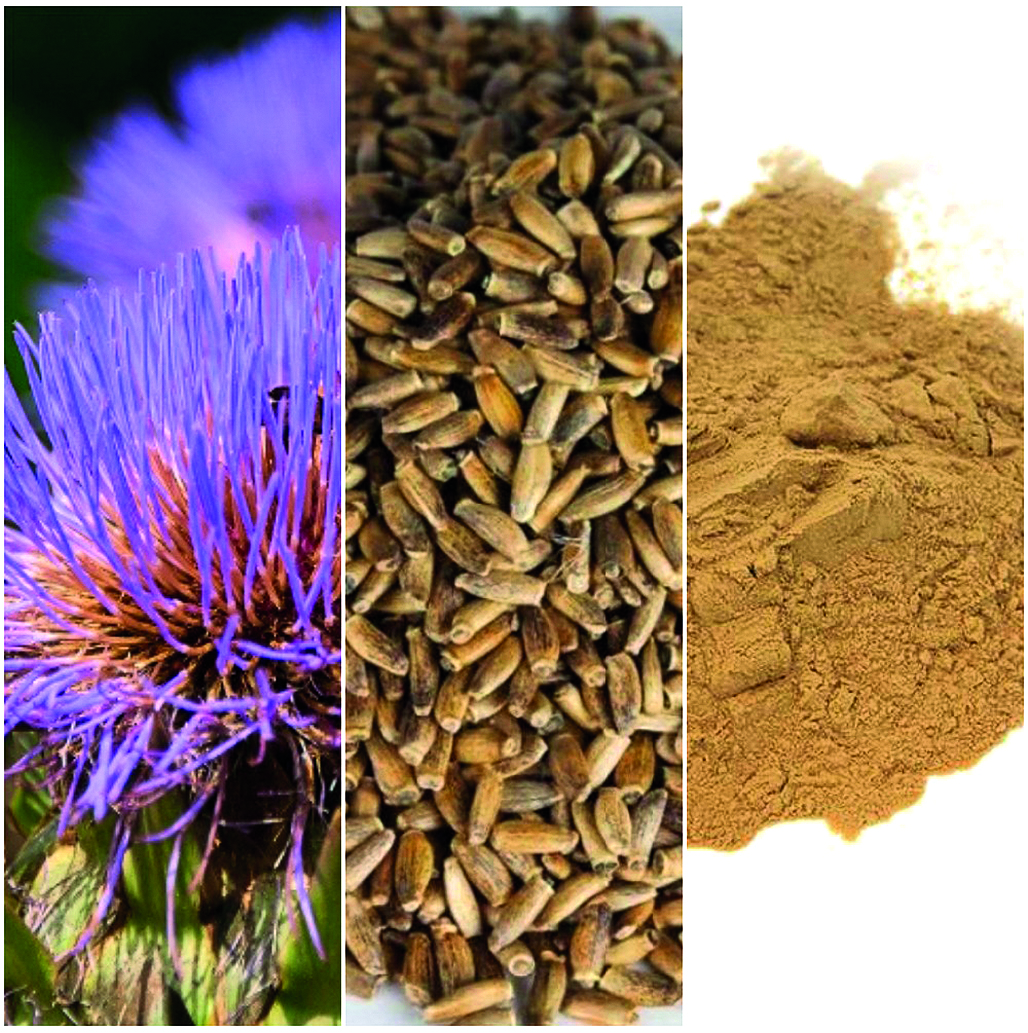
Introduction. Currently, the problem of liver diseases is widespread among the population, especially non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, as well as medicinal liver lesions. In this regard, there is a need to find new solutions in the development of hepatotropic therapy drugs. In clinical practice, several hepatoprotective agents are often used simultaneously in the form of separate drugs or combinations. The combined use of substances in one finished dosage form (FDF) can provide both an enhancement of a particular pharmacological effect and an expansion of the spectrum of hepatotropic action. Components of plant origin are often introduced into the composition of combined hepatoprotectors. Silybum marianum L. fruits contain at least 2.4 % of the amount of flavolignans in terms of silybin, which causes the hepatoprotective effect of medicines based on them and explains the prospects of using this vegetable raw material in the treatment of liver diseases.
Aim. Development of technology for obtaining a dry extract of Silybum marianum L. fruit, enriched with silybin.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. fruits from producer 2, harvested in June 2022. The quality indicators of the finished product, a dry extract of Silybum marianum (L.) fruit, were determined by the methods described in the SP XIV ed. Statistical processing of the research results was carried out in accordance with SP XIV ed., Volume I, p. 289, GM.1.1.0013.15 "Statistical processing of the results of a chemical experiment".
Results and discussion. The optimal method of extraction of medicinal plant raw materials is proposed, which allows to obtain the highest yield of biologically active substances. A method of purification of ethanol-water extraction after extraction is proposed. The technology of dry extract of Silybum marianum (L.) fruit has been developed. Standardization of the obtained dry extract was carried out.
Conclusion. In the course of the study, the technology of dry extract of Silybum marianum (L.) fruit was developed. The quality indicators of phytosubstantiation, dry extract of Silybum marianum (L.) fruits enriched with silybin were determined.
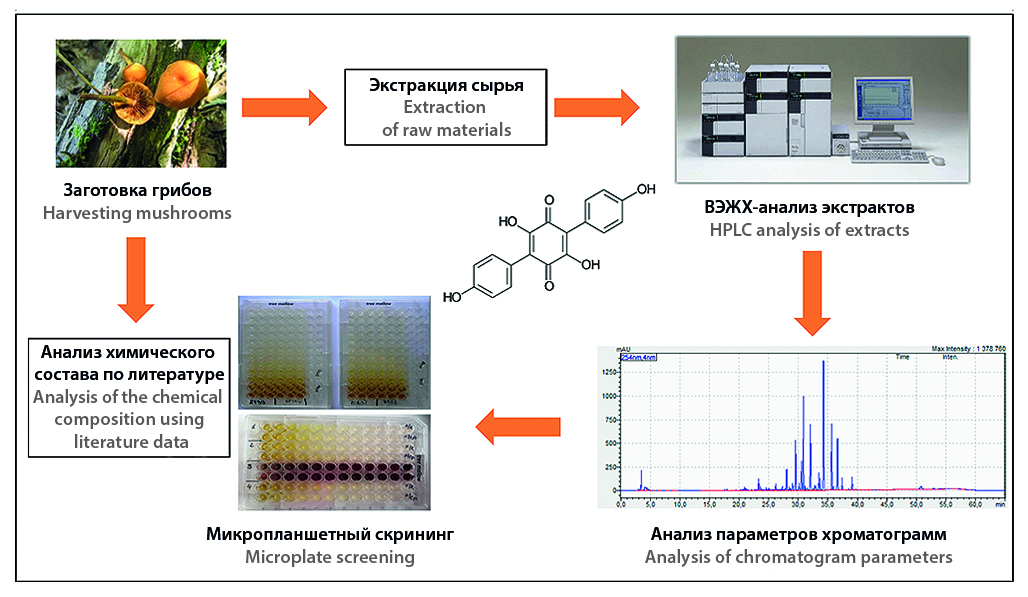
Introduction. The emergence of new strains of microorganisms that are multidrug resistant (MDR) in relation to the antimicrobial drugs used is one of the pressing problems of modern medicine. To prevent an increase in MDR-related deaths, the search for new antibiotics and their introduction into medical practice must be continuously ongoing. Infectious diseases are also accompanied by cell damage and the development of free radical oxidation processes, therefore the search for new antioxidants is also an important task. Considering the powerful biosynthetic potential of basidiomycetes, this group of fungi has every prospect of becoming a new source of biologically active substances in general, as well as antibiotics and antioxidants in particular. Cap mushrooms, represented mainly by basidiomycetes, number about 14,000 species and are an accessible source of raw materials for the search for promising antimicrobial compounds and antioxidants.
Aim. Study of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of total extracts obtained from cap mushrooms against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans and assessment of the suitability of cap mushrooms as a natural source of substances with antimicrobial and antioxidant activity.
Materials and methods. The antifungal and antibacterial activity of the extracts was determined by the micromethod of two-fold serial dilutions in a liquid nutrient medium in 96-well plates in duplicate. The study of this type of biological activity was carried out against reference (type) strains Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Candida albicans NCTC 885-653. To study antioxidant activity using DPPH, we used alcoholic extracts from the fruiting bodies of mushrooms obtained by maceration with 96 % ethanol at a ratio of raw materials to extractant of 1 to 8 for 24 hours, an aqueous solution of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and an ethanol solution of Trolox.
Result and discussion. In relation to S. aureus, a representative of gram-positive flora, the studied extracts of cap mushrooms showed low activity, on average about 2500 or 5000 μg/ml. In relation to E. coli, a representative of gram-negative flora, 8 % of the studied cap mushroom extracts showed an average activity of about 1250 μg/ml. The largest number of cap mushroom extracts – 19% of all studied species – showed activity against the yeast micromycete C. albicans. The highest activity against C. albicans was observed in extracts of the mushrooms Cantharellula umbonata with an MIC of 625 μg/ml, Cortinarius olivaceofuscus with an MIC of 625 μg/ml, and Hypomyces chrysospermus with an MIC of 312 μg/ml. During screening of antioxidant activity, the studied extracts were divided into three groups: with high (more than 50 % PPR), medium (from 15 to 50 % PPR) and low (less than 15 %) antioxidant activity. It was shown that the sum of phenolic compounds significantly correlates with the level of antioxidant activity in all three groups, but in the groups with medium and low antioxidant activity there are also other non-phenolic groups of compounds that make a significant contribution to the total antioxidant activity.
Conclusion. Cap mushrooms are a promising source of biologically active substances with antifungal and antioxidant activity.
Introduction. Ebastine is a second-generation antihistamine drug available in the form of orally disintegrating tablets and film-coated tablets. Ebastine substance exhibits high bioavailability, but low solubility in water and gastrointestinal tract media. The technology of solid dispersions based on polymer carriers by hot melt extrusion is proposed to solve the problem of ebastine low solubility.
Aim. Composition development of extrudate and its production technology to create an amorphous solid dispersion of ebastine in oder to increase the recovery rate and bioavailability.
Materials and methods. Ebastin micronized (JSC "Active Component", Russia); ebastin crystalline (Arevipharma GmbH, Germany); VIVAPHARM® PVP/VA 64 (JRS Pharma GMbH & Co. KG, Germany). Extrudates were obtained on a HAAKE™ miniCTW co-rotating twin-screw laboratory extruder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany). Extrudates were studied by differential scanning calorimetry, synchronous thermal analysis, powder X-ray diffraction and FTIR-spectroscopy. The quantitative content of the active ingredient was determined by spectrophotometry. The content of related impurities in the amorphous solid dispersion of ebastine was determined by HPLC.
Results and discussion. The technology of amorphous solid dispersion of ebastine by hot melt extrusion was developed. The pharmacokinetic properties of ebastine were significantly improved. The process of obtaining solid dispersion with 20 % of ebastine was optimized in order to reduce the content of impurities in the extrudate.
Conclusion. The maximum concentration of ebastine for proper quality amorphous solid dispersion based on PVP/VA64 amounted to 20 %. Obtaining a solid dispersion by hot melt extrusion with ebastine content in PVP/VA64 higher than 30 % is impossible because the melt does not possess the glass transition property.
Introduction. With the emergence of empagliflozin in the pharmaceutical market, there has been an increase in publications on the primary and secondary pharmacodynamics of the drug, and the list of potential indications for the use of this sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitor is increasing. Hypotheses about pharmacological effects and mechanisms of their implementation are tested both in large-scale clinical studies and in animal experiments.
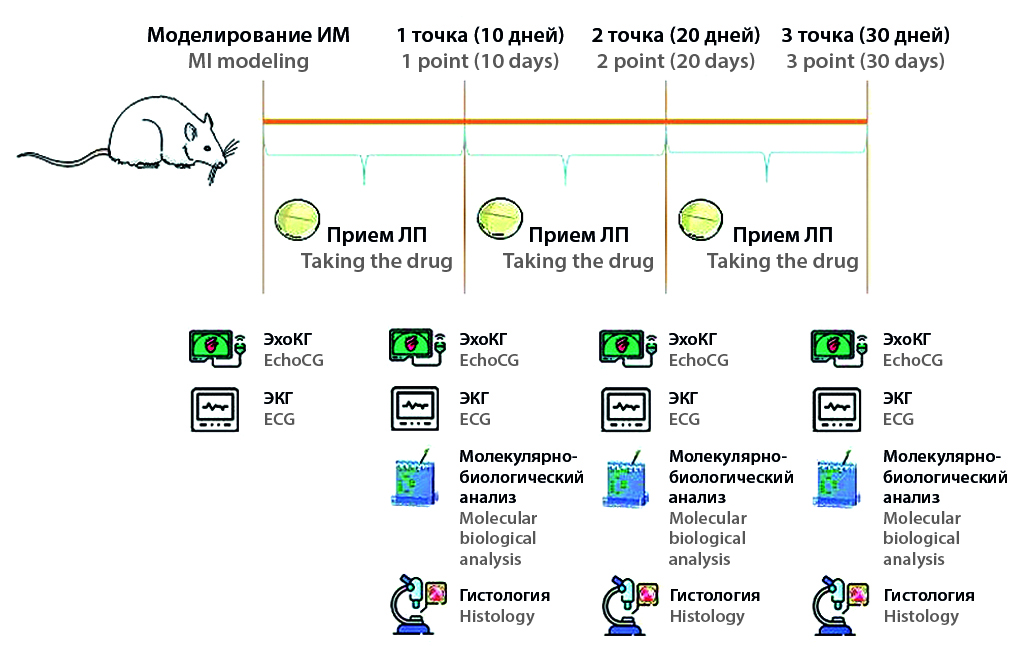
Aim. The purpose of this work was to study the effectiveness of empagliflozin by echocardiographic, histological and molecular biological analyses at the three most significant points of the dynamic transition from acute myocardial infarction to post-infarction chronic heart failure in laboratory male rats.
Materials and methods. The experiment was performed on 60 male outbred rats. Myocardial infarction was modeled in narcotic animals by permanent ligation of the left coronary artery. Based on echocardiographic (EchoCG) study data, animals were randomized to two groups: control infarction: untreated pathology group treated with placebo and pathology group treated with empagliflozin 1 mg/kg per os intragastric daily from the first day of the experiment. At 10, 20 and 30 days after the operation, the animals were also subjected to EchoCG testing, and a group of 10 animals from each group were euthanized for histological examination and molecular analysis.
Results and discussion. Empagliflozin use in animals after myocardial infarction modeling contributed to a significant increase in myocardial performance on days 10, 20 and 30, reaching a maximum on day 20 (47.58 ± 1.87 %). The drug promotes long-term preservation of the area of damage to the heart muscle with early formation of mature connective tissue, and also increases myocardial resistance to hypoxia by increasing the amount of HIF-1.
Conclusion. Based on the studies carried out, it can be concluded that it is possible to use the sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 empagliflozin in the formation of post-infarction chronic heart failure in the conditions of normoglycemia.
Introduction. The article presents the results of a study of the influence of parameters of microcapsulation on the properties of microcapsules obtained by diffusion of an emulsion solvent. The results obtained made it possible to establish optimal parameters of the process, such as the mixing speed, the type of mixing device, the volume of the aqueous phase, the concentration of the polymer in the oil phase, the ratio of medicinal substance : polymer, temperature conditions.
Aim. The aim of the work was to study the influence of the parameters of the microcapsulation process on the properties of microcapsules obtained by diffusion of an emulsion solvent.
Materials and methods. Ibuprofen was used as a model substance for microcapsulation. Eudragit® RS 100 was chosen as the carrier polymer. To assess the shape and nature of the microcapsule surface, a microscope Levenhuk D80L LCD was used, and the size of microcapsules was determined using a laser particle analyzer Microsizer 201C (VA Instalt, Russia).
Results and discussion. The influence of the parameters of the microcapsulation process on the properties of ibuprofen microcapsules as a model substance obtained by diffusion of an emulsion solvent has been studied. The optimal parameters of the technology are established, the dependences between the critical parameters of microcapsulation and the properties of the resulting microcapsules are determined.
Conclusion. In the course of the study, the choice of technological parameters of microcapsulation by diffusion of an emulsion solvent was proposed and justified. The experimental data obtained on the example of ibuprofen as a model substance will be used as the basis of the experiment when preparing microcapsules based on other substances soluble in organic solvents.
Introduction. A personalized choice of antihypertensive combinations and doses is one of the promising trend in the field of combination therapy of arterial hypertension (AH). A polypill as a solid gelatin capsule with combination of mini-tablets can be used to realise this concept.
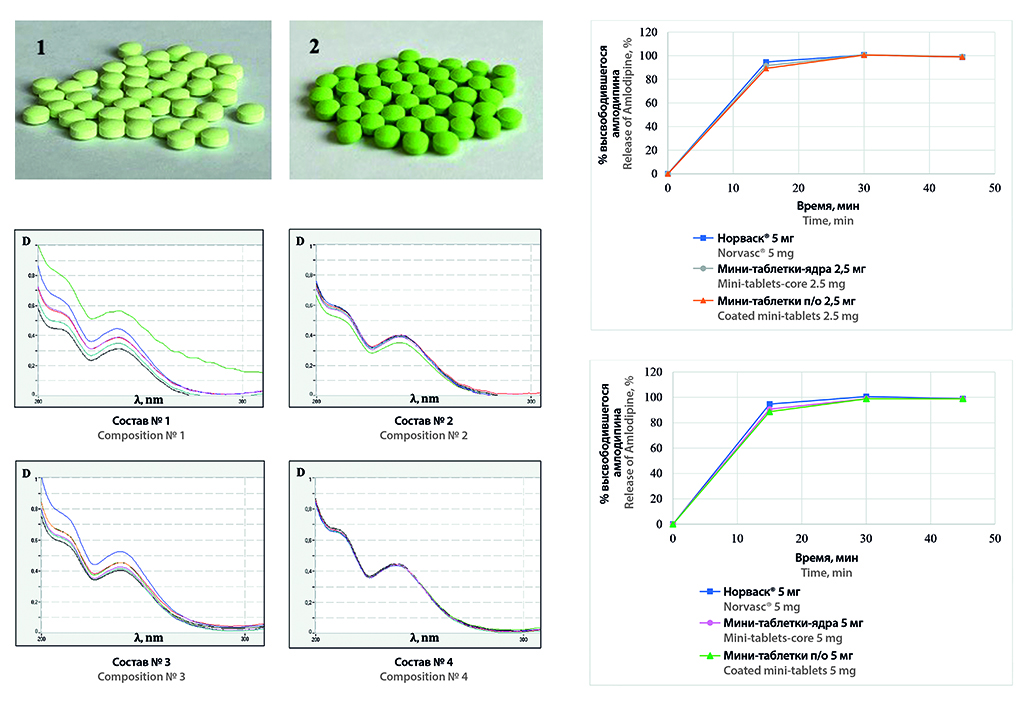
Aim. Development of the composition and technology of Amlodipine 2,5 mg and 5 mg film-coated mini-tablets as a polypill-component for the personalized therapy of AH.
Materials and methods. Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) Amlodipine besylate (Glochem Industries Private Ltd., India) and excipients, such as diluent, disintegrant, lubricant, dye and premix for film coating, were used. Norvasc®, 5 mg tablets were used as a reference drug to estimate the release profile of Amlodipine. API and excipients were mixed in a «drunken barrel» mixer DGN-II (Shanghai Unique Machinery Technology Co., Ltd., China); mini-tablets were obtained on a DP30A laboratory automatic single-punch tablet press (Beijing Gylongli Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd., China); film coatings on mini-tablets-cores were applied by using a BGB-1 laboratory machine (Chongqing Jinggong Pharmaceutical Machinery Co., Ltd., China). Assessment of technological characteristics of API and tablet mixtures and quality control of mini-tablets were conducted by the methods of State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XIV ed.
Results and discussion. As a result of the study, the optimal composition of the excipients of the fillers group (lactose monohydrate, MCC and anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate in a ratio of 1 : 1 : 1) for the production of Amlodipine 2,5 mg and 5 mg mini-tablets-cores by direct compression was established. The technology of applying film coatings was developed. The equivalence of the release profiles of Amlodipine from the developed mini-tablets to the release profile of the reference drug was established.
Conclusion. The composition and technology of Amlodipine 2,5 mg and 5 mg film-coated mini-tablets as a polypill-component for the personalized therapy of AH were developed.
Introduction. The current growth of the pharmaceutical market and stiff competition require from drug manufacturers make a more detailed and thorough fine-tuning of existing production lines. Direct compression technology is a modern and cost-effective technology for solid dosage form drug manufacturing. Roll-compaction tehnology (dry granulation) can be an alternative approach to optimize the manufacturing of formulations, for which the use of wet granulation or direct compression technologies is not possible due to their physical and chemical properties.
Aim. The goal of this work is to investigate the possibility of manufacturing Rebamipide tablets by using direct compression technology and dry granulation technology (roll-compaction), avoiding such complicated and more expensive technology as wet granulation. Also aim of this work is study the impact of production methods on such quality factors as disintegration and dis-solution time.
Materials and methods. In this study were used such materials as Rebamipide substance (α-[(4-Chlorobenzoyl)amino]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-quinolinepropanoic acid) (experimental sample), MCC-102 (J. Rettenmaier & Söhne (JRS), Germany), Starch pregelatinized (Colorcon LTD., England), Kollidone SR (BASF, Germany), Croscarmellose sodium (J. Rettenmaier & Söhne (JRS), Germany), Anhydrous citric acid (Scharlau), Sodium lauryl sulfate (BASF, Germany), Aerosil 200 vv Pharma (Evonik Industries AG, Germany), Sodium stearyl fumarate (J. Rettenmaier & Söhne (JRS), Germany), Calcium stearate (FACI, Italy), Film coating VIVACOAT® PA-1P-000 (J. Rettenmaier & Söhne (JRS), Germany). Also were used such equipment as Y shape blender («AZT FARMA K.B.», Russia), roll compactor LGC100 (Beijing Gylongli Automation Tech. Co., Ltd, China), rotary tablet press PG16G (Beijing Gylongli Automation Tech. Co., Ltd, China), tablet coating system Labcoat™ M (O'Hara Technologies lnc, Canada), ionising air gun Simco Cobra (SimcoIon, Netherlands), flowability tester ERWEKA GT (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany), powder density tester ERWEKA SVM 122 (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany), vibrating sieve CISA RP 200N (CISA Cedaceria Industrial S.L., Spain), tablet hardness, thickness and height tester SOTAX HT 10 (SOTAX AG, Switzerland), dissolution tester DT 626/1000HH (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany) and disintegration tester ZT321 (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany).
Results and discussion. In a series of experiments were obtained tablet’s cores and film coated tablets by direct compression and roll-compaction methods. Experimentally it was found, that in tablets with similar formulations roller compaction technology provides slower disintegration and dissolution time, compared to direct compression method. This fact should be taken into account during drug development when planning the rate of release of the active ingredient.
Conclusion. As a result of the experiments it was shown a direct correlation between the use of a certain technology and its impact in such quality indicators as disintegration and dissolution time of tablets. It was also found that dry granulation technology provides a more technologically suitable tablet mass.
Introduction. Plant biologically active substances (BAS) are valuable for drug development in view of their pharmacological effects and metabolic proximity to the human body. As an example of a useful herbal raw material, the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, which contain species-specific flavonoids, baicalin and scutellarin, possess the potency of creating antiviral drugs and functional nutrition systems with antioxidant and adaptogenic properties. In order to levelling the existing limitations of using intact plant in pharmaceutical practice, we proposed a nature-saving and ergonomic approach of cultivation of S. baicalensis cells under in vitro conditions. This technology allows to extract active substances of S. baicalensis without causing damage to the environment and contributes to the reduction of the time required to produce the necessary amount of plant material with an increase in the efficiency of production processes.
Aim. The development of dry extract technology from S. baicalensis callus biomass.
Materials and methods. The object of the study – biomass of S. baicalensis cells obtained from callus culture. Functional characteristics (friability, Hausner’s coefficient, Carr’s index, fractional composition, as well as porosity and hygroscopicity) of S. baicalensis biomass and dry extract on its basis were determined according to the methods of the EAEU Pharmacopoeia. Extraction of plant material was carried out by maceration method with heating in a water bath with reflux condenser. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of BAS in the dry extract was carried out by spectrophotometry and high-performance liquid chromatography. Quality indicators and functional characteristics of the finished product were evaluated in accordance with pharmacopeial requirements.
Results and discussion. The functional characteristics of the S. baicalensis biomass were evaluated and the possibility of obtaining a dry extract on its basis was confirmed. We selected parameters of BAS extraction process, established the presence of baicalin in the biomass extract and carried out a comparative evaluation of aglycone profile in the extract based on callus culture and roots of intact plant. The properties of the finished product were evaluated for compliance with regulatory requirements, as well as technological characteristics.
Conclusion. The quality indicators of the dry extract of the S. baicalensis biomass satisfy the normative conditions. The technological characteristics of dry extract are suitable for the utilisation as a phytosubstance for the development of medicines of combined type and dietary supplements.
Introduction. Orally dispersible dosage forms are one of the new trends in the field of drug delivery systems. One type of such dosage forms is oral lyophilisates that are obtained by freeze-drying a pre-prepared mixture containing the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients. This dosage form provides immediate release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient in the oral cavity using a less amount of excipients.
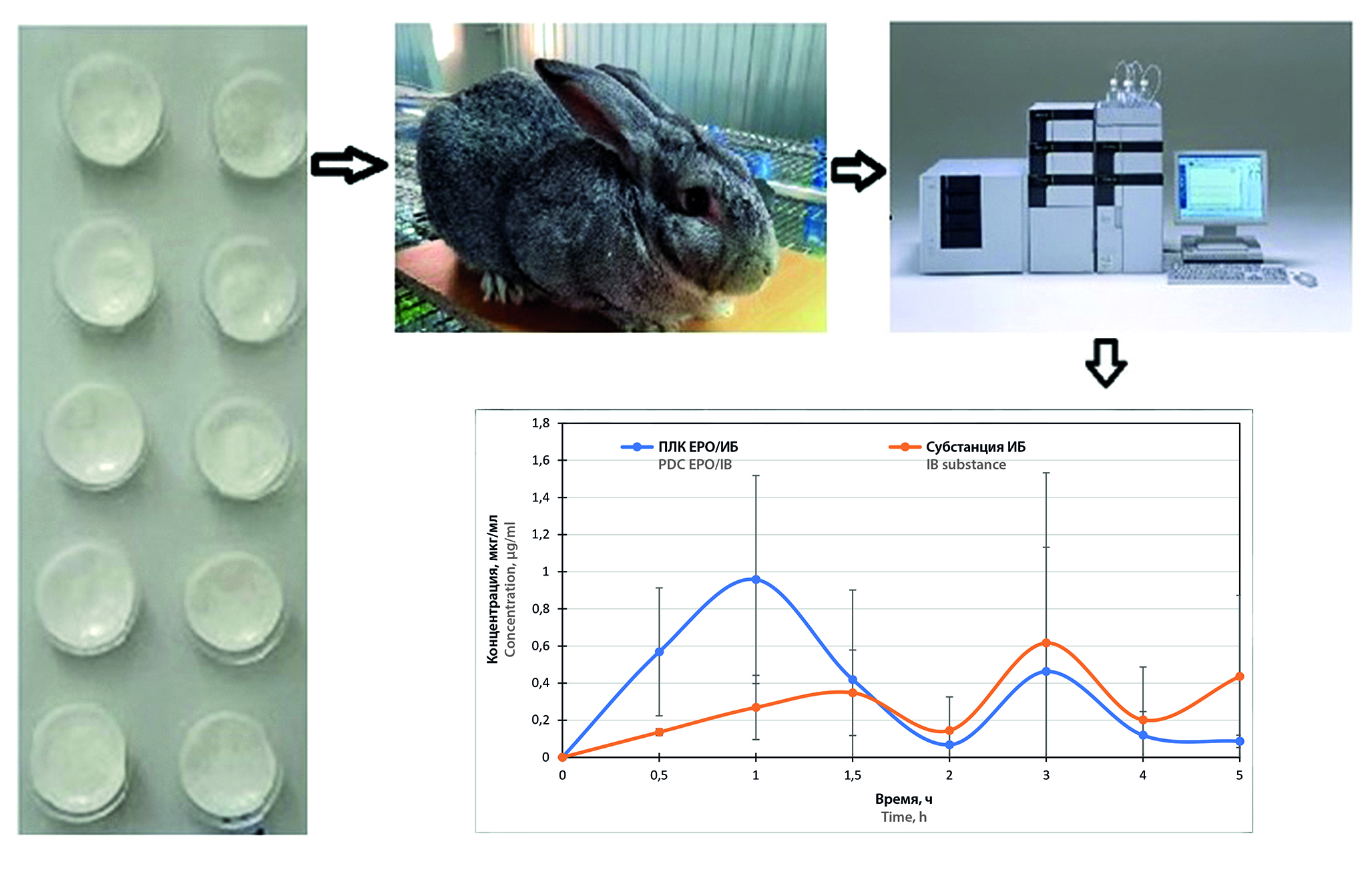
Aim. Pharmacokinetic studies of previously obtained lyophilisates based on the polymer-drug complex Eudragit® E PO / ibuprofen (PDC EPO-IB) and the interpolyelectrolyte complex (IPEC) Carbopol® Ultrez 10 / Eudragit® E PO (IPEC C10/EPO) and metronidazole.
Materials and methods. Lyophilisates of the following compositions were obtained: 1) 100 mg of metronidazole and 50 mg of IPEC C10/EPO or 2) 100 mg of PDC EPO-IB, the first or second composition of the carrier with API was dispersed in 50 % maltodextrin syrup, Span®80 was added – 1.42 % from the total mass of the mixture. The mixture was poured into blisters for tablets, frozen in a FreeZone 1L laboratory dryer (Labconco, USA) for 24 hours at a temperature of –49 °C, and the main drying was carried out at a pressure of 0.350 mbar. Soviet Chinchilla rabbits were administered one lyophilisate containing PDC EPO/IB or IPEC C10/EPO with metronidazole; the substances ibuprofen (50 mg) and metronidazole (100 mg) were used as reference drugs. The concentration of API was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) on an LC-20 Prominence chromatograph (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan) with UV detection. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using a model-independent method using the Thermo KinetikaTM (version 5.0, Build 5.00.11, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) program.
Results and discussion. According to the obtained pharmacokinetic profiles, the maximum concentration of ibuprofen from EPO/IB PDC is achieved within the first hour after oral administration. The second peak in the profiles shows the absorption of the remaining portion of the API into the blood from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), both in the case of EPO/IB PDC and in the case of ibuprofen from the substance. The relative bioavailability of EPO/IB PDC was Frel = 86.06 %. Lyophilisates based on IPEC C10/EPO provide the maximum concentration of metronidazole after 30 minutes (Cmax = 4.659 μg/ml). Relative bioavailability was Frel = 107.6 %.
Conclusion. According to studies, the maximum concentration of ibuprofen and metronidazole is achieved within the first hour after oral administration of lyophilisates containing PDC EPO-IB and IPEC C10/EPO. Absorption of medicinal substances in the oral cavity occurs due to the components included in the dispersible dosage form, as well as due to the presence of a ЕРО copolymer, PDC and an IPEC, which are able to linger on the oral mucosa due to the presence of mucoadhesive properties. Thus, the pharmacokinetic studies of ibuprofen and metronidazole from the obtained lyophilisates prove the suitability of the obtained forms for immediate release systems.
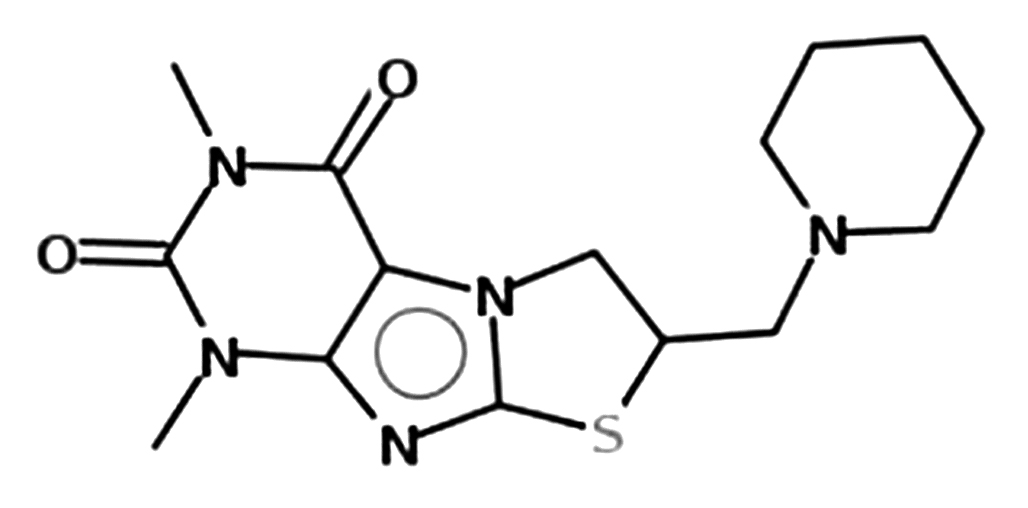
Introduction. Cytochromes P450 depression is the reason for the low effectiveness of etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy of hepatitis. Recent experimental and clinical studies demonstrated the need for use of inducers of hepatocytes monooxygenase system to increase the effectiveness of treatment of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. 6,8-dimethyl-2-piperidinomethyl-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[2,3-F]xanthine is a promising inducer of hepatocytes monooxygenase system with detoxifying and cytoprotective activity demonstrated in models of acute hypobaric hypoxia, liver ischemia, unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, toxic hepatitis. Development of a dosage form for 6,8-dimethyl-2-piperidinomethyl-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[2,3-F]xanthine requires evaluation of its technological properties which was the aim of the present study.
Aim. Preparation of a tablet dosage form for 6,8-dimethyl-2-piperidinomethyl-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[2,3-F]xanthine by direct pressing.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was the substance of 6,8-dimethyl-2-piperidinomethyl-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[2,3-F]xanthine (DPDX270216001 series). Lactose monohydrate (200-559-2, LLC "Neftegazkhimkomplekt", Russia), microcrystalline cellulose (100-32-2, Silverline chemicals Ltd., India), potato starch, hydroxypropyl cellulose (ZW180113, Fengchen Group Co., Ltd., Китай), talc (LLC "Agat-Med", Russia), magnesium stearate (209-150-3, Ataman Chemicals) were used as excipients. Evaluation of the substance properties was carried according to the following indicators: appearance, loss on drying, fractional composition, flowability, bulk density, porosity, tablet compression (cohesion), ejection force of the tablet from matrix. Tablet masses were evaluated according to the following indicators: flowability, bulk density, tablet compression (cohesion), ejection force of the tablet from matrix. The tablets were obtained by the method of direct pressing. The analysis of obtained tablets were carried out according to the following parameters: average weight, crushing strength, disintegration. The tests were carried out in accordance with the Russian Federation State Pharmacopoeia.
Results and discussion. The substance demonstrated poor compression (cohesion), low flowability, low bulk density and high porosity. The addition of lactose monohydrate and microcrystalline cellulose improved the cohesion (compression) parameter, but increased the ejection force of the tablet from matrix. The subsequent addition of magnesium stearate reduced the ejection force of the tablet from matrix by 5 times. The flowability of the tablet mass increased to 3,5–4,0 g/s, the disintegration time of the tablets increased (13–14 min). The introduction of 10 % disintegrators into the mold improved the disintegration rates.
Conclusion. Based on the studied properties of the substance, was developed the optimal ratio of tablet mass. The possibility of obtaining a dosage form – tablets of 6,8-dimethyl-2-piperidinomethyl-2,3-dihydrothiazolo[2,3-F]xanthine by direct pressing was show.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. Vegetable raw materials processing products are becoming very popular. Of particular value are the products of essential oil production – aromatic waters or hydrolates. Hydrolates are widely used as cosmetics because they contain a number of biologically active water-soluble components of essential oil, but unlike the latter they have a softer effect on the skin, which allows them to be used in their pure form.
Aim. To study the chemical composition, antibacterial and antioxidant activity of hydrolates.
Materials and methods. Hydrolates were used as objects of research of production JSC "AEMSZ" derived from plants: Lavandula angusifolia, Hyssоpus officinаlis, Sаlvia officinаlis, Rosmarinus officinalis, Rosa damascеna × Rosa gallica. The composition was analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography. Antibacterial properties of hydrolates were studied with the use of bioluminescent marine bacteria Aliivibrio fischeri F1 and recombinant test-bacteria Escherichia coli MG1655 (pXen7). The study of the antioxidant effect was carried out by the method of Fe3+-induced lipid peroxidation of egg lipoprotein suspension in vitro.
Results and discussion. It was found that salvia hydrolate contains α- and β-thujone, β-caryophyllene, α-terpineol; lavender hydrolate – camphene, linalool, linalyl acetate, geraniol, geranyl acetate; rosemary hydrolate – camphene, 1,8-cineol, β-pinene; rose hydrolate – phenylethanol, geraniol, citronelol, nerol; hydrolate hyssop – pinocamphone, isopinocamphone, spatulenol, β-caryophyllene. The antibacterial properties of the studied hydrolates were manifested in the inhibition of test bacteria bioluminescence and growth. Hydrolates of hyssop, lavender and rosemary were characterized by the greatest activity, rose and salvia had a lesser effect. It was also shown that hyssop and lavender hydrolates exhibited the bactericidal properties. Through the studying the antioxidant effect, the dynamics of accumulation of products of free-radical oxidation of lipids was observed, which in the presence of hyssop and rosemary hydrolates decreased by 40 and 36 %, respectively, in comparison with the control.
Conclusion. As a result of the research, it was found that the studied hydrolates have pronounced antibacterial properties. Antioxidant properties of Hyssopus officinalis and Rosmarinus officinalis hydrolates were also revealed. Prospects for further research are the development of medicinal and cosmetic products based on the hydrolates of the above-stated essential oil cultures.
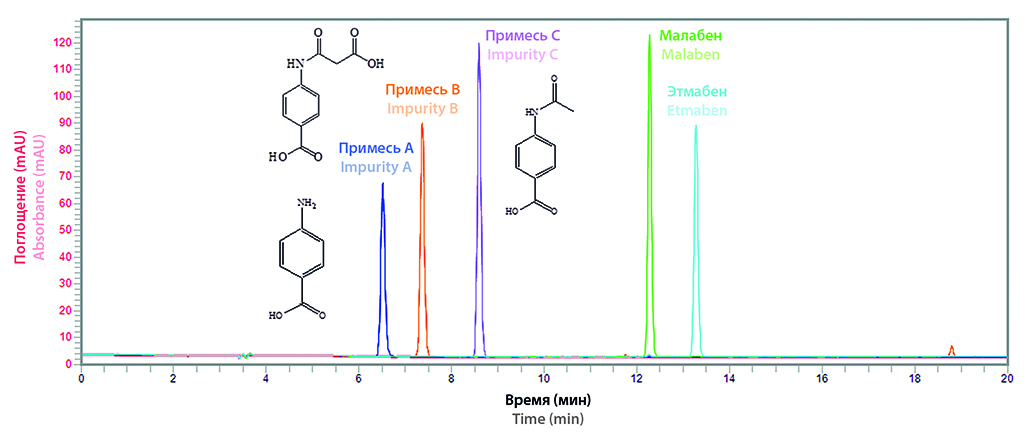
Introduction. For tablets “Malоben, 60 mg” and “Etmaben, 300 mg”, permission was received to conduct phase I clinical trials, so they required a full cycle of research and standardization.
Aim. Development of a unified analytical procedure for the determination of related impurities in samples (RS, API, FPP) of Malоben and Ethmaben.
Materials and methods. RSs were obtained at the Department of Organic Chemistry of the St. Petersburg State Chemical and Pharmaceutical University; the synthesis of APIs and the production of FPP were carried out on an industrial scale in pharmaceutical production. The studies were carried out on a Flexar liquid chromatograph (PerkinElmer, USA), equipped with a pump (formation of a gradient on the low-pressure side), an autosampler, a column thermostat, a UV detector and a chromatographic column Intersil® ODS-3V, 5 µm, 100 Å, 250 × 4, 6 (Phenomenex, Japan).
Results and discussion. In the research, uniform optimal chromatographic conditions were selected using the HPLC method to determine the RP in RS, API and FPP of Maloben and Ethmaben. Column C18 250×4.6 mm, mobile phase 0.1% phosphoric acid and acetonitrile (gradient elution), flow rate 1 ml/min, sample volume 10 µl, UV detector (270 nm). They were validated in terms of specificity, linearity, detection limit, precision, robustness, and solution stability. Analytical concentration levels were selected for the formation of draft regulatory documents. Using the developed analytical technique, samples of RS, API and tablets of malоben and ethmaben were analyzed.
Conclusion. A full cycle of research was carried out, an analytical methodology was developed and related impurities were identified in RS, API and FPP of Maloben and Ethmaben.
Introduction. The quality of viable cell-based products (such as biomedical cell products and advanced therapy medicinal products) must be maintained during the full production cycle to ensure their safety and efficacy for patients. The minimum required number of viable cells is one of the quality control criteria in the final product release specifications. This study looks into the process of validation of automated viable cell counting methods.
Text. The study reviewed the latest data on specific validation characteristics for automated cell counters as compared to manual counting methods. We identified the main problems with the validation methods. Based on the review of scientific and regulatory literature, we identified the key validation parameters, methods of their evaluation and measurement, and reporting of results. We described the validation algorithm for an automated cell counter, including such steps as the selection of reference standards, selection of the number of experimental points, experimental design, mathematical evaluation of the obtained results, and determination of the acceptance criteria.
Conclusion. Based on the data reviewed, the authors developed recommendations for the validation of automated viable cell counting procedures.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
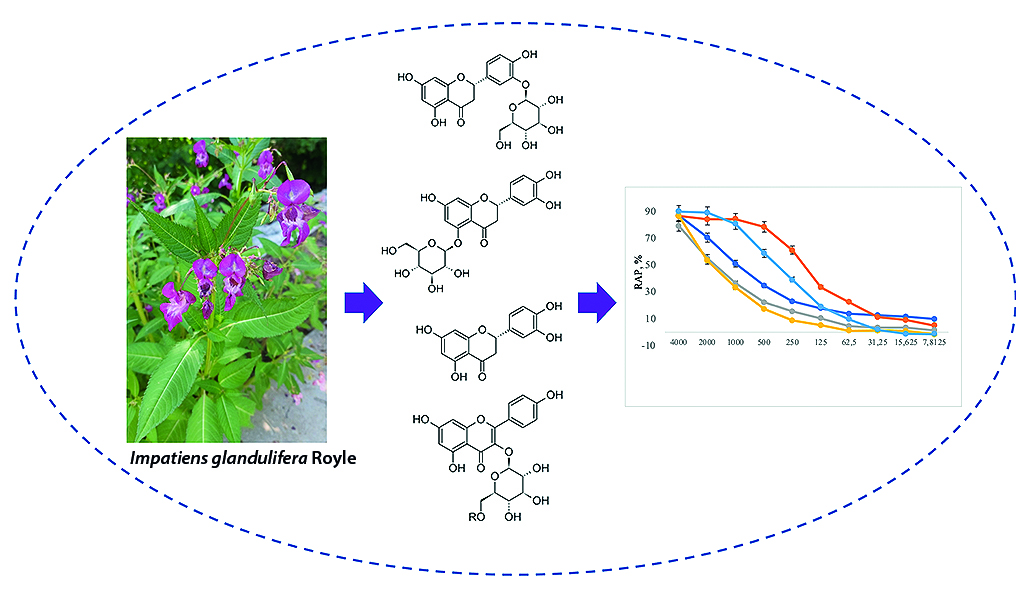
Introduction. The genus Impatiens L. includes about 850 species, which are found mainly in tropical and subtropical climate zones. The Indigenous people of Pakistan used pastes and extracts from I. glandulifera for the treatment of joint pain, anxiety and skin allergies [6]. Flowers of I. glandulifera are used in Bach flower remedies, which are used for sedation, relaxation and helping to balance emotional states.
Aim. Isolation and structural elucidation of 11 phenolic constituents from the aerial parts of I. glandulifera and the evaluation of their antioxidant activity.
Materials and methods. The aerial part of Impatiens glandulifera Royle was collected in the Leningrad region near the village of Orekhovo in 2021. Fractions were analyzed by analytical high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a Prominence LC-20 (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with a diode array detector. The isolation of individual compounds was carried out by column chromatography on open glass columns with sorbents of different selectivity, as well as by preparative HPLC using a Smartlina (Knauer, Germany) equipped with a spectrophotometric detector. The structure of isolated individual compounds was established by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy (Bruker Avance III 400 MHz, Germany). To study the antioxidant activity, we used solutions obtained by dissolving the isolated substances in a mixture of dimethyl sulfoxide and ethanol; an aqueous solution of vitamin C and an alcoholic solution of Trolox (Sigma-Aldrich, Japan).
Result and discussion. Phytochemical analysis of the aerial parts of Impatiens glandulifera Royle. resulted in the isolation of 11 polyphenolic secondary metabolites (1-11) and their structures were elucidated. The antioxidant activity of all isolated compounds was evaluated.
Conclusion. The maximum RAP values of eriodyctiol (3), kaempferol (1), and quercetin (2) did not differ significantly (p = 0.585) from those of the comparator preparations: vitamin C and Trolox, which indicates that the antioxidant effect of these three isolated compounds is comparable to the well-known antioxidants. However, the semi-effective concentrations of these substances are two or more times lower (p = 2.56 · 10–4) comparted with vitamin C.
Introduction. Cerebrovascular diseases (CVD) are one of the most pressing medical and social problems due to the high rate of mortality and disability. Stroke is the leading cause of CVD. About 15 million strokes are registered annually in the world according to the World Federation of Neurological Societies. It should be noted that CVD of ischemic origin has a tendency to rejuvenation and growth. Traditionally, in clinical practice, antihypoxic, antioxidant agents, as well as drugs with neuroprotective and neurorehabilitation effects are used to treat CVD. In connection with the increase in the incidence of CVD, there is an urgent need to search for promising neuroprotectors.
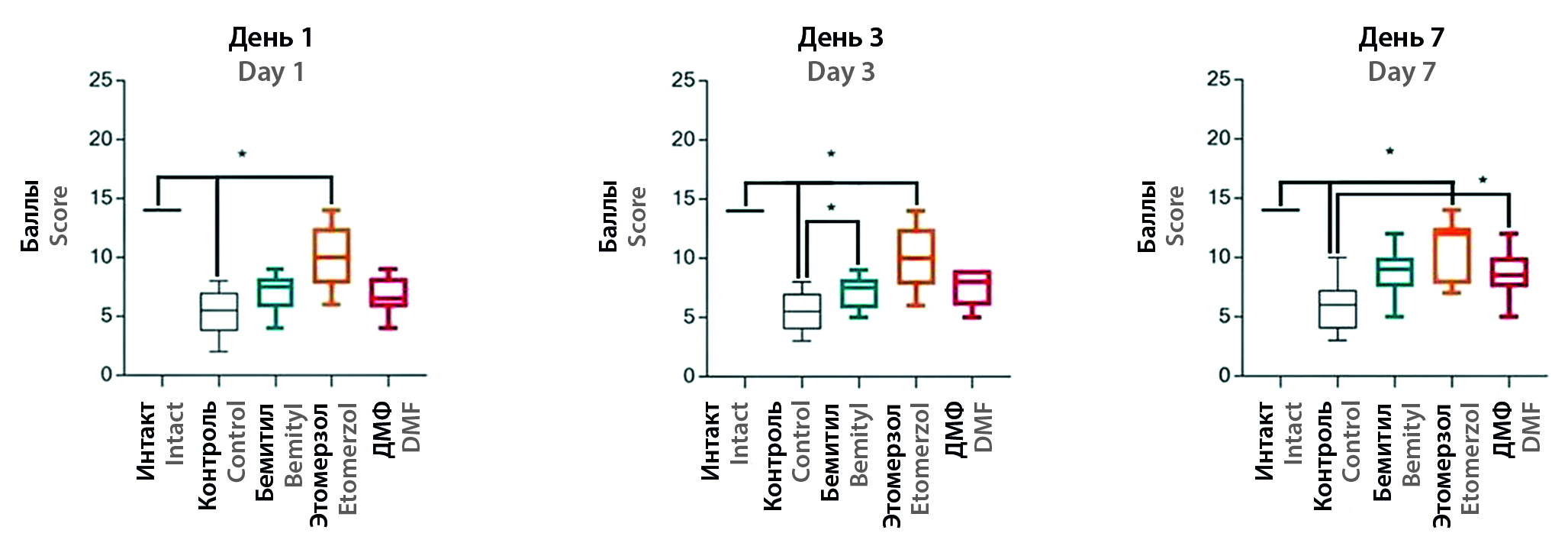
Aim. To study the neuroprotective activity of 5-ethoxy-2-ethylthiobenzimidazole (etomerzol) and 2-ethylthiobenzimidazole (bemityl) in a model of middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Materials and methods. Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (ОMCA) was used as a model. The object of the study was inbred male rats of the Dark Agouti line, randomized into five groups: a group of intact animals and four groups with OSMA: a control group, a group with the introduction of 5-ethoxy-2-ethylthiobenzimidazole (etomerzole, 25 mg/kg), a group with the introduction 2-ethylthiobenzimidazole (bemityl, 25 mg/kg) and a group with the reference drug dimethyl fumarate (DMF, 100 mg/kg). On the 1st, 3rd, and 7th days after the operation, the "Limb Stimulation" (SC) test was performed. On the 7th day, the tests "Open field" (OP) and "Elevated plus maze" (EPM) were performed. Euthanasia was performed on the 7th day in an induction chamber (Bioscape GmbH, CO2 box for euthanasia, Germany).
Results and discussion. The study showed a pronounced pharmacological effect of etomerzole in a model of acute ischemic stroke. The introduction of bemitil, etomerzol and DMF significantly reduced the neurological deficit 24 hours after OSMA and improved the psycho-functional state on the 7th day. Thus, in the etomerzol group on the first day after surgery, the neurological deficit was reduced by 1.9 times (p < 0.05), and by 3 and 2.0 times (p < 0.05) compared with the control group. While bemityl and DMF reduced the index by 1.3 (p < 0.05) and 1.4 times (p < 0.05) on the 3rd day and by 1.5 times (p < 0.05) on the 7th day. In the OP test in the etomerzol group, an increase in HDA by 2.7 times (p < 0.05) was observed compared with the control. The rate of peering into minks in the etomersol and bemitil groups was higher than in the control group by 2.6 (p < 0.05) and 3.4 times (p < 0.05), respectively. Search and research activity was increased in the same groups by 2.0 (p < 0.05) and 2.2 times (p < 0.05) compared to control animals. In the PCL test, the etomerzol and DMF groups showed an increase in the number of uprights in the sleeves compared to the control group by 2.7 (p < 0.05) and 3.8 times (p < 0.05), respectively. In the etomerzol and bemityl groups, there was an increase in the number of overhangs by 3.4 (p < 0.05) and 6.2 times (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. The data obtained during the study of the activity of benzimidazoles after ischemic stroke indicate a significant increase in the motor activity of animals in the OP tests, which may indicate a psychostimulating and potential nootropic effect of etomerzole and bemitil, and an increase in the number of racks and hangings in the PCL test can be regarded as manifestation of anxiolytic activity. In our study, the severity of the pharmacological effects of DMF was inferior to benzimidazoles. However, a significant decrease in neurological deficit in the SC test and an increase in the number of uprights in the sleeves in the PCL may indicate the presence of anxiolytic activity in the drug. The results obtained underline the importance of conducting additional studies to evaluate the effectiveness of DMF in OSMA.
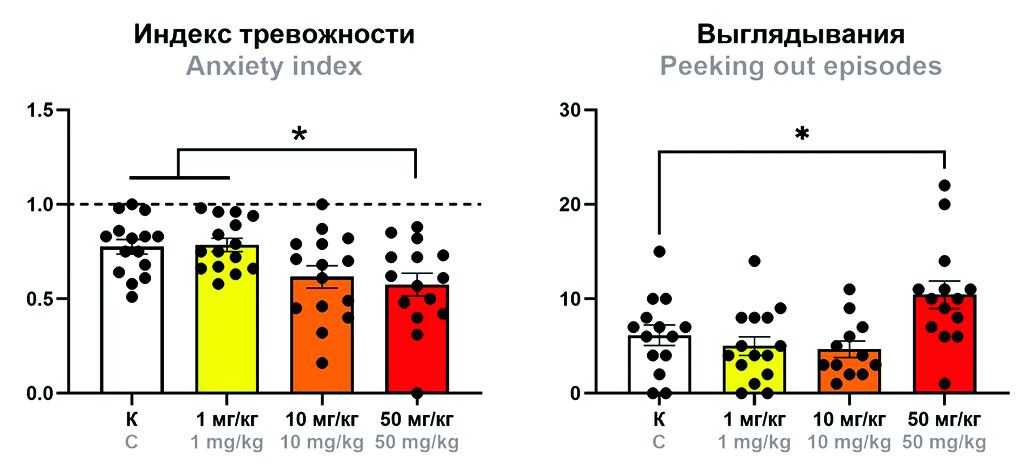
Introduction. α2-adrenergic agonists are not only used as antihypertensive and sedative agents, but are also of interest as potential medications for the treatment of neurological disorders. Previous research has shown a compound from this class, 6-oxo-1-phenyl-2-(phenylamino)-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-ol (mafedine), to exert strong neuroprotection under experimental conditions. Despite its long record of development, the effects of mafedine on animal behavioural characteristics remain unknown.
Aim. This work was aimed at evaluating the effects of mafedine sodium at three doses (1, 10, or 50 mg/kg) on white outbred mouse behavior in three tests: Open Field, Elevated Plus Maze, and Light/Dark Box.
Materials and methods. Experiments were carried out on 60 white outbred male mice weighing 20–22 g, randomized into 4 groups (n = 15): 1) control (0,9 % saline); 2) mafedine (1 mg/kg); 3) mafedine (10 mg/kg); 4) mafedine (50 mg/kg). All agents were administered via single intraperitoneal injections 20 min before testing. Animal behavior was assessed using the Open Field, Elevated Plus Maze, and Light/Dark Box tests following conventional protocols with group reassignment between tests and an inter-test time interval of at least 2 days. Statistical analysis was carried out using the Prism 8.0.2 software package.
Results and discussion. At 1 or 10 mg/kg, mafedine did not affect animal behaviour in either of the tests. At 50 mg/kg, it produced an anxiolytic effect, as indicated by the decrease in the anxiety index values for the Elevated Plus Maze test as well as the increase in peeking out frequency in the Light/Dark Box test, compared to respective control values.
Сonclusion. Mafedine sodium salt at doses between 1 and 50 mg/kg was shown to produce no adverse effect on mouse behaviour, indicating a good safety profile of the compound. The discovered anxiolytic effect of mafedine at the highest dose validates its further research not only as a neuroprotector, but also as an anti-anxiety agent.
Introduction. It is known that a number of species of the genus Cistus are used in Mediterranean folk medicine in the form of infusions and herbal teas to treat digestive problems and acute respiratory virus infection. Empirical data have accumulated that sage incense extract improves the condition of patients with chronic cholestatic liver diseases (CLDs). Currently, only ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is the generally accepted drug for the treatment of most CLDs.
Aim. Comparative efficacy evaluation of Cistus salviifolius extract (at 2 doses levels) compared to the reference medicine ursodeoxycholic acid Ursosan® (at a therapeutic dose) in intragastric administration to mice in a cholestasis model induced by intragastric administration of alphanaphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) oil solution during 20 Days.
Materials and methods. The cholestase model was induced by intragastric administration of an alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate oil solution to mice during 20 days. The following biochemical parameters were determined in the serum of experimental animals: alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, total protein, total cholesterol, bilirubin, triglycerides, albumins. Histological analysis was performed on the liver and gallbladder.
Results and discussion. Cistus salviifolius extract at a therapeutic dose of 253 mg/kg and at a dose exceeding the therapeutic dose (506 mg/kg), as well as the reference medicine of Ursodeoxycholic acid Ursosan® at a therapeutic dose of 150 mg/kg reduced the level of aspartate aminotransferase in serum increased after ANIT administration to a level of the control group without pathology. Deviations of other parameters from the control group (alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, total protein, total cholesterol, bilirubin, triglycerides, albumins) were statistically insignificant. Histological analysis of the liver and gallbladder demonstrated that the severity of ballooning degeneration and cholecystitis were significantly reduced in groups which was treated by Cistus salviifolius extract at two doses, but not in the group with reference drug. The severity of cholestasis was poorly influenced by Cistus salviifolius extract in contrast to ursodeoxycholic acid, which was more effective for this pathology.
Conclusion. The conducted study against the background of reports on the effectiveness of the Cistus salviifolius extract in clinical practice allows to recommend its use as a component of combined therapy of a patient with hepatobiliary pathology and as a pharmacoprevention in healthy people in the presence of risk factors.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)