FROM EDITOR
The two-day 18th Congress "Drug Development and Registration" was held on February 26–27, 2025 at the Caliber technopark in Moscow.
Within the International Congress "Drug development & registration" was held an open discussion "HTMP, features of production, registration, quality control" in Moscow on February 27, 2025.
We present to your attention a new interview as part of the Leaders' Opinion series. Today’s guests were the director of the research and development department of the GEROPHARM company, Roman V. Drai, and the general director of the LLC "Center of Pharmaceutical Analytics", Igor E. Shokhin. The interviewer was Natalya V. Kuldzhanova, director of the scientific and production journal "Drug development and registration".
The fourth part of the article presents main pharmaceutical forms made by the Apothecary prikaz’s specialists. The key point is for the first time published analysis by K. S. Hudin of XVII century documents. These papers contain lists of medicines made by pharmaceutists and alchemists of minerals and herbal raw material as well as prescriptions of using these drugs (vodkas, oils, ointments, patches, sugars, syr-ups, sweets, balms, etc.) by clerks of the Apothecary prikaz.
EVENTS
From November 19 to 22, 2024, the 26th International Exhibition of Equipment, Raw Materials and Technologies for Pharmaceutical Production "Pharmtech & Ingredients – 2024" was held in Moscow.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
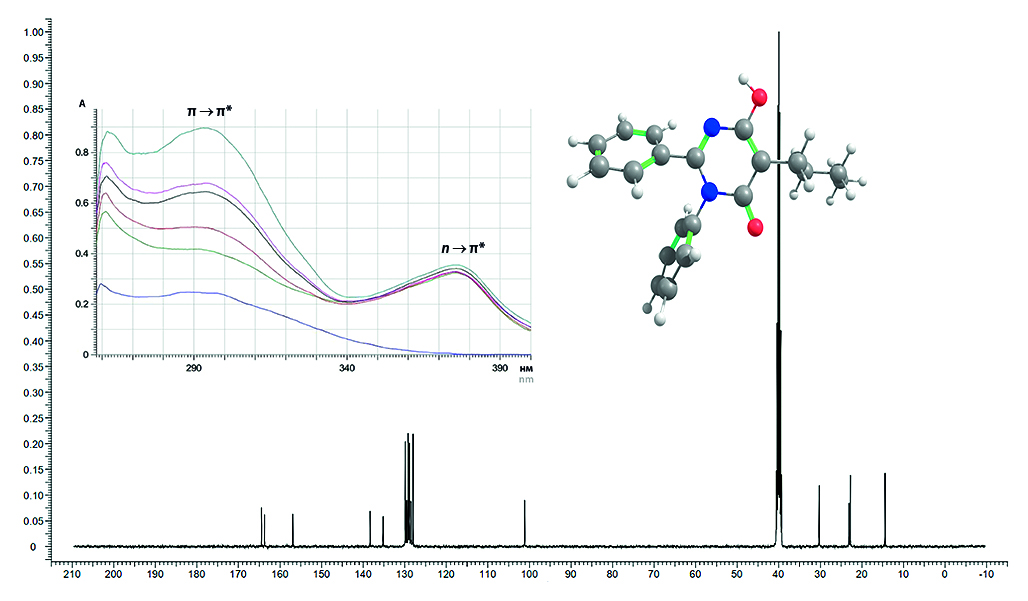
Introduction. The development of methods for analyzing new potentially active pharmaceutical substances is an important part of substance standardization. An integrated approach to confirming the structure of a substance is especially important when the substance may exist in different tautomeric forms, since the properties of the substance may change depending on tautomerism, affecting, among other things, the pharmacological activity.
Aim. The aim of our study was to determine the tautomeric composition of the potential active pharmaceutical substance 5-butyl-6-hydroxy-2,3-diphenylpyrimidin-4(3H)-one in solid state and solution for the subsequent development of its dosage form and determination of bioavailability.
Material and methods. The object of the study was the substance 5-butyl-6-hydroxy-2,3-diphenylpyrimidin-4(3H)-one. Spectra were taken to confirm the structure: infrared on a PerkinElmer Spectrum 3 device (PerkinElmer Inc., USA) in the frequency range from 4000 to 400 cm–1, nuclear magnetic resonance 1H and 13C on a pulsed broadband spectrometer Bruker AM-500 (400 and 100 MHz) (Bruker, Germany) in DMSO-d6 solvent, ultraviolet using SF-2000 (LLC "OKB Spektr", Russia) in the wavelength range of 250–400 nm, and high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) was also carried out.
Results and discussion. A feature of pyrimidine hydroxy derivatives is the presence of tautomeric forms, which can affect both the physicochemical properties of the substance and its pharmacological activity. The study found that in the solid state, 5-butyl-6-hydroxy-2,3-diphenylpyrimidin-4(3H)-one is in equilibrium between the diketo form and the enol form, and when the substance is dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), the enol form is predominant. The purity was confirmed by HPLC-MS/MS.
Conclusion. The structure of 5-butyl-6-hydroxy-2,3-diphenylpyrimidin-4(3H)-one was confirmed by IR and NMR spectroscopy. UV spectra were obtained, and HPLC-MS/MS was performed to exclude possible absorption of ultraviolet radiation by impurities.
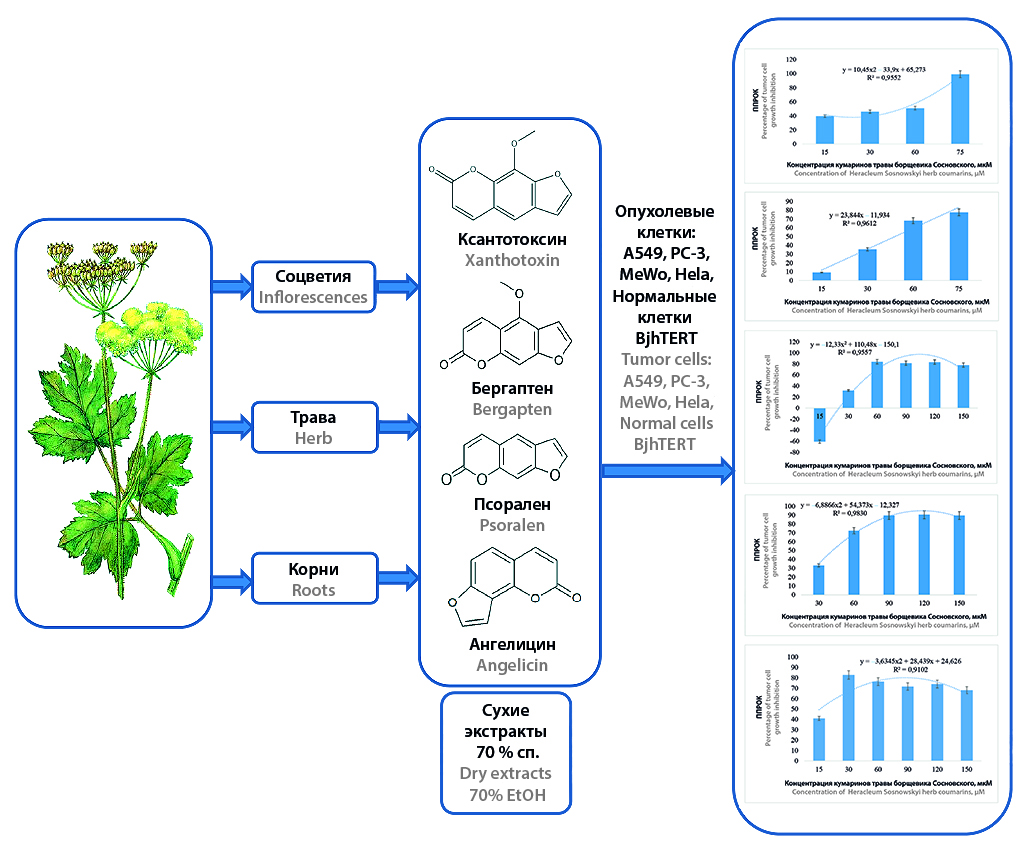
Introduction. The search for new antitumor agents among plants of local flora is one of the options for expanding the existing list of chemotherapeutic drugs. A promising source of such agents may be an invasive and weedy species for the territory of the Republic of Belarus and the Russian Federation – Heracleum Sosnowskyi. This species contains coumarins, for which antitumor properties have been established, so Heracleum Sosnowskyi can be considered a promising raw material source of these biologically active substances.
Aim. To analyze the cytostatic effect of extracts from the herb, inflorescences and roots of Heracleum Sosnowskyi on tumor cell cultures in vitro.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was air-dried herbs and inflorescences harvested during the flowering period and roots harvested during the dying off period of the above-ground part of Heracleum Sosnowskyi. Aqueous-alcoholic extracts were obtained, from which the solvent was distilled off, the resulting dry residue was dissolved in phosphate-salt buffer pH 7.4. Identification and quantification of coumarins were carried out by high performance liquid chromatography. Antitumor (cytostatic) effect in vitro was studied on the following cell cultures: lung carcinoma A549, prostate adenocarcinoma PC-3, skin melanoma MeWo, cervical adenocarcinoma Hela and immortalized foreskin fibroblasts BjhTERT. Cell viability was assessed under MTT test conditions on a flatbed spectrophotometer. Metabolic activity was monitored using 4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2-yl-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide. Negative control (buffer), cell growth control, positive control (doxorubicin) and test samples were formed.
Results and discussion. Extracts from the herb of Heracleum Sosnowskyi showed a statistically significant cytostatic effect on the tumor cell lines A549, PC-3, cervical adenocarcinoma Hela and MeWo. Extracts from roots and inflorescences showed a statistically significant cytostatic effect on the cell lines Hela and MeWo. The cytostatic effect depended on the concentration of coumarins in terms of xanthotoxin. Extracts from the herb had a cytostatic effect on normal BjhTERT cells; roots and inflorescences did not significantly affect their growth. The cytostatic effect of extracts from Heracleum Sosnowskyi herb on A549 and PC-3 cell lines was superior to the effect of doxorubicin, on MeWo and BjhTERT cell lines it was comparable to that of doxorubicin. When comparing semi-effective concentrations, it was found that all studied extracts caused growth suppression at lower concentrations, i.e. they had higher activity compared to doxorubicin. Extracts from herb more strongly inhibit the growth of A549 cells; Extracts from roots and inflorescences more strongly inhibit the growth of Hela cells.
Conclusion. Herb, roots and inflorescences of Heracleum Sosnowskyi have a pronounced cytostatic effect in vitro, which makes it expedient to further study this plant within the framework of coumarins isolation and establishment of mechanisms of influence on the growth of tumor cells in comparison with normal cells.
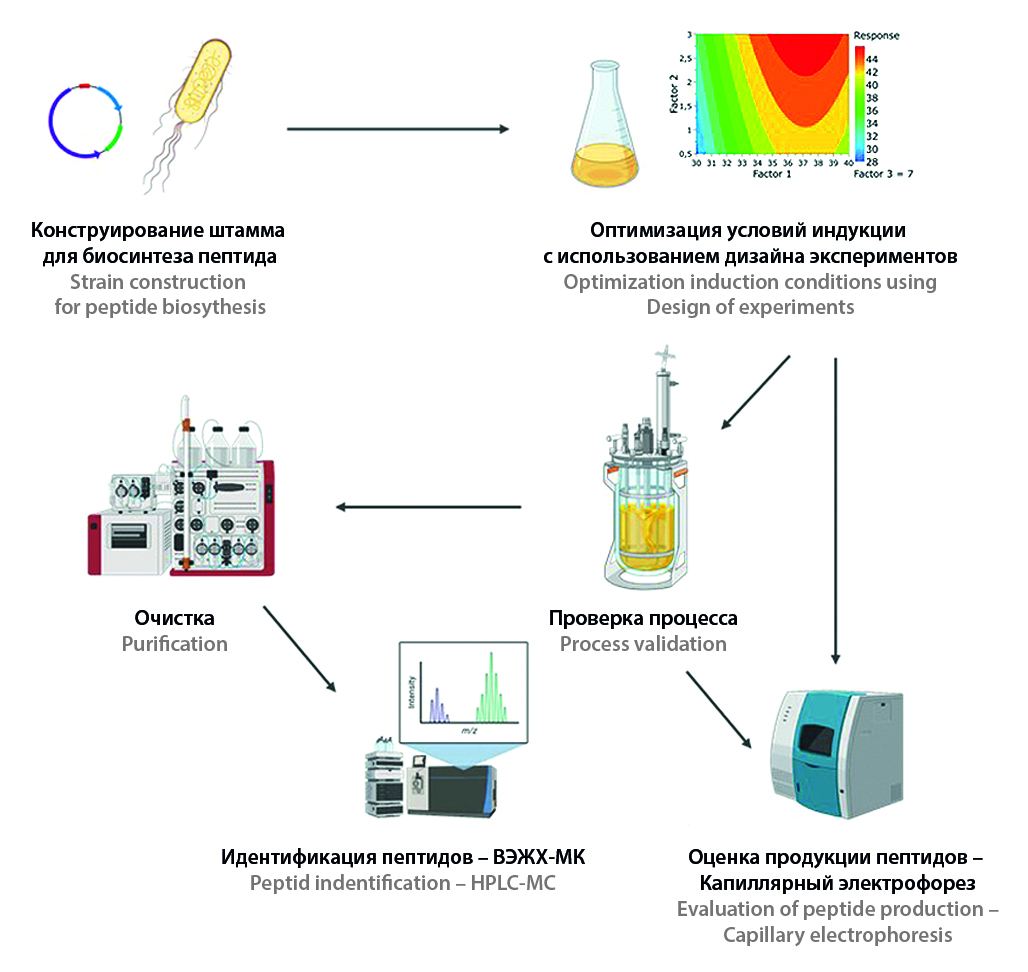
Introduction. Peptides with a molecular weight of less than 5 kDa have been used in medicine and biotechnology over the past decade for the treatment of various diseases. However, chemical synthesis peptide has several disadvantages, including low yield, reduced efficiency, and high costs. An alternative approach to peptide production is the use of the Escherichia coli expression system. The development of effective peptide synthesis technology remains a critical task because of the low productivity of recombinant strains.
Aim. Developing highly efficient strains of Escherichia coli BL21 expressing therapeutic peptides with a molecular weight of less than 5 kDa in E. coli and their cultivation technology.
Materials and methods. Genetic constructs were obtained using the restriction-ligase method, and their authenticity was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Cultivation technology was developed using the Design of Experiments approach. The cultivation condition was validated in the Biostat B bioreactor. Hybrid proteins were purified by metal-chelate chromatography, followed by hydrolysis ULP proteas to obtain the target peptides. The quantitative content of the target protein was determined by capillary electrophoresis, and the authenticity of the protein was confirmed by HPLC-MS and ELISA.
Results and discussion. Highly efficient peptide-producing strains were developed. Cultivation conditions were optimized: рН 7.5 ± 0.5, cultivation temperature 37 °C, induction optical density 28 ± 2, IPTG concentration 0.05 мМ. The productivity of the producer strains was up to 4.82 ± 0.05 g/L. Furthermore, samples of the target peptides were isolated and purified.
Conclusion. The productivity of peptides in this study were significantly higher than in previous research. The presented strategy for strain development, cultivation and purification technology can be used production of therapeutic peptides with diverse physical chemicals characteristics in the future.
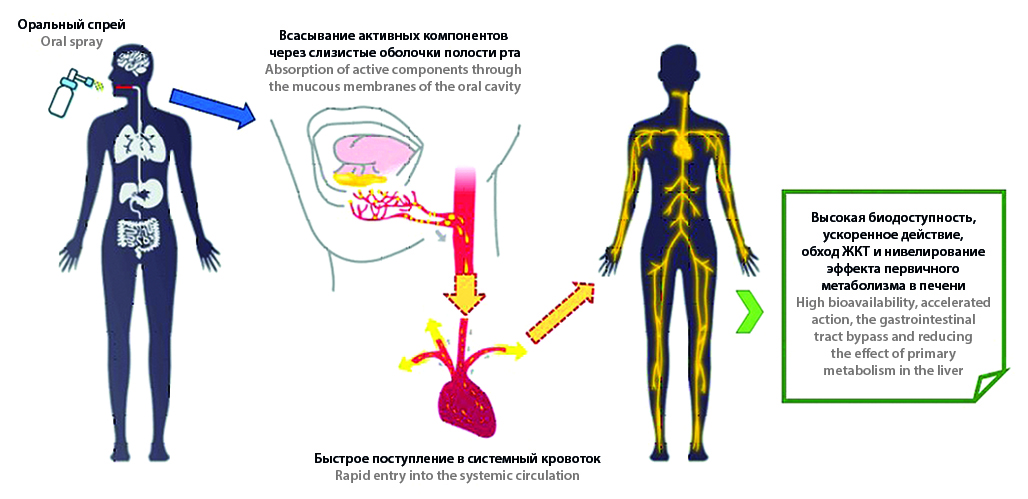
Introduction. Modern pharmaceutical development enables to introduce into practice more than ever new active ingredients delivery systems and forms enhancing actives activity compared to traditional approach (methods). A nowadays pace of life often providing improper feeding and micronutrients intake imbalance leads to necessary administration of micronutrient additional doses in the form of different pharmacies. Over the last years vitamins and minor nutrient elements spray forms are becoming more attractive for introduction into pharmaceutical practice. These dosage forms are characterized by the production availability, usability, easy dosage and sufficiently high bioavailability for both normal patients and ones having gastrointestinal tract diseases and other problems connecting with the food consumption and digestion.
Text. Drug delivery by oral mucosa attracts more attention due to its potential advantages compared to other methods. Until recently this administration way was considered mainly for topical application. However, in recent years number of developments connecting with oral cavity application as a portal for delivery of drugs active ingredients, vitamins and micronutrients into systemic blood has kept steadily growing. Diverse forms of oral drugs for sublingual and buccal administration have been developed by many scientific and clinical teams. Spray forms among them are of particular interest as the most economically viable and easy to use. Most of these developments deal with vitamins D and B12, which arises from the acutest problems of their deficiency among global population, on the one hand, and low bioavailability due to negative effects by dietary intake, gastrointestinal tract health condition and other factors, on the other hand. Other micronutrients such as thiamin, niacin, pyridoxin, ascorbic acid, coenzyme Q and iron are examined and launched into the market in an oral spray form for sublingual application.
Conclusion. The current results of development and comparison study of micronutrients oral forms, in particular, randomized controlled trial data indicate a sublingual administration efficiency which either is similar to or exceeds traditional administration ways.
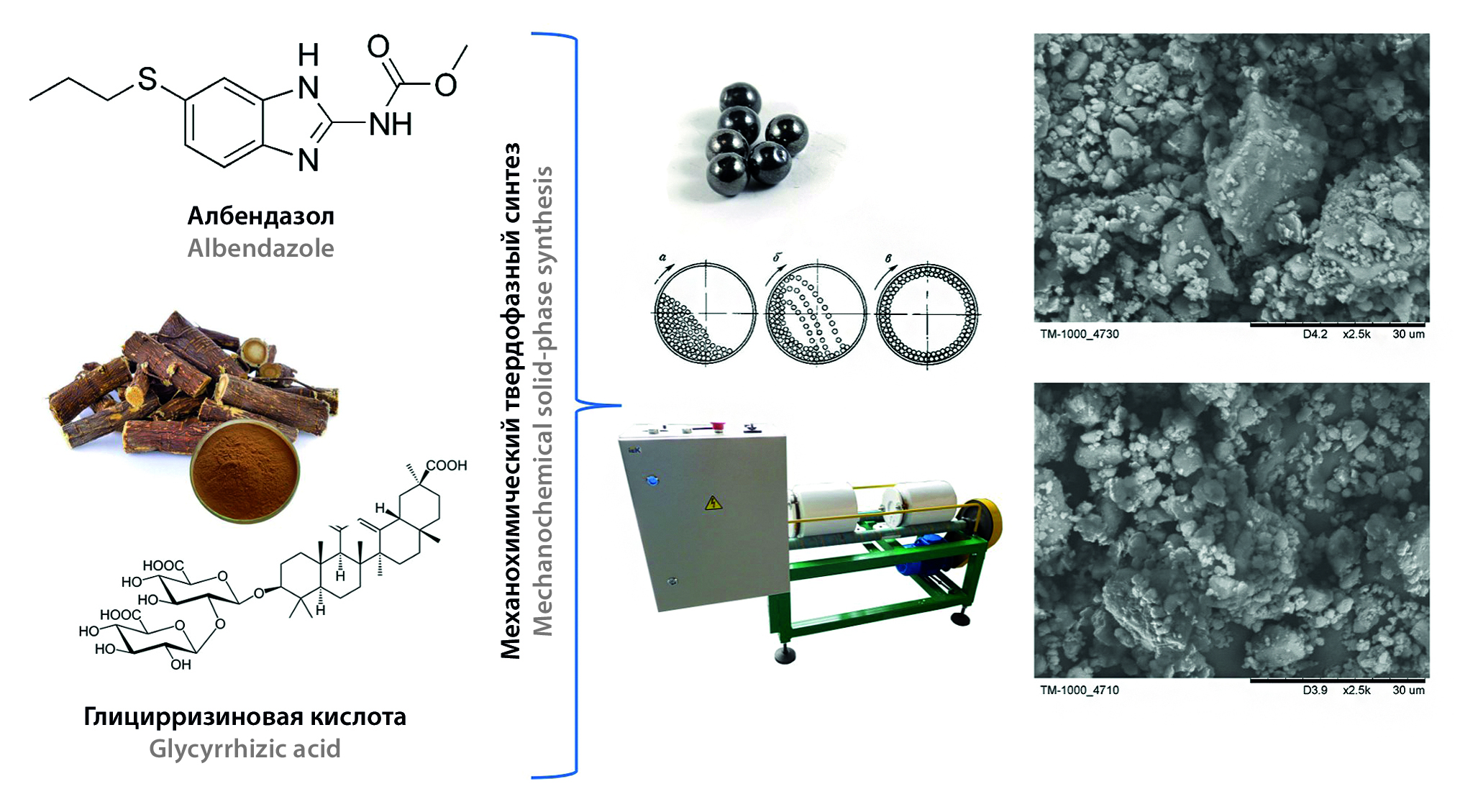
Introduction. The use of the method of mechanochemical synthesis to obtain solid dispersions (SD) of albendazole (ALB) has allowed increasing its anthelmintic activity and bioavailability, as well as reducing its toxicity, and therefore the issue of developing the composition and technology of an affordable domestic drug based on SD of ALB in a rational dosage form (DF) is relevant.
Aim. Development and pharmacotechnological study of suspension for oral administration based on TD ALB obtained by mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were ALB substance (ALB), licorice dry extract (LE) and their SD obtained by mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis in a mass ratio of 1 : 5, 1 : 10 and 1 : 20, with a mechanical treatment duration of 2 hours, 8 hours and 16 hours. Substances approved for medical use are used as excipients. The study of the solubility of ALB from SD was evaluated by the content of ALB in an aqueous medium using high-performance liquid chromatography. The study of the properties of SD and the obtained DF was carried out in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation (SP RF) XV edition.
Results and discussion. The technological properties of SD do not change significantly depending on the mass ratio of medicinal substance (MS) to the carrier and the time of their machining, as a result of which the determining factor in choosing the optimal SD for the development of a DF is the value of the solubility of ALB in water. The use of the wet granulation method and the addition of a filler, stabilizer and preservative to the SD make it possible to obtain powders for the preparation of a suspension with satisfactory technological characteristics.
Conclusion. During the study, the technological characteristics of SD ALB with LE obtained by mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis were studied, and the optimal SD was determined from the point of view of the highest solubility of ALB in water. Excipients were selected, the composition of the suspension restored from SD ALB granules with optimal technological parameters was developed. Pharmacotechnological studies of suspensions based on SD ALB were conducted.
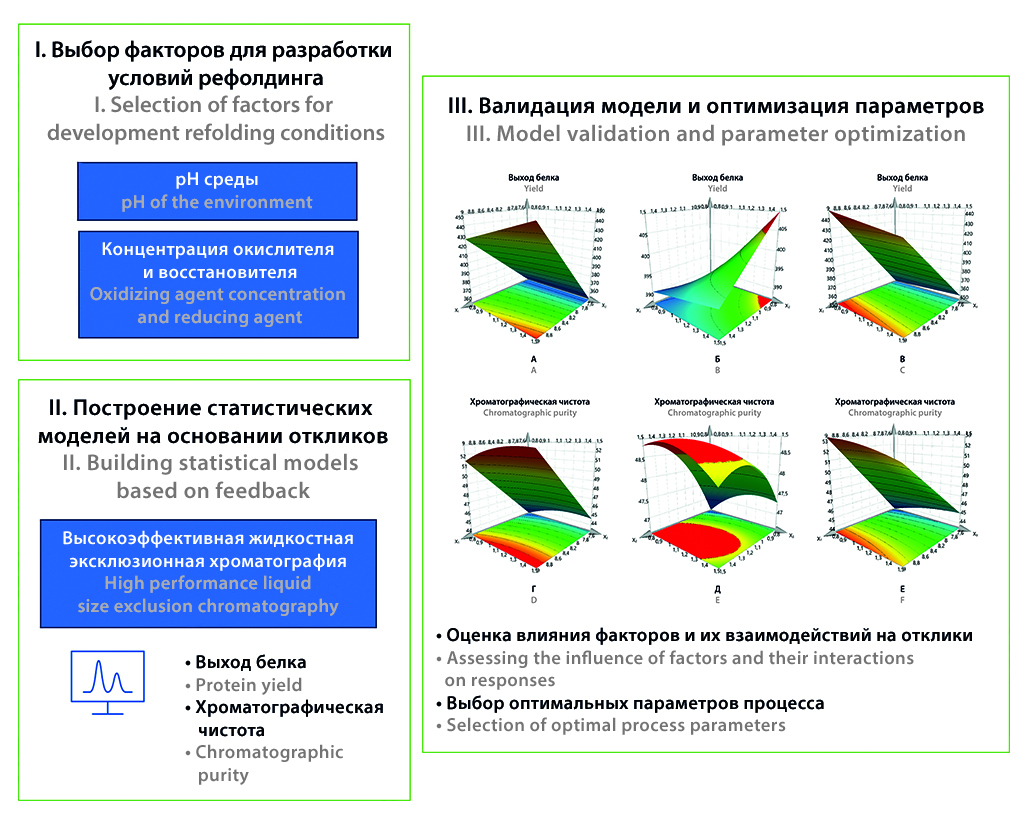
Introduction. The production of Fc-fused proteins in prokaryotic systems often results in the formation of insoluble aggregates due to improper folding of polypeptide chains. To obtain functional proteins, a refolding step is required. However, developing refolding parameters can be time-consuming. The optimization of renaturation conditions using the Design of Experiments (DoE) approach allows for the calculation of optimal process parameters and the evaluation of contributing factors and their interactions.
Aim. This study aims to evaluate the effects of denaturation buffer pH, as well as oxidative and reducing agent concentrations, on the efficiency of Fc-fusion protein refolding in vitro and to determine optimal refolding parameters.
Materials and methods. Fc-fusion protein inclusion bodies were obtained from an Escherichia coli BL21 bacterial expression system. The experiment was designed using an orthogonal composite design (Orthogonal Central Composite Design, CCO). Experimental design, statistical data processing, and parameter optimization were conducted using MODDE (v. 12.1, Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics AB, Germany). Chromatographic purity and yield of the target protein, as determined by high-performance size-exclusion chromatography, were used as response variables.
Results and discussion. The DoE approach successfully optimized the Fc-fusion protein refolding process. Response surface plots were constructed, and the optimal factor values were determined. The statistical models demonstrated high predictive accuracy and data reproducibility. The refolding process was successfully validated under optimized conditions, resulting in a decrease in high-molecular-weight impurities and improperly folded protein forms. The chromatographic purity of the target protein increased by more than 10 %, as confirmed by high-performance size-exclusion chromatography.
Conclusion. The study established significant effects of buffer pH, redox pair concentrations, and their interactions on the yield and chromatographic purity of the Fc-fused protein. The interplay between oxidative and reducing components and buffer pH was demonstrated. Increasing the buffer pH led to improved refolding efficiency.
Introduction. Cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide. Naphthoquinones are a group of natural organic compounds with a wide range of activity, including cardio-, hepato-, neuroprotective effects, as well as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antitumor activity. 1,4-naphthoquinone is easily oxidized, reduced, and may be easily attached with nucleophiles. Well-developed methods of chemical modification of naphthoquinones make them attractive for the development of new types substances. It is known about the antitumor effect of natural naphthoquinone compounds – plumbagin, shikonin, lapachol. Antitumor antibiotics such as doxorubicin and daunorubicin have a 1,4-naphthoquinone fragment in their structure.
Text. This review is devoted to the analysis of information on the mechanisms of antitumor action of synthetic derivatives of 1,4-naphthoquinone. Possible targets of their antitumor action are discussed.
Conclusion. An analysis of the literature data showed that synthetic compounds based on the 1,4-naphthoquinone molecule have antitumor activity. The mechanism of antitumor action may be associated with the induction of apoptosis through the signaling pathway of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the pathway of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), inhibition of cell division cycle phosphatase (Cdc25), accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), inhibition of angiogenesis. The data obtained by researchers from different countries confirm the prospects of searching for new compounds with antitumor activity among synthetic derivatives of 1,4-naphthoquinone for the development of new medicines based on them.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
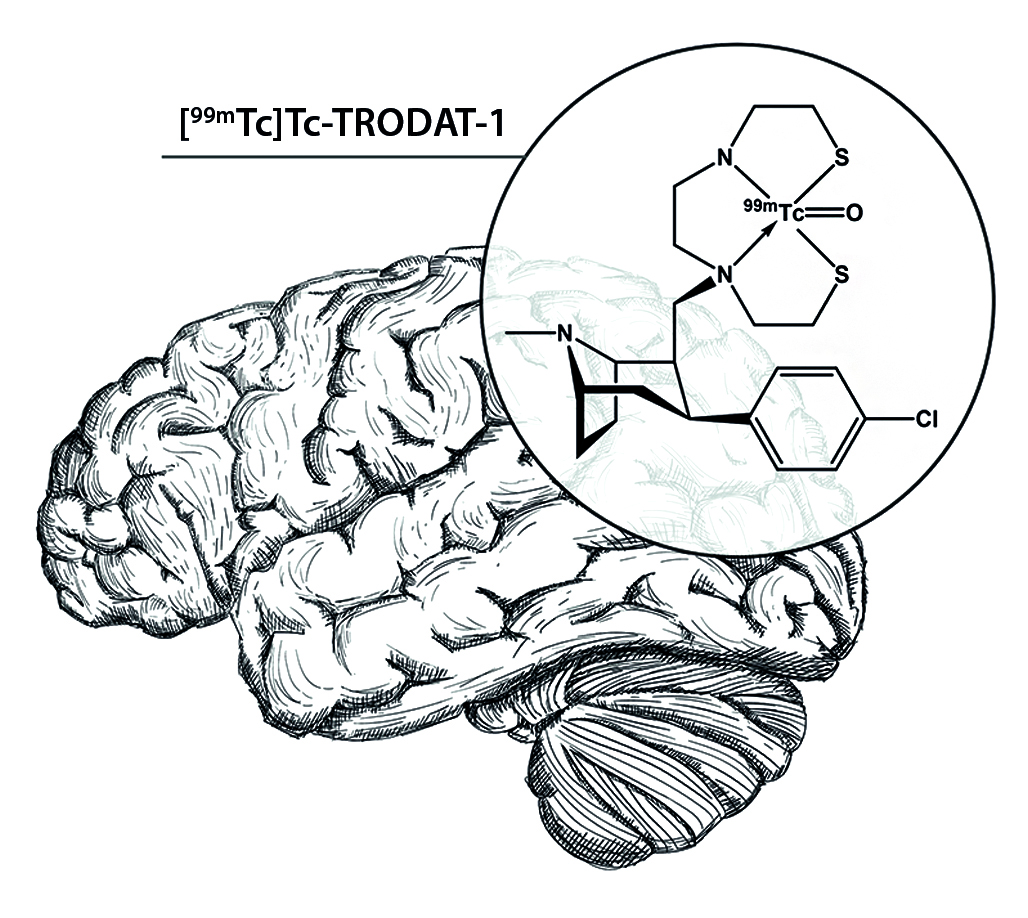
Introduction. The symptoms of Parkinson's disease are mainly associated with the formation of intraneuronal protein inclusions with Lewy bodies, and the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons of the Substantia nigra and their axons. Existing diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease often take into account symptoms occurring in the later stages of the disease. Thus, for a more accurate diagnosis in the early stages, it is necessary to confirm pathologic changes in brain tissue by molecular imaging methods such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). At the same time SPECT is a more accessible method of diagnostics of neurodegenerative diseases in comparison with PET, because of the possibility to obtain medical radionuclides for SPECT imaging using mobile generator systems, in particular 99Mo/99mTc generator. Among the formulations based on 99mTc and tropane derivatives proposed for dopamine transporter (DAT) imaging, [99mTc]Tc-TRODAT-1 (technetium-99m-labeled tropantiol) is the most effective. Currently, various compositions of the freeze-dried kits for the synthesis of [99mTc]Tc-TRODAT-1 have been proposed, facilitating the process of its production in situ, which, together with the availability of technetium-99m generator in a healthcare facility, as well as favorable pharmacokinetics, makes [99mTc]Tc-TRODAT-1 a drug of choice for routine use in clinical practice.
Text. In this review, various approaches to design and optimize the composition of the freeze-dried kits for the synthesis of [99mTc]Tc-TRODAT-1, including the amount and ratio of active ingredient and excipients, synthesis conditions, in particular the temperature regime, synthesis time and pH of the reaction mixture, have been considered.
Conclusion. Development and optimization of the composition of the freeze-dried kits for the synthesis of [99mTc]Tc-TRODAT-1 is an urgent task in the context of improving its use in clinical practice. Based on the published data, clear dependencies can be traced, which may form the basis for further development and optimization of the composition of the freeze-dried kits for [99mTc]Tc-TRODAT-1 synthesis for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases by SPECT in the Russian Federation.
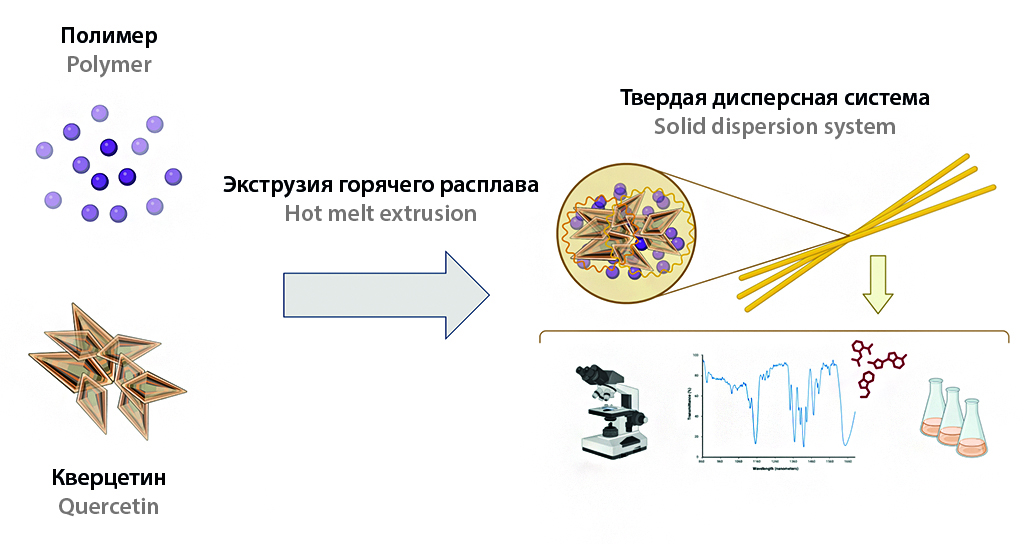
Introduction. Flavonoids, despite their pronounced therapeutic benefits, are limitedly used in medicine as active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) owing to a complex of unsatisfactory physicochemical properties. In order to study the mentioned problem, we decided to use quercetin as model compound with extremely low water solubility and dissolution in gastrointestinal (GI) tract media. Therefore, the main idea appears to study the possibility and prospects of hot melt extrusion (HME) application for enhancement the solubility properties of quercetin in the composition of solid dispersion system (SDS) based on hydrophilic polymeric carrier (polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate, PVP/VA). Consequently, there is a necessity to select effective drug-to-polymer ratio in solid dispersion for providing better solubility and dissolution properties.
Aim. Assessment of PVP/VA effect on quercetin solubility properties in binary solid dispersion prepared by HME.
Materials and methods. Quercetin substance with purity 98 % was purchased from Molekula Limited, United Kingdom. PVP/VA (copolymer of polyvinylpyrrolidone with vinyl acetate in the ratio of 60 : 40, VIVAPHARM® PVP/VA 64) as carrier was procured from JRS PHARMA (JRS PHARMA GmbH & Co. KG, Germany). Quercetin SDS were prepared using micro-conical twin screw compounder HAAKE™ MiniCTW (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany). The obtained samples were analyzed by phase-contrast microscopy, FTIR spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Quercetin quantitative content in SDS were determined by UV-spectrophotometry.
Results and discussion. The improvement of water solubility and dissolution rates of quercetin SDS in comparison with pure substance was observed for all solid dispersion compositions irrespective to drug-to-polymer ratio. Notably, with reduction of quercetin content in SDS compositions the PVP/VA contribution was increased. We found partial or even complete amorphization of API in formulations with 1 % and 5 % quercetin content, resulting in the improvement of water solubility properties, stability of solutions and increased dissolution rates in GI tract media. Water solubility of 1 % SDS relative to pure substance was enhanced by 353-fold. At the same time, the complete release of quercetin from 1 % SDS was achieved in 40 minutes in the hydrochloric acid and citrate buffer, and also quercetin dissolution of 90 % in 60 minute was observed in phosphate buffer.
Conclusion. 1 % quercetin SDS based on PVP/VA appears to be the most promising for solid dosage forms development.
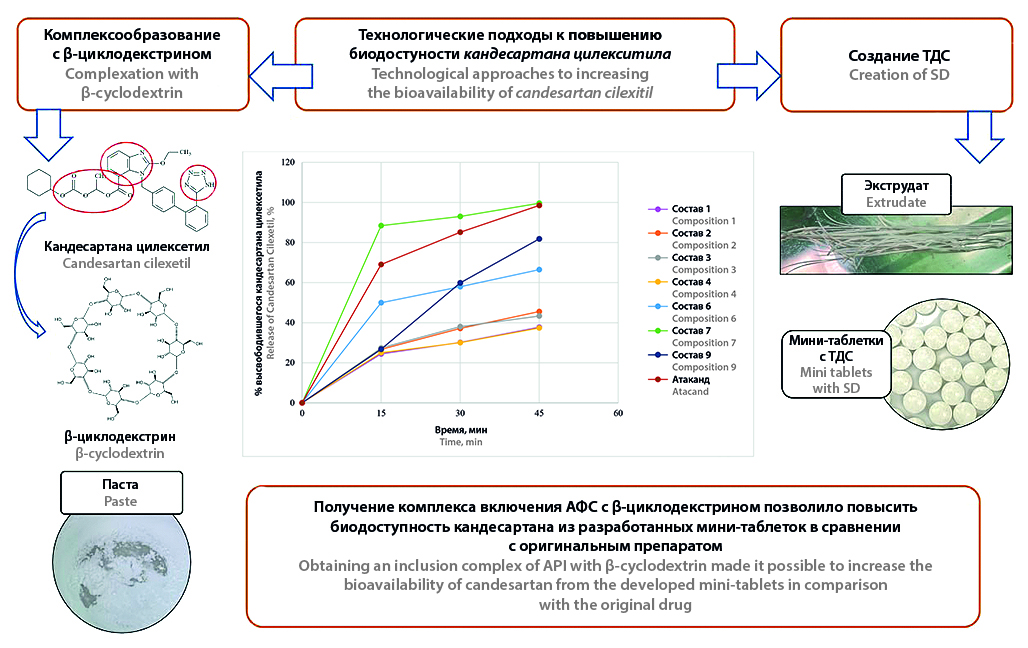
Introduction. The polypill in the form of a hard gelatin capsule containing mini-tablets of the original antihypertensive combination is being developed at the Saint-Petersburg State Chemical and Pharmaceutical University. One of the components of the polypill is Candesartan, which has high antihypertensive activity and organoprotective properties. The active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) of Candesartan Cilexetil is characterized by low solubility in water and gastrointestinal tract media, therefore increasing the solubility of this substance can lead to a significant improving the bioavailability.
Aim. Comparative analysis of technological approaches to increasing the bioavailability of the poor soluble API Сandesartan Сilexetil in a mini-tablet dosage form.
Materials and methods. API Сandesartan Сilexetil, β-cyclodextrin (β-CD), copolymer of polyvinylpyrrolidone and vinyl acetate and excipients for the production of mini-tablets, such as diluents, binders, disintegrant, dusting components were used. The release profiles of Candesartan Cilexetil from the developed mini-tablets were assessed in comparison with the original drug Atacand®, 8 mg tablets. The complex of candesartan cilexetil with β-CD in a 1 : 1 ratio was prepared by three methods: dry mixing, paste method and lyophilization. A solid dispersion (SD) of candesartan was obtained by hot melt extrusion. The API complexes with β-CD and SD were characterized by FTIR-spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Tablet mixtures were produced by dry mixing and wet granulation technology. Mini-tablets were obtained on a laboratory automatic single-punch tablet press. Quality control of the mini-tablets was conducted by the methods of State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV ed. and United State Pharmacopeia methods.
Results and discussion. Comparative analysis of technological approaches to increasing the bioavailability of Candesartan Cilexetil showed, that preparation of a complex including API with β-CD in a 1 : 1 ratio using the paste method with further using of wet granulation technology allowed to obtain mini-tablets with improved release of poor soluble API compared to the original drug. On the contrary, the use of TDS in mini-tablet technology led to a slower release of API compared to the original drug. The developed mini-tablets of Candesartan composition № 7 met pharmacopoeial requirements by all acceptance criteria.
Conclusion. The creation of complex of Candesartan Cilexetil with β-CD by the paste method with further using of wet granulation technology is the optimal technological approach to increasing the bioavailability of the poor soluble API Candesartan Cilexetil in mini-tablets.
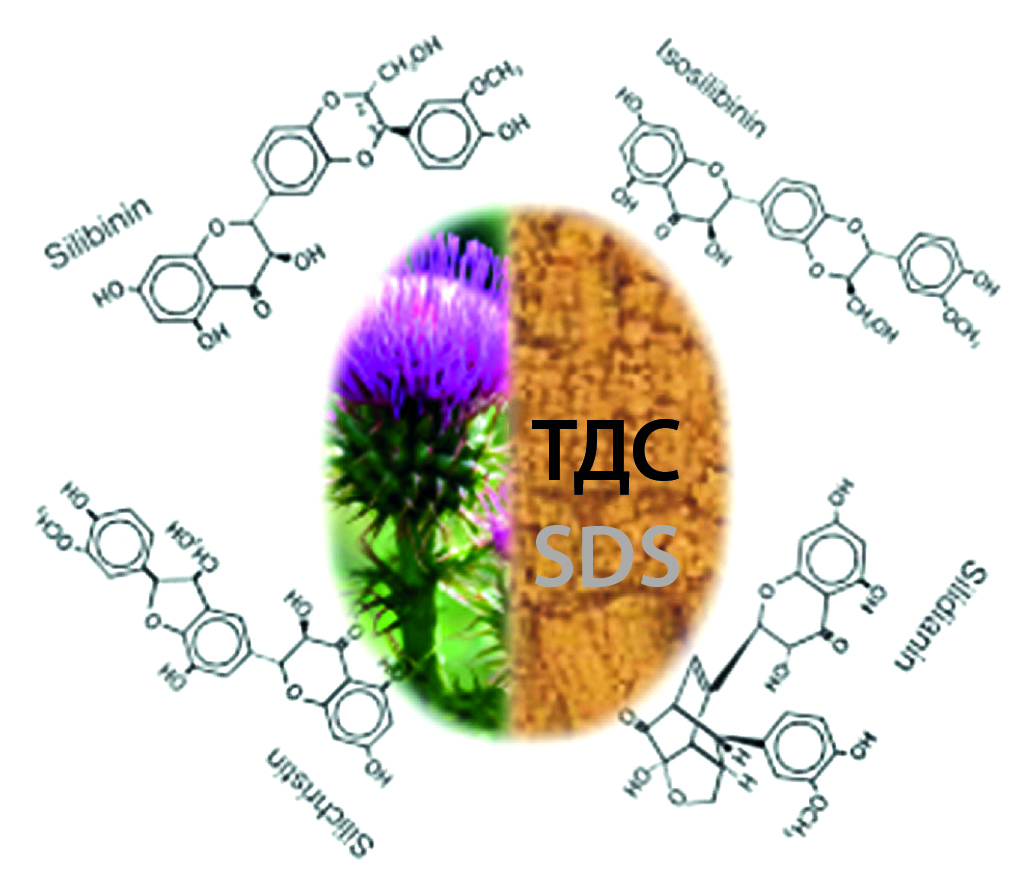
Introduction. Silymarin is one of the main components used in preparations for hepatotropic therapy. Silymarin is contained in the dry extract of seeds and fruits of milk thistle (Silybum marianum L. Gaertn.), however it has poor bioavailability due to the crystalline state and low solubility of silymarin flavolignans in water at room temperature, as well as their poor absorption. One of the methods for increasing the bioavailability of medicinal substances consists in their introducing into solid dispersion systems (SDS). The most suitable method for obtaining SDS with extracts is the solvent method, since it does not require the use of a high temperature regime during the obtaining process of SDS.
Aim. To develop the technology for solid dispersion system from milk thistle dry extract by solvent method to increase the bioavailability of this phytosubstance.
Material and methods. The obtaining of the solid dispersion systems from milk thistle dry extract by solvent method was carried out with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP K-29/32), polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate 6 : 4 (PVPVA 64), hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC), gelatin and sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS). The quality indicators of the SDS: particle size distribution, bulk density, residual humidity and hygroscopicity were carried out according to the methods of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation (GP RF) XV edition. The quantitative determination of biologically active substances (BAS) was carried out in accordance with the GP RF XV ed. by the amount of flavolignans in terms of silybin.
Results and discussion. During the development of solid dispersion systems by solvent method, SDS samples from milk thistle dry extract (MTDE) with different polymers were studied. As a result of studying the particle size distribution, several SDS samples were selected. The SDS samples were compared with the MTDE sample. The "Dissolution" test showed that the micronization of MTDE in form of SDS by solvent method, containing polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate – PVP VA 64 is the best alternative for increasing the silybin releasing-degree from the extract and increasing its bioavailability. According to the content of the sum of flavolignans in terms of silybin, the selected SDS sample meets the requirements of the normative documentation for milk thistle dry extract. In addition, the conditions for the development of SDS do not significantly affect the quantitative content of silybin compared with the content of the control sample of MTDE. The technological characteristics of SDS have been investigated and their qualitative improvement compared to the MTDE sample has been established. The interaction between the polymer carrier and the milk thistle extract was evaluated by the IR-fourier spectroscopy method.
Conclusion. The SDS from milk thistle dry extract was developed by solvent method. For the developed SDS, quality indicators such as the content of the sum of flavolignans in terms of silybin, residual humidity, bulk density, particle size distribution and hygroscopicity were determined. The solid dispersion system from milk thistle extract was analyzed by IR-fourier spectroscopy. The physico-chemical compatibility between the milk thistle extract and the polymer-carrier polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate is shown. The development of the SDS from milk thistle dry extract significantly increased the bioavailability of the phytosubstance by increasing the silybin releasing-degree of the SDS by 3 times compared with the control sample of MTDE.
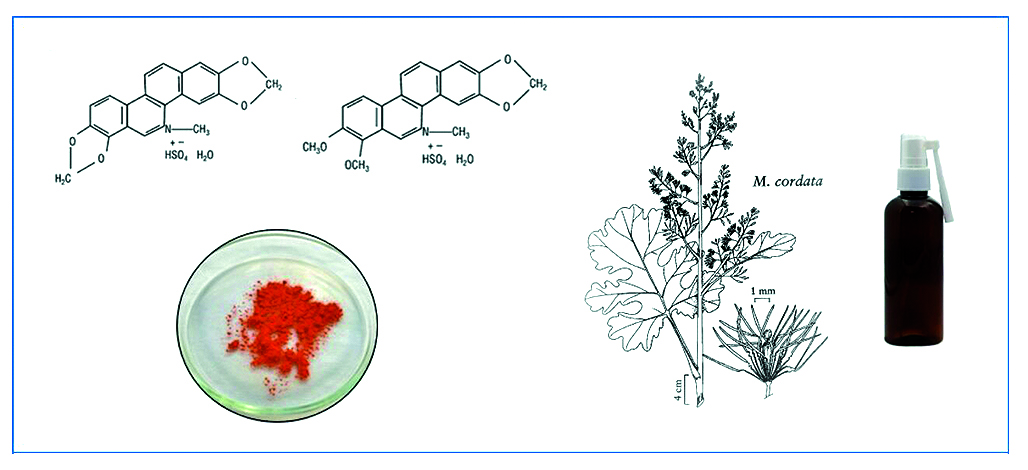
Introduction. One of the most common bacterial infections includes acute and chronic tonsillitis, affecting 10 to 15 % of adults and approximately 20–25 % of children worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. The focus of this study was an original substance, sangviritrin, containing no less than 96.5 % of the sum of bisulfates of two alkaloids: sanguinarine and chelerythrine. Given the high antimicrobial activity of sangviritrin, the research aimed to develop a local delivery system based on this medicinal substance.
Aim. The aim of this work was to develop an oral medicinal form of sangviritrin.
Materials and Methods. Sangviritrin, produced by the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, was used as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. The selection of auxiliary components was carried out in accordance with the methodologies specified in the State Pharmacopoeia XV edition. The organoleptic properties of the substance and spray samples were studied using A. I. Tenzova's method. The local irritant action of the spray was assessed using the conjunctival test method on chinchilla rabbits weighing 3.5–4.3 kg. Quantitative determination of sangviritrin in the medicinal form was performed using spectrophotometric methods at a wavelength of 321 ± 2 nm on a spectrophotometer SPECORD® 200 PLUS (Analytik Jena GmbH+Co. KG, Germany).
Results and Discussion. Optimal auxiliary component compositions were selected based on measurements of spray technological parameters. A comprehensive approach was justified for correcting the organoleptic properties of the substance, involving the introduction of a minimal amount of sweeteners and additional use of β-cyclodextrin. Examination of the local irritant action indicated a "weak or absent" degree of local irritation.
Conclusion. A local delivery system for sangviritrin has been developed for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
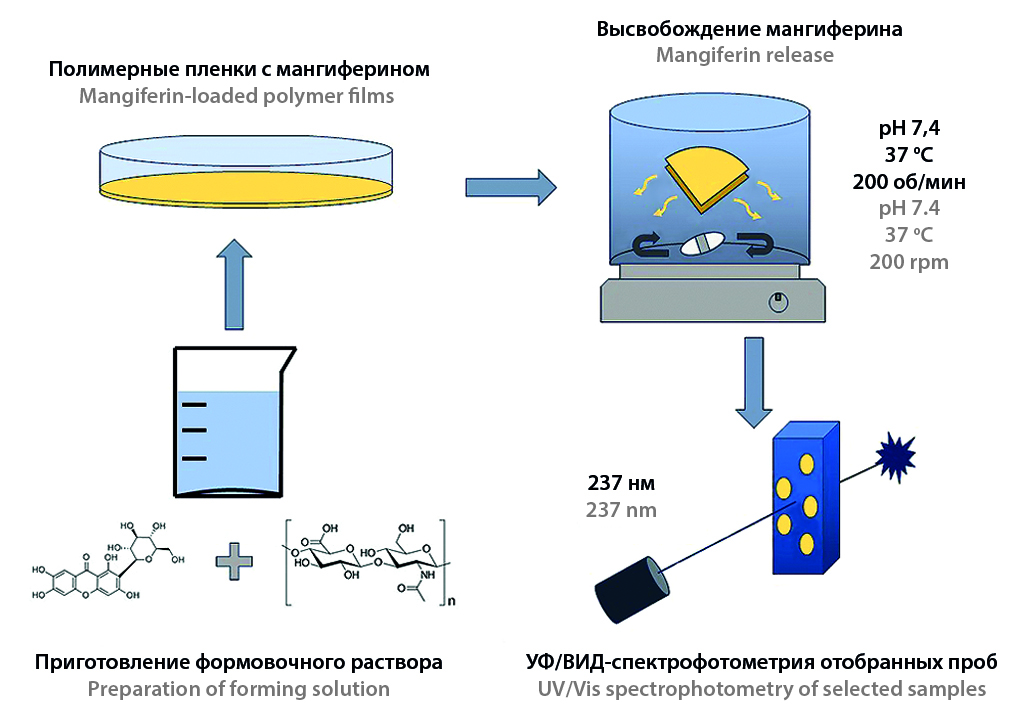
Introduction. Currently, the use of natural biologically active agents (BAA) as effective antibacterial drugs for both external and internal use is becoming widespread. Polyphenol mangiferin, extracted from the leaves of the Mangifera indica plant, is the most attractive BAA. Despite high antimicrobial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative strains of bacteria, the use of mangiferin is limited by its low aqueous solubility. To increase solubility and, accordingly, bioavailability, various approaches are used, in particular, encapsulation in polymer and biopolymer matrices. One of the promising biopolymers for the encapsulation of biologically active substances is hyaluronic acid, which is completely biocompatible with the tissues of a living organism and is capable of complete biodegradation under the influence of enzymes (hyaluronidases).
Aim. Study of the release kinetics of the biologically active agent (mangiferin) from a polymer matrix based on hyaluronic acid with different molecular weights.
Materials and methods. Polymer films obtained by casting method from 1.5 wt.% forming solutions of hyaluronic acid with a molecular weight of 1.30 and 2.48 MDa with different contents of mangiferin were used as the objects of the study. The weight ratio of hyaluronic acid to mangiferin varied from 5 to 25. Released mangiferin was measured by UV/Vis spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 237 nm. A phosphate buffered saline with pH 7.4 was used as a model medium. The mangiferin release kinetic was assessed using various mathematical models.
Results and discussion. Mangiferin release kinetic from a polymer matrix based on hyaluronic acid has a release sigmoidal pattern. The release mechanism has a complex nature of the Super Case II transport type, with the exception of a sample with a low content of mangiferin and hyaluronic acid with molecular weight equal to 1.3 MDa, for which an abnormal release pattern is detected (non-Fickian diffusion), due to the hydrophilic nature of hyaluronic acid, the rapid swelling of the polymer matrix, as well as a significant leading in the diffusion of mangiferin compared to the relaxation rate of the polymer. The most suitable model is the Weibull model, which describes the mangiferin release kinetics with greater accuracy compared to other mathematical models.
Conclusion. The results obtained indicate the potential possibility of using the developed polymer films as biomedical materials for external use, which provide transdermal delivery of pharmaceutical agents. The authors of the study are planning to develop a methodology for prolonged and controlled release of a loaded biologically active agent, including by various cross-linking agents.
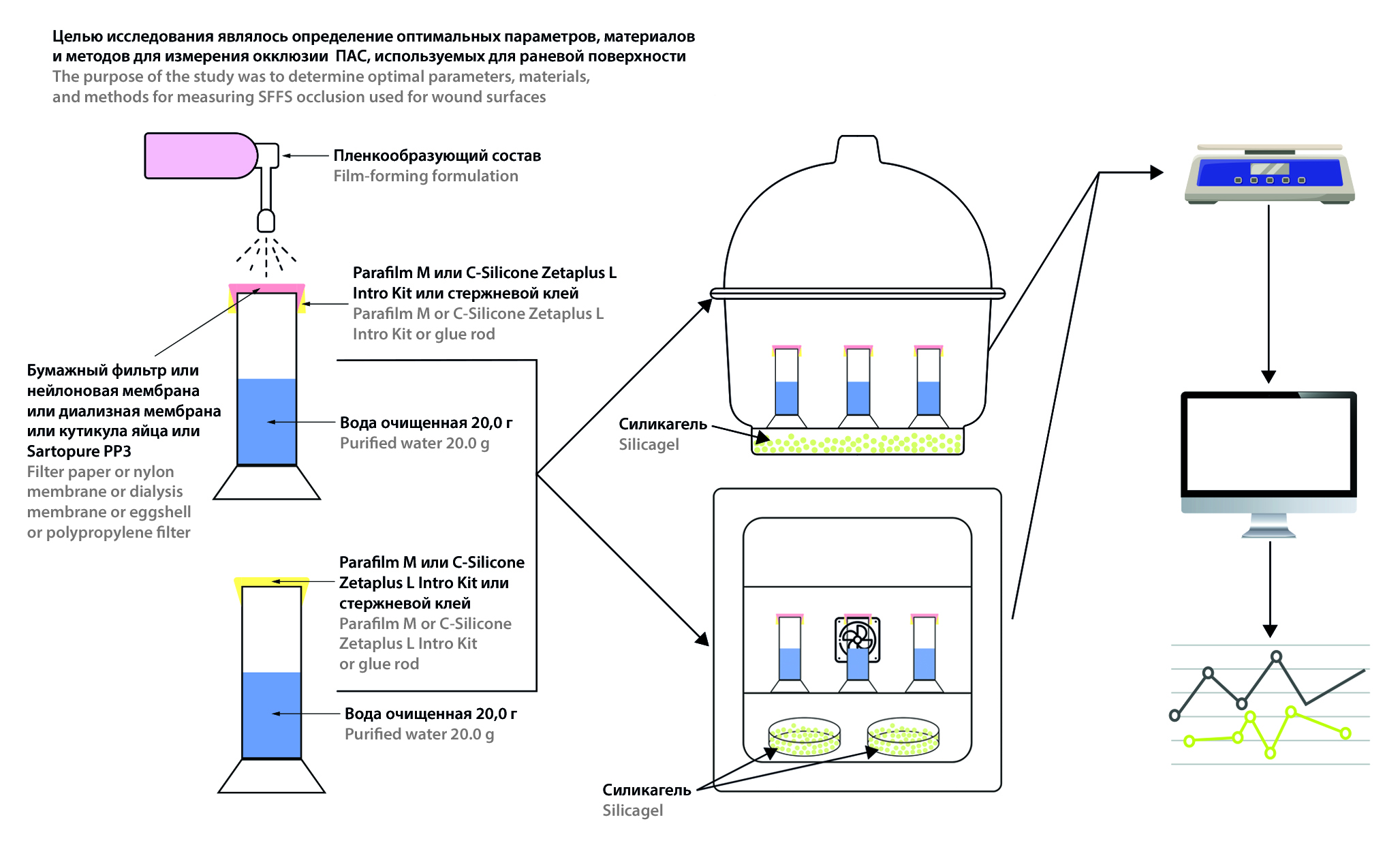
Introduction. Spray film-forming systems (SFFSs) are dosage forms that form an in situ film when sprayed. One of the key features of SFFSs is partial vapor permeability, a special case of occlusion. Various methods assess vapor permeability by determining the occlusion factor, but disparate approaches in studies prevent harmonizing results and identifying optimal parameters.
Aim. Development of a methodology for determining the vapor permeability of spray film-forming systems, measuring the occlusion factor and studying the most significant factors affecting the accuracy of determining this characteristic.
Materials and methods. Determination of vapor permeability was carried out using a special setup, consisting of a cell with water and a membrane fixed over it, on which the model composition was applied. Measurement cylinders of 25 ml (Russia) or penicillin vials with a smooth neck of 10 ml (Russia), membranes for filtration and dialysis (nylon, EPM.K, LLC RME "Technofilter", Russia), dialysis bags MEMBRA-CEL® (cellulose acetate, Viskase Companies, Inc., USA) and Sartopure® PP3 (polypropylene, Sartorius Stedim Biotech, Germany) were used. As sealants to isolate airflow around the membrane Parafilm M, C-silicone ZetaPlus L Intro Kit (Zhermack, Poland, Italy), hotmelt adhesive Master Hand (Union Source Со., Ltd., China), UV-curable material "UNIREST" (LLC "StomaDent", Russia) were used. Comparative analysis of materials was carried out on a model composition containing 0.5 % (m/o) Kollicoat® MAE 100P (BASF, Germany), 3 % (m/o) Soluplus® (BASF, Germany), 2 % (m/o) Kollisolv® PEG-400 (BASF, Germany), 70 % ethyl alcohol (SOJSC "Ferein", Belarus).
Results and discussion. The combination of Parafilm M and the presented sealants showed high performance. Synthetic membrane occlusion factor for the model substance varied depending on the membrane type from 9.35 ± 3.58 to 16.86 ± 6.09, reflecting low-medium degree of occlusion.
Conclusion. In this study optimized techniques for determining the vapor permeability for SFFS were developed. It was observed that rationalized membrane selection, consideration of the probability of moisture absorption by the membranes, method of sealing and cell calibrations, temperature and humidity levels, and vapor pressure were necessary.
Introduction. One example of new polymers for target delivery systems are zeolites (ZEO) and zeolite imidazole frameworks (ZIF). ZEO are actively used in industry, ecology, pharmacy and biomedicine, having high porosity, adsorption capacity and physico-chemical stability. ZIF, as a type of metal-organic framework, are characterized by high thermal and chemical resistance, biocompatibility and adjustable porosity, which makes them promising for drug delivery. Both polymers, due to their properties, open up new opportunities for the creation of targeted drugs with prolonged action and minimal side effects. The purpose of this review is to characterize ZEO and ZIF as promising polymers for targeted delivery systems and to consider their basic properties.
Text. The article discusses the structure and methods of analysis of zeolites and zeolite imidazole frameworks, methods of their synthesis, mechanism of action, and applications of polymers as directed delivery systems.
Conclusion. The review shows that the chemical and physical properties of ZEO and ZIF polymers make it possible to develop effective targeted drug delivery systems used in oncology, ophthalmology, dentistry and orthopedics. Low cytotoxicity, regulated polymer pore loading and the effectiveness of intracellular targeting confirm the prospects of using ZEO and ZIF in medicine.
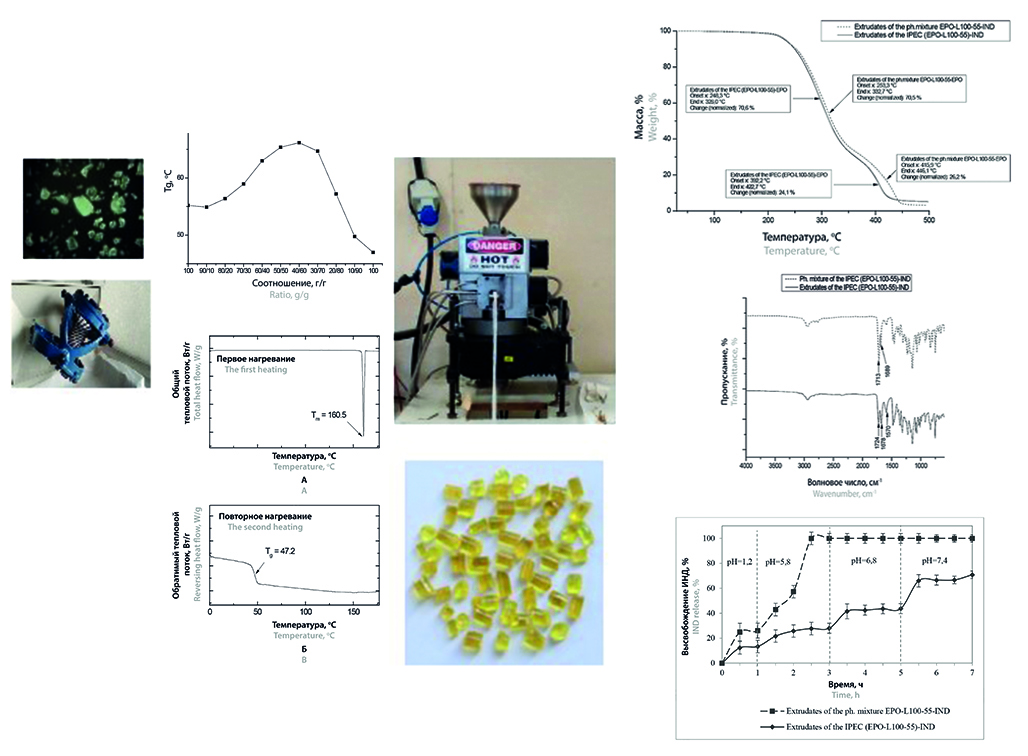
Introduction. As a result of the study, 4 types of pellets with indomethacin based on Eudragit® copolymers of EPO and L100-55 grades, their physical mixture (PM) being similar in composition to the synthesised interpolyelectrolyte complex (IPEC) EPO/L100-55 – 1.95 : 1 (mole/mole) were obtained using reactive HME method. The development of thermal extrusion conditions using the modulated DSC method showed the applicability of this approach for preliminary modelling of the occurring processes. Characterised using thermal and spectral analysis methods, the obtained granules include indomethacin in the amorphous form formed from the original γ-form as a result of reactive thermal extrusion of the samples. The study of indomethacin (IND) release from the obtained granules in modelling the progression through the GI tract under mimicking conditions has shown the prospectivity of all types of the developed systems for the creation of constructs with targeted release of IND into model buffer media corresponding to: the fasted or feed state simulated gastric fluids, as well as the fasted state simulated intestinal fluid correspondent to the upper parts of the small intestine (EPO and PM EPO/L100-55), the cecum and right half of the colon (L100-55) and the proximal colon (IPEC). Recently, due to the pronounced plasticity resulting from the low glass transition temperature (Tg), many of the Eudragit® copolymer types (E, RL, RS, FS, NE, NM) have found increasing application in the intensively developing field of pharmaceutical technology – thermo extrusion granulation, called pharmaceutical melt extrusion (PME). Despite the progressive number of studies on the use of the PME method, there is an undeserved lack of research on the feasibility of polycomplex systems based on copolymers of the Eudragit® family. At the same time, it is known that combining oppositely charged pairs of thermoplastic Eudragits using PME technology allows the development of oral delivery systems with adjustable permeability of polymer links in the structure of pellet coatings due to the formation of interpolymer-bonded chain sequences of reacting macromolecules during drug release in gastrointestinal (GI) simulating media with progressive increase of pH values from the stomach to the colon. Unfortunately, although there are many examples in the literature on the application of PME, including reactive HME, to produce drug delivery systems based on Eudragit® EPO copolymer (due to its low Tg value), there are practically no studies in which an interpolyelectrolyte complex (IPEC) involving chemically complementary pairs of Eudragits is used as a thermoextruded carrier.
Aim. Development and study of hot-melt extruded granules based on interpolymer anionic-cationic combinations of Eudragit® copolymers for indomethacin delivery.
Materials and methods. Thermal extrusion conditions were selected and refined using rheometry, high-temperature microscopy and modulated differential scanning calorimetry (mDSC) to simulate and reproduce the thermal extrusion conditions. The pellets obtained on a single screw extruder were characterised using mDSC, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), IR and NIR spectroscopy. The study of indomethacin release from granules under mimicking GI tract conditions was carried out by method 2 – ‘rotating paddle’ according to GPh. RF.
Results and discussion. Hot melt extruded pellets were obtained from the compositions of binary mixtures (EPO-IND, L100-55-IND, IPEC (EPO-L100-55)-IND), at which they had the maximum value of glass transition temperature – Tgmax. For EPO-IND it was 30/70, and for IPEC (EPO-L100-55)-IND and L100-55-IND – 40/60. According to the results of IR spectroscopy, the samples of thermoextrudates containing EPO in their composition, namely EPO-IND, EPO-L100-55-IND PM and IPEC-IND, are characterized by a shift of the IND band from 1689 to 1678 cm–1, indicating the transition of the initial crystalline form of IND into amorphous form as a result of physicochemical interaction of EPO with IND, which is also confirmed by the results of thermal analysis. In addition, in all thermoextruded samples containing EPO, IR spectra are characterized by the appearance of a band at 1570 cm–1, confirming the formation of ionic bonds due to the interaction of ionized carboxyl groups of IND and L100-55 with dimethylamino groups of EPO. NIR spectroscopy confirmed the presence of both amorphous and crystalline forms of the γ-form of IND in the structure of the IPEC (EPO-L100-55)-IND-based extrudate, which is apparently due to the partial transition of the metastable amorphous form to the crystalline form over time. The release of IND from EPO-IND extrudates at pH 1.2 is very rapid, reaching 100 % within half an hour. The character of IND release from extrudates with L100-55-IND is a delayed-sustained profile, the control of the release rate being determined by the properties of the forming copolymer (L100-55). The release of IND from EPO-L100-55-IND PM-based extrudates, as in the case of EPO-IND extrudates, starts at pH 1.2, but provides only a negligible yield of IND release (about 30 %). Due to the content of acid-resistant L100-55 in the PM composition, the rapid IND release shifts from acidic environment (pH = 1.2) to slightly acidic (pH = 5.8) providing 100 % IND release by 2.5 hours of the experiment. The release of IND from polycomplex extrudates (EPO-L100-55)-IND is characterized by a pulse release profile.
Conclusion. As a result of the study, 4 types of pellets with indomethacin based on Eudragit® copolymers of EPO and L100-55 grades, IPEC with their participation and a physical mixture similar to it were obtained by reactive thermal extrusion. The resulting granules were characterised using thermal and spectral techniques. The study of indomethacin release from the obtained granules showed the promising application of the developed systems for targeted delivery to different parts of the GI tract, from the stomach to the proximal colon.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
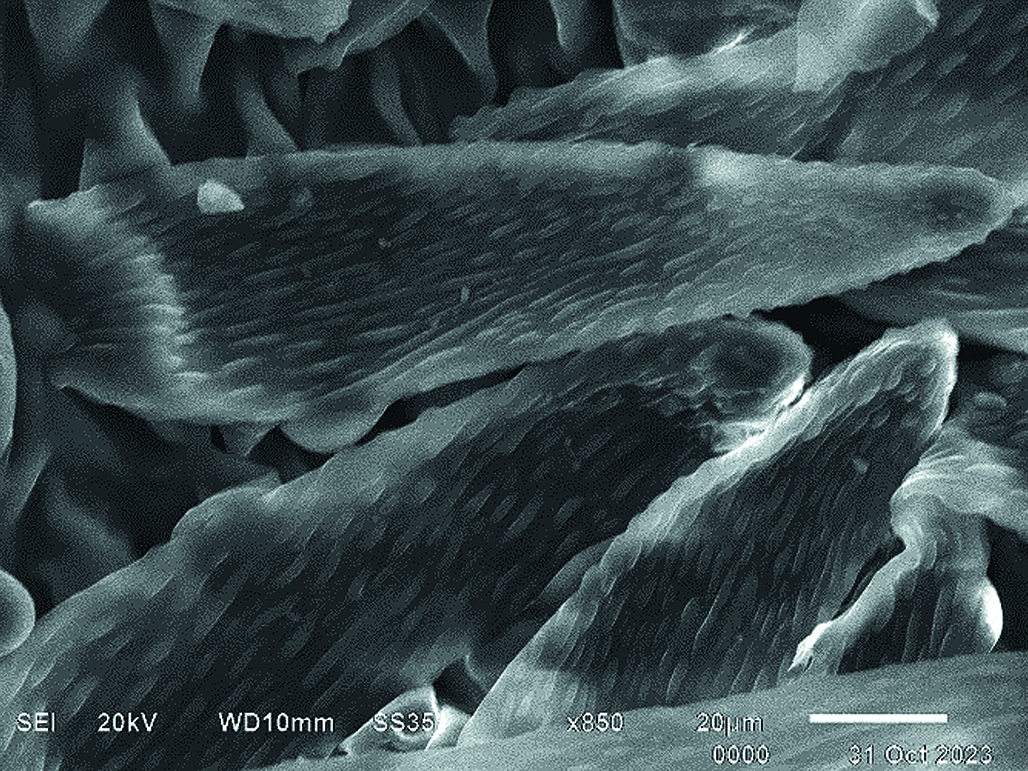
Introduction. Horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.) is a plant widely used in official and folk medicine in many countries. Pharmacopoeia raw materials in the Russian Federation are only horse chestnut seeds. Flowers, due to the fraction of phenolic derivatives and triterpene saponins contained in them, are a promising medicinal plant raw material, presumably having a venotonizing and membrane-protective effect. To obtain medicinal herbal preparations based on horse chestnut flowers, it is required to have regulatory documentation containing a list of quality indicators, including a description of the signs of its authenticity (morphology and anatomy). Scanning electron microscopy is one of the advanced methods that have recently been increasingly used in medicine and pharmacognostic analysis. Unlike light microscopy, the method provides a three-dimensional spatial representation of diagnostically significant signs of medicinal plant raw materials.
Aim. The aim of the study was to study the morphology of the surface of horse chestnut flowers by scanning electron microscopy.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was dried whole flowers of horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.), collected in the Voronezh region in 2023 at the beginning of flowering. The pieces of flowers were pre-sprayed with silicon on an automatic spraying unit Q150R ES (Quorum Technologies Ltd., Great Britain). Micrographs were obtained using the JSM-6510LV electron microscope (JEOL Ltd., Japan).
Results and discussion. The micrographs obtained during the analysis showed diagnostically significant features of the flower structure: the epidermal cells of the corolla petals are polygonal, irregularly shaped, some elongated with sinuous folds. Pollen grains can be collected in cluster-like clusters, located separately or found singly. The surface of the corolla petal is covered with numerous often twisting hairs having a rough-warped structure and a cone-shaped base with a clearly defined attachment point. The surface of the staminate filaments is striated, with longitudinal folds with single unicellular hairs. The anther has a folded shape, its surface is lined with scaly epidermal cells with rough and thickened walls. The surface of the calyx, including the pedicel, is also densely pubescent with numerous trichomes.
Conclusion. The scanning electron microscopy method was used for the first time to study the morphological and anatomical features of horse chestnut flowers. The structure of the main diagnostically significant structures of this LRS has been clarified. The morphology of the epidermis surface of the petals of the corolla and calyx, trichomes, pollen filaments, anthers and pollen grains of flowers has been determined. It has been established that carbon and oxygen are the predominant elements of the raw materials.
Introduction. «Dissolution test» for drugs is one of the key studies of control and, in many ways, is designed to simulate the bioavailability of the active substance under the conditions of use. However, there are several drugs containing active pharmaceutical substances that are poorly soluble under standard conditions. For this substances action is local, so, they are practically not absorbed in the human body, but showed the necessary therapeutic effect. This work discusses the development of conditions for «Dissolution test» in lipophilic-based suppositories containing natamycin, which is an antifungal agent related to tetraene macrolides, poorly soluble in water and, therefore, in standard buffer solutions intended for this test.
Aim. Choose the conditions for conducting «Dissolution test», under which it will be possible to achieve complete release of the active substance from lipophilic-based suppositories on «Pimafucin» and «Primacin».
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are lipophilic-based suppositories containing natamycin. The study was carried out using dissolution testers (Rotating Basket and Flow Cell apparatus) and an HPLC system to define the amount of natamycin released.
Results and discussion. The research objects were analyzed under «Dissolution test». The work shows the possibility of conducting a test with complete release of the active substance by adding surfactants and an organic solvent, which is acceptable for quality control dissolution medias.
Conclusion. Conditions for «Dissolution test» have been developed for suppositories containing natamycin.
Introduction. Due to the increasing resistance to antimicrobial drugs of different spectrum of action in the population, the issue of searching for new drugs with antimicrobial activity is currently the most relevant. Peppermint (Mentha piperita L.) is known for its medicinal properties, which are due to the presence of many biologically active compounds in the medicinal plant. The composition of extracts from the leaves of peppermint includes essential oil, the main component of which is menthol, as well as non-volatile phenolic compounds – flavonoids (luteolin etc.) and phenylpropanoids (rosemary acid, salvianolic acid, chlorogenic acid etc.).
Aim. To screen and compare the antimicrobial activity of aqueous-alcoholic extracts from peppermint leaves and mint varieties and to perform comparative qualitative analysis by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
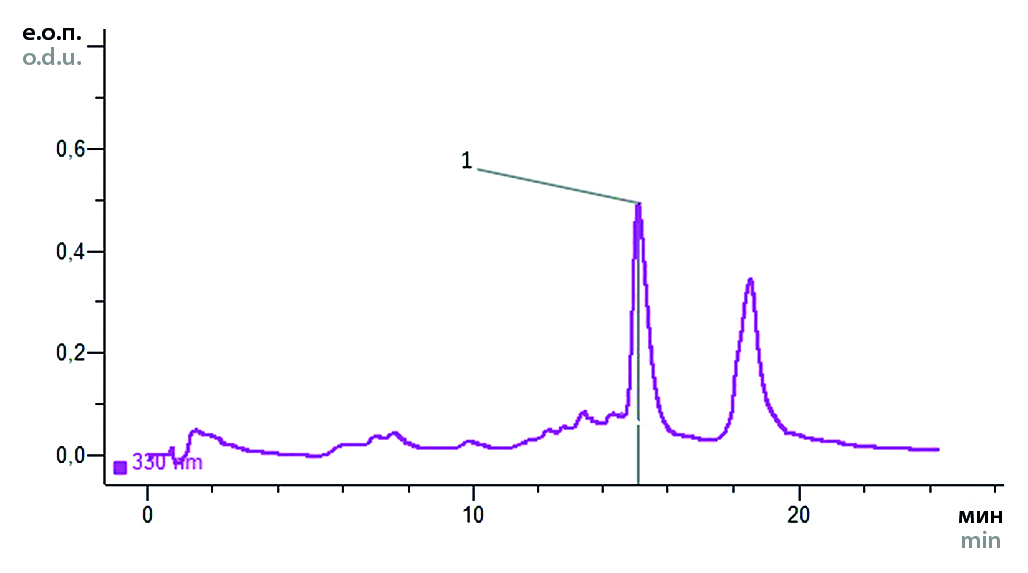
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were aqueous-alcoholic extracts on 70 % ethyl alcohol obtained by fractional percolation method from leaves of varieties of peppermint (Mentha L.) and alcoholic solutions of standard samples of luteolin and menthol. The minimum inhibitory concentration was determined by double serial dilutions in Mueller – Hinton nutrient broth (Bio-Rad, USA). Bacillus cereus (ATCC 29213) Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853), Candida albicans (ATCC 90028) strains were used as test cultures. Chromatographic analysis was carried out by HPLC on a Milichrome-6 microcolumn liquid chromatograph (NPASC "Nauchpribor") under the following conditions: gradient mode, steel column KAX-6-80-4 (No. 2; 2 × 80 mm; Separon-C18, 7 μm), eluent system: acetonitrile (PFA) – 1 % acetic acid (PFB) solution (1 : 9; 2 : 8; 3 : 7; 8 : 2), elution rate – 100 μl/min, eluent volume – 2500 μl. The substances were detected at a wavelength of 330 nm. The volumes of injected samples were 2 μl.
Results and discussion. In the course of the study it was found that all the tested samples give a stable prevailing antimicrobial effect against the strains of test cultures.
Conclusion. The data obtained in the course of the conducted study indicate the prospect of obtaining medicinal herbal preparations based on mint leaves of different species and varieties, showing antimicrobial activity, and their introduction into medical and pharmaceutical practice.
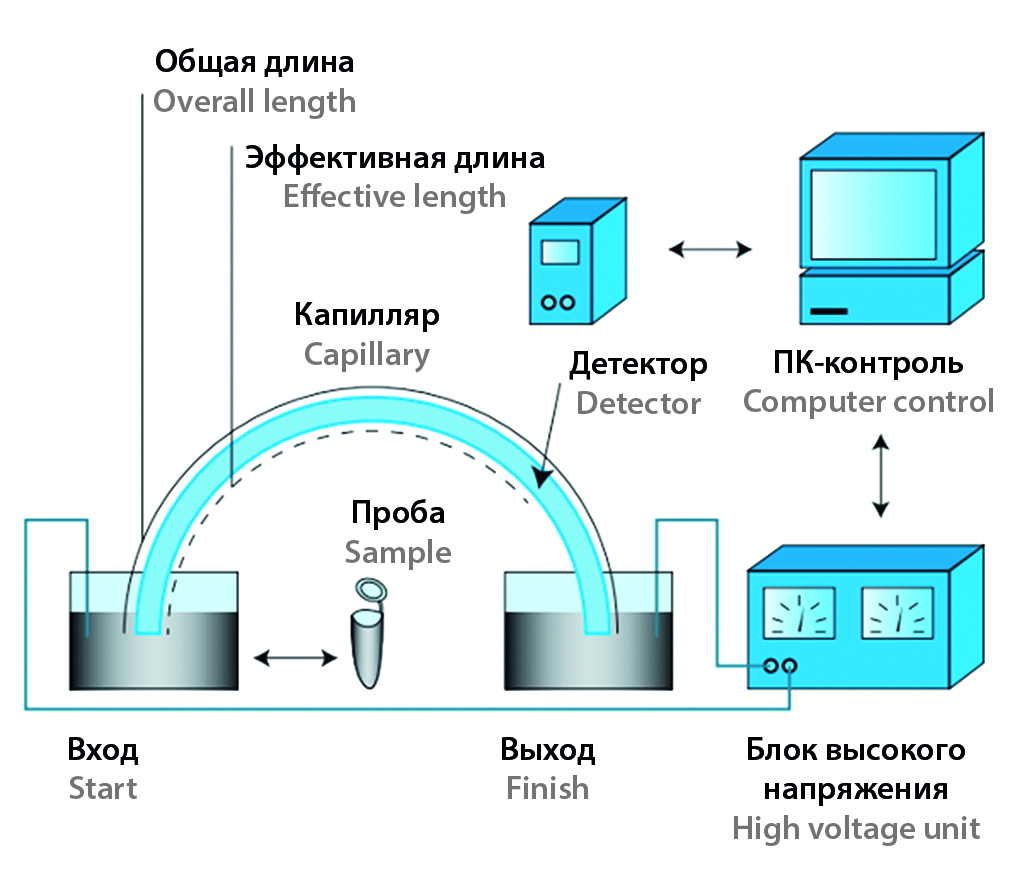
Introduction. Capillary electrophoresis is a method of separating a mixture of substances in a high voltage field. The method is used to analyze compounds of organic and inorganic nature and has a number of advantages: cheapness, safety, simplicity of equipment. The method is also gaining popularity in the analysis of the chemical composition of plant raw materials.
Aim. The study of the vitamin composition in plant raw materials of representatives of the genus Rubus L. by capillary electrophoresis.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were the dried leaves and/or fruits of plants such as Rubus caesius L. (European dewberry), Rubus nessensis Hall (European blackberry), Rubus allegheniensis Porter (allegany blackberry), Rubus ulmifolius Scott (elmleaf blackberry), Rubus saxatilis L. (roebuck berry), Rubus idaeus L. (raspberry), Rubus chamaemorus L. (cloudberry), Rubus arcticus L. (arctic raspberry). Detection and quantitative determination of water-soluble vitamins was carried out in the capillary electrophoresis system Kapel-104T (Group of Companies "Lumex", Russia). The analysis was carried out in a variant of capillary electrophoresis – micellar electrokinetic chromatography.
Results and discussion. Under the specified analysis conditions, 5 B vitamins (nicotinamide, riboflavin, pyridoxine, nicotinic acid, thiamine) and vitamin C (ascorbic acid) were identified. The vitamin content in different types of raw materials varied. It is noted that riboflavin, ascorbic and nicotinic acids are present in almost all the studied objects. In terms of quantitative content, the predominant vitamins in the leaves are nicotinamide, ascorbic acid and pyridoxine, in fruits – ascorbic acid and thiamine. The total vitamin content in the leaves is higher than in the fruits, which is explained by different drying conditions.
Conclusion. By the method of capillary electrophoresis, it was possible to detect and quantify water-soluble vitamins in plant raw materials using the example of some representatives of the genus Rubus L. In general, the vitamin content in the studied raw materials is low, some of them are marked by the largest number of these compounds – R. caesius L. and R. saxatilis L.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
Introduction. Currently, neurological diseases occupy one of the first places in terms of the DALY (Disability-adjusted life year) index and are the second cause of death in the world. There is a tendency towards rejuvenation and an increase in morbidity. Drug therapy aimed at neuroprotection and improving the restoration of neurological functions according to clinical recommendations includes a succinate-containing drug – Cytoflavin. However, these recommendations are based on a very limited number of studies (4 studies for cytoflavin). Due to the huge amount of work in the field of the use of succinate-containing drugs as neuroprotectors, the lack of quantitative assessment of research results, it seems promising to conduct systematic reviews and meta-analysis in this area.
Aim. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of cytoflavin as a neuroprotector based on a systematic review.
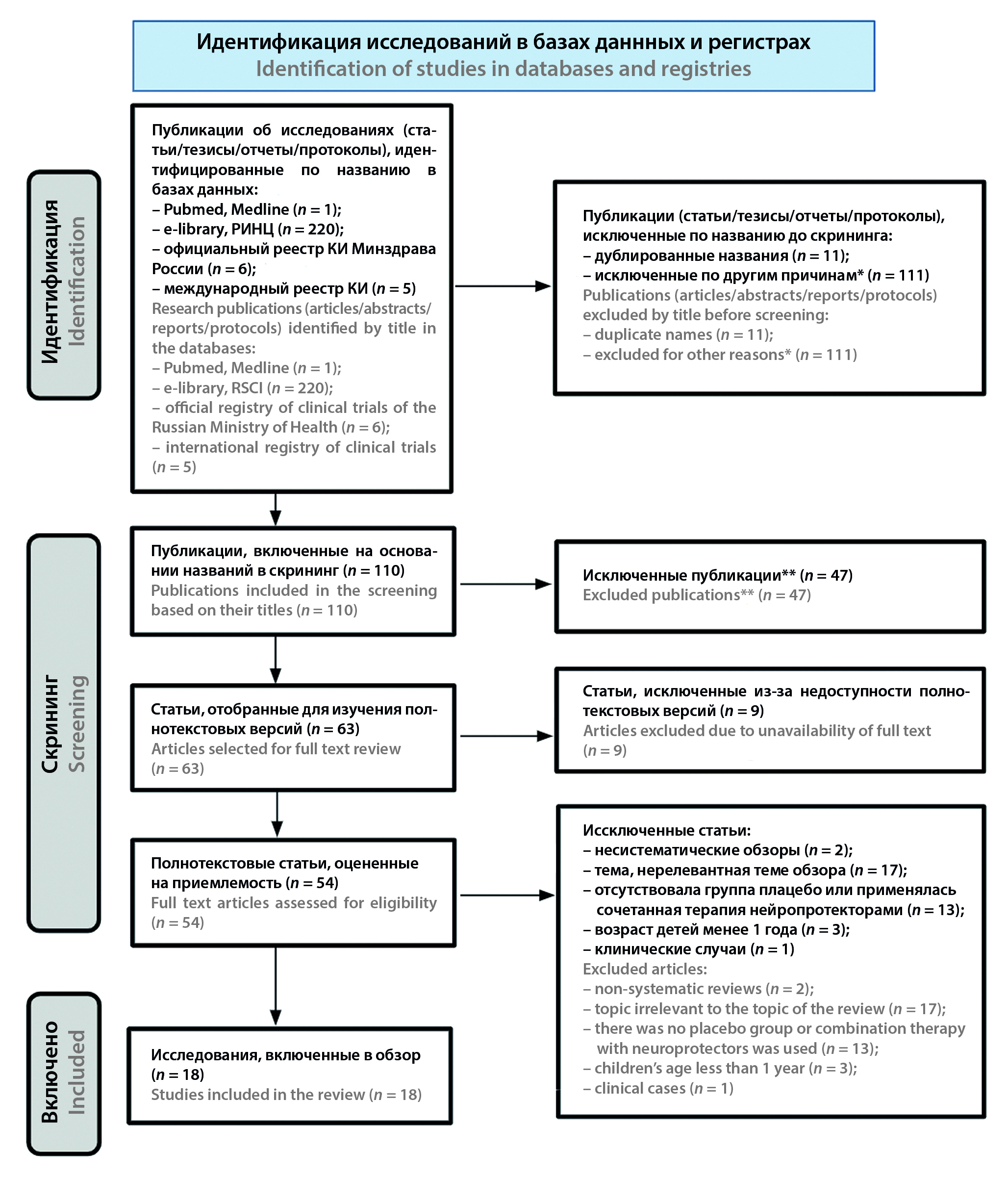
Materials and methods. A systematic review of the research results was conducted according to the criteria of PRISMA 2020. The search for publications was carried out using PubMed, Medline databases, as well as Russian scientific electronic libraries eLibrary.Ru and RSCI. Materials were also searched in the systems of the national and international registry of clinical trials.
Results and discussion. The review included 18 publications, including a description of the therapy of 10 pathologies of neurological origin. The largest part of the studies was devoted to the treatment of ischemic stroke (n = 4/18; 22.22 %) and manifestations of cognitive dysfunction (n = 5/18; 27.78 %). The pool of materials included studies of various designs, but most of them were represented by open comparative randomized/non-randomized studies. An analysis of the sources showed that the positive effect of the use of cytoflavin and the expediency of including its therapy regimen is noted in all publications. However, many studies have low statistical power due to the small sample sizes of patients, their heterogeneity and incompleteness of providing treatment data and the lack of randomization.
Conclusion. According to the results of most clinical studies, it has been shown that the use of cytoflavin is safe, and its administration in neurological diseases of various origins is advisable due to a decrease in the frequency of adverse neurological outcomes in patients. For an objective research result, a meta-analytical assessment of the publications included in the review is required.
Introduction. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the leading causes of chronic liver disease worldwide, are associated with a wide range of psychoneurological complications and conditions. However, the causal relationship between liver and nervous system disease remains poorly understood, which warrants the development of clinically relevant and valid animal models thereof.
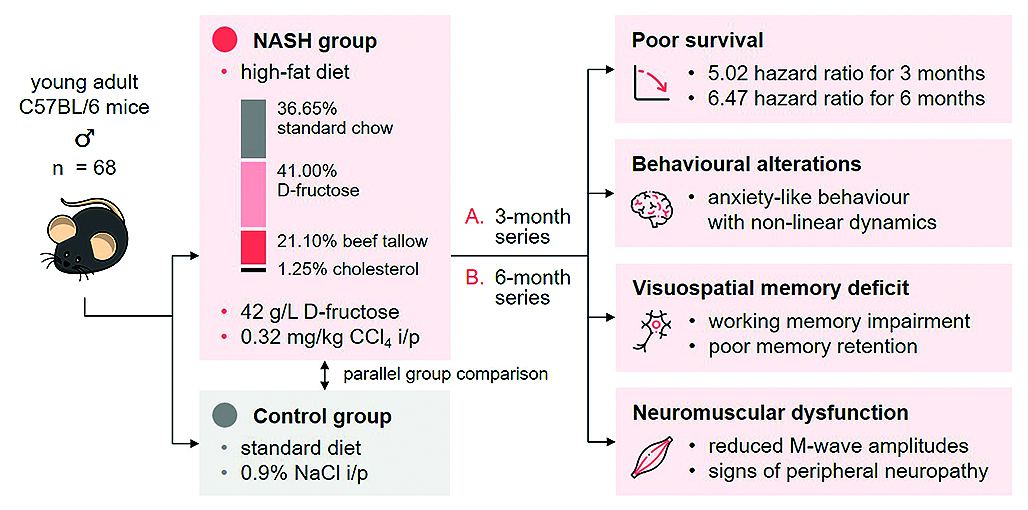
Aim. The objective of this work was to characterize the short- and long-term psychoneurological and peripheral neuronal deficits that complicate different stages of NAFLD/NASH in mice.
Materials and methods. 68 adult male C57Bl/6 mice were randomized into Control or NASH groups. NASH was induced over 3 (Experiment 1) or 6 (Experiment 2) mo using a combined model including a high-fat diet and low doses of carbon tetrachloride. Control group received standard chow, drinking water, and equivolume normal saline. Animal behaviour was assessed by the Open field (OF), Elevated plus maze (EPM), and Light/dark box (LDB) tests at 1, 2, 3, and 6 mo of NASH induction. Visuospatial memory was assessed by the Spontaneous alternation in the T-maze and Novel object recognition tests at 1, 2, and 3 mo of NASH modelling, and using the Barnes maze at 6 mo of NASH induction. Following 3 mo of NASH induction, needle electroneuromyography (ENMG) was performed on the gastrocnemius and biceps muscles with the electrical stimulation of the sciatic and musculocutaneous nerves, respectively. Liver pathology was confirmed by histomorphology. Statistical analysis was performed using Prism 10.2.3 and R 4.2.3 with RStudio 2024.09.0.
Results and discussion. Experimental modelling was associated with poorer overall survival (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) and substantial evidence of liver injury, i.e. cholestatic hepatitis, medio- and macrovesicular steatosis, focal necrosis and fibrosis of varying severity (p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Mice with NASH exhibited markers of elevated anxiety in the OF, EPM, and LDB tests (p < 0.05, p < 0.01), which were mostly specific to the very onset of liver disease (1 mo) as well as its later stages (6 mo). NASH was also associated with a significant decrease in spontaneous alternation at 3 mo (p < 0.01), negative object disrimination at 2 mo (p < 0.05), and poorer memory retention in the Barnes maze (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) compared with Control. ENMG data analysis revealed significantly lower peak M-wave amplitudes (p < 0.01) and threshold currents (p < 0.05) in the gastrocnemius, and increased peak latency in the biceps in the NASH group (p < 0.05).
Сonclusion. Experimental alimentary/toxic NASH in male C57Bl/6 mice is associated with increased anxiety-like behaviour, visuospatial memory acquisition and retention impairment, and evidence of axonal and demyelinating peripheral motor neuropathy.
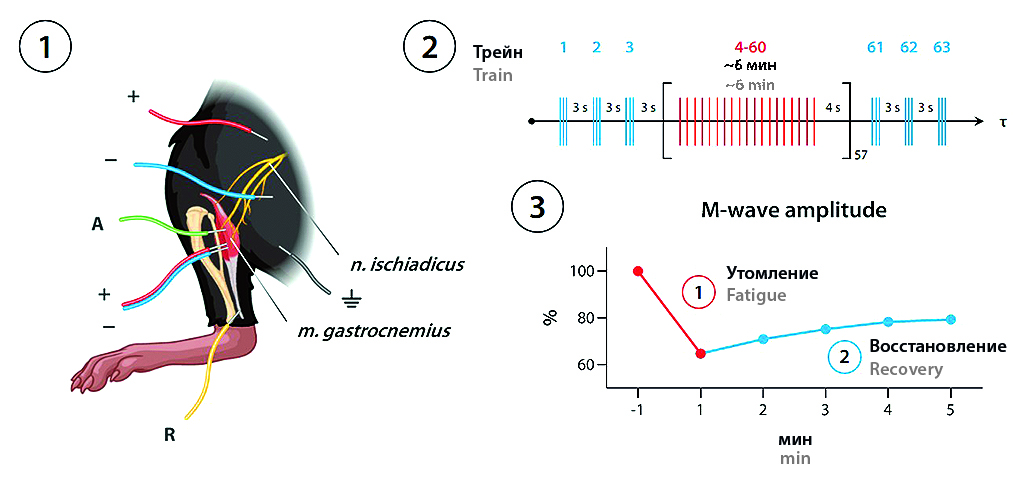
Introduction. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance, impaired glucose tolerance, and hyperglycaemia. T2DM is a proven risk factor for peripheral neuropathies as well as muscle contractility and function impairments. The biguanide metformine, experimental compound maloben, and preparations of various Panax species have a considerable potential for the treatment of T2DM and its skeletal muscle complications. As a test to evaluate muscle contractility and the effectiveness of its recovery, Gregory et al. have developed a protocol of electrical stimulation-induced fatigue (ESIF) which includes measuring grip strength after fatiguing the biceps brachii muscle with high-frequency electrical stimulation using implantable electrodes.
Aim. In this work, we attempted to assess the applicability of a modification of said protocol in order to evaluate the myotropic effects of metformin, maloben, and extracts from suspension cell cultures of Panax ginseng C.A. Mey. (PGE), P. vietnamensis Ha & Grushv. (PVE), and P. japonicus (T. Nees) C.A. Mey. (PJE) in the leptin-resistant db/db mice, one of the most popular modern T2DM models.
Materials and methods. The experiments were carried out in 60 young adult (2 months old) male C57Bl/Ks-db+/+m (db/db) mice weighing 45–50 g, randomized into 6 groups: 1) Control (n = 10; 0.9 % saline); 2) PGE (n = 10; 50 mg/kg); 3) PVE (n = 10; 50 mg/kg); 4) PJE (n = 10; 50 mg/kg); 5) maloben (n = 10; 60 mg/kg); 6) metformin (n = 10; 300 mg/kg). All drugs were administered via oral gavage using a feeding tube once daily for 2 months. Following the treatment period, forelimb and all-four limb grip strength (g) was assessed using the Grip Strength Meter (TSE Systems, Germany). Using stimulation electroneuromyography, we measured the compound muscle action potential (CMAP) amplitudes in the gastrocnemius induced by single-stimulus sciatic nerve stimulation, and assessed the dynamics of CMAP amplitudes during the first 5 min following the ESIF protocol completion.
Results and discussion. Following treatment period completion, no significant changes were observed between the groups in grip strength or gastrocnemius CMAP amplitude under single-stimulus stimulation. Controlled ESIF of the muscle caused a 18.83–35.23 % (relative to baseline) decrease in CMAP amplitudes (p < 0.01 for all groups) that was significantly smaller in the PVE, PJE, and maloben groups vs. control (p < 0.05). The post-ESIF recovery period was associated with a 10.18–14.79 % increase in CMAP amplitudes that was significant in all groups except PGE (p < 0.01 for control, PVE, and PJE; p < 0.05 for maloben and metformin). No significant differences from control were observed in any of the treatment groups regarding net recovery.
Сonclusion. The proposed protocol represents a functional test suitable to assess the recovery effectiveness of electrical activity of a skeletal muscle following its controlled fatigue. Using the described protocol, we were able to detect beneficial effects of PVE, PJE, and maloben (but not PGE or metformin) on the recovery of gastrocnemius contractility following tetanization in diabetic db/db mice. The ESIF test is sensitive to the myotropic effects of metabolic agents, minimally invasive, and acceptable under chronic experiment conditions.
Introduction. Combination therapy of chronic heart failure (CHF) is an urgent and important treatment strategy, as it allows to achieve an improvement in the prognosis, optimal control of the symptoms of the disease and an increase in the quality of life of patients.
Aim. Comparison of the effectiveness of the malonic acid derivative ethmaben, the sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor empagliflozin and their combinations with the variability of the starting drug in experimental post-infarction chronic heart failure in rats.
Materials and methods. In a model of post-infarction chronic heart failure, reproduced by permanent ligation of the left coronary artery in rats, an echocardiographic study was used to compare etmaben and empagliflozin monotherapy with a combined regimen of these drugs. The concentration of etmaben in the myocardium was assessed by HPLC.
Results and discussion. Antagonism between etmaben and empagliflozin was revealed, manifested by a decrease in the effect of combination therapy in relation to any of the components, a decrease in the concentration of malonic acid derivative in the myocardium under the action of a type 2 sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor was shown.
Conclusion. Based on the data obtained, additional studies of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of etmaben were planned.
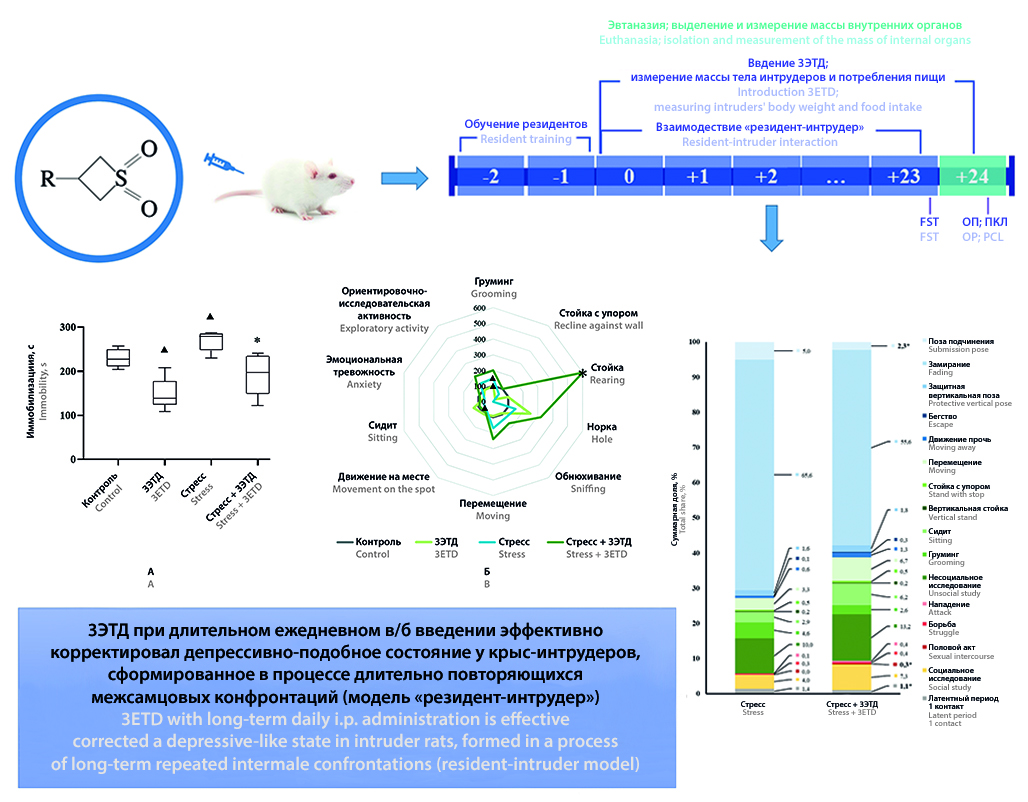
Introduction. Among the various animal models of depression used to study the pathogenesis of depression and to evaluate the antidepressant action of new compounds, models based on social stress are characterized by high constructive, face and predictive validity. The rat model of depression based on the repeated social defeats allows to induce a depressive-like state corresponding to depression in humans and to evaluate the effect of new substances with antidepressant activity.
Aim. To study the antidepressant effect of 3-ethoxythietane-1,1-dioxide (3ETD) on rats using resident-intruder paradigm.
Materials and methods. White outbred male rats weighing 200–250 g (intruders) received 3ETD (2 mg/kg, groups "3ETD" and "Stress + 3ETD") or saline (groups "Control" and "Stress") intraperitoneally daily for 24 days. Thirty minutes after the administration, the animals of the "Stress" and "Stress + 3ETD" groups were subjected to 10-minute interaction with the residents (outbred male rats weighing 350–400 g). On day +23, intruders were tested in the forced swimming test, on day +24, the open field and elevated plus maze tests were performed. The body weight of the intruders and the amount of food consumed were recorded daily. At the end of the experiment, the weight coefficients of their internal organs were recorded.
Results and discussion. Chronic repeated confrontation with residents led to the development of a depressive-like state in intruders by day +23. 3ETD exhibited antidepressant properties, eliminating the effects of social stress in intruders: 3ETD reduced despair behavior in the forced swimming test, increased exploratory, social, and motor activity of animals, the proportion of active forms of protective behavior, and reduced the proportion of passive forms during the resident-intruder interaction.
Conclusion. 3ETD, when administered intraperitoneally daily at a dose of 2 mg/kg for 24 days, exhibited a pronounced antidepressant effect, eliminating the depressive-like state in rats caused by repeated social defeats.
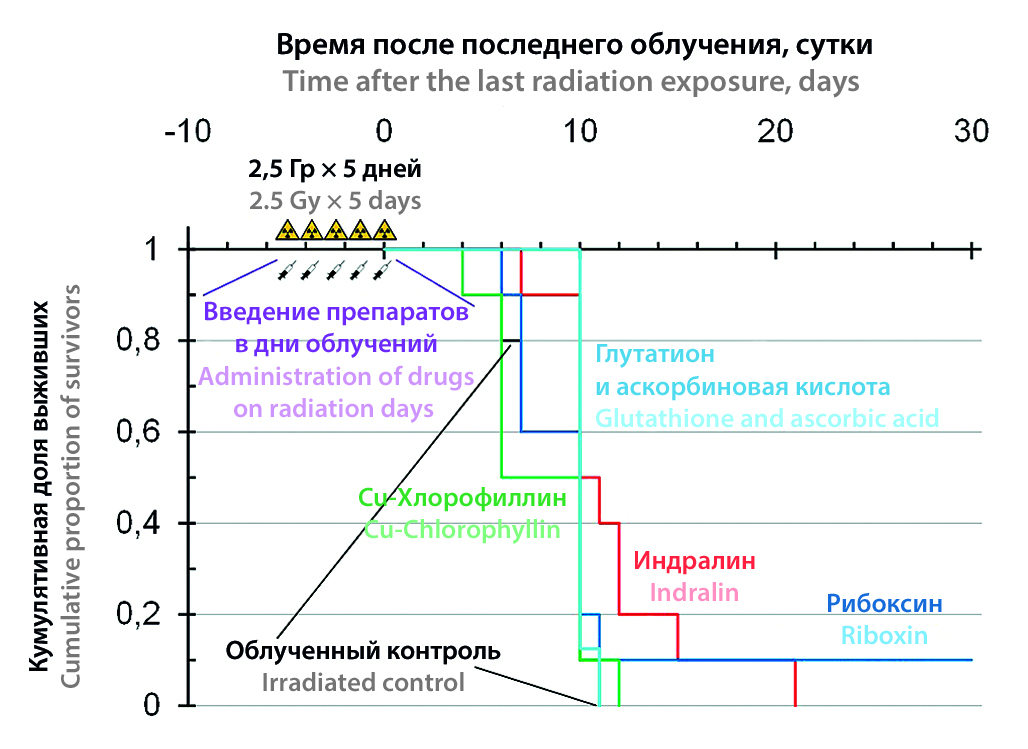
Introduction. The problem of effectiveness and safe pharmacological means of reducing the consequences of exposure to the ionizing effect is becoming increasingly urgent. This solution is difficult due to the high chemical toxicity of all known modern effective radioprotectors. Nowadays, much attention is paid to the study of the radioprotective properties of the so-called effects. But in most of these works, the experimental model was subjected to a one-time acute irradiation. At the same time, a safe and effective radioprotective drug under conditions of fractionated irradiation will be useful in radiation therapy for oncological diseases and during space missions, as well as in conditions of radiation contamination of territories.
Aim. Comparison of the radioprotective effect of copper chlorophyllin, riboxin, also called inosine, and the combined use of glutathione and ascorbic acid with that of the reference Russian radioprotector indralin during fractionated exposure to X-ray radiation.
Materials and methods. Male ICR (CD-1) mice were exposed to five daily irradiations of 2.5 Gy. On the days of each irradiation, experimental animals were administered chlorophyllin (20 μg/g), indralin (50 μg/g) in a solution of tartaric acid or glutathione (250 μg/g) and ascorbic acid (150 μg/g) before irradiation or riboxin (200 μg/g) after irradiation. The survival of mice was assessed within 30 days after the last irradiation.
Result and discussion. Only the use of Riboxin ensured the survival of 10 % of irradiated animals, but without a statistically significant increase in the average life expectancy of dead animals relative to the group of intact mice. A significant increase in this parameter was provided only by the use of indralin. Copper chlorophyllin had no radioprotective effect. Perhaps the use of metal-free chlorophyll derivatives in the future will be able to have a radioprotective effect under these conditions. The combined use of glutathione and ascorbic acid led to the death of 2 out of 10 mice during the period of irradiation and drug administration, without providing an increase in survival during the observation period.
Conclusion. The use of copper chlorophyllin and glutathione with ascorbic acid did not increase the survival rate and average life expectancy of deceased mice irradiated at a dose of 12.5 Gy, distributed into 5 fractions of 2.5 Gy. The use of indralin only increased the life expectancy of dead animals. Riboxin contributed to the survival of 10 % of the corresponding group.
ERRATUMS
Drug development & registration. 2024;13(4):45–59. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.33380/2305-2066-2024-13-4-1897. Published: 15.11.2024.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)