FROM EDITOR
On February 26 and 27, 2025, the annual two-day congress "Drug development and registration" will be held in Moscow. The topics of the congress traditionally cover all key stages of the life cycle of a drug, from development to post-registration studies.
We present to your attention a new interview as part of the Leaders' Opinion series. Today’s guest is Natalya Malykh, Vice President for Business Development at Pharmasyntez Group of Companies. The interviewer was Natalya V. Kuldzhanova, director of the scientific and production journal "Drug development and registration".
The third part of the article is devoted to a review of sources reflecting the functions of the apothecary order. To these sources Historian scientists include: petitions, memories and releases (copies) from petitions, correspondence with regional authorities, decrees and decree royal letters, voivode's formal replices, order records, paintings (lists) of objects and people, order books, fairy tales and inspections, receipt and expenditure books and preserved recipes. In addition, in the corpus of documents of the apothecary order there are extracts from the report, interrogation speeches, copies of court cases, genealogical paintings, rank, boyar scribe books, etc. Analysis of the content of these sources allows us to establish the role of the apothecary order in the structure of state management of the pharmacy business.
"Custom" isolation is the development of an isolation methodology and the isolation of a customized compound in a specific time frame through a combination of analytical methods that take into account the characteristics of a particular plant and the physicochemical properties of the isolated components.
EVENTS
On October 7, 2024, within the framework of the BIOTECHMED forum, the main plenary session "Movement towards technological leadership – national projects of technological sovereignty for healthcare" was held.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
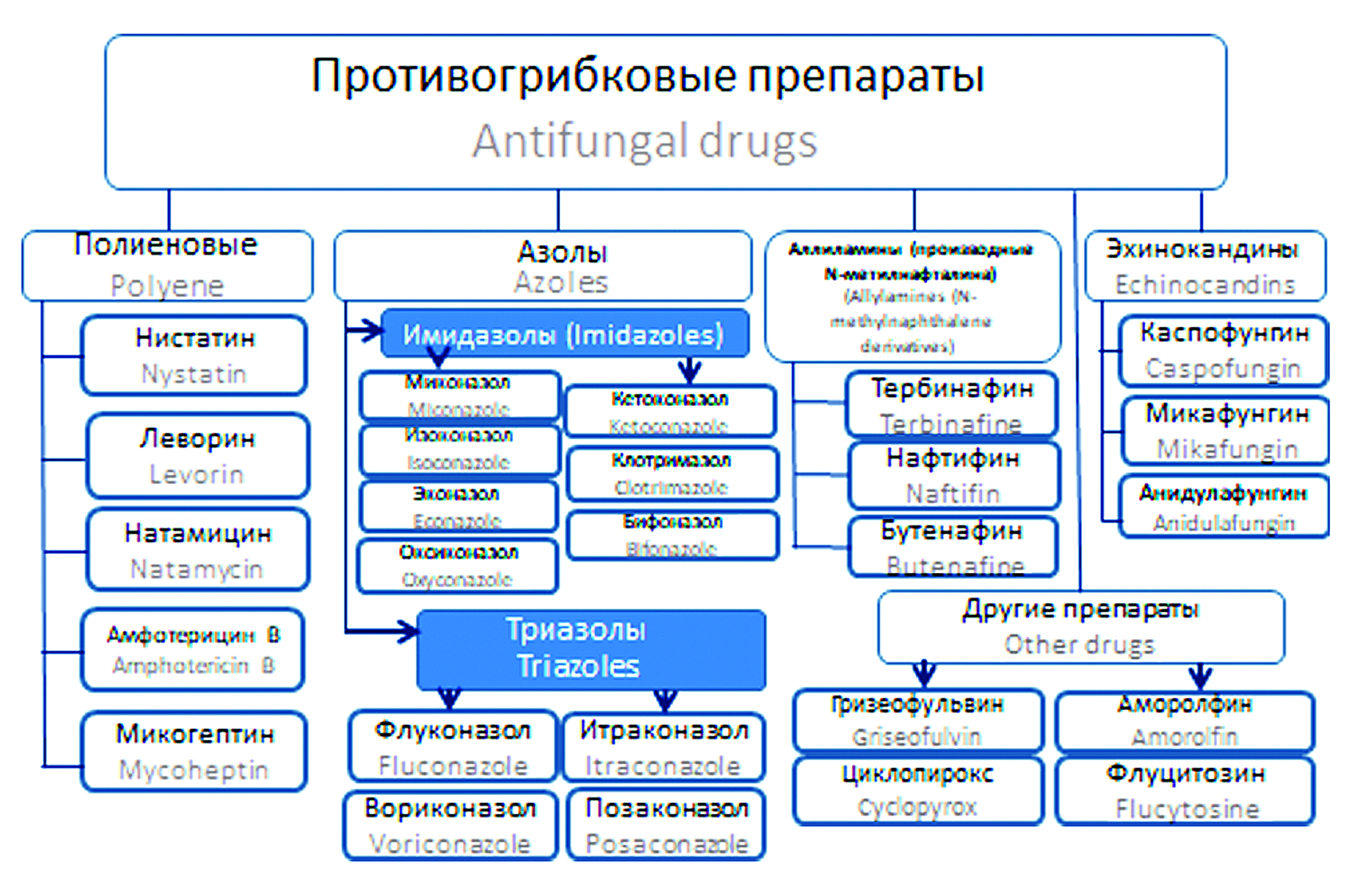
Introduction. Information about mycoses and antifungal drugs of the modern type is often fragmentary and unsystematic, which requires correction.
Aim. To systematize the latest information about fungi and mycoses, means of combating them and the problems encountered along the way, to highlight the latest achievements in the field of synthesis and research of the activities of 1,2,4-triazole as a potential fungicidal compound.
Materials and methods. The materials were the authors' research published in advanced scientific journals, conducted around the world in the field of studying fungi, antifungal drugs, and the search for new antifungal agents.
Results and discussion. The article provides an overview of current information on the morphobiological features of fungi, updating their taxonomy and nomenclature, shows the role of fungi in nature and the development of fungal infections in humans and animals, structured information on the classification of mycoses and their pathogens. The latest information is also provided on the pharmacological properties of the main currently existing antifungal drugs, the mechanisms of formation of resistance to them in fungi, in a comparative aspect with other groups of antimycotic drugs, the prospects of azoles and their derivatives as new fungicidal drugs and disinfectants are shown. Literature studies have shown that 1,2,4-triazole derivatives have a wide range of antifungal activity, which extends to other types of activity.
Conclusion. It was noted that the significant prospects of triazoles are due, among other things, to the fungicidal effect on resistant strains of fungi-pathogens of human and animal infections. The advantage of the new derivatives is the low level of concentrations suppressing fungi, low cytotoxicity, which allows them to be used for intravenous administration in the future. Updating information on the effectiveness of new antifungal compounds will help researchers systematize knowledge about the properties of azoles, which can contribute to the search and development of new potential candidates for antifungal drugs with high efficiency and selectivity, and contribute to the formation of new research directions for the search for effective means of combating mycoses in various fields of human activity.
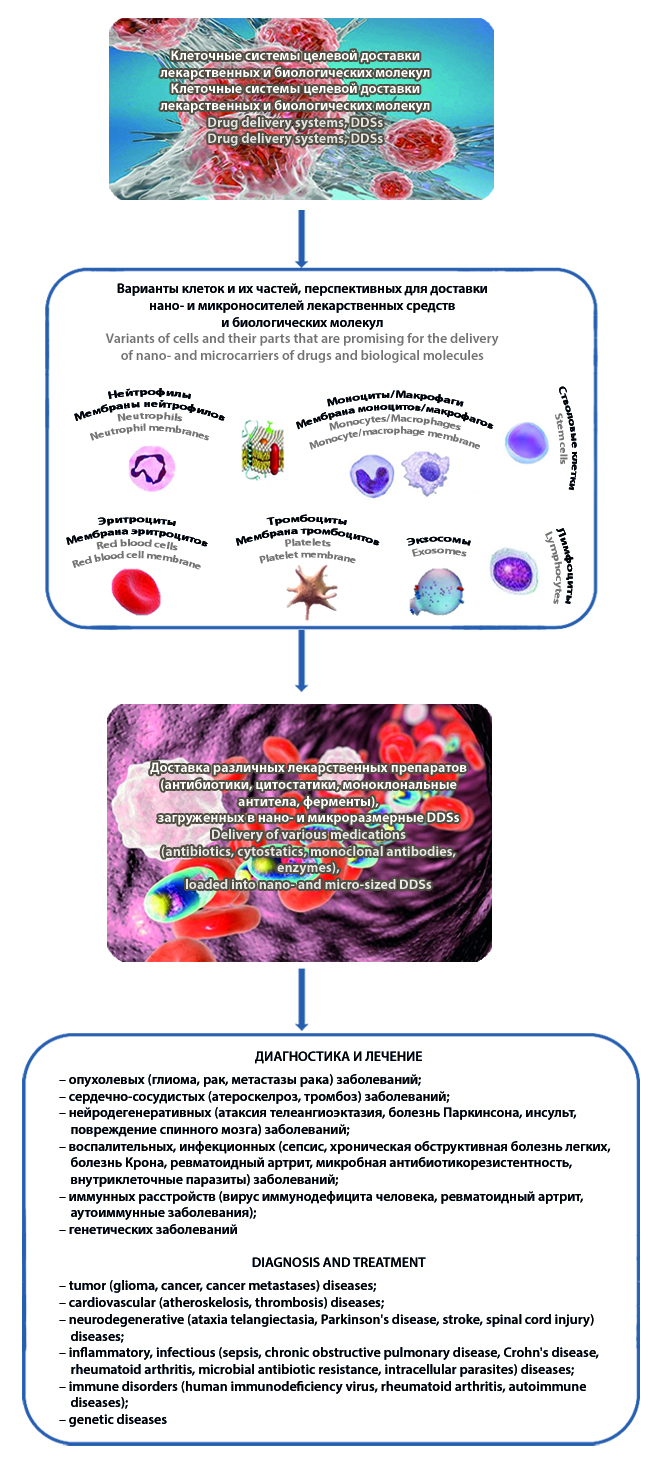
Introduction. Cellular systems for targeted delivery of drug and biological molecules (drug delivery systems, DDSs) are currently considered as a promising solution to the problems of nano- and micro-sized drug carriers.
Text. The review briefly examines fundamental and applied issues in the development of cellular DDSs, the morphofunctional diversity of which theoretically makes it possible to solve the problems of pharmacotherapy of various diseases. Sources are presented summarizing clinical protocols for the use of cellular DDSs, which are, however, limited to antitumor and anti-inflammatory therapy. The advantages, as well as particular and general disadvantages of using certain cells (blood cells, immunocytes, stem cells) as promising platforms for translation into clinical practice of delivery vehicles for various drugs (antibiotics, cytostatics, monoclonal antibodies, enzymes, etc.) loaded into nano- and micro-sized DDSs.
Conclusion. Despite the obvious and impressive successes of fundamental and applied research in this area, a difficult path lies ahead in optimizing the processes of targeted delivery and controlled release of drug and biological molecules using cellular DDSs.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
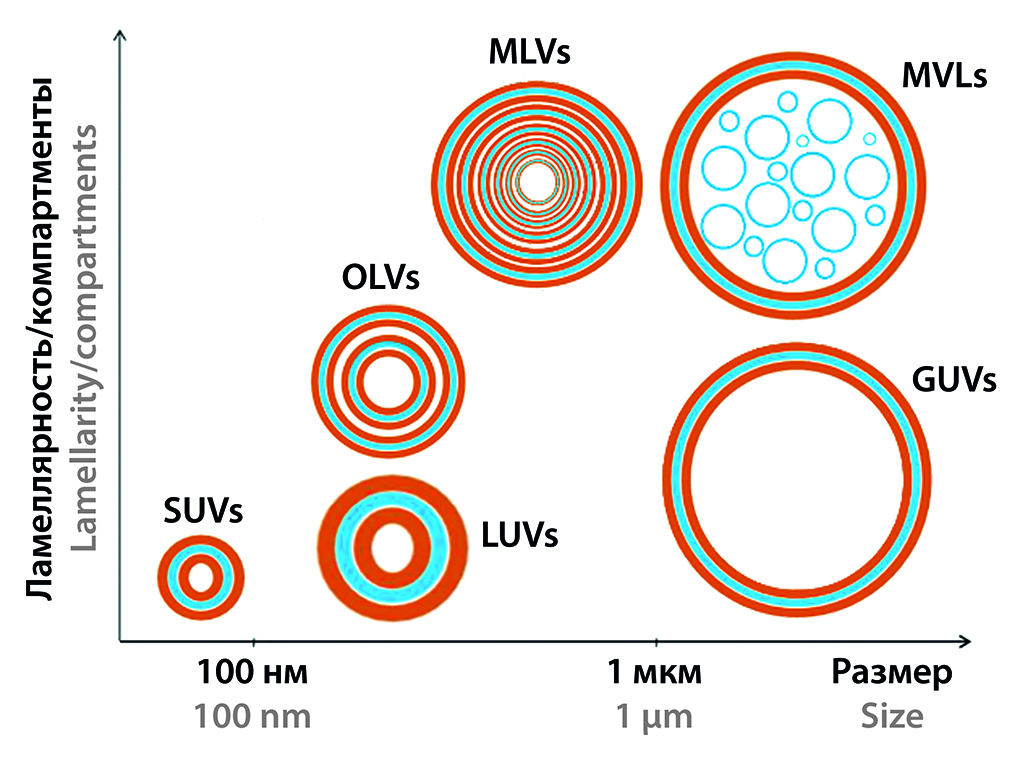
Introduction. This review article is focused on the modern classification of liposomes, preparation methods, stabilization and the role of structural components, visualization, and pharmacokinetics. Part 1 discusses the first three aspects mentioned above.
Text. Depending on the size and number of bilayers, liposomes are classified into simple, long-circulating, cationic, immuno-liposomes, and sterically stabilized. The lipid components of liposomes can have a pronounced effect on target organs and tissues. Metabolites of the main components of liposomes have their biological activity, depending on their combination and dosage. All of the above indicates the promise of using liposomes not only as carriers of drugs but also as independent effectors that can have a significant impact on human metabolism in various diseases. The advantages and limitations of methods for preparing liposomes, and the features for manufacturing stealth liposomes are discussed. A special section of the article is dedicated to liposome stabilization.
Conclusions. The information discussed in the review article may be useful in the development of pharmaceutical formulations in liposomes. Liposomes are not only promising nanocontainers for targeted drug delivery, but also metabolically active complexes with a wide spectrum of activity.
Introduction. In the second part of the review we discussed aspects of visualization, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of liposomes.
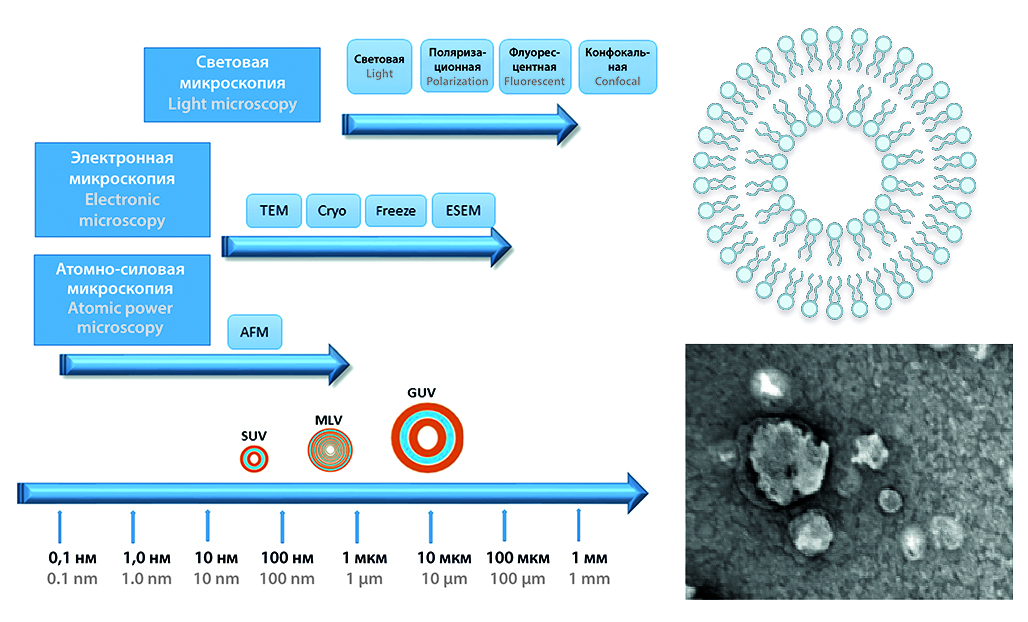
Text. Many different methodsh as been proposed for the visualization of liposoms morphology and quality such as light microscopy, ESEM, TEM, AFM, etc. Each method have own advantages and limitations which are discussed in the article: In general, the selection of method depends on the specific morphological characteristics and level of details. It is important to understand the specificity of the liposomes and the visualization method for correct preparation of samples. Adequately performed pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies can also be used as a tool for liposome visualization. The nature of active pharmaceutical ingredients, dose, lipid components, size of liposomes, charge, coating of liposomes with excipients and route of administration significantly affects the pharmacokinetics of liposomal forms. Additionally, the interaction of liposomal forms with the immune system, reticuloendothelial system and blood components play an important role in their absorption, distribution and elimination.
Conclusion. The better understanding of the absorption, biodistribution, metabolism and clearance of liposomal formulations is essential for the development of modern drugs.
Introduction. The production of solid dosage forms from hygroscopic substances is a complex technological task. The addition of hygroscopic substances into a polymer matrix allows to reduce their moisture absorption capacity.
Aim. Reducing the hygroscopicity of deliquescent substances and obtaining sustained release solid dosage forms by using solid dispersion systems.
Materials and methods. Substance: DEAE; excipients: Kollidon® VA 64, Soluplus®, PEG 1500, PEG 6000, PEG 8000, Poloxamer Kolliphor® P 188 and Kolliphor® P 407; reagents: hydrochloric acid, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium hydrogen phosphate. The melt of the components was obtained on a twin-screw laboratory extruder and cast into silicone molds. The resulting solid dosage forms were studied for disintegration in three environments corresponding to the sections of the human gastrointestinal tract.
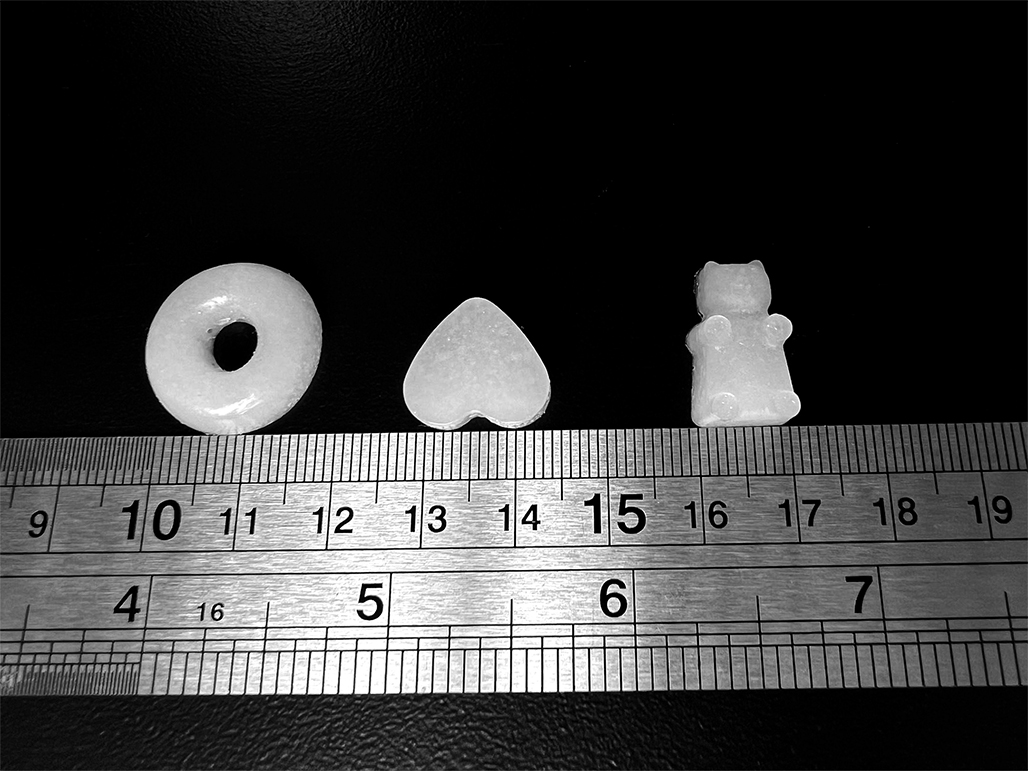
Results and discussion. The active pharmaceutical substance DEAE is characterized as deliquescent substance. The introduction of DEAE into PEG-polymer matrices made it possible to reduce the hygroscopicity of solid dosage forms in the form of bars. The introduction of solubilizers into the melt made it possible to obtain bars with the appropriate organoleptic properties. The release of DEAE from bear- or toroid-shaped bars occurs on average 29–47 % faster than from heart-shaped bars.
Conclusion. Compositions based on Soluplus® and Kolliphor® P 407 have proven promising for further development of tiles containing DEAE. In order to create tiles with a slow release, it is recommended to use heart-shaped forms, as they have a smaller surface area.
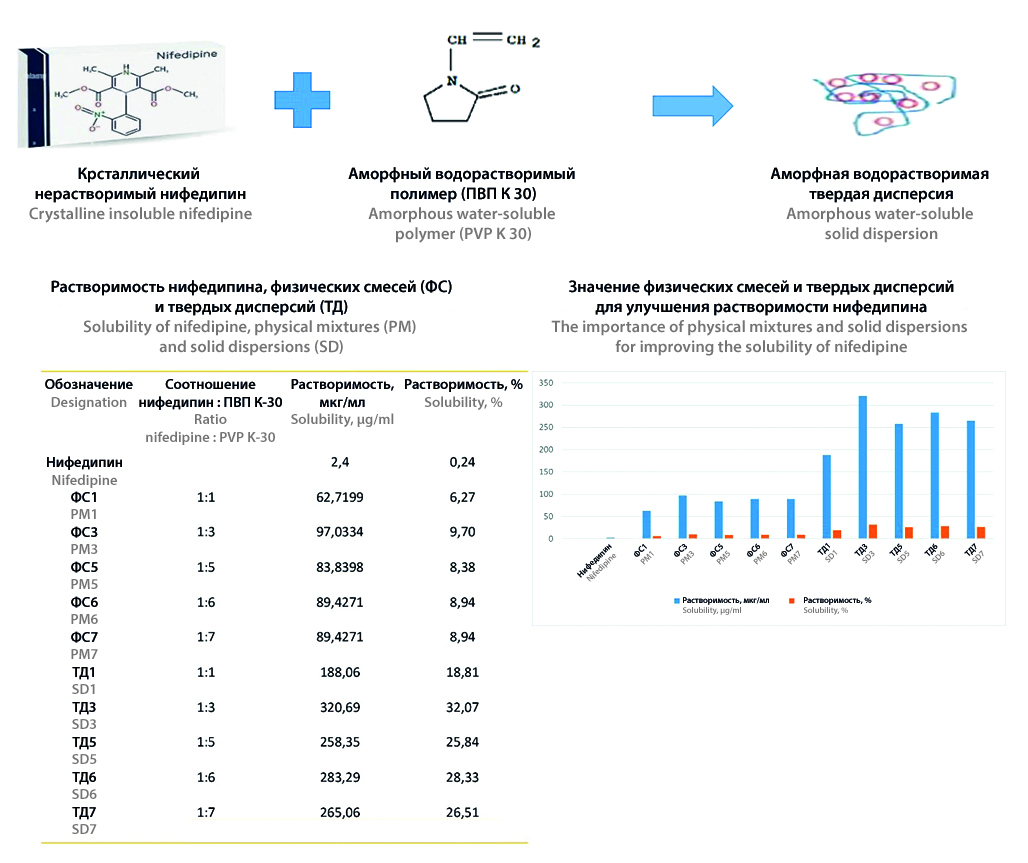
Introduction. Poor aqueous solubility significantly hinders the bioavailability of numerous orally administered drugs. Nifedipine, a widely-used cardiovascular agent, is categorized as practically insoluble according to pharmacopoeias, thus presenting a significant challenge in formulation development. This study investigates the potential of solid dispersion (SD) technology and physical mixtures to improve the dissolution profile of nifedipine.
Aim. Development of a technological method for increasing the solubility of nifedipine by developing physical mixtures and SD with the aim of creating a dosage form with improved properties.
Materials and methods. Nifedipine, methanol, nifedipine standard samples, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium heptanesulfonate, phosphoric acid (85 %), purified water, and pvp K-30. Solubility studies were performed by HPLC using three objects: nifedipine, a physical mixture (PM), and SD of nifedipine with PVP K-30. The study assessed the effect of different ratios (nifedipine : PVP K-30) in the physical mixture and SD on nifedipine solubility. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy) and powder X-ray diffractometry were used to characterize the samples.
Results and discussion. A notable increase in nifedipine solubility was observed in both PM3 (1 : 3 nifedipine : PVP K-30) and SD3 (1 : 3 nifedipine : PVP K-30). PM3 exhibited a solubility of 9.70 %, while SD3 demonstrated a remarkable enhancement to 32.07 % compared to the pure nifedipine (0.24 %). FTIR analysis did not reveal significant interactions between nifedipine and PVP K-30. PXRD results confirmed the transition of nifedipine from a crystalline to amorphous form within the hydrophilic PVP K-30 matrix, contributing to the observed solubility enhancement.
Conclusion. The study highlights the effectiveness of SD technology in significantly improving nifedipine solubility and potential bioavailability. The 134-fold increase in solubility achieved with SD3 at a 1 : 3 ratio demonstrates the significant potential of this approach for enhancing the pharmacokinetic properties of poorly soluble drugs. This research opens up new avenues for developing innovative formulations with improved dissolution characteristics and potentially enhanced therapeutic efficacy.
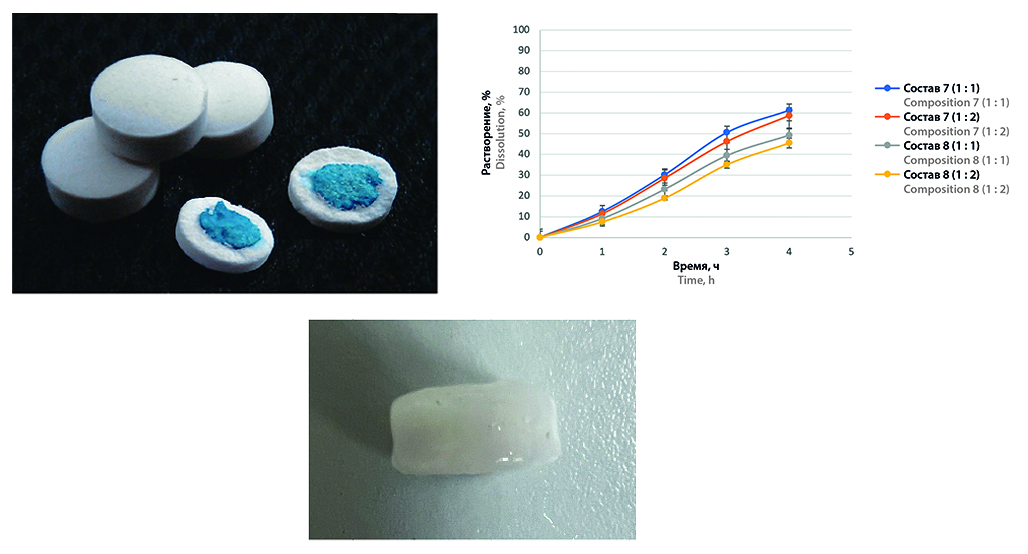
Introduction. The development of universal approaches to work with hygroscopic substances is an urgent task of pharmaceutical technology. Coating of tablets with hygroscopic substances deserves special attention. Pressed coatings represent a promising method for coating hygroscopic tablets. Such coating can contribute both to imparting the specified release characteristics to the tablet, and to the protection of APS from environmental factors, as well as can be an alternative to obtaining matrix tablets of prolonged action with hygroscopic substances in those cases when direct contact of APS with the polymeric carrier is undesirable.
Aim. Study of the possibility of using pressed coatings to control the kinetics and release site of hygroscopic substances from tablets using DEAE as an example.
Materials and methods. The object of the present study was the substance bis{2-[(2Z)-4-hydroxy-4-oxobut-2-enoyloxy]-N,N-diethylethanaminium} butanedioneate (DEAE), shellac (BonuLac®, Biogrund GmbH, Germany); copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate (AquaPolish® 712, Biogrund GmbH, Germany); copolymer of polyvinylpyrrolidone and polyvinyl acetate (Kollidon® SR, BASF, Germany), ethyl cellulose (Acros Organics, USA). Lactose monohydrate (Tablettose® 80, Meggle AG, Germany) was added to the formulations as an excipient. The superdisintegrant crospovidone XL and the lubricant sodium stearyl fumarate (JRS, Germany) were used to improve disintegration.
Results and discussion. The properties of the pressed coatings were studied. Shellac-based coating mixture may be suitable for obtaining enteric soluble coating for dissolution in medium with pH 4.5. PVP and PVA copolymer does not provide stability of coatings in acidic medium, but its introduction into formulations with ethyl cellulose, as well as into formulations with copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate allows to achieve uniform release in all media within 5 hours.
Conclusion. The study showed the possibility of using pressed coatings to control the kinetics of API release. The coating obtained using this technology can be used for hygroscopic substances. This method is a useful alternative when it is necessary to separate the matrix-forming polymer and the API, which have synergistic hygroscopic properties.
Introduction. Development of broad-spectrum antibacterial medicines for treatment of bacterial and fungal infections of animal skin is an urgent task of pharmaceutical industry, medicine and agricultural industry. The most promising dosage form for the treatment of superficial infectious diseases is gel. The most important advantages are the absence of side effects associated with ingestion, as well as the formation of a protective film that prevents re-infection of the animal.
Aim. To develop the composition of topical form in the form of gel on the basis of active pharmaceutical substance with a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action for therapy of infectious diseases of animal skin.
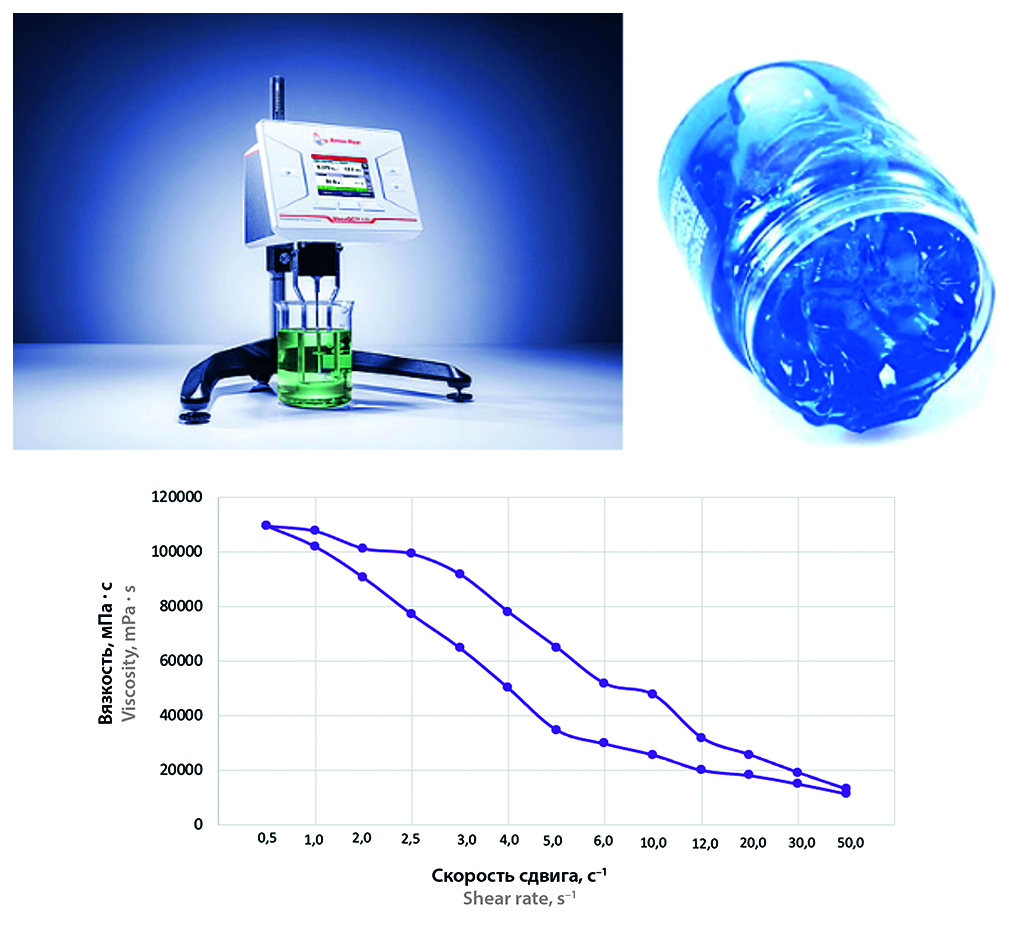
Materials and methods. The object of the study was an original substance – thiadiazole derivative, obtained by the organic synthesis department of the Department of Organic Chemistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education SPHFU of the Ministry of Health of Russia. Gel formers (sodium alginate and carbomer), propylene glycol, surfactants (surfactants), etc. were used in the work. The obtained thiadiazole gels were studied in terms of pH, appearance, thermostability, colloidal stability, film formation, in addition, the rheological properties of the gels were determined.
Results and discussion. It was found that gels in which sodium alginate and carbomer acted simultaneously as gel formers had thixotropic properties providing the best stability of the structure. The gels in which glycerin was added formed an elastic film preventing damage and drying of the animal skin.
Conclusion. As a result of this study, a topical formulation in the form of a gel containing a new thiadiazole derivative was developed for the treatment of infectious diseases of animal skin.
Introduction. Microparticles are of great interest for use in various drug delivery systems. The intranasal route of administration holds a special place due to its several advantages, including ease of use, minimal side effects, and the ability for rapid delivery of drug directly to the brain. The drug in the microparticles acts locally, thereby ensuring the release of the drug in the required amount in the target organ. The drug from the nose enters directly into the brain through the olfactory region along the sensory nerves. The development of microparticles with the ability to mucoadhesion on the surface of the nasal mucosa will increase the bioavailability of drugs used in the treatment of diseases and disorders of the central nervous system (CNS).
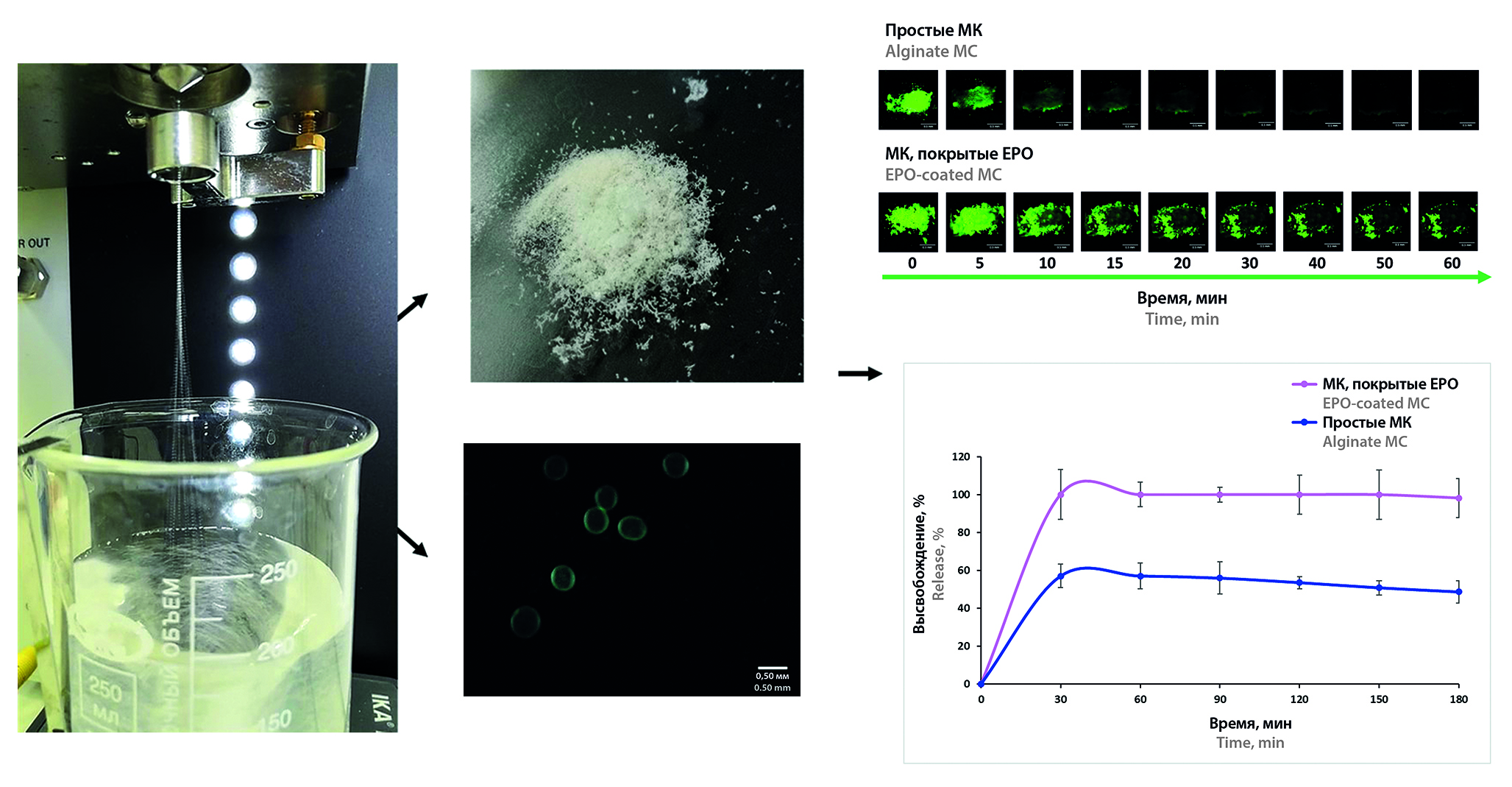
Aim. Development and study of microcapsules with mucoadhesive properties for the intranasal delivery system of levodopa.
Materials and methods. Microcapsules (MC) were obtained by ultrasonic electrospraying method on a B-390 encapsulator (BUCHI, Switzerland) followed by filtration under vacuum, washing with deionized water and freeze-drying at –50 °C and 0.05 mBar for 48 h in a FreeZone 1 L dryer (Labconco, USA). The structural features of MC were studied by optical microscopy using Evident CX33 microscope with high-resolution camera (Olympus, Japan). For evaluation of the images, we used ImageView™ software (version x64, 4.11.22376.20230402). Morphology of prepared microcapsules were also detected using a portable ultraviolet light source (Jialitte F114, China) by a digital USB microscope (OT-INL40 1000X, China). The mucoadhesive properties of sodium fluoresceinate-loaded MC were studied using isolated sheep nasal mucosa in an SI60 incubator (Stuart, UK) at 37.0 ± 0.5 °C. Fluorescent images were obtained using a TLC Visualizer 3 high-resolution imaging system (CAMAG®, Switzerland). ImageJ 1.53e software (ImageJ, USA) was used to process the obtained macroscopic images and plot graphs. The encapsulation efficiency, % (EE%) and loading capacity, % (LC%) of levodopa loaded MC were assessed using UV spectrophotometry on an Evolution™ 220 device (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) at a wavelength of 202 nm. The release of levodopa from MC was performed using a CE 7smart flow cell (SOTAX AG, Switzerland), method IV (State Pharmacopoeia XV of the Russian Federation), at a temperature of 37 ± 0.5 °C for 3 hours in an artificial nasal fluid (ANF) medium. The amount of released drug was determined using an Evolution™ 220 UV spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) at a wavelength of 202 nm.
Results and discussion. A method for MC preparation was developed, the device parameters and the optimal composition of microparticles were selected. Two types of MC were obtained: alginate MC and MC coated with Eudragit® EPO (EPO), which have mucoadhesive properties. The average diameter of alginate MC was 0.365 ± 0.018 mm, EPO-coated MC – 0.426 ± 0.017 mm. Alginate MC are washed off the surface of isolated sheep nasal mucosa 5 minutes after irrigation with ANF, and EPO-coated are retained for 1 hour. EE% of MC with levodopa is above 90 %. LC% of EPO-coated is higher than that of alginate MC. The release of levodopa into the ANF medium from EPO-coated MC was 100 % after just 30 minutes of the study, while for alginate MC it was no more than 60 ± 6.1 % after 3 hours.
Conclusion. EPO-coated MCs exhibit mucoadhesive properties on the nasal mucosa surface and their further study is promising for use in intranasal levodopa delivery systems.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. The problem of development and implementation of own drugs in Kazakhstan today is acute and urgent. The solution to this problem is possible through the use of own resources – domestic medicinal plant raw materials. A promising medicinal raw material is Artemisia cina – an endemic medicinal plant of the of the Turkestan region of Kazakhstan.
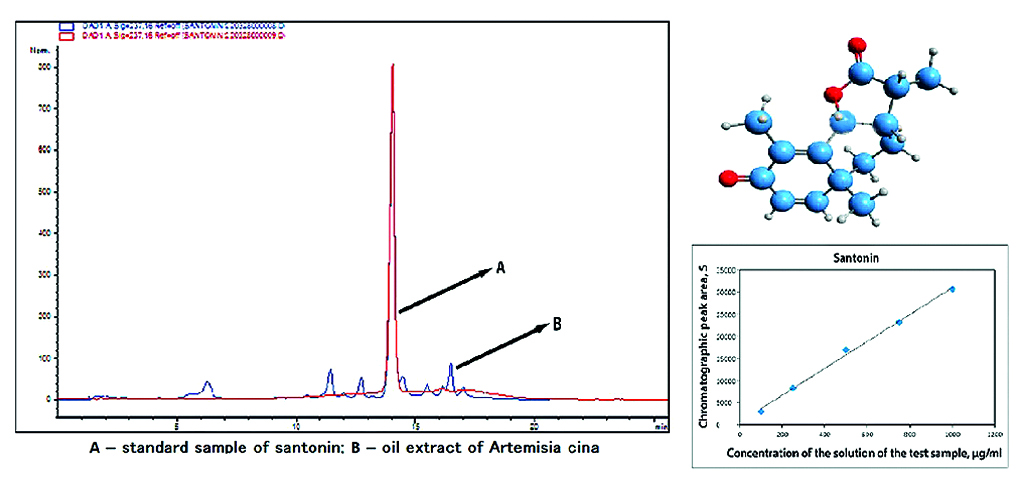
Aim. Designing a liquid chromatography methodology to analyze the oil extract obtained from Artemisia cina.
Materials and methods. Standard sample (SS) of santonin, Artemisia cina’s oil extract. The substance was identified and quantitatively determined using an Agilent Technologies 1200 liquid chromatograph (USA) equipped with ChemStation software.
Results and discussion. The main active substance of the oil extract was analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. Choosing the separation conditions for the column involves determining the best composition of the mobile phase and the rate of elution. There were used a reversed-phase system with sorbent C18 and a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and a phosphate buffer with a pH of 6.8. Chromatographic studies of the substance were carried out in a gradient mode at an analytical wavelength of 237 nm. The retention time of the standard sample (SS) of santonin matched the retention time (tR) of santonin isolated from the oil extract of Artemisia cina and amounted to 14.3 minutes.
Conclusion. A liquid chromatography method has been established for the identification and quantitative determination of the oil extract, focusing on the main active substance, santonin.
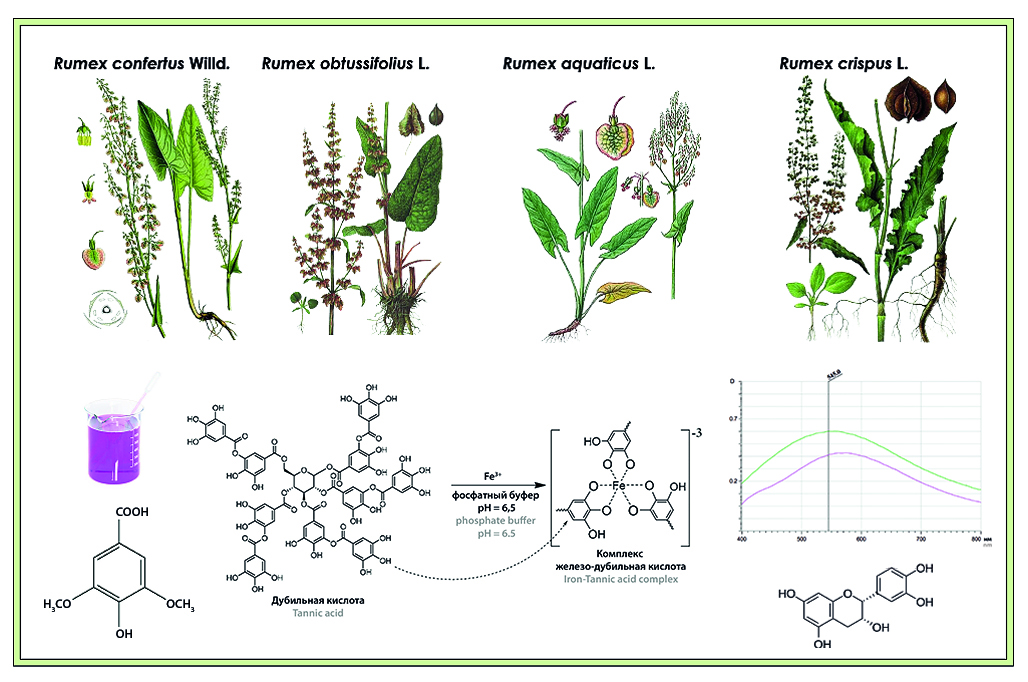
Introduction. Study of the chemical composition of medicinal plant raw materials and comparative analysis of the dynamics of accumulation of biologically active substances in related medicinal plants is necessary for the creation of highly effective and safe drugs. Similar metabolome to the officinal representative of the genus Rumex (hereinafter referred to as R.) – R. confertus – the metabolome of species widely distributed in Russia: R. crispus, R. obtusifolius, R. aquaticus, which determines the perspectivity of studying these species. Scientific and practical interest is represented by the study of the group of biologically active substances possessing antibacterial activity – tannins at different phenological stages of plant development.
Aim. Quantitative determination of tannins by permanganatometry and spectrophotometry methods in underground organs of R. confertus, R. crispus, R. obtusifolius, R. aquaticus, harvested in different phases of vegetation: regrowth, flowering and withering periods.
Materials and methods. Aqueous extracts from underground organs of the studied Rumex species were analyzed. Extractions and solutions obtained during the study were analyzed by permanganatometry, spectrophotometry and HPLC. The compounds from the group of tannins were identified by the wavelength of absorption maximum.
Results and discussion. The quantitative content of tannins was evaluated by permanganatometry, spectrophotometry and HPLC.
Conclusion. Tannins were detected and quantified in extracts from underground organs of R. confertus, R. crispus, R. obtusifolius, R. aquaticus and the dependence between their quantitative content and vegetation phase was analyzed.
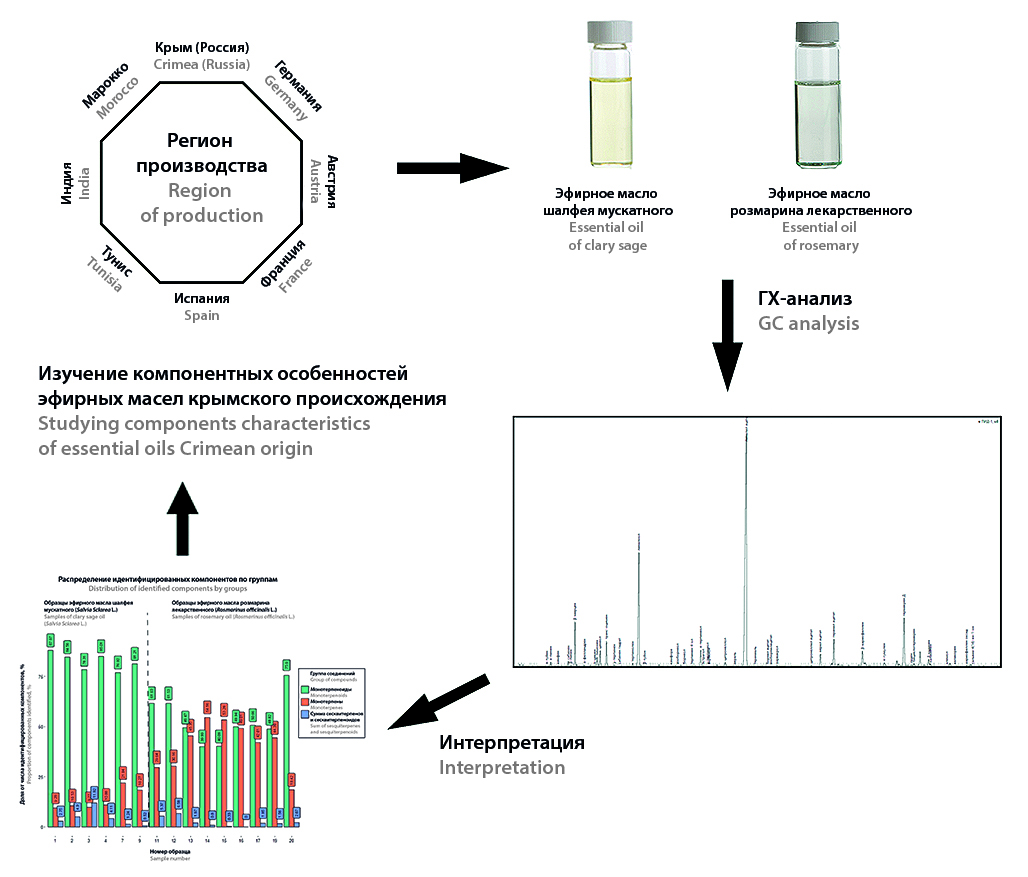
Introduction. Chromatographic profiling is the most efficient way to authenticate essential oils, the key limitation of which is the number of chromatographic profiles developed. The profiling methodology allows to take into account the geographical variability of essential oils by differentiating the profile into essential oilseed growing zones. Despite the presence of developed chromatographic profiles at the moment there is no information about the possible geographical variability of the demanded essential oils of clary sage and rosemary, obtained from local essential oilseed raw materials.
Aim. Comparative study of the component composition of essential oils of clary sage and rosemary produced from raw materials of Russian and foreign origin for the characterisation of domestic essential oils.
Materials and methods. The essential oils were analysed on the software and hardware complex of the gas chromatograph "Crystal 5000.2" with flame ionisation detection. Separation was carried out on a capillary column HP-5MS UI and on a capillary column DB-WAX. The components were identified by comparing the calculated linear retention indices obtained on two columns of different polarity with reference values.
Results and discussion. The analysis of the essential oils of clary sage and rosemary identified 42 and 33 compounds, on average representing 93.7 and 96.2 % of all sample components, respectively. For the samples of clary sage of Crimean origin, a number of patterns were noted, potentially suitable for separating its component composition from essential oils of other origin. Based on the study of the component composition of the essential oil of rosemary Crimean origin, it is suggested that it is attributed to the essential oil of rosemary Spanish type in accordance with ISO and Ph.Eur.
Conclusion. The results of the study allowed to put forward a number of assumptions regarding the possibility of isolation of a specific chromatographic profile of essential oils of clary sage and rosemary from Crimea. Further experimental verification of the put forward assumptions will allow to determine the possibility of introducing clear classification criteria for oils of Crimean origin.
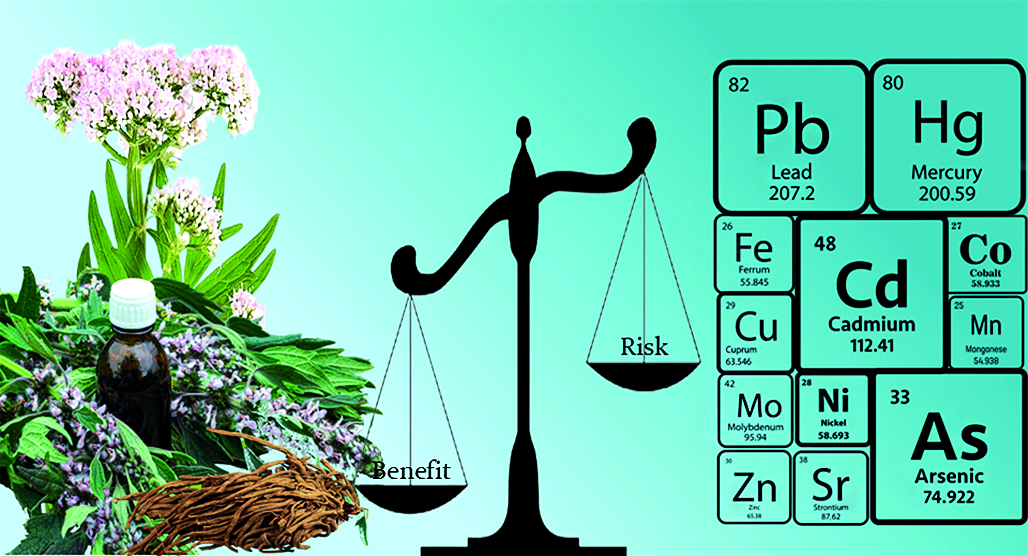
Introduction. Liquid dosage forms based on medicinal plant raw materials are very convenient to use and must meet safety requirements. In the context of harmonization of pharmacopoeial requirements, determining the total content of heavy metals in tinctures is not enough. Risk assessment is necessary to calculate the permissible concentrations of heavy metals in tinctures.
Aim. To assess the safety of using tinctures in terms of the content of heavy metals and arsenic within the framework of a risk-oriented strategy.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were 20 samples of valerian and motherwort tinctures manufactured by various enterprises. The quantitative content of 15 elements (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sr, Tl, V, Zn) was determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.
Results and discussion. The concentrations of elements in tinctures varied in the range of 0–1.84 μg/g. Manganese and zinc were found in maximum quantities, while cadmium, molybdenum and vanadium were found in minimum quantities. Mercury was not detected in any of the samples. The content of toxic elements in the tinctures did not exceed the levels of permissible concentrations regulated by the normative documentation of the Russian Federation. Total hazard indices (HI) were calculated at the levels of the median and 90th percentile of the content of elemental toxicants. In the tinctures, they were, respectively: valerian – 0.016 · 10–5 and 0.027 · 10–5, motherwort – 0.022 · 10–5 and 0.028 · 10–5. The obtained values were significantly lower than 1.0. Calculation of individual carcinogenic risk (CR) of elemental carcinogens (Cd, As, Cr, Pb) entering the body with tinctures of valerian and motherwort showed that the CR values were in the range of 4.9 · 10–9–6.84 · 10–7, which did not exceed the permissible threshold value (1 · 10–6).
Conclusions. The actual content of toxic elements (Pb, Cd, As, Hg) in tinctures of valerian and motherwort was 0–0.006 μg/g, which did not exceed the levels of permissible concentrations. Calculations of non-carcinogenic risks when using tinctures of valerian and motherwort showed that the total impact of 15 studied elements on human health when consuming a daily dose of tinctures is characterized as permissible, periodic monitoring of the content of non-standardized elements in samples of herbal medicines is not required. It was established that the studied tinctures of valerian and motherwort are not oncogenic factors and do not require risk reduction measures.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
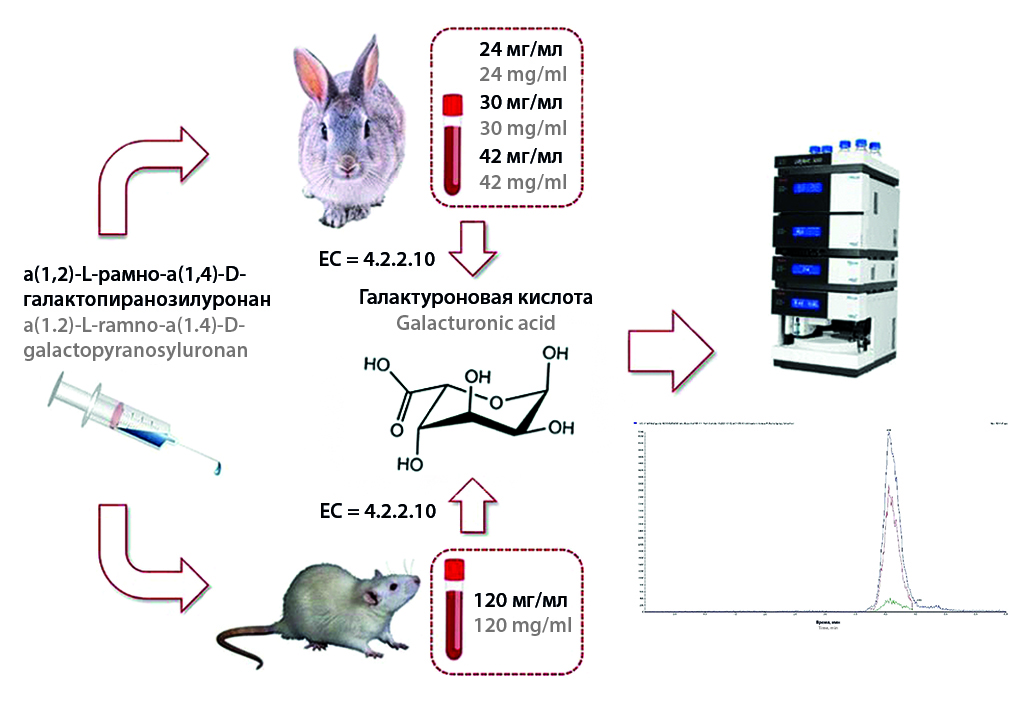
Introduction. α(1,2)-L-rhamno-α(1,4)-D-galactopyranosyluronane is a water-soluble heteropolysaccharide isolated from the rhizomes of calamus marsh (Acorus calamus L.) and has antitumor, antimetastatic, immunomodulatory and hepatoprotective effects, protective effect on hematopoiesis suppressed during cytostatic treatment.
Aim. Validation of the bioanalytical method for the determination of α(1,2)-L-rhamno-α(1,4)-D-galactopyranosyluronane Acorus calamus L. and the study of the pharmacokinetic parameters of a new drug based on it after a single administration of 120 mg/kg to rats and 24, 30, 42 mg/kg to rabbits.
Materials and methods. In the study, 8 male rats (average weight – 300 g) were used as the main animals. 6 male rabbits (average body weight – 2.5 kg) were used as an additional animal species. The dose assessment experiment was carried out on 24 rabbits (body weight – 2.3–2.5 kg). The quantitative determination of α(1,2)-L-rhamno-α(1,4)-D-galactopyranosyluronane Acorus calamus L. in the blood plasma of animals was carried out by HPLC-MS/MS, the analytical form was galacturonic acid. The method of sample preparation of biological samples included the stage of enzymatic hydrolysis of α(1,2)-L-rhamno-α(1,4)-D-galactopyranosyluronane Acorus calamus L. with a solution of pectinase for the formation of galacturonic acid.
Results and discussions. The pharmacokinetics of the new drug α(1,2)-L-rhamno-α(1,4)-D-galactopyranosyluronane Acorus calamus L. was studied after a single dose of 120 mg/kg to rats and 24, 30, 42 mg/kg to rabbits. The average residence time of the drug in the rabbit's body was 1.0 ± 0.21 hours, the half-life was 0.7 ± 0.15 hours. The average residence time of the drug in the rat body was 1.16 hours, the half-life T1/2 was 0.80 hours. After a single intravenous administration to rabbits of 24, 30 and 42 mg/kg, the maximum concentration in the systemic bloodstream is reached 5 minutes after administration and averages 133.95 ± 27.04, 145.86 ± 40.90 and 226.13 ± 41.27 µg/ml, respectively, the half-life ranged from 0.22 to 0.26 h, the half-life from 3.52 to 3.96 hours.
Conclusion. The pharmacokinetic parameters of α(1,2)-L-rhamno-α(1,4)-D-galactopyranosyluronane Acorus calamus L. were evaluated in animals based on the use of the method of quantitative determination of galacturonic acid by HPLC-MS/MS.
Introduction. In the developed world, among the main causes of disease and death is type 2 diabetes. It is a significant public health issue with rising prevalence, with more than 380 million patients estimated to be affected by 2025.
Aim. To evaluate the effect of ketogenic diets on glycemic control in patients with type II DM in Kirkuk and Mosul provinces.
Materials and methods. Patients with T2DM in both Mosul and Kirkuk cities were enrolled in this study to evaluate the effect of keto diet on HbA1c level and Lipid profile variations between 1/9/2022 to 1/4/2023.
Results and discussion. This study shows that the distributions of patients according to age and gender there was about 43.3 % female and 56.7 % male and the age variations, female with age above 56 years old was 30 % while male 60.7 %. A significant p value was shown in HbA1C variations before and after keto diet (0.0001), also in lipid profile of a significant p value before and after keto diet (0.001) regarding total Glyceride a significant p value highly was (0.002). Due to the large particle size of LDL-C, it has been hypothesized that this elevation in LDL-C would not likely cause cardiovascular problems. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, the low-calorie-ketogenic VLCK diet (<50 g of carbohydrates per day) is a safe, well-tolerated, and recognized medical nutritional therapy option when used in conjunction with an interventional weight loss program that offers support for lifestyle and behavioral modification over a 4-month period.
Conclusion. Diabetic and ketogenic diet there is a good clear relationship regarding the HbA1c and lipid profile. Further studies are required for larger numbers of patients and longer duration follow up.
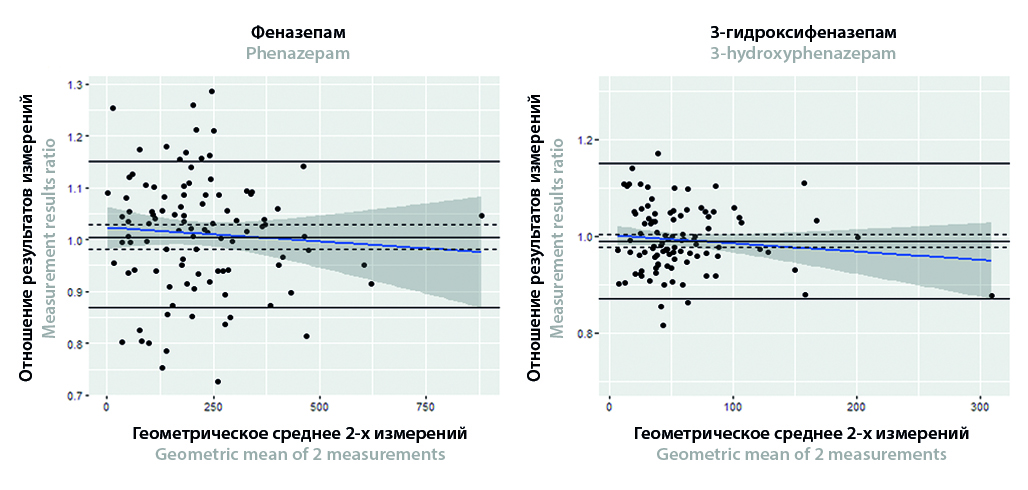
Introduction. In conducting of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), often such situation arises where the drug concentration has measured by different methods or in different laboratories. To combine and analyze the data obtained with different methods, it is necessary to perform cross-validation procedure. Insufficient attention is paid to the statistical approaches used for this purpose.
Aim. Performing cross-validation of different analytical methods for the quantitative determination of phenazepam (PHEN) and 3-hydroxyphenazepam (3-OH-PHEN) using the Bland – Altman analysis.
Materials and methods. PHEN and 3-OH-PHEN concentrations in the blood plasma of patients (n = 100) with alcohol withdrawal syndrome were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). The quantification of both analytes in each sample was measure twice by two different methods: solid phase extraction (SPE) and supported liquid extraction (SLE). Both methods have been fully validated before the experiment began. Cross-validation was performed at the end of the experiment using data from study samples. The Bland – Altman analysis was used to evaluate accuracy and precision. Deming regression was also used to identify a systematic error between measurement results.
Results and discussion. The regression equations have been obtained between concentrations both analytes measured by different sample preparation methods. 95 % confidence intervals (CI) of the regression coefficients of both equations included one, and 95 % CI of the intercepts included zero. 95 % CI of the geometric mean of the individual SLE/SPE ratios was within the acceptable range (0.87; 1.15). These results confirm the absence of the influence of quantitative methods on the measurement of both analytes concentration. 66.7 % CI of the percent difference between two measurements was within acceptable limits (–0.2; 0.2), not exceeding 20 % of the range of their mean value. This confirms the acceptable precision between the methods. The estimated CIs were displayed in the Bland – Altman plots.
Conclusion. The statistical approaches used in the work have confirmed the reproducibility of the results of different sample preparation methods. In addition to cross-validation, the statistical algorithm from this paper using Bland – Altman analysis can be successfully employed to assess accuracy and precision during bioanalytical method validation and evaluation of the acceptance of analytical runs, as well as to determine the level of reproducibility of incurred samples.
Introduction. The development of heart failure is closely associated with the appearance of life threatening arrhythmias, which are often a terminal event for these patients. An analysis of randomized clinical trials of inhibitors of sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 indicates the clinically significant potential of these drugs as agents with antiarrhythmic properties. However, at the moment the full mechanism by which this effect can be realized is still not fully understood.
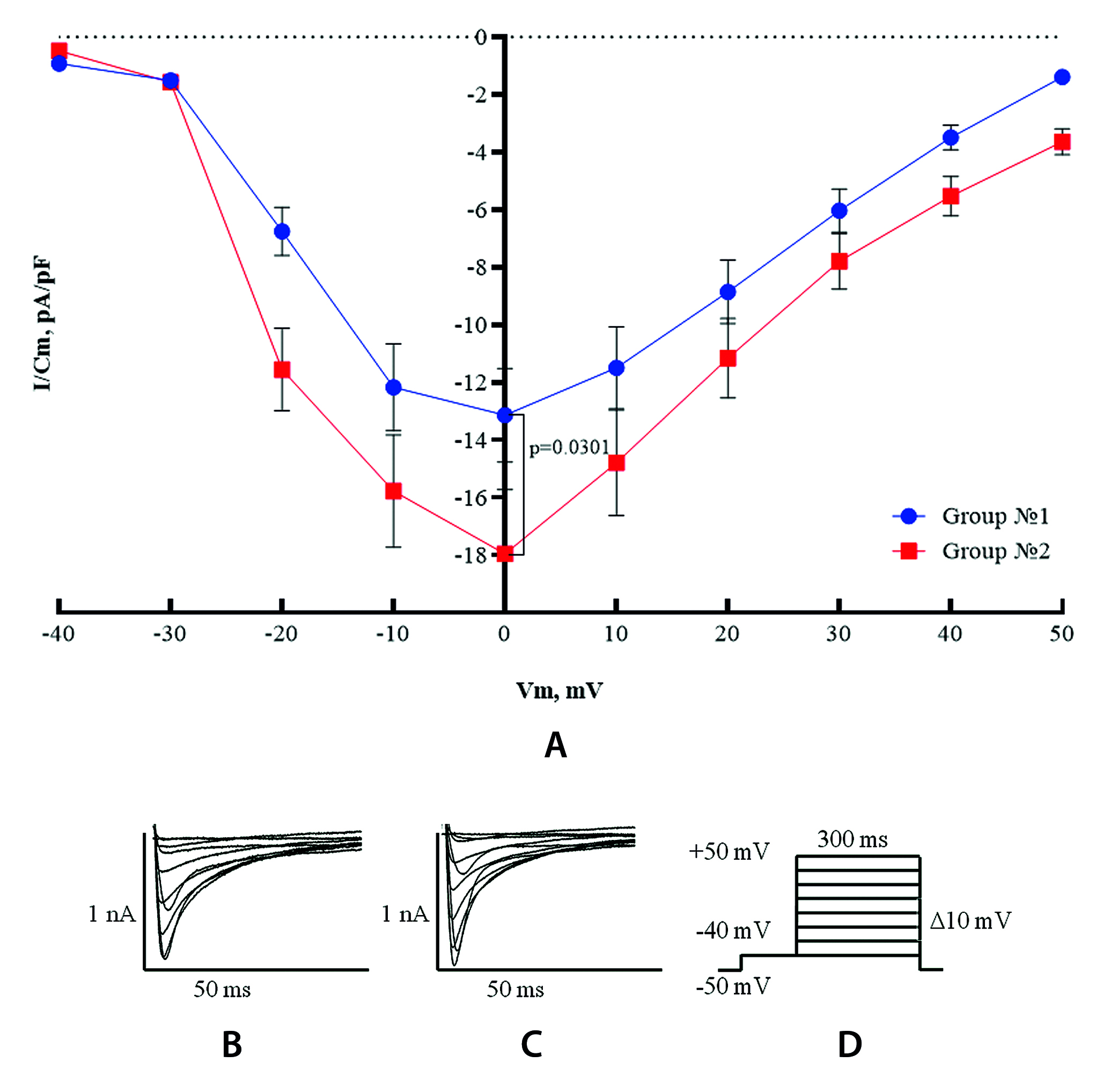
Aim. To evaluate the effect of empagliflozin on the transmembrane calcium currents and the intracellular calcium transients on isolated ventricular cardiomyocytes of mice under conditions of normoglycemia.
Materials and methods. In the experiment, ventricular cardiomyocytes were isolated from 12 outbred male mice. 2 groups were formed: group № 1 – control ventricular cardiomyocytes; group № 2 – ventricular cardiomyocytes after two hours incubation with 5 µmol/L empagliflozin solution. Transmembrane calcium currents were recorded and intracellular calcium transients were assessed.
Results and discussion. Incubation of ventricular cardiomyocytes with empagliflozin significantly increased ICa current density and accelerated Ca2+ temporal dynamics. The amplitude of the Ca2+ wave and the rate of rise and decay were increased and the duration of the Ca2+ wave was shortened.
Conclusion. The result of the experiment indicates that empagliflozin is able to modulate Ca2+-dependent mechanism of the excitation-contraction-coupling, enhancing and accelerating Ca2+ release into cytoplasm and reuptake. This presumably can optimize, namely reduce the time of systole and enhance it, which may be one of the important elements in the manifestation of empagliflozin antiarrhythmic properties.
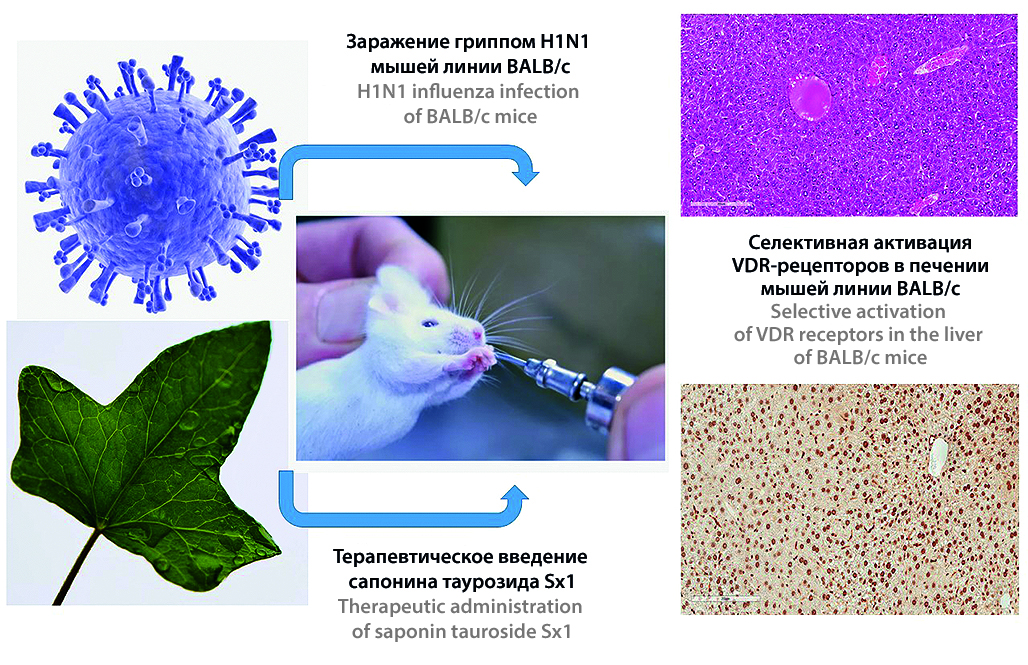
Introduction. Respiratory infections, including influenza, are often accompanied by hepatitis in humans which pathogenesis is not fully understood. According to the available datan D deficiency is presumably a risk factor in the occurrence of acute respiratory viral infections due to its modulation of immune response. Recent studies indicate that several plant compounds can interact with vitamin D receptors (VDRs) and modulate the activity of VDRs. The biologically active components saponins have found widespread use in clinical practice due to their wide range of biological and pharmacological effects which mechanisms are still largely unclear.
Aim. To study the effect of oral administration of saponin tauroside Sx1, obtained from Crimean ivy, on life expectancy and activation of vitamin D receptors in the liver of mice during experimental viral infection of varying severity.
Materials and methods. The 11 subgroups were formed from male BALB/c mice, were used in the experiment depending on the infectious dose of influenza virus, 5 LD50 virus or 10 LD50 virus, respectively, including control. Saponin tauroside Sx1 was used as a corrector. Immunohistochemical studies were carried out automatically in a BOND-MAX immunohistainer (Leica, Germany). Primary rabbit polyclonal antibodies to the vitamin D receptor were used.
Results and discussion. Due to the administration of tauroside Sx1 at a dose of 200 μg/mouse/day increases the average life expectancy of animals receiving saponin by 4.6 days. Reducing the infectious dose of IV from 10 LD50 to 5 LD50 also changed the onset of death of animals by 2 days in both groups. With different infectious doses of the virus, on the 10th day of the experiment in the subgroups, the expression of vitamin D receptors changes without correction. In subgroup 2V, the number of total positive cells was lower than the control group. Moreover, in the 2Vir subgroup, VDR expression was significantly higher than the control group.
Conclusion. The saponin tauroside Sx1 at a dose of 200 µg/mouse/day has a fairly pronounced antiviral effect during experimental infection of mice with the influenza A/H1N1 virus, which is manifested by an increase in the average life expectancy of animals (for 4.6 days) and a decrease in the mortality rate during severe influenza infection, compared with the control group, where 100 % mortality was observed by the 14th day of the experiment. The introduction of saponin on the 4th day of the experiment in all subgroups reduces the total number of immune cells that intensively express VDR.
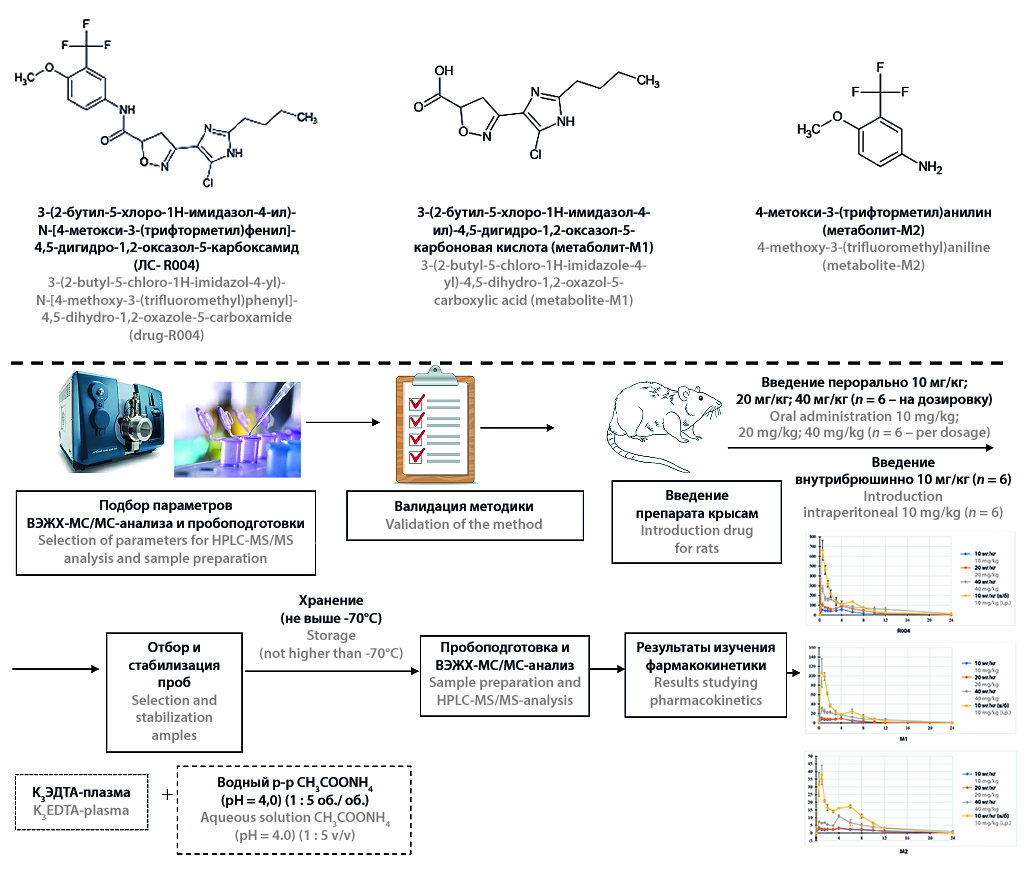
Introduction. 3-(2-butyl-5-chloro-1H-imidazole-4-yl)-N-[4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxamide (R004) is a prospective new molecule for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. This compound is at the stage of preclinical research, during which its pharmacokinetics must be studied along with efficacy and safety. In this case, it is necessary to establish the main pharmacokinetic parameters of the drug and its metabolites in blood plasma after a single administration.
Aim. Evaluation of linearity of pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of 3-(2-butyl-5-chloro-1H-imidazole-4-yl)-N-[4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxamide and its main metabolites in plasma after a single administration of the substance to rats.
Materials and methods. Substance R004 was administered to rats once orally at dosages of 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg and intraperitoneally at a dosage of 10 mg/kg. The study was carried out using 24 Wistar rats: 6 rats were used for each of the dosage. Blood samples were collected before administration and 30 min, 1 h, 1 h, 30 min, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 10 h, 12 h, 24 h after administration of the drug. The obtained plasma was stabilized with a 250 mM ammonium acetate solution to prevent hydrolysis of R004. Plasma samples were prepared by means proteins precipitation by acetonitrile solution of internal standards. Measurement of the concentration of R004 and its metabolites 3-(2-butyl-5-chloro-1H-imidazole-4-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylic acid (M1) and 4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline (M2) was performed using HPLC-MS/MS. A non-compartment approach was applied for evaluation pharmacokinetic parameters.
Results and discussion. The developed bioanalytical method has been fully validated in accordance with the requirements of the EAEU guideline for conducting bioequivalence study and ICH M10 guideline. The analytical range of determination in plasma of R004 was 2–2000 ng/ml, M1 and M2 – 1–1000 ng/ml. The dependence of the parameters Cmax and AUC0–t of the studied compound and its metabolites on the administered dose was linear. Thus, the value of the correlation coefficient of Cmax R004 was 0.9995, and value of the correlation coefficient of AUC0–t was 0.9991. The presence of enterohepatic recirculation R004 has been determined. The relative bioavailability of R004 was 21.26%.
Conclusion. The developed method was successfully applied for the pharmacokinetic research. R004 and its metabolites have linear pharmacokinetics in case of oral administration.
Introduction. In the modern world, more attention is paid to the problem of increasing cases of mycosis. In October 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) published the first fungal priority pathogens list which constitute the greatest danger to human health. Among mycotic infections, one of the leading positions in frequency is occupied by various forms of candidiasis. The WHO has classified Candida albicans as a critical priority group. Therefore, the search for new effective antimycotics is relevant. A new derivative of 1,3,4-thiadiazole was synthesized at Saint-Petersburg State Chemical and Pharmaceutical University. In vitro experiments, it was shown that it has a wide spectrum of antifungal activity in effectiveness comparable to voriconazole.
Aim. To evaluate the antifungal activity of 2-[(1Z)-1-(3,5-diphenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl]-3,5-diphenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-3-ium (thiadiazole derivative, TD) chloride drug substance in non-invasive bowel candidiasis and acute septicemia (sepsis) models caused by C. albicans.
Materials and methods. Simulations of non-invasive intestinal candidiasis were performed by infecting BALB/c mice with candida with free access to a drinking bottle containing C. albicans yeast cells suspension. Previously, dysbiosis was caused in animals by adding a solution of antibiotics (vancomycin, clindamycin, gentamicin) in drinking water. Simulations of C. albicans-induced acute septicemia were performed by infecting BALB/c mice with intravenous yeast culture suspension. After the mice were infected, the test substance and the comparators Voriconazole and Fluconazole were administered intragastrically once daily. At the end of the experiment, the number of fallen animals were estimated and microbiological examination of internal organs was carried out.
Results and discussion. It was shown that the number of yeast cells secreted from the large and small intestines in mice with non-invasive intestinal candidiasis after administration of a new thiadiazole derivative at all doses tested (1, 5, 10 mg/kg) were significantly reduced compared with control group No. 6 without treatment. At 10 mg/kg, the test substance demonstrated anticandidosis effects at the level of comparators drugs, Voriconazole and Fluconazole. In mice with septicemia, mortality also depended from the dose of the thiadiazole derivative, but only 10 mg/kg proved to be an effective dose.
Conclusion. The study revealed that the new thiadiazol derivative 2-[(1Z)-1-(3,5-diphenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-ylidene) methyl]-3,5-diphenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-3-ium showed antifungal activity against Candida albicans in the model of non-invasive intestinal candidiasis and the model of septicemia (sepsis). At 10 mg/kg, TD was found to be active at the level of comparators, Voriconazole and Fluconazole.
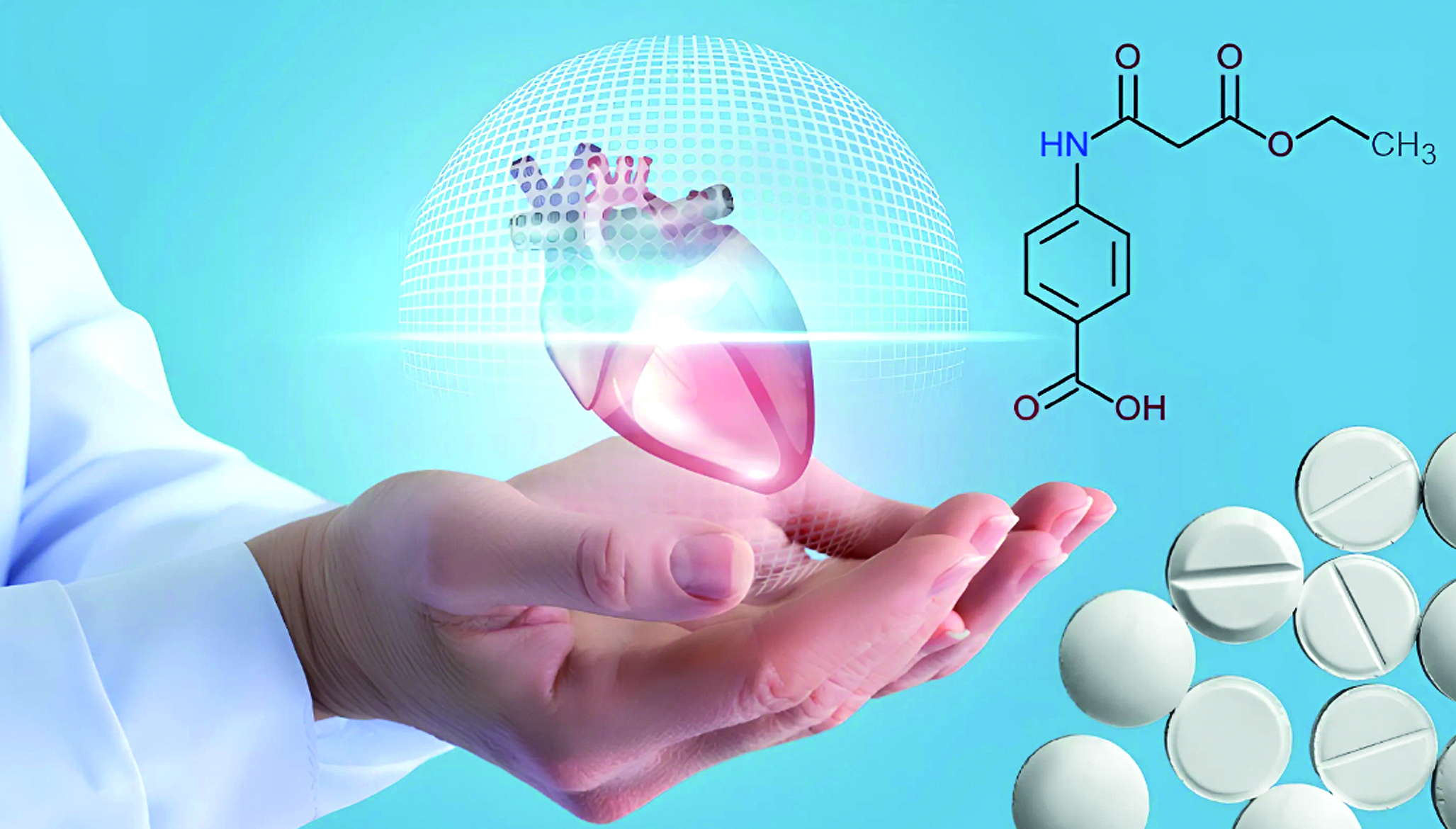
Introduction. Etmaben is a malonic acid derivative that has shown cardiotropic activity and is a promising candidate for treating ischemic heart disease and chronic heart failure. It is currently undergoing Phase I clinical trials, and its pharmacokinetics have not yet been studied in humans.
Aim. The aim of the study is to investigate the pharmacokinetics of Etmaben, film-coated tablets, 300 mg (SPCPU, Russia) in healthy volunteers after fasting administration of different doses following both single and multiple dosing over a 7-day period.
Materials and methods. The open-label, non-randomized clinical trial involved 48 healthy volunteers divided into 6 cohorts. Volunteers in cohort 1 received a single dose of 600 mg of etmaben, cohort 2 received 900 mg, and cohort 3 received 1200 mg. Cohorts 4, 5, and 6 received daily doses of 600 mg, 900 mg, and 1200 mg, respectively. Plasma concentrations of etmaben were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry detection. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using Microsoft Excel with the Boomer extension (Department of Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism, Allergan, Irvine, CA 92606, USA).
Results and discussion. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated for 6 cohorts of 8 volunteers after single and multiple dosing of Etmaben at doses of 600, 900, and 1200 mg. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of etmaben was reached on average within 0.5 h. Cmax values ranged from 2.708 ± 1.461 µg/mL to 19.871 ± 4.415 µg/mL. The maximum half-life was 0.874 ± 0.236 h, with an elimination rate constant not exceeding 1.053 ± 0.149 h–1. The mean residence time (MRT) of etmaben in plasma did not exceed 1.527 ± 0.272 h. The average volume of distribution was above 45 L, and clearance exceeded 42 L, indicating significant tissue distribution and rapid drug elimination. Due to low area under the curve values and high elimination rates, the accumulation of etmaben is minimal.
Conclusion. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated, and averaged pharmacokinetic profiles were constructed in linear and semilogarithmic coordinates after single and multiple dosing of various etmaben doses. This study represents the first investigation of etmaben pharmacokinetics in humans, paving the way for subsequent clinical trials.
REGULATORY ISSUES
Introduction. The strategy of drug supply to the population of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2025 highlights the need to ensure the rational use, safety and quality of medicines in the range of priority tasks. At the same time, the use of effective medical technologies in pediatric patients is limited both by the range of medicines approved for use in the pediatric population and by the requirements regarding compliance of the pharmaceutical design of the drug with the intended purpose in the target age group. The Russian pharmaceutical market is characterized by a monotonous and persistent tendency to expand the assortment matrix and increase the indicators of real and potential capacity, including in the segment of medicines for pediatrics. However, despite the introduction of new market positions for children into civil circulation, the gradual accumulation of data on the safety, clinical and clinical-economic effectiveness of drugs in the pediatric population, the expansion of the panel of possibilities of production pharmacies, the change in the legal status of registered drugs prescribed by off-label, based on evidence-based experience of use for a new purpose, the issues of the validity of medical prescriptions with an acceptable profile of convincing evidence in relation to pediatric patients in the context of the occurrence and development of a number of pathologies remain open.
Aim. The aim of the work was to determine the prospects for optimizing the provision of medicines to pediatric patients based on the development of the pharmaceutical market in the segment of medicines for children.
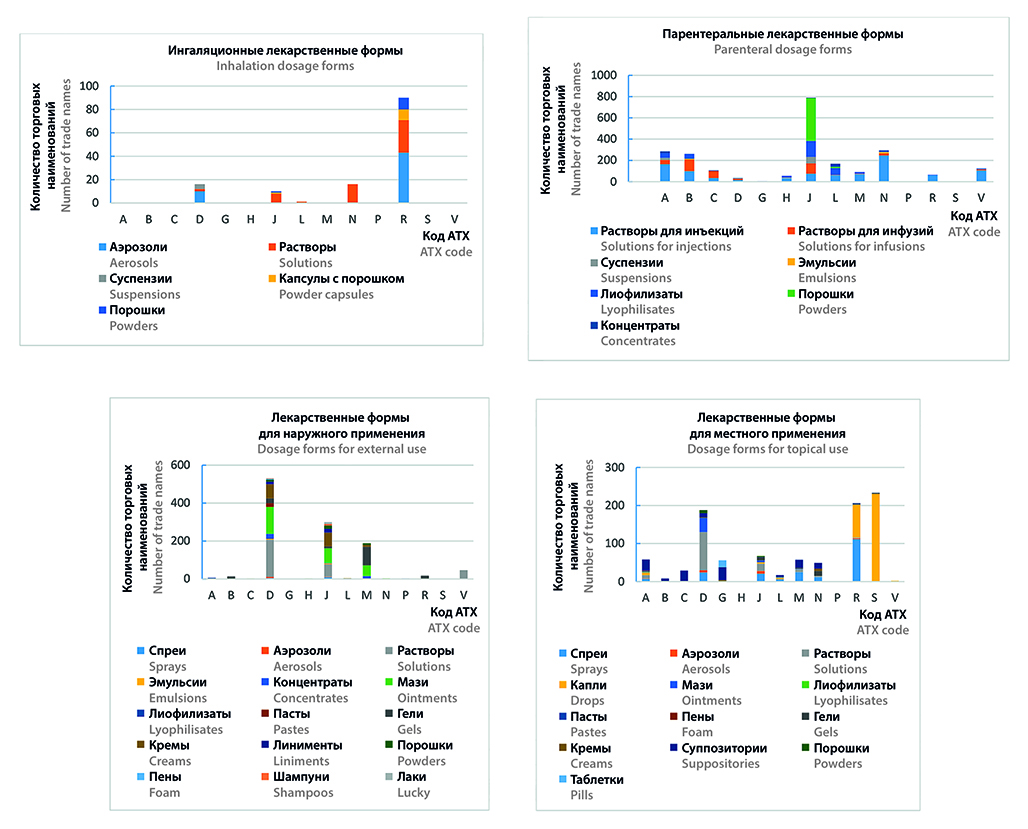
Materials and methods. The information base of the study was made up of data from the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation for 2010–2022, GRLS as of 01.01.2023, as well as instructions for the medical use of medicines. The target age group of patients was determined in accordance with the Recommendation of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commission. The content analysis method is used to search scientific literature in the PubMed and eLibrary electronic databases, analyze information from instructions for the medical use of medicines (LP), restrictive lists, GRLS, and the state register of prices for VED. The analysis of morbidity data was carried out using the statistical analysis method. Grouping, ranking and systematization were used in the framework of a structural analysis of morbidity, as well as an analysis of the assortment matrix of drugs for pediatrics within the established market boundaries. Graphical analysis was used to visualize the data. Data processing was carried out using MS Excel 2021.
Results and discussion. It was found that in the period from 2010 to 2022, against the background of an increase in the number of children by 11.22 %, there was an increase in primary morbidity by 13.41 % in general. Respiratory diseases prevail in the structure of primary morbidity of children, amounting to 62.61 %. Having analyzed the matrices of the national pediatric code formulary, covering 554 INNs, it turned out that within the pharmacotherapeutic groups J, L, N and P themselves, a decrease in WHO indicators of 16–57 % was recorded. An assessment of the supply on the national market allows us to conclude that 19.55 % of drugs approved for use in pediatric practice are contraindicated in patients under 12 years of age. As a result of the assortment ranking along the route of administration, the predominance of oral forms was established, covering 39.88 % of the assortment matrix.
Conclusion. Assessing the dynamics of morbidity in the context of analyzing the structure of the market of drugs for pediatrics allows us to identify priority niches for the pharmaceutical industry in the segments of medicines for the pharmacological correction of respiratory diseases, as well as drugs for the treatment of oncological pathologies, autoimmune disorders, obesity, diabetes mellitus and neurological disorders. The range of medicines presented today, taking into account the forms of release and age restrictions for the treatment of pediatric patients, demonstrates insufficient filling of the market with drugs in special children's dosage forms that ensure acceptability to modern concepts of therapy in pediatrics and accurate dosing of active substances in accordance with the age of the child, which, in turn, reveals the prospects for the pharmaceutical development of medicines with a design that corresponds to the purpose in the target age group.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)