FROM EDITOR
On 15 June 2024, Alexey Ivanovich Slivkin, the head of the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Technology of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Voronezh State University, Professor, Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Honored Worker of Higher Education of the Russian Federation turns 80 years old.
The second part of the article presents the structure of the Apothecary order at the time of its final formation. This publication also focuses on the personnel who served in the organization. The chiefs of the Apothecary order are listed from the moment of its setting up until its final reorganization, as well as the positions of the main and auxiliary personnel. The functions of the Apothecary order, which are traditionally divided into palatial and state, are analyzed. The first ones include medical, veterinary, purveyance, horticultural, expert and production functions. The state ones are constabulary-medical, military-medical, educational and administrative functions. The particular interest consists in the special function of the Apothecary prikaz – the collection, storage and study of scientific works on medicine.
Pharmaceuticals and medicines play an important role in maintaining human health. However, like any other products, they may contain potentially dangerous substances the so-called genotoxic impurities which can harm human health when consumed, so quality control of pharmaceutical products is of particular importance. Genotoxicity is the ability of a substance to have an irreversible effect on the structure and functions of DNA in cells thereby causing DNA death and errors in its replication, mutations and chromosomal aberrations. One of these substances is N-nitrosamines, which are formed as a result of the interaction of secondary amines with nitrites or nitrates. The Labconcept Group is the official distributor of leading manufacturers of analytical and general laboratory equipment. The Labconcept offers comprehensive solutions for equipping laboratories of various fields, including for the pharmaceutical industry. In this article, we will consider the possibility of determining such impurities using the EXPEC G-Chrom MS triple quadruple gas mass spectrometer using N-nitrosamines as an example.
EVENTS
The 9TH Pan-Russian GMP conference with international participation was held on August 21–23 in the capital of the Republic of Bashkortostan – Ufa. This year's motto is "GMP – continuous development".
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
Introduction. Representatives of the Ericaceae family are quite common in Russia and are promising for the creation of new medicines of plant origin. At the same time, only 4 of them are official. The study of biologically active substances and pharmacological activity of Andromeda polifolia L., Chamaеdaphne calyculata (L.) Moench, Ledum palustre L., Empetrum nigrum L. with rich resource reserves is promising.
Aim. Comparative study of the composition of total flavonoid fractions from A. polifolia, C. calyculata, L. palustre, E. nigrum and study of their effect on the NO-stimulating activity of peritoneal macrophages
Materials and methods. The crushed aboveground part (leafy shoots) was previously depigmented with chloroform, treated with 70 % aqueous acetone, then acetone was removed. Flavonoids were extracted with ethyl acetate from the aqueous phase. The identification of flavonoids was carried out by HPLC (UltiMate 3000 chromatograph) according to the coincidence of retention times and spectral characteristics, the calculation of the content was carried out by simple normalization. The effect of the samples on nitric oxide production was studied on macrophages of C57BL/6 mice. Endotoxin control in the samples was carried out using a LAL test and cell incubation in the presence of polymyxin B.
Results and discussion. The composition of flavonoid fractions from A. polifolia, C. calyculata, L. palustre and E. nigrum has been studied. 8 phenolic compounds were found in C. calyculata shoots, including isoquercitrin, herbacetin, naringenin and naringin – for the first time for this species. 5 compounds were detected in A. polifolia shoots, including isoquercitrin and herbacetin, for the first time for this species. 5 and 4 compounds were identified in L. palustre and E. nigrum shoots, respectively, while quercetin glycosides are predominant in all samples: isoquercitrin, hyperoside and rutin. The fraction of C. calyculata flavonoids at doses of 1, 5, 10 mcg/ml inhibits the production of nitric oxide by macrophages by 30 %, and E. nigrum flavonoids at doses of 100 and 200 mcg/ml, on the contrary, enhance the production of nitrites by macrophages by 33 and 37 %, respectively.
Conclusion. A comparative study of the composition of total flavonoid fractions from A. polifolia, C. calyculata, L. palustre, and E. nigrum, which are capable of activating both M1 and M2 polarization of peritoneal macrophages in mice, has been conducted, which requires further in-depth study. The flavonoids C. calyculata and E. nigrum are promising for further study.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
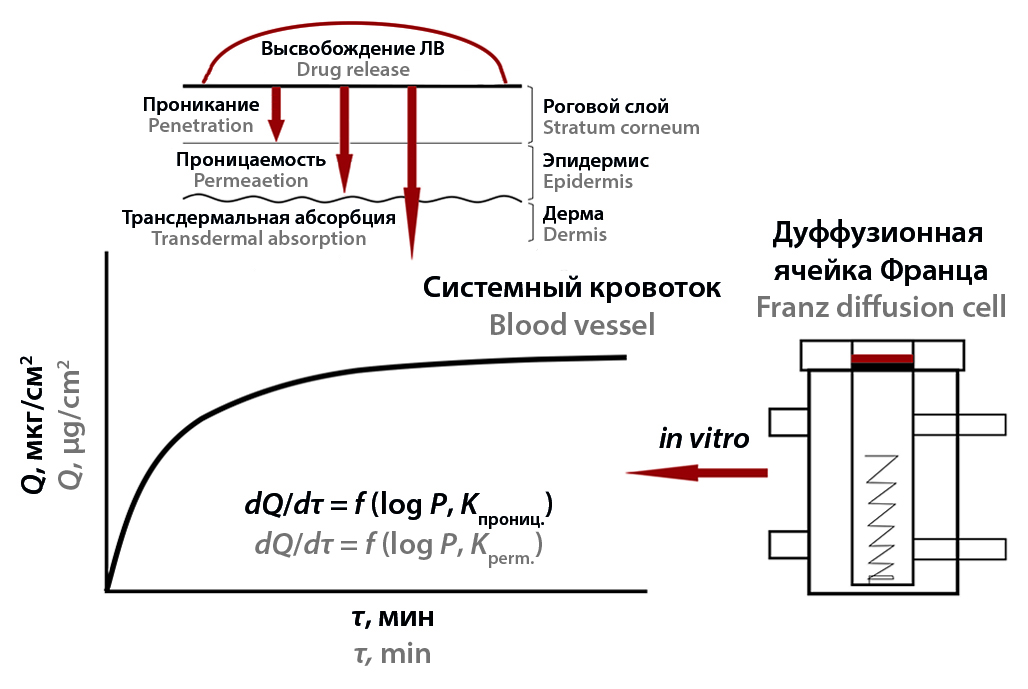
Introduction. The review considered the basic concepts of drug release and kinetic modeling of this process from dosage forms (DF) according to the dissolution profile using a vertical Franz diffusion cell.
Text. Drug release from dosage forms (ointments, gels, transdermal patches and polymer films) is usually described as the processes of drug dissolution in the biological system. Formally, this process, in accordance with pharmacopoeial methods, is assessed using various solubility tests. The theoretical aspects of drug release are based on the theory of mass transfer of substances from a polymer matrix into a system that simulates a biological environment. Drug release can be carried out via the passive diffusion mechanism according to Fick and "non-Fick" diffusion, drug desorption from the inner side of the membrane, as well as other mechanisms. Drug release is determined both lipophilicity and the membrane nature, both various physicochemical parameters of the drug. One of the correlation characteristics of mass transfer is the assessment of the permeability coefficient for a specific membrane that simulates skin. Permeability coefficient describes the rate of penetration of a drug per unit concentration in distance/time units. An example of relationship of "structure-permeability" correlation are the equations relating the permeability constant and lipophilicity to the molecular weight of the drug. The paper showed statistical methods of data analysis (MANOVA, ANOVA) and model-dependent methods (zero order, first order, Higuchi model, Korsmeyer – Peppas model, Hixson – Crowell model, etc.). The ideal drug delivery of non-degradable and non-disaggregating drugs describes as drug release model by zero-order reaction. For drug release of water-soluble drugs from a porous matrix, first-order reaction model is more typical. Kinetic models of fractional power functions are used usually as the cube root law (Hixson – Crowell model) or the square root law (Higuchi model) to describe the process of drug release from gels and dermal films and patches. The Korsmeyer – Peppas model allows us to evaluate the mechanism of mass transfer with Fickian diffusion or another process.
Conclusion. Mathematical modeling of the drug release kinetics from soft dosage forms is an important element for the development and optimization of their compositions. The study of the drugs release from soft dosage forms, including TTS and polymer films, as well as the release from solid dosage forms, is based on establishing correlations between the kinetics of the release and dissolution profile. The main release models, regardless of the DF, remain the following models: zero order, first order, Korsmeyer – Peppas, Higuchi, Hickson – Crowell, the empirical or semi-empirical constants of which vary significantly depending on the DF and the release mechanism (Fickian diffusion or another drug mass transfer mechanism). Correlation relationships QSPeR or QSPR, using the coefficients of permeability, diffusion and lipophilicity, provide information on the mass transfer of drugs through the skin.
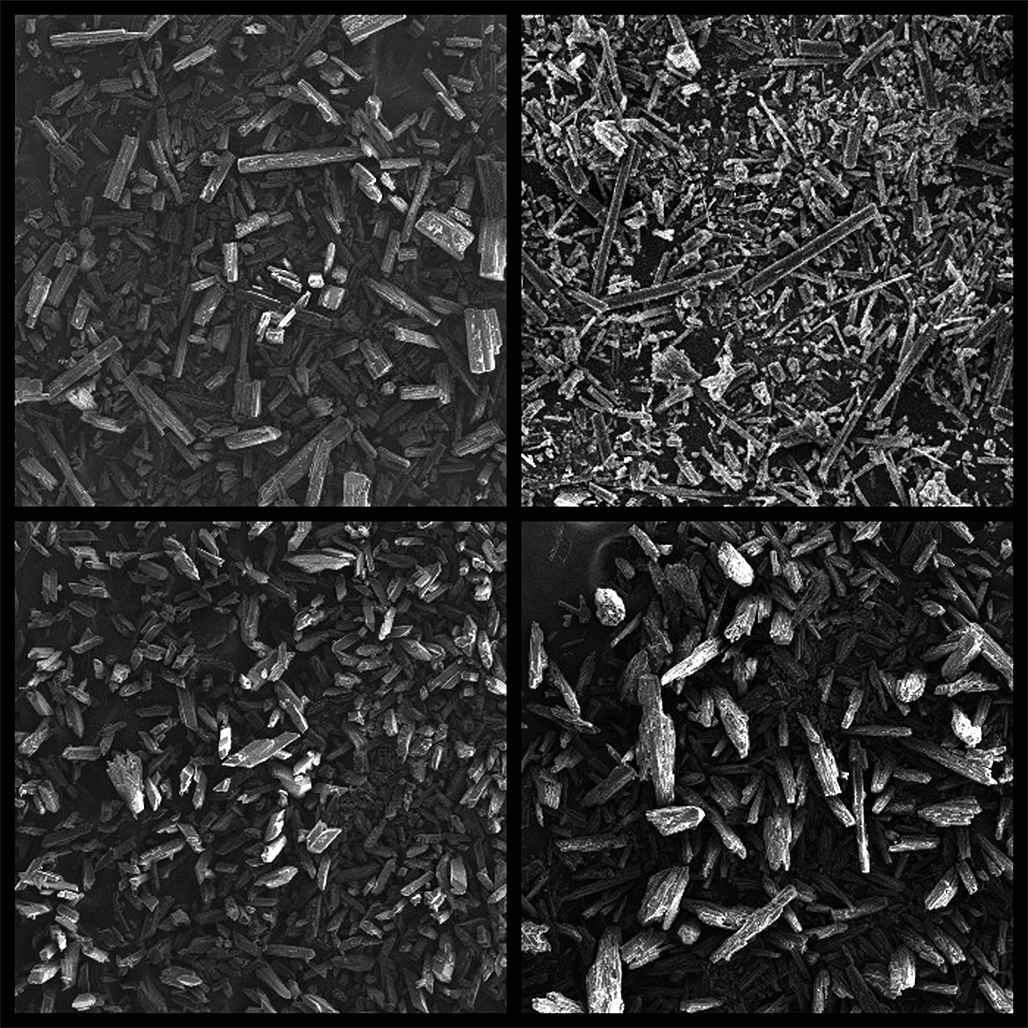
Introduction. In the modern world, there are many pharmaceutical substances that have various structure. During the development of finished dosage forms (FDPs) it is necessary to take into account many factors, such as physicochemical and technological properties of substances and excipients, manufacturing technology and others. This work is focused on the application of these approaches in practice in relation to a substance with anisodiametric crystal shape. Rebamipide was chosen as an example of such substance with poor technological characteristics for investigation and manufacturing technology selection.
Aim. Research of approaches to examine a substance with anisodiametric crystal shape (Rebamipide in this case) to determine its physicochemical and technological properties in purpose of theoretical substantiation of the best method of manufacturing mass for tabletting.
Materials and methods. In this study were used such materials as Rebamipide substance (α-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-quinolinepropanoic acid) (experimental sample). Also were used such equipment as flowability tester ERWEKA GT (Erweka GmbH, Germany), powder density tester ERWEKA SVM 122 (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany), vibrating sieve CISA RP 200N (CISA Cedaceria Industrial S.L., Spain), powder diffractometer D8 ADVANCE (Bruker Corporation, USA), calorimeter DSC 204 F1 (NETZSCH, Germany), Hitachi TM-100 electron microscope (Hitachi, Japan).
Results and discussion. The properties of Rebamipide substance were evaluated, such as polymorphism, melting point, microscopy and evaluation of technological characteristics. Application of the SeDeM method allowed to determine the critical parameters of the substance that need to be corrected.
Conclusion. It was found out experimentally that Rebamipide substance has polymorphism, high melting point, needle-shaped crystals, poor bulkiness and compactability, which was confirmed by the use of SeDeM method.
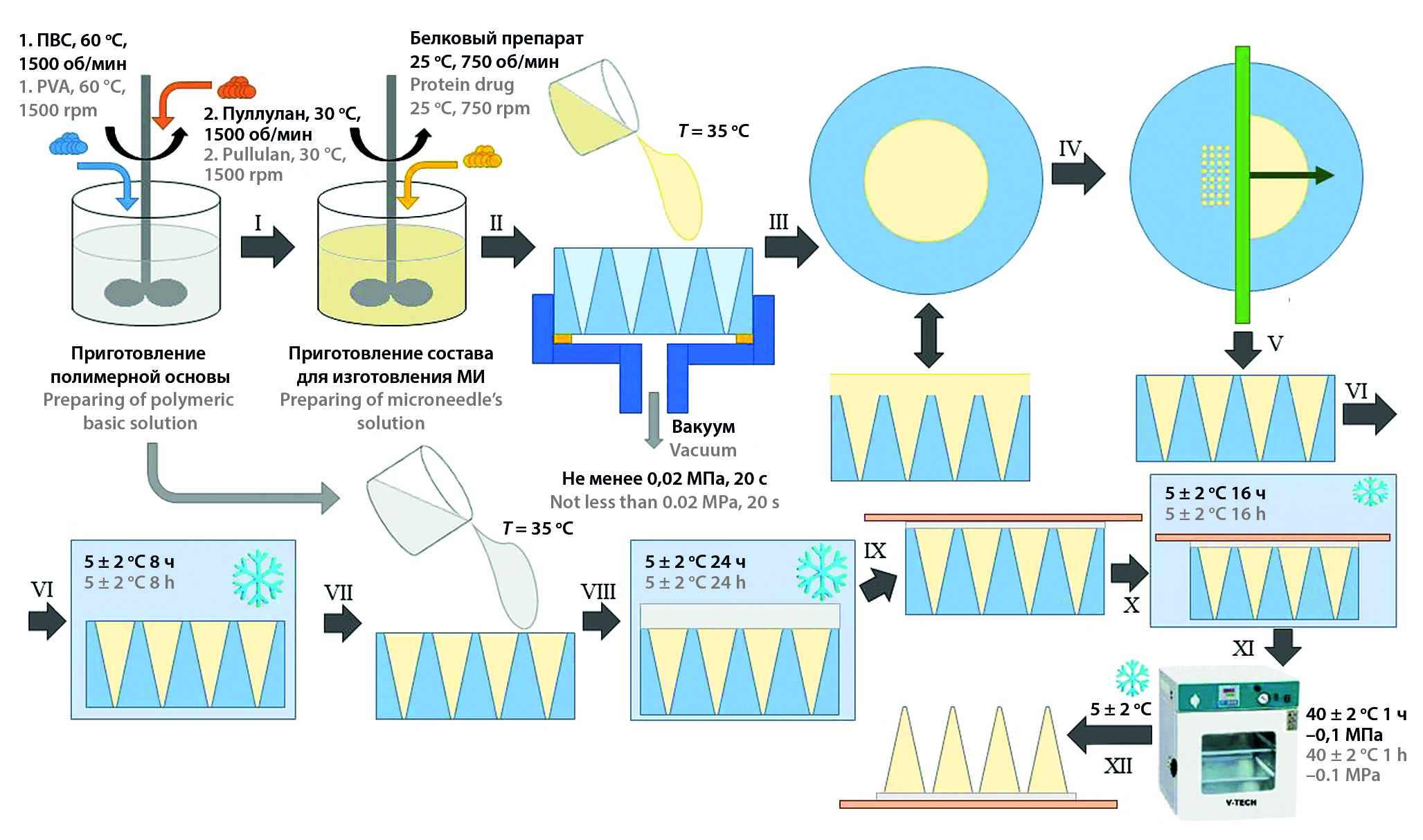
Introduction. Dissolving polymeric microneedles are attractive drug delivery system especially for vaccine delivery. Still there are a lot of obstacles in developing scalable manufacturing process of them.
Aim. To develop a scalable manufacturing process for producing polymeric dissolving microneedles, which can enable keeping protein activity during manufacturing process.
Materials and methods. Microneedles were produced from aqua solution of 20 % w.v. pullulan and 3 % w.v. polyvinyl alcohol by casting in hollow negative polyethylene terephthalate mold. Human serum albumin was chosen as a model protein for this investigation.
Results and discussion. There were chosen the mode of mold filling and microneedle drying process, which can guarantee keeping of protein activity during manufacturing process.
Conclusion. The designed technology can be easily scaled up and used for producing vaccine drug delivery systems, because it doesn’t contain any restraining processes.
Introduction. The development of defect-free film coating modes is an urgent task when transferring film-coated tablets technology. Technology transfer is an integral stage of the life cycle of any drug approved for industrial production. During the development of the technological process, deviations may occur, to eliminate which it is necessary to introduce auxiliary operations or change the chain of technological equipment.
Aim. Optimize the process of applying a film coating to tablets of the core of the vitamin and mineral complex.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were biconvex core tablets in the form of a boat of a vitamin and mineral complex consisting of vitamins C + E + B1 and minerals. To ensure the required technological properties, auxiliary substances were used: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium croscarmellose, potato starch, calcium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide. Ready-made film-forming mixtures (Colorcon®) in beige Opadry® II 85F 270000 were used as film-forming compositions. The film coating was applied in the craters with a perforated drum BG-80 (Pro-face, China) and BGK-150 (Zhejiang Canaan Technology Limited, China).
Results and discussion. The process of applying a film coating to the core tablets of a vitamin and mineral complex has been studied. The analysis of the current technological chain showed a number of disadvantages – a large amount of manual labor, the need for matting the drum, the duration of the process, low loading, braking of the production cycle due to lagging at the stage of applying the film shell. To solve the discovered problems, a project was developed to scale the technology at the stage of applying a film shell to tablets-the cores of a vitamin and mineral complex. During the implementation of the process, new equipment was purchased and installed for production. The development of the technological process made it possible to multiply the one-time loading into the boiler (by 2–3 times), automate the process due to the automatic operation function according to the parameters set before the start of the technological process, and exclude the matting of the drum from preparatory work. The quality of film-coated tablets has improved, and the risk of defects has significantly decreased.
Conclusion. During the study, it was proved that transferring the film coating process to another piece of equipment can improve the quality of the resulting film-coated tablets and optimize the technological process. A multiple increase in the loading size is not carried out at the same time by changing the number of nozzles and the inner section of the hose for applying the film coating material.
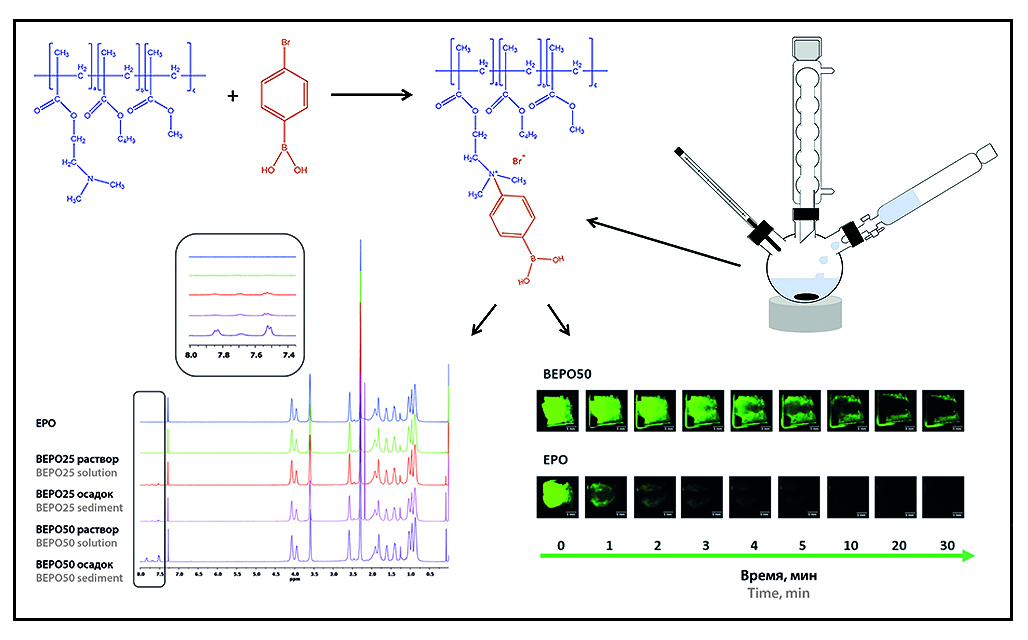
Introduction. In the pharmaceutical technology field there is great interest in polymers with mucoadhesive properties, as they increase the drug retention time on the mucosal surface and increase the bioavailability of the drug. There are various mucoadhesive drug delivery systems: tablets, films, gels, suspensions of micro- and nanoparticles, etc. The ability to adhesion depends on the excipients, especially on their chemical structure. Molecular weight, surface charge, flexibility of the polymer chain and the presence of various functional groups play an important role. Polymers under the trade name Eudragit®, produced by the German concern Evonik Nutrition & Care GmbH, have been used in the pharmaceutical field for several decades to produce controlled-release oral dosage forms. Eudragit® EPO (EPO) is a ternary copolymer based on methacrylic acid derivatives and has mucoadhesive properties due to the presence of dimethylamino groups in its structure. The proposed chemical modification of Eudragit® EPO with a phenylboronic acid derivative, due to the presence of hydroxyl groups in their structure, leads to additional interaction with mucin oligosaccharides, providing enhanced mucoadhesive properties of this polymer.
Aim. Synthesis and study of a chemically modified Eudragit® EPO using 4-bromophenylboronic acid in order to increase the mucoadhesive properties of the copolymer for use in transmucosal drug delivery systems.
Materials and methods. The synthesis of chemically modified Eudragit® EPO (BEPO) was carried out for 24 hours at 50 °C, followed by purification by dialysis using a dialysis membrane (MMO = 12–14 kDa; Medicell International Ltd, UK) for 7 days and freeze drying at –50 °C and 0.05 mbar using Heto Power Dry LL 3000 (Thermo Electron Corporation, USA) for 5 days. Confirmation of the formation of ВЕРО was carried out by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy on a Nicolet iS5 spectrometer (Thеrmо Fisher Sciеntific, USA) and 1H-NMR spectroscopy on a DPX 400 MHz device (Bruker, Germany). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and modulated differential scanning calorimetry (mDSC) were performed using Discovery TGA™ and Discovery DSC™ (TA Instruments, USA), respectively. The study of mucoadhesive properties was performed by the ability to retain the copolymer on the isolated sheep nasal mucosa at 37.0 ± 0.5 °C for 30 minutes.
Results and discussion. BEPO was prepared with a substitution degree of dimethylamino groups with phenylboronic acid of 25 % (BEPO25) and 50 % (BEPO50). The yields of BEPO25 and BEPO50 were 40.70 and 30.79 %. The new characteristic band appears at 1605 cm–1 in the IR spectrum of BEPO, which indicates the attachment of phenylboronic acid to EPO. In the 1H-NMR spectrum of BEPO, the formation of additional peaks in the range of 7.8 and 7.5 ppm is observed, which are absent in the EPO spectrum, which indicates the presence of phenylboronic acid. According to TGA results the samples of boronated EPO have the thermal stability similar to the original EPO. The results of DSC analysis show that the glass transition temperature (Tg) of BEPO samples is somehow higher than the original EPO, which is probably associated with a decrease in the amount of free dimethylamino groups in the terpolymer structure. BEPO50 is retained on the surface of isolated sheep nasal mucosa for 30 minutes, while EPO is washed off with artificial nasal fluid in 5 minutes.
Conclusion. The development and study of BEPO is a promising direction for further use in transmucosal drug delivery systems.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. Determination of pesticide residues presence in herbal plants and preparations based on them is an important step in confirming safety at the stage of the quality control of herbal plants. The usage of organophosphate pesticides (OPs) for the purposes of treatment of medicinal plants in the growing process is increasing. Scientific sources provide information on the detection of OPs in herbal plants, including quantities exceeding the allowed percentage limits as it is settled in regulatory documentation. At the same time, the problem of the distribution of particular kinds of OPs in the organs of herbal plants and their persistence remains understudied.
Aim. The present research aims to study the distribution in various parts of the herbal plants (marigolds, valerian, and stinging nettle) and the persistence of malathion and diazinon.
Materials and methods. Stinging nettle, that grows everywhere, exclusively cultivated marigolds, and valerian were selected as model plants. All of the plants were divided into three equal groups. Young plant shoots were processed twice with "Aliot" products containing 570 g/l of malathion and "Terradox" containing 40 g/kg of diazinon. The first group of plants was processed with pesticides following the manufacturer's instructions. The second group was treated in quantities, that were three times higher than the recommended dosage. The third group (control), was not processed with pesticides. Samples of various parts of growing herbal plants were analyzed at certain time points with the HPLC-MS/MS method according to the developed methodology. In order to study the persistence, we carried out a repeated analysis of dried samples stored without access to sunlight 0.5 years after the first one according to the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV.
Results and discussion. The authors found malathion and diazinon in all of the analyzed parts of medicinal marigolds, in leaves and roots of nettle dioecious, in deciduous shoots and rhizomes with roots of valerian officinalis. The highest proportion of pesticides was discovered in underground plant organs. When processed according to the instructions, in marigold and nettle roots and in rhizomes with valerian roots 16.7 mg/kg, 4.5 mg/kg, and 1.7 mg/kg of malathion and 19.6 mg/kg, 4.1 mg/kg, and 1.5 mg/kg of diazinon were found, respectively. These quantities exceed the allowed limits. The quantity of pesticides in the flowers of medicinal marigolds does not exceed the permissible values. The research on the persistence of these OPs data demonstrates that malathion and diazinon persist in plant tissues for a long time.
Conclusion. As a result of the research quantitative characteristics of the distribution of malathion and diazinon in various parts of medicinal marigolds, medicinal valerian, and dioecious nettle, as well as the rate and the extent of degradation of OPs during six months, were determined.
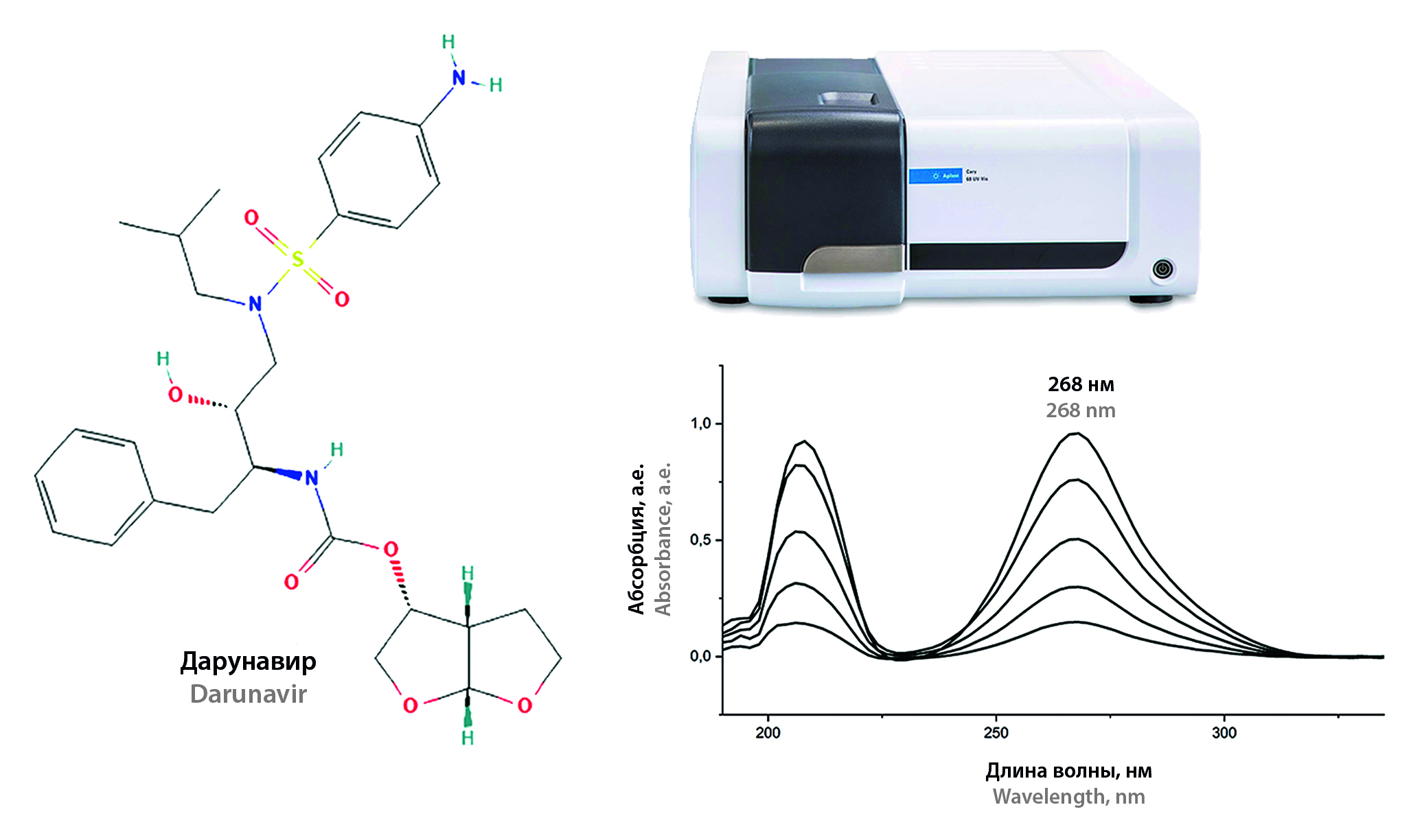
Introduction. Darunavir as an effective antiretroviral drug is widely used in clinical practice, including for the treatment of pediatric patients, as well as pregnant women, and for personalized therapy. Currently darunavir is used in the production of finished dosage forms, both in the form of crystalline ethanolate and in the form of an amorphous substance. In this regard, there is a need to develop and improve methods for the quantitative determination of darunavir. As an inexpensive and effective alternative to common chromatographic and titrimetric methods, spectrophotometric determination of darunavir in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum (UV spectrophotometry) may be used.
Aim. To develop and validate a method for the quantitative determination of amorphous darunavir in the substance by UV spectrophotometry.
Materials and methods. The following substances and consumables were used for the research: powdered amorphous darunavir substance (USP); darunavir reference standard (MSN Pharmachem Pvt. Ltd., India); methanol for HPLC Gradient Grade 99.9 % (High purity); acetonitrile for HPLC Gradient Grade 99.9 %; glacial acetic acid for HPLC; 0.1 M perchloric acid solution (in anhydrous acetic acid) for titration in non-aqueous media; nylon syringe filters with a pore diameter of 0.22 microns. Spectrophotometric determination of darunavir was carried out using an Cary 60 spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, USA) and a UNICO 2800 spectrophotometer (United Products & Instruments, Inc., USA). To prepare standard solutions, we used analytical balance Analytical Balance MS105/A (METTLER TOLEDO, Switzerland), analytical balance GH-120 (AND, Japan) class A measuring glassware, graduated pipettes ISOLAB.
Results and discussion. The method was developed and validated for the following characteristics: specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, analytical range. According to the study results, the main validation characteristics of the method meet the acceptance criteria.
Conclusion. A new method for the quantitative determination of amorphous darunavir by UV spectrophotometry was successfully developed and validated. The method may be used to control the quality of substances of amorphous darunavir, including the intrapharmaceutical control.
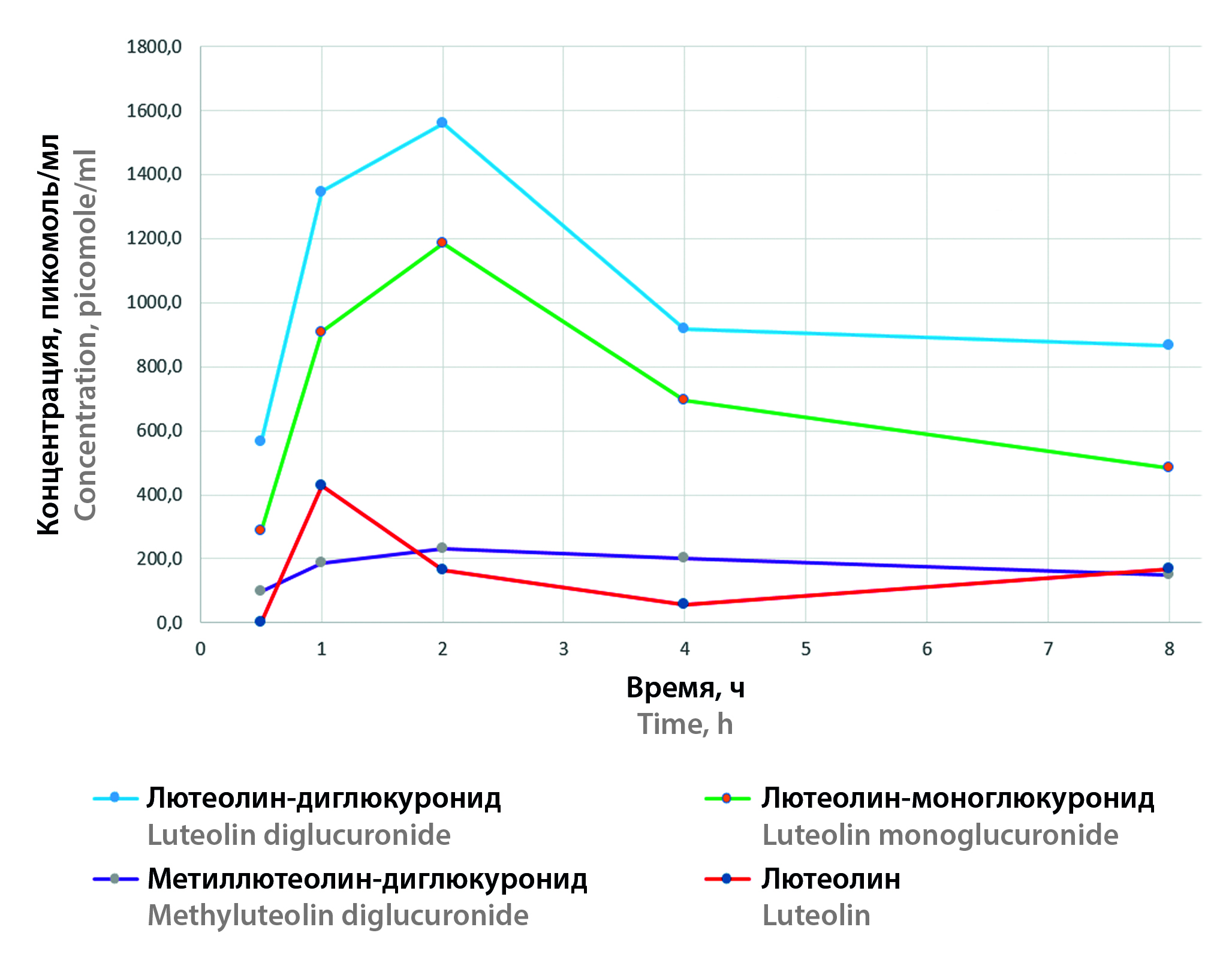
Introduction. The development and registration of antiviral drugs is an urgent task. Flavonoids, in particular, luteolin-7-glycoside (cinaroside, luteolin-7-O-glycoside) demonstrate high broad-spectrum antiviral activity in vitro, and the industrial regulations for the production of luteolin-7-glycoside from the leaves of holly willow have already been developed at the VILAR. One of the problems with the introduction of flavonoids into medical practice is their low bioavailability and intensive biotransformation. Existing publications provide contradictory data on the pharmacokinetics of luteolin-7-glycoside, and therefore our own research was conducted.
Aim. To develop a methodology for the quantitative analysis of luteolin-7-glycoside and its metabolites in blood plasma and to test it on laboratory animals.
Materials and methods. Animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the requirements of the "Guidelines for conducting preclinical studies of medicines". To develop a method of analysis and further clarify the time intervals of blood sampling, time points were analyzed: 30, 60 minutes, 2, 4, 8, 24 hours after administration of the test substance. Tubes with citrate blood of laboratory animals were centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes. The plasma was placed in an Eppendorf-type test tube, frozen and stored at –20 °C until chromatographic analysis was performed. Blood plasma sample preparation was carried out by precipitation with methyl alcohol, the supernatant was chromatographically separated on a column Luna® 5 µm C18 column 100 Å 250 × 4.6 mm in a gradient mode in a water-acetonitrile system and a modifier – 0.2 % formic acid. The metabolites were identified by high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. To do this, the spectral characteristics of the peaks that appeared on the chromatograms of blood plasma samples after oral administration of luteolin-7-glycoside were interpreted. The concentration of the analyzed substances was assessed by the internal standard method, which was rutin. To determine the concentration of luteolin, a standardized luteolin substance was used as a standard sample, the concentration of the remaining metabolites was estimated in terms of luteolin.
Results and discussion. It was found that after oral administration of luteolin-7-glycoside in starch paste to laboratory animals, native luteolin-7-glycoside was not detected in blood plasma. The main metabolites were luteolin-diglucuronide and luteolin-glucuronide, their maximum plasma concentrations are about three times higher than luteolin and methyllyuteolin-diglucuronide. The results are compared with data from other studies.
Conclusion. The absence of native luteolin-7-glycoside in blood plasma after oral administration makes it necessary to seriously reconsider the relevance of the conclusions obtained during studies of its activity in vitro. However, in the presence of antiviral activity in vivo, there is an urgent need for further research to establish the real mechanisms of action of this medicinal substance.
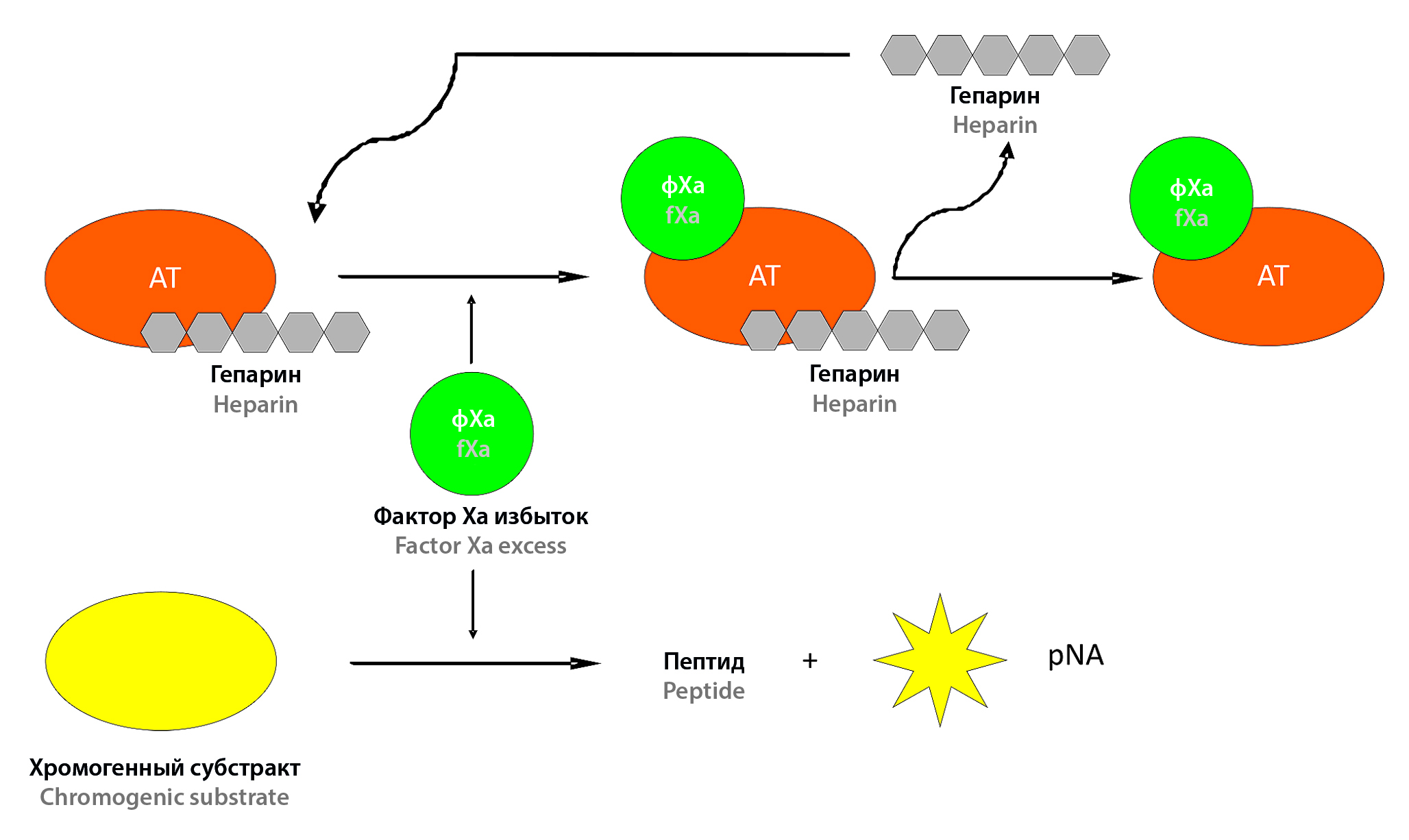
Introduction. The data on the wide clinical use of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) preparations are presented, necessitating the need for efficient and high-quality production of appropriate pharmaceuticals. The revealed variability of anticoagulant activity of LMWH preparations implies the provision of production with validated methods of control and certification. The aim of the work is to study the possibility of control of anticoagulant activity and assessment of functional compatibility of LMWH preparations when using domestic test systems.
Text. The data on analytical characteristics of chromogenic and coagulometric methods performed with the help of domestic test systems are presented. Their parameters correspond with the existing international requirements. The possibility of the mentioned methods to certify LMWH preparations correctly and reproducibly is shown. The given research results testify to the possibility of clotting methods to determine the bioequivalence of the studied preparations of LMWH.
Conclusion. The presented data prove the expediency of production control and certification of LMWH preparations by domestic test systems.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
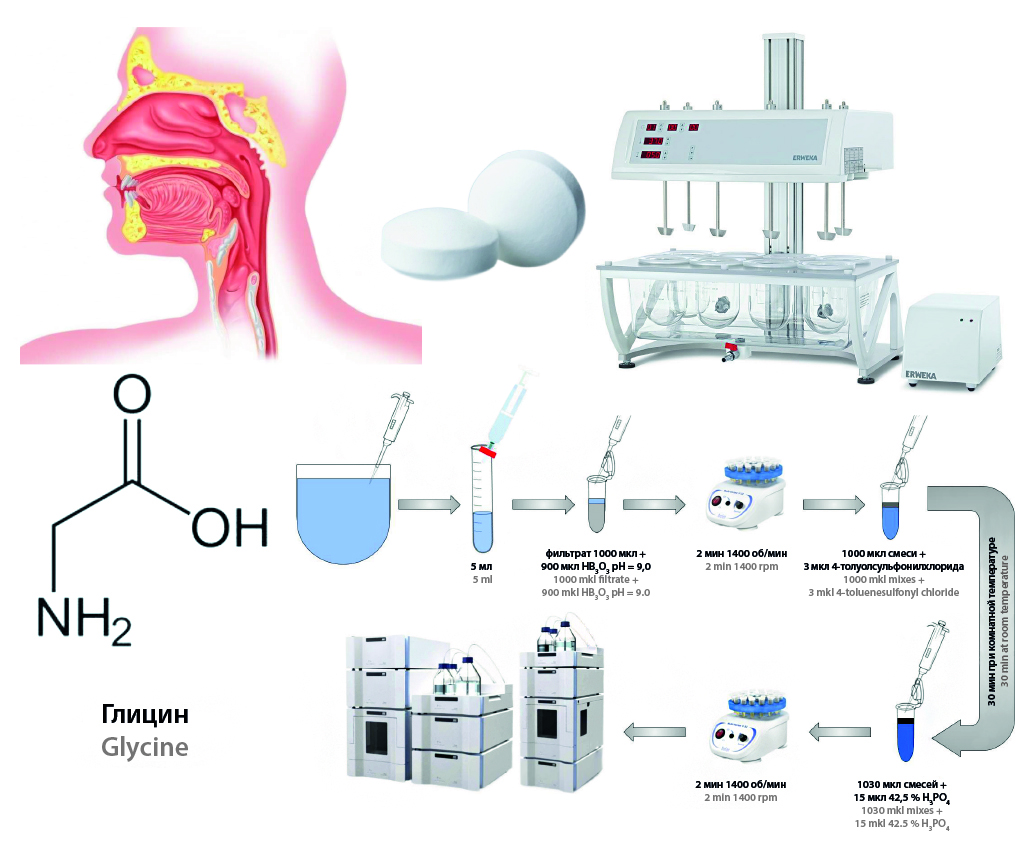
Introduction. Biorelevant dissolution media reconstitute the composition of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract. They are used as dissolution media in the evaluation of dissolution profiles of different dosage forms. Simulated biological fluids allow prediction of in vivo test results. The development of the composition of simulated salivary fluid allows the evaluation of drug properties under physiologically relevant conditions.
Aim. Evaluation of the release of the drug product "glycine, sublingual tablets, 100 mg", domestically produced in Simulated Saliva 5 pH 6.8.
Materials and methods. The preparations used for analysis were: «Glycine, sublingual tablets, 100 mg», domestically produced with valid expiration date. Comparative dissolution kinetics test was carried out on the dissolution test apparatus DT 6 (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany). Chromatographic separation and detection were performed on a Waters W1525 Binary HPLC Pump high-performance liquid chromatograph (Waters Corporation, USA) equipped with column and sample thermostat, degasser, autosampler and Waters 2487 Dual Absorbance Detector (Waters Corporation, USA). Detection was performed at a wavelength of 254 ± 2 nm after derivatization of the glycine molecule with 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride. A Grace Platinum C18-EPS 5 μm 4.6 × 250 mm Grace Platinum C18-EPS 5 μm 4.6 × 250 mm column (Grace, USA) and a Grace Platinum C18-EPS 5 μm 4.6 × 250 mm pre-column (Grace, USA) were used. The following software was used for the study: validated Microsoft Excel spreadsheet for calculating glycine release values.
Results and discussion. The technique for quantitative determination of glycine was developed and validated under CDKT in purified water medium and Simulated Saliva 5 pH 6.8. The validated analytical range of the methodology was 10–110 % of the nominal concentration of the dosage form in 300 mL volume of medium. The developed analytical technique was validated in the biopredictive in vitro test of glycine preparations. During the study in Simulated Saliva medium for drug formulations, more discriminative data were obtained, which were expressed as: different dissolution rate, curvature of the slope of the dissolution profile and time to reach the plateau in contrast to the dissolution medium purified water.
Conclusion. The quantification technique was developed and validated for biopredictive tests of tablets "Glycine, sublingual tablets, 100 mg". The analytical range of the technique was 10–110 % of the nominal concentration of the dosage form in 300 mL volume of medium. The results of the test in artificial saliva medium were more discriminatory.
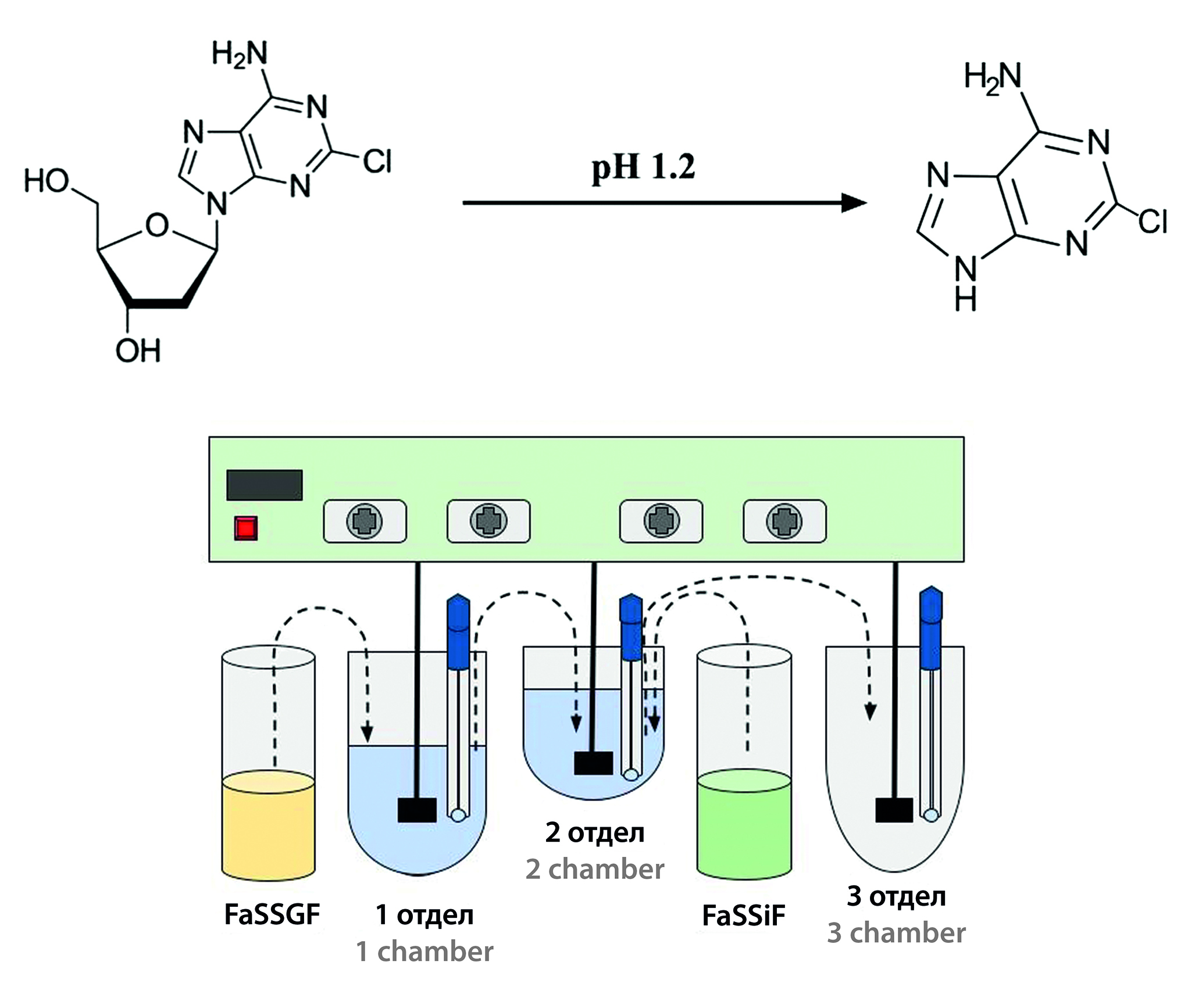
Introduction. The introduction of devices – analogues of GIS (hereinafter–- Gastro-intestinal simulator) is one of the current ways to develop in-vitro assessment of the quality of solid dosage forms. Testing on a physiologically relevant test device (hereinafter referred to as PRT) makes it possible to predict pharmacokinetic profiles due to more relevant conditions, including the use of biorelevant dissolution media, physiological volumes of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as transit between them.
Aim. Conduct a study of cladribine tablets on a physiologically relevant tester in order to predict the behavior of the drug in the human gastrointestinal tract.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are "Mavenclad®, tablets, 10 mg" (series 2200754, expiration date until 04.2025, NERPHARMA, S.r.L., Italy) and "Cladribine, tablets, 10 mg" of domestic production with valid expiration date. During the study, the reagents necessary for the preparation of biorelevant dissolution media and quantitative determination by HPLC. Physiologically relevant test were carried out using an apparatus of our own production, consisting of a DT-6 dissolution tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany), a water bath equipped with a Thermomix WB-4 heating element (B. Braun, Germany), and peristaltic pumps (Kamoer, China). The quantitative content of released cladribine was assessed using a highly efficient liquid chromatograph "Khromatek-Kristall HPLC 2014" (ZAO SKB "Khromatek", Russia) using a validated method at a wavelength of 252 nm, analysis time – 7 min, column – Grace HPLC Column Platinum C18-EPS, 250 × 4.6 mm, 5 mm (Grace, USA), temperature – 35 °C, elution mode – isocratic (A : B 80 : 20), mobile phase A – 0.1 % H3PO4 solution, phase B – acetonitrile.
Results and discussion. Profiles were obtained to assess the dynamics and degree of release of the studied drugs in various parts of the human gastrointestinal tract. Despite the expected degradation of cladribine in an acidic environment (pH1.2), under physiologically relevant conditions, the drug reached the third section (small intestine model) without degradation. Complete release of cladribine from the test and reference dosage forms was observed. Also, in the future, based on the data obtained, it is possible to predict pharmacokinetic profiles using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling approaches.
Conclusion. A PSF study was conducted for the drugs "Mavenclad®, tablets, 10 mg" and "Cladribine, tablets, 10 mg". Quantitative determination was carried out by HPLC-UV method. The test results showed complete release of both drugs and reaching the intestinal tract, indicating the absence of degradation of cladribine in the region simulating the stomach.
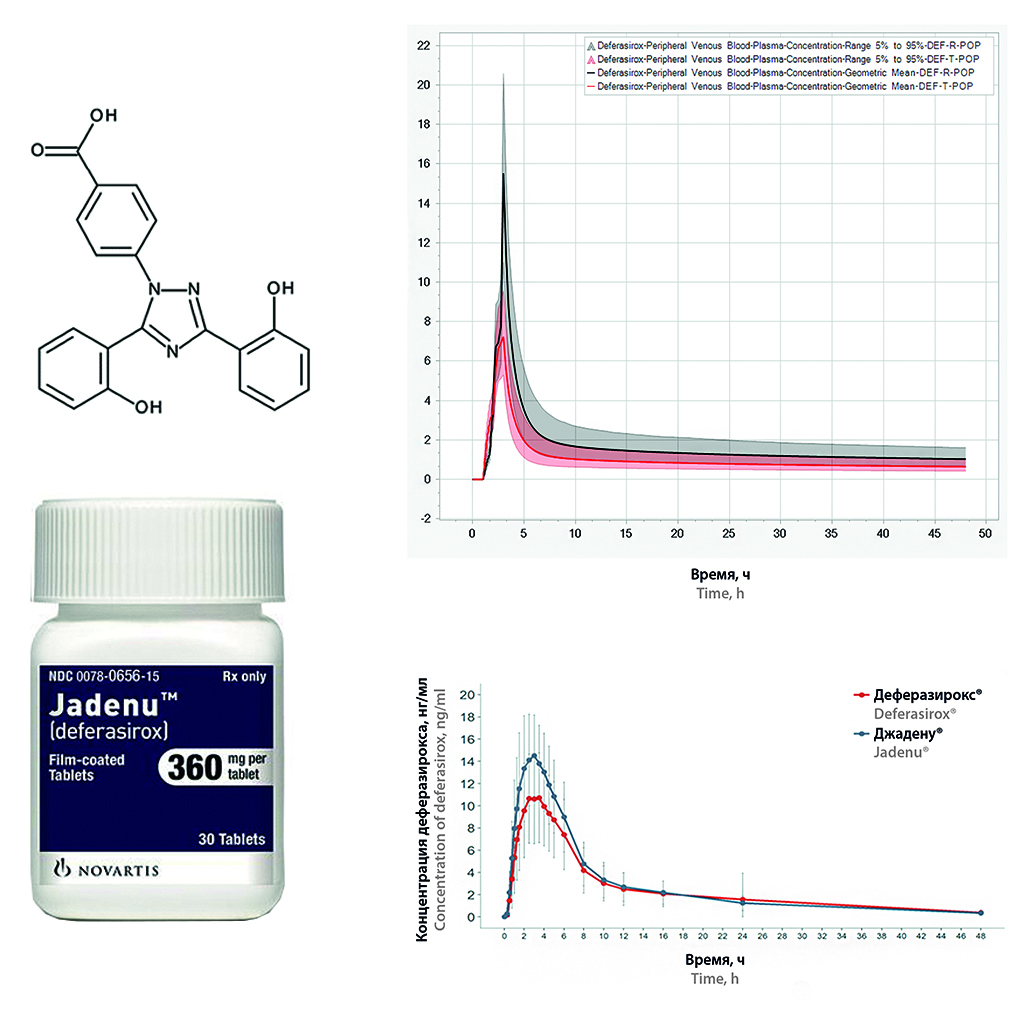
Introduction. Deferasirox is a complexing drug and belongs to class II according to the biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS), has acidic properties and belongs to subclass “a” (acid). This class is characterized by high permeability and low solubility, which limits the absorption of the active substance into the blood. As a result, the development of drugs with an active substance that can be assigning BCS to this class is a difficult task, and for generic drugs it is also associated with a high risk of obtaining unproven equivalence during clinical trials. To minimize the above risks, a physiologically relevant test was carried out with further data processing and construction of putative pharmacokinetic profiles.
Aim. The aim of the study is to conduct a physiologically relevant test (PRT) to predict in vitro pharmacokinetic profiles and compare them with in vivo data as part of a bioequivalence study of deferasirox.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are "Deferasirox, film-coated tablets, 360 mg" of a domestic manufacturer and "Jadenu®, film-coated tablets, 360 mg" (WTN22 series, expiration date until 10.2023, Novartis Pharma Stein AG, Switzerland). A physiologically relevant test was performed on the device SC PRT-6, Compliance. Quantitative analysis was carried out by HPLC-UV method.Pharmacokinetic profiles were modeled using PK-Sim® (Systems Biology Software Suite 11.2, Bayer Technology Services GmbH, Germany) based on data obtained from physiologically relevant test.
Results and discussion. A physiologically relevant drug test for deferasirox was performed and release profiles were obtained, which formed the basis of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model together with data on the physicochemical properties of the studied compound and literature data on the pharmacokinetics of deferasirox. The pharmacokinetic profiles obtained as part of the simulation on a virtual population were compared with data obtained during clinical trials.
Conclusion. A physiologically relevant test for the drug deferasirox was carried out, quantitative determination in the samples was carried out by HPLC-UV. The test resulted in data that allowed prediction of pharmacokinetic profiles that reflected the same differences observed in the profiles of the test and reference drug in the comparative pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence study of deferasirox drugs.
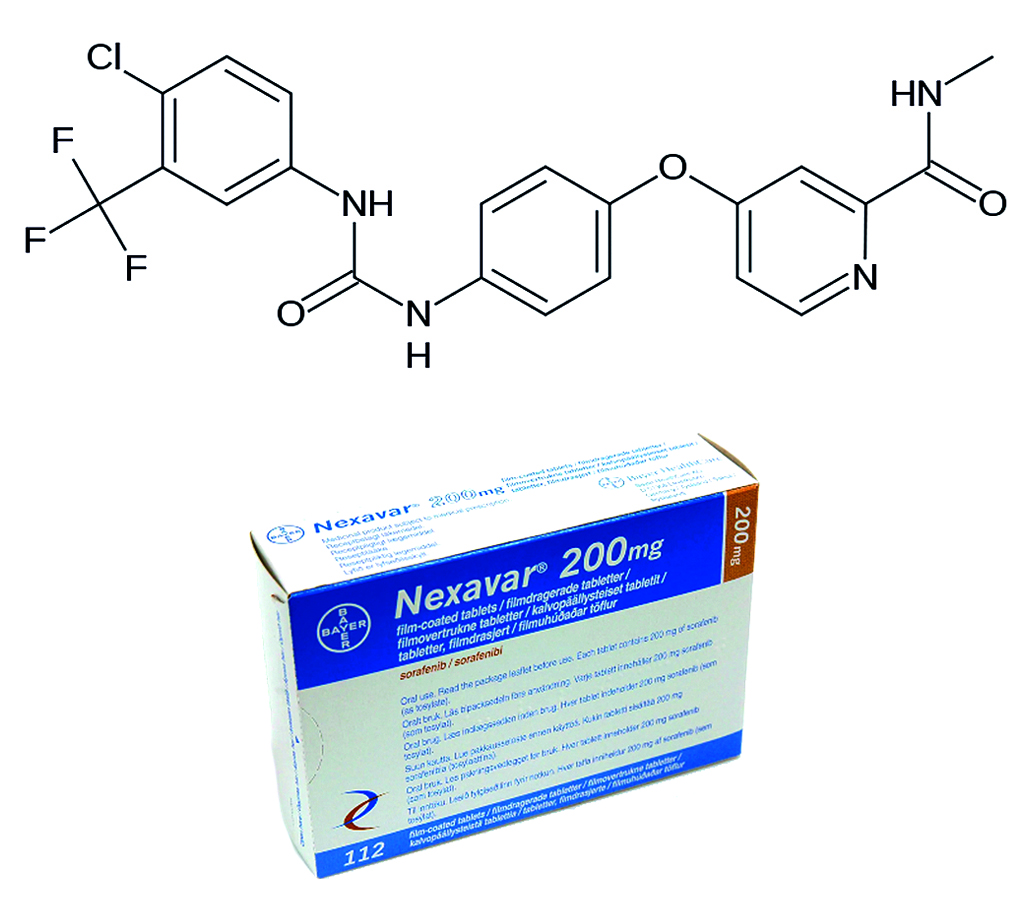
Introduction. Sorafenib is an antineoplastic drug belonging to class IIc according to the biopharmaceutical classification system (BCS) due to the presence of both acidic and basic properties. In addition to low solubility, sorafenib is characterized by high variability during clinical trials, in particular bioequivalence studies (BE). To selecting batches that can be recommended for BE studies, the dissolution kinetics test is currently widely used, however, the results of this test are not always sufficient and additional tests, for example, a physiologically relevant test, are advisable. To minimize the risks of obtaining nonequivalent results during the BE study, a physiologically relevant test (PRT) was carried out with further data processing and interpretation of the results of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling (PBPK).
Aim. The aim of the study is to conduct a physiologically relevant test (PRT) for the purpose of selecting a candidate batch for subsequent BE study of sorafenib drugs using the physiologically based pharmacokinetic model (PBPK).
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are Nexavar®, film-coated tablets, 200 mg (Bayer AG, Germany) (one batch) and Sorafenib, film-coated tablets, 200 mg (two batches) (Russia). The physiologically relevant test was performed on the SC PRT-6 device (LLC "Scientific Compliance", Russia). Quantitative analysis was performed by HPLC-UV on the Chromatec-Crystal HPLC 2014 device (CJSC "Chromatec", Russia). The plasma concentration profiles were simulated using PK-Sim® software (Systems Biology Software Suite 11.2, Bayer Technology Services GmbH, Germany).
Results and discussion. As part of the study, a method for the quantitative determination of sorafenib was developed and validated, a method for sample preparation was developed, and a method for conducting the PRT for sorafenib, as a representative of the IIc subclass of BCS, was developed. Based on the study results, release profiles were obtained that were used to select a candidate series for the BE study. The series were selected based on the PBPK analysis on a virtual population consisting of 36 healthy volunteers with activated enteropathic circulation, characteristic of sorafenib.
Conclusion. The PRT was carried out for the drug sorafenib. Quantitative determination was carried out by HPLC-UV according to the developed and validated method. The test resulted in obtaining data that were subjected to PBPK analysis. It was shown that the studied batches have high risks of non-equivalence during the bioequivalence study.
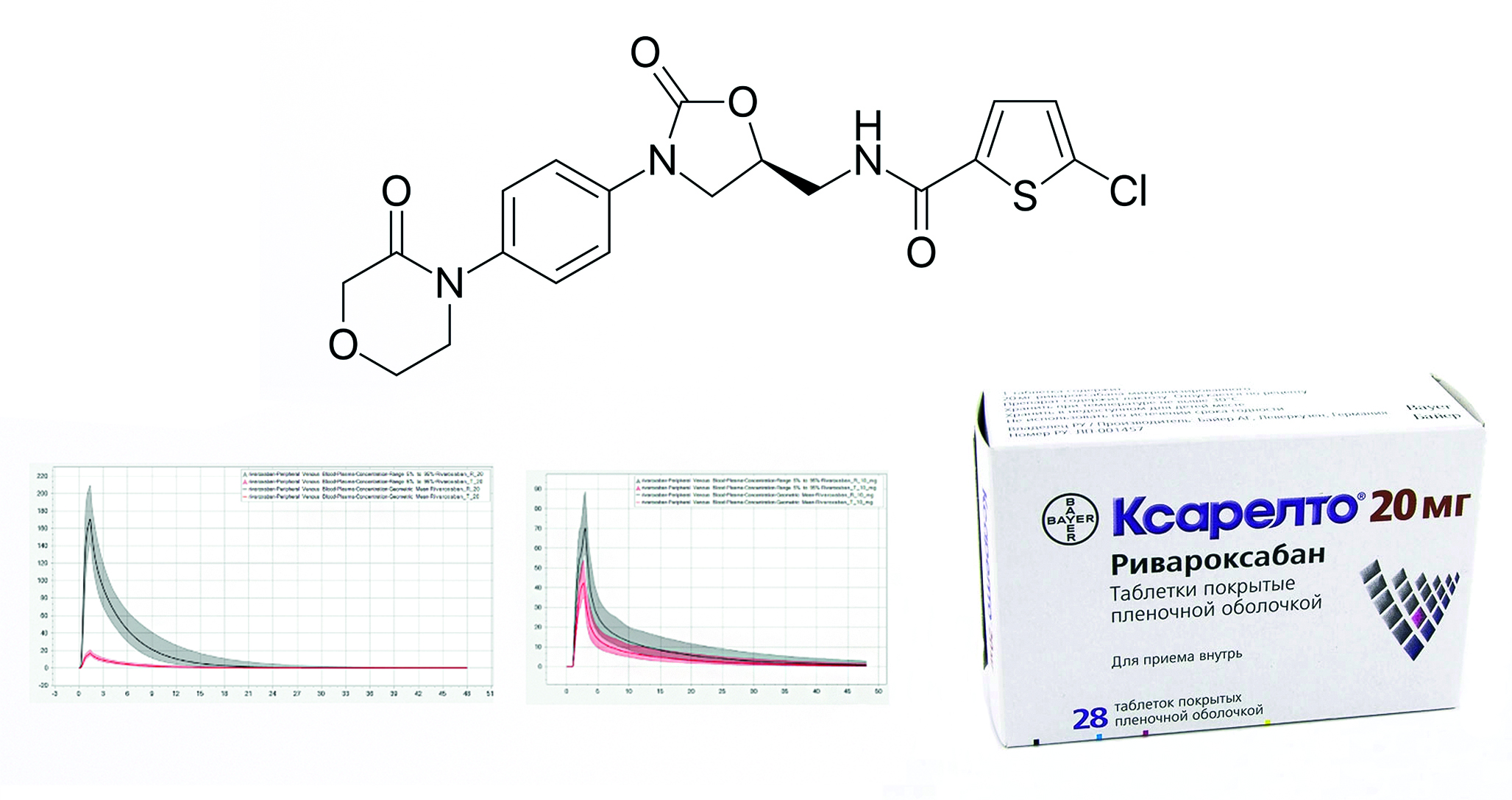
Introduction. The most important stage of pharmaceutical development of a generic drug is a clinical trial involving humans – a bioequivalence study. Considering the importance of finding rivaroxaban drugs in the list of vital and essential drugs, as part of ensuring technological sovereignty, the use of scientific robust and effective methods for determining the quality of the dosage form is required.
Aim. Conduct a study of rivaroxaban tablets on a physiologically relevant tester to predict pharmacokinetic profiles.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are "Xarelto®, film-coated tablets, 10 mg" (series BXJS871, with an expiration date of October 31, 2024, Bayer AG, Germany), "Xarelto®, film-coated tablets, 20 mg" (series BXKDF32, with an expiration date of May 17, 2026, Bayer AG, Germany) and "Rivaroxaban, film-coated tablets, 10 mg" and "Rivaroxaban, film-coated tablets, 20 mg", domestically produced, with valid expiration dates. During the study, reagents were used to prepare dissolution media and perform quantitative determination. The physiologically relevant test was performed on the SC PRT-6 device (LLC "Scientific Compliance", Russia). The quantitative content of released rivaroxaban within the comparative dissolution kinetics test in a medium of 0.1 in a medium of 0.1 % sodium lauryl sulfate solution in a phosphate buffer solution pH 6.5 was carried out on a SF-2000 spectrophotometer (LLC "OKB Spektr", Russia). The quantitative content of released rivaroxaban within the comparative dissolution kinetics test in biorelevant dissolution media and physiological relevance test was assessed on a high-performance liquid chromatograph "Chromatec-Crystal HPLC 2014" (CJSC "Chromatec", Russia). Pharmacokinetic profiles were modeled in the PK-Sim® (Systems Biology Software Suite 11.2, Bayer Technology Services GmbH, Germany) program based on the data obtained within the physiologically relevant test. The clinical study of rivaroxaban tablets was a prospective, open-label, randomized, crossover, two-stage comparative study in two groups of volunteers with a single dose of drugs on the fast condition. The study randomized 30 healthy male volunteers aged 18–45 years.
Results and discussion. A complex of in vitro tests was conducted, profiles were obtained that allow us to evaluate the dynamics and degree of release of the studied drugs in various parts of the human gastrointestinal tract. A comparison of the sequential and hybrid schemes for conducting the physiological relevance test was carried out. Within the framework of the set of tests, qualitative and quantitative correlation with the clinical trials data was observed only for the hybrid physiological relevance test scheme. Based on the results of physiological relevance test using different schemes, pharmacokinetic profiles for a pair of drugs were predicted and the prediction error was assessed.
Conclusion. A set of scientific in vitro tests was conducted for the drugs "Xarelto®, film-coated tablets, 10 mg and 20 mg", "Rivaroxaban, film-coated tablets, 10 mg and 20 mg". Based on the physiological relevance test results, pharmacokinetic profiles for a pair of drugs were predicted with low error and high reliability. As part of the comparison of data obtained during clinical trial and modeling, the smallest prediction error was noted when performing physiological relevance test using a hybrid scheme.
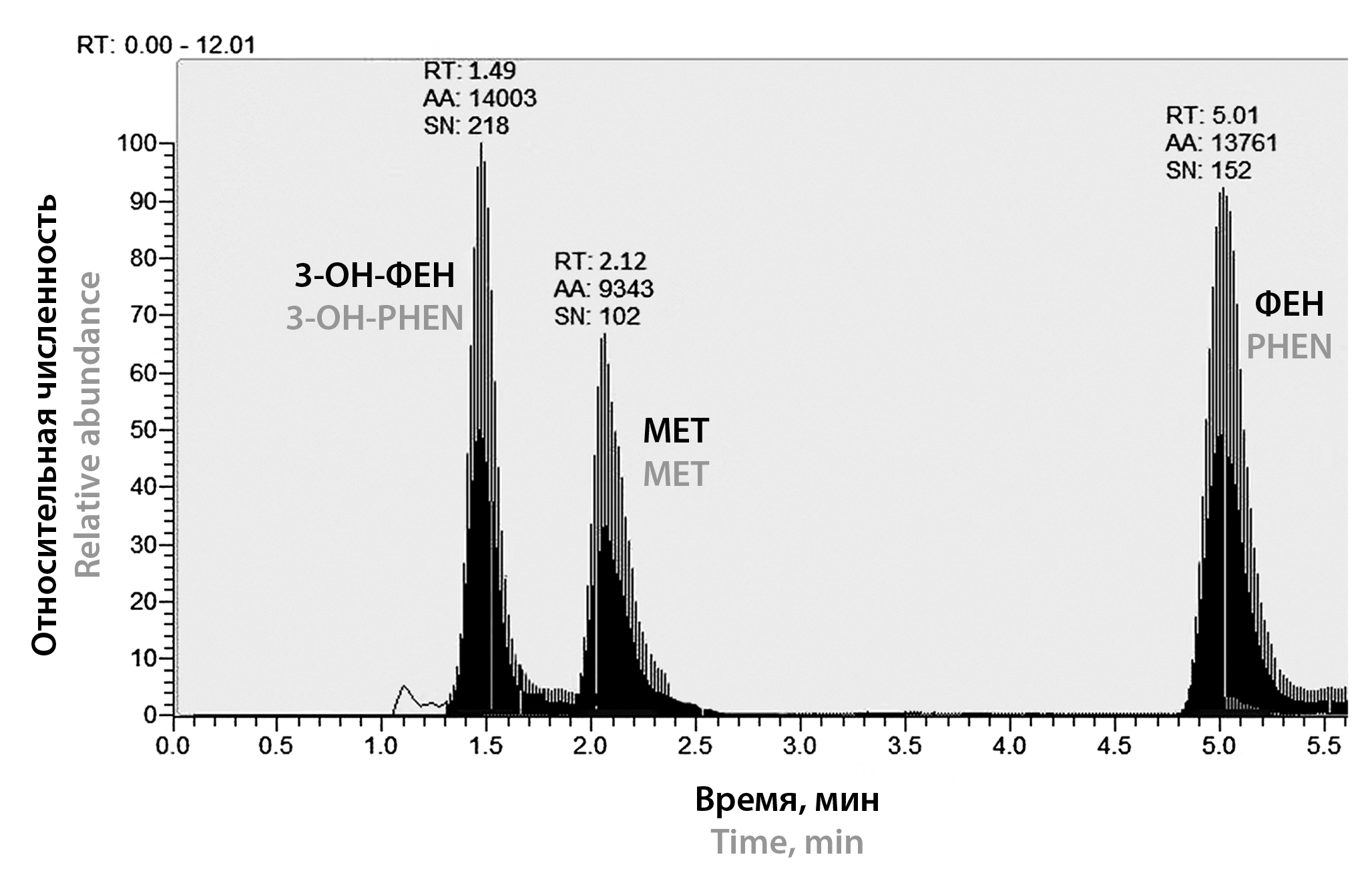
Introduction. The presence of the active metabolite (3-hydroxyphenazepam, 3-OH-PHEN), the wide interindividual variability of the therapeutic effect of phenazepam (PHEN), as well as its active moiety in the blood, determine the relevance of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). To do this, the researcher must have an express analytical technique with a wide analytical range, a low limit of quantification (LLOQ), and with robustness with different sample preparation methods.
Aim. Development and validation of quantitative methods for PHEN and 3-OH-PHEN in human blood plasma with different sample preparation methods.
Materials and methods. The determination of PHEN and 3-OH-PHEN has been performed by high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Solid-phase extraction (SPE) and liquid extraction with support (SLE) otherwise called liquid-liquid extraction in the solid phase were used for sample preparation. Metoprolol was utilized as an internal standard (IS). Gradient elution profile between mobile phase A (0.2 % aqueous formic acid) and B (100 % acetonitrile) has been used. Column: Hypersil GOLD® C18, 50 × 2.1 mm, 3.5 μm.
Results and discussion. Two methods have been developed for the quantitative determination of PHEN and 3-OH-PHEN in human blood plasma using different sample preparation methods: SPE and SLE. The conditions of chromatographic separation and mass spectrometric detection of the analytes are selected. The following validation characteristics were determined for both methods: selectivity, calibration curve, accuracy, precision, degree of extraction, LLOQ, carry-over effect, matrix factor, stability of standard solutions and analyte in the matrix.
Conclusion. The validation results of the developed methods meet the established criteria, which allows them to be used for the quantitative determination of PHEN and 3-OH-PHEN in human blood plasma. The wide analytical range for both methods 1–1000.00 ng/ml allows the use them for pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence studies, as well as in toxicology.
Introduction. The use of doxorubicin in clinical practice has shown cumulative and dose-dependent toxic effects on cardiomyocytes, leading to an increase of mortality risk among patients with cancer and as a resulting to restrictions in the indications for its use.
Text. A dangerous adverse reaction of doxorubicin is cardiomyopathy, leading to congestive heart failure. Cardiotoxicity is based on at least several pathophysiological mechanisms (described in more detail in the first part of the review), leading to damage to cardiomyocytes as a result of oxidative stress with the formation of free radicals, dysfunction of mitochondria, autophagy, release of nitric oxide and inflammatory mediators, as well as changes in gene expression and proteins leading to apoptosis. The current (second) part of the review provides detailed information on the actual understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the described cardiotoxicity, the effect of doxorubicin on other heart cells. The use of cardioprotective strategies will reduce the severity and likelihood of developing cardiotoxicity. This article describes strategies based on reducing the maximum cumulative dose, changing the speed of doxorubicin administration, using pegylated liposomal formulations and cardioprotective agents, as well as exercise.
Conclusion. Despite the huge number of scientific papers devoted to various aspects of cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin, its prevention and treatment, this issue requires more careful study and development of more advanced methods of early diagnosis, prevention and more effective therapy the complication.
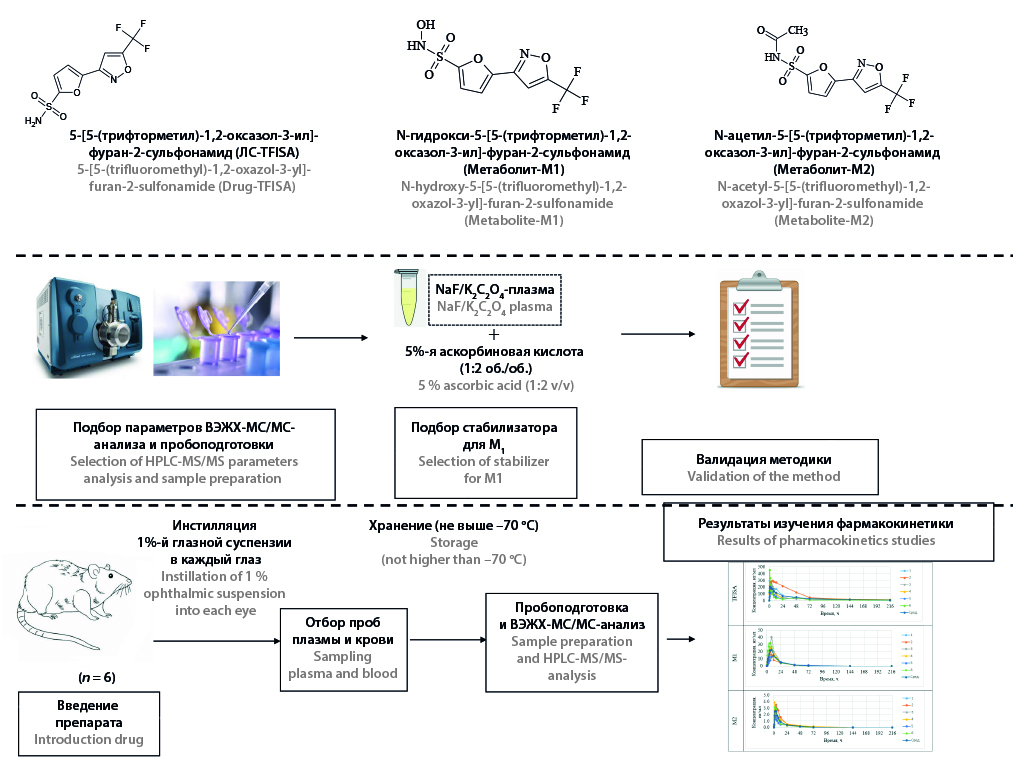
Introduction. The study of the systemic exposure of a new original drug is an essential part of its preclinical study. 5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide is a new selective carbonic anhydrase II inhibitor for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Methods for the quantitative determination of this compound and its N-hydroxy- and N-acetyl metabolites in the plasma of laboratory animals have not been previously developed.
Aim. Development and validation of a method of quantitative determination of 5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide and its metabolites N-hydroxy-5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide (M1) and N-acetyl-5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide (M2) in rat and rabbit blood plasma by HPLC-MS/MS.
Materials and methods. Protein precipitation by methanol was applied for sample preparation. 5-[2-(morpholine-4-carbonyl)-1,3-oxazole-5-yl]-thiophene-2-sulfonamide was used as an internal standard. A 5 % aqueous solution of ascorbic acid was added to the plasma samples at volume ratio 1 : 2 to prevent decomposition of N-hydroxy-5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide. The combination of sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate was selected as an anticoagulant. Chromatographic separation was performed on Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 column (150 × 3.0 mm, 3.5 µm) with Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 pre-column (12.5 × 2.1 mm, 5.0 µm) using a mobile phase based on a 0.1 % aqueous solution of formic acid and methanol. Mass spectrometric detection was carried out in the MRM mode using electrospray ionization in negative polarity. The method was tested during a pharmacokinetic study of a 1 % ocular suspension of 5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide on 6 Wistar rats. Blood samples were collected before administration, as well as 30 min, 1 h, 1 h 30 min, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 144 h, 216 h after administration. The non-compartment approach was used for calculation pharmacokinetic parameters.
Results and discussion. The developed method has been validated in parameters of selectivity, calibration curve, accuracy and precision, matrix effect, dilution integrity, carry over, reinjection reproducibility, stability. The analytical range of determination of 5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide in plasma was 10–4000 ng/ml, M1 – 1.0–400.0 ng/ml, M2 – 0.1–40.0 ng/ml. The selected combination of anticoagulant and stabilizer solution allows storage of plasma samples in freezing chamber for 28 days.
Conclusion. The developed method has been fully validated and confirmed its suitability for quantitative determination of 5-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazole-3-yl]-furan-2-sulfonamide and its metabolites in the blood plasma of laboratory animals. The method has been successfully used for pharmacokinetic study of 1 % ocular suspension of the drug.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)