FROM EDITOR
On May 31, 2024, for the sixth time, the "Russian Business Guide. PEOPLE OF THE YEAR" award was held at the Congress Center of the Russian Chamber of Commerce and Industry. The gala event is held with the support of the Chamber of Commerce and Industry of the Russian Federation.
We present to your attention a new interview as part of the Leaders' Opinion series. The second guest of the series was the head of the medical department of GEROPHARM Igor E. Makarenko.
The paper presents well-known iconical, as well as new, recently discovered facts about the history of the creation and formation of the Apothecary prikaz as a structure of Russian state administration of medicine. This paper makes references to the scientists-historians of medicine who have made a special contribution to the study of the history of Russian pharmacy and the Apothecary prikaz. In particular the special role of V. Richter, N. E. Mamonov and N. Ya. Novombergsky in search, research, and preparing for publishing documents of the Apothecary prikaz is noted. Despite more than 200 years of studying of Apothecary prikaz’s documents, many disputes about the time of its setting up continue to the present day. The structure and functions of this organization in common structure of the Moscow state are still being discussed.
The use of IR spectroscopy in the quality control of medicines is regulated by the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, the Pharmacopoeia of the USA and the European Pharmacopoeia. Labconcept Group, a leading supplier and manufacturer of analytical and general laboratory equipment, offers IR spectrometers i-Red 7800 series under its own brand SILab. The IR spectrometers of the i-Red 7800 series are supplied with a wide range of additional accessories allowing to solve any identification and quality assessment tasks pharmaceutical substance, quantitative analysis.
EVENTS
The two-day congress "Drug development and registration" was held on February 27 and 28, 2024 at Sechenov University in Moscow. The organizers of the congress are the Center of Pharmaceutical Analytics and the journal "Drug development and registration". The event was attended by 170+ listeners, more than 60 speakers were with us, and we were supported by 20+ partners.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
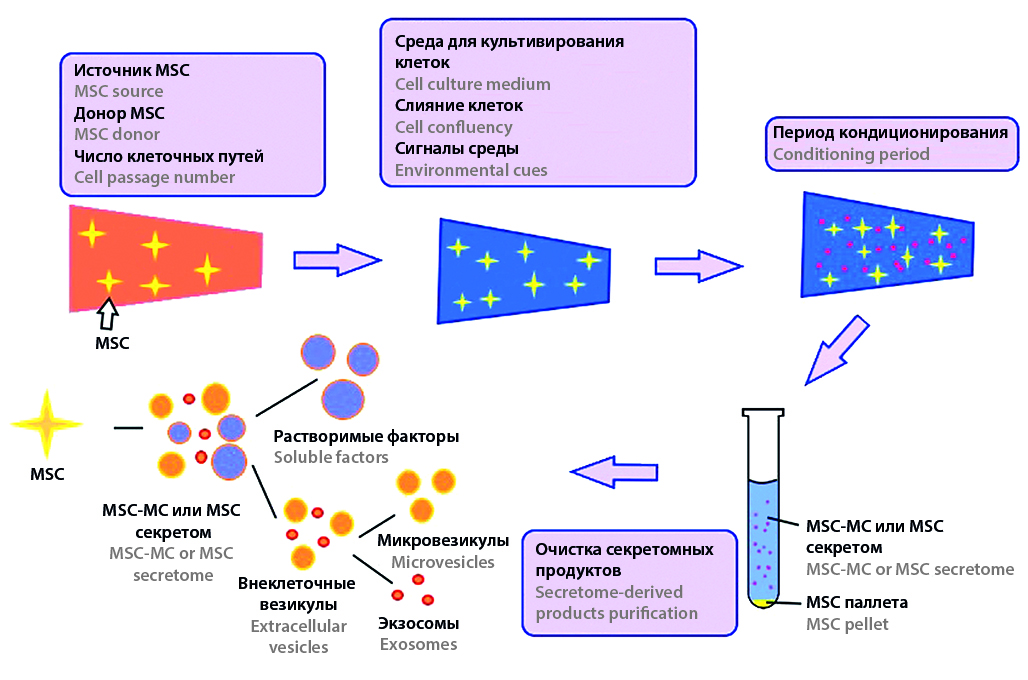
Introduction. The secretome of mesenchymal stem cells (SMSC) is widely used in medicine. It is most often used due to its immune-modulating and regenerative properties in the treatment of autoimmune, immuno-mediated and other diseases due to its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and regenerating action. In many studies, exosomes isolated from SMSC are used as a therapeutic agent. In recent years, the interest in the development of products containing SMSC for external use has increased. Similar drugs are planned to be used in the treatment of diabetic wounds, for skin regeneration, the treatment of inflammatory diseases, as well as alopecia. There are multiple studies on increasing collagen secretion and reducing skin photosensitivity in preclinical studies, which confirms the significant potential for the use of SMSC in dermatology and cosmetology. The purpose of this review was to study the potential of using conditioned medium in medicines for external use, approaches to standardization of SMSC as a pharmaceutical substance and methods of increasing percutaneous delivery.
Text. SMSC as an active pharmaceutical ingredient is a transparent liquid from yellow to orange in color with a characteristic odor. The pH of the ready-to-use SMSC composition ranges from 7.0 to 7.5, which allows it to be used in topical and external applications without the addition of stabilizers or pH correctors. Problems of delivery of SMSC through the epidermis are most often solved by placing the secretome in hydrogels, using exosomes or technology using microneedles. Since 2022, after legislative changes, measures have been taken to register and introduce into clinical practice domestic drugs based on cellular products. However, as the analysis showed, it will take some time before the appearance of original medicines based on SMSC, and today in the Russian Federation only products related to cosmetics and veterinary drugs, as well as zoocosmetics, are produced so far.
Conclusion. SMSC may also prove to be a safer and more effective substance for the potential treatment of a wide range of acute and chronic diseases. But despite the large number of positive results of using SMSC for wound healing in animals, as well as clinical studies on skin regeneration, there are no studies of its safety and effectiveness, as well as standardization of the production process.
Introduction. Aronia Мitschurinii (Aronia × mitschurinii A.K. Skvortsov & Maitul) is a species obtained by crossing chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott) and mountain ash (Sorbus aucuparia L.). This plant is more widely known in the literature as chokeberry. Mitschurin сhokeberry is actively cultivated in the Russian Federation (RF) and neighboring countries to obtain the main raw material – fruits. Aronia should not be confused with chokeberry, which does not grow wild and is practically not cultivated in the Russian Federation due to the inedibility of the fruit and the low decorative value of the plant. The leaves, unlike the fruits, of Mitschurin chokeberry are not yet used as medicinal plant raw materials (MPR). However, according to preliminary studies, they are a promising source of biologically active substances (tannins, flavonoids, leukoanthocyanins, vitamins, a complex of microelements, etc.), exhibiting astringent, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Therefore, an urgent task is to develop indicators of the authenticity of raw materials based on the presence of the main groups of biologically active substances, as well as methods and standards for their quantitative content for the formation of draft regulatory documentation for Michurin chokeberry leaves.
Aim. The purpose of the study was to study the profile of biologically active substances of Michurin chokeberry leaves, growing in the territory of the Central Black Earth Region of the Russian Federation, to determine the target groups that determine the pharmacological activity of this raw material.
Materials and methods. Leaves of Michurin chokeberry for research were harvested during the period of technical maturity of the fruit (August – September 2023) from a plant cultivated in the city of Michurinsk (Tambov region) and dried. Primary screening was carried out for the presence of individual groups of biologically active substances in the leaves of Michurin chokeberry, using known qualitative reactions. The composition of flavonoids was determined by thin layer chromatography. Quantitative determination of the main groups of biologically active substances was carried out according to known methods using modern physicochemical methods of spectrophotometry and capillary electrophoresis.
Results and discussion. Tannins, flavonoids, alcohol-soluble saponins, leukoanthocyanins, amino acids, ascorbic acid and polysaccharides in the form of mucilage were found in the leaves of Aronia mitschurinii. No alkaloids were found. TLC analysis of flavonoids revealed at least 4 adsorption zones with yellow-green fluorescence, one of which was identified as rutin. The thiamine content in the leaves was 0.99 ± 0.084 mg/kg; riboflavin – 0.43 ± 0.025 mg/kg; choline – 44.4 ± 3.9 mg/kg; extractives – 31.52 ± 0.22 %; the amount of flavonoids in terms of rutin – 3.48 ± 0.21 %; the amount of tannins in terms of catechin – 8.63 ± 0.32 %; the amount of anthocyanins in terms of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside – 11.62 ± 0.69 %. In the leaves of Aronia mitschurinii, 17 amino acids were identified (total content 5.88 %), 7 of them are essential (2.71 %). The predominant amino acids are leucine and glutamic acid – 18.37 and 10.88 % of the total amino acid content, respectively. The quantitative content of eight free organic acids was also determined (total content 0.49 %). The predominant acids are citric, malic and sorbic.
Conclusion. As the target groups of biologically active substances responsible for the pharmacological activity of Aronia mitschurinii leaves, it is most rational to consider a complex of polyphenols (flavonoids, anthocyanin compounds and tannins), the content of which is quite high. According to the spectral characteristics, the dominant biologically active substances in the sum of flavonoids, tannins and anthocyanins are rutin, catechin and cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, respectively. This type of raw material can be considered as a promising source of biologically active substances for the purpose of further obtaining herbal plants preparations with antioxidant, capillary-protective, astringent and anti-inflammatory effects.
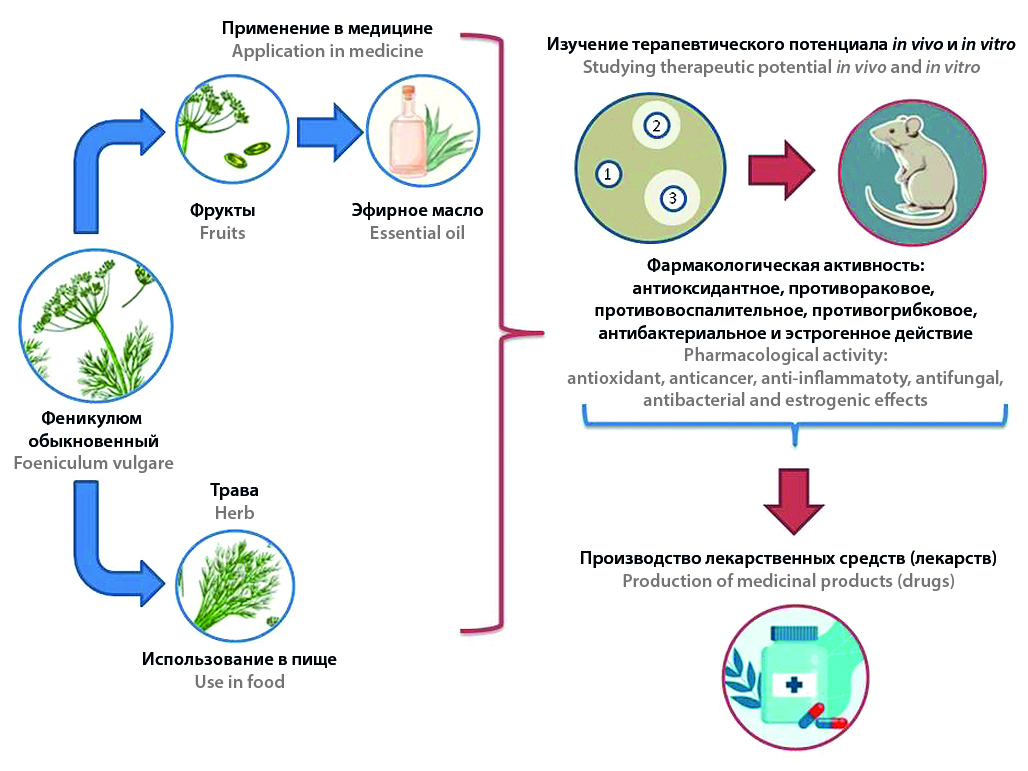
Introduction. Foeniculum vulgare Mill., commonly known as fennel or drugstore dill, is very common as one of the world's oldest spice plants, which has significant economic importance and wide application in the pharmaceutical industry. In medical practice, the fruits of this plant are mainly used, which are included in the State Pharmacopoeia of the XIV edition and are a source of essential oil. They are used as an antispasmodic and carminative agent in the form of an infusion. Fennel grass harvested before flowering is used for food, as well as fruits, stems and inflorescences of the plant as a seasoning.
Text. The purpose of this study is to summarize scientific papers on the morphological characteristics, phytochemical compounds, therapeutic properties and basic mechanisms of pharmacological activity of F. vulgare. A systematic literature search was conducted using relevant keywords such as "fennel", "Foeniculum vulgare Mill.", "therapeutic" and "pharmacology" in well-known databases, including ScienceDirect, Scopus, EBSCO and Medline. The search covered articles published before April 25, 2023 in available journals. The results of the study showed that fennel has a wide range of pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antibacterial and estrogenic effects. These effects can be explained by the presence of aromatic compounds, in particular anethole, estragole and fenchone, which are abundantly present in fennel.
Conclusion. The diverse pharmacological properties and rich chemical composition of fennel make it a promising raw material for the development of new medicines. Further study of the therapeutic potential of fennel through in vivo and in vitro studies will contribute to the establishment of mechanisms of pharmacological action of biologically active substances (BAS) of fennel.
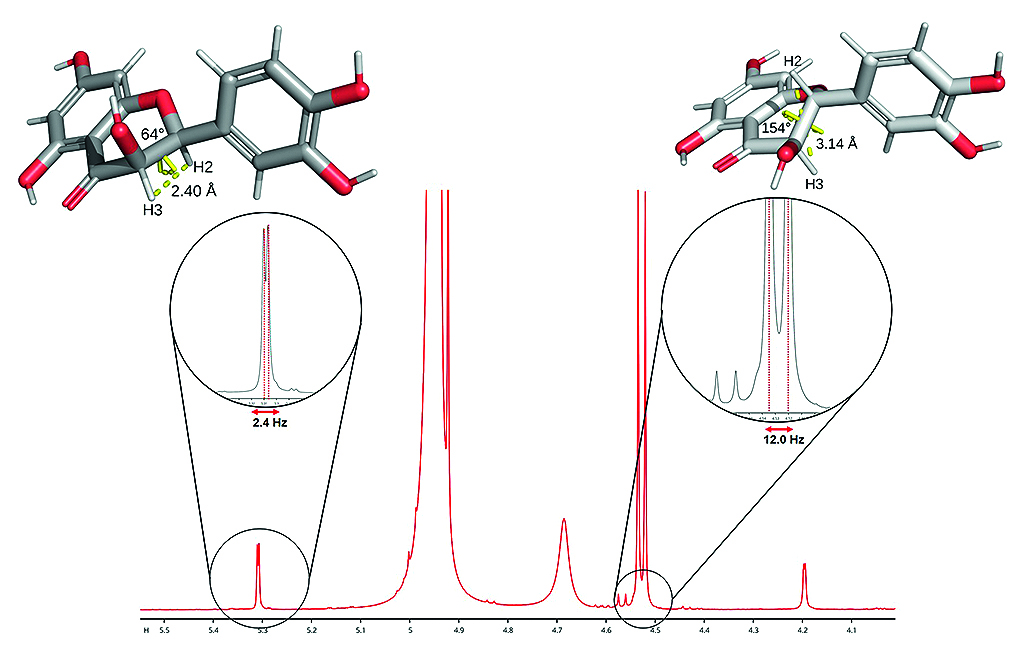
Introduction. The structure of dihydroquercetin (DHQ) is characterized by two chiral centers at positions 2 and 3 of the benzopyran cycle, resulting in possible diastereomers: trans- and cis-isomers. Therefore, the development of methods for qualitative and quantitative control of DHQ diastereomers in analyzed samples is essential for patient safety management. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is one of the physicochemical methods that can be used for this purpose.
Aim. The study objective was to accumulate the analytical and structural characteristics of cis-DHQ by NMR spectroscopy of the spheroidal form of this flavonoid (DHQs).
Materials and Methods. 1D 1H, 1H,1H-COSY, 1H,1H-NOESY, and 1H,13C-HSQC NMR spectra were acquired at 298 K on an 800 MHz NMR spectrometer equipped with a TXI triple resonance probe. The number of scans was 32. The mixing time in the NOESY experiment was 400 ms. The 1H and 13C were analyzed using CcpNmr software. The dihedral angles were calculated by applying the Karplus equation.
Results and discussion. In trans-DHQ, the chemical shift values for H2 and H3 are 4.93 ppm and 4.52 ppm, respectively, and in cis-DHQ they are 5.31 ppm and 4.20 ppm, respectively. The spin-spin coupling constants between H2 and H3 of trans- and cis-DHQ are 12.00 Hz and 2.40 Hz, respectively. Thus, the dihedral angles for the trans- and cis-isomers are 154° and 64°, respectively. We found that DHQs contains 12.5 % of the cis-isomer.
Conclusion. Our experiments confirmed that NMR spectroscopy can discriminate between trans- and cis-DHQ based on the chemical shift values for the cross-peaks of H2 and H3. The second major finding was that this method can be considered as a more selective quantitative analysis than HPLC with UV detection without reference. One of the most important results of this study for drug development is the updated information on the structural parameters of DHQ diastereomers in the liquid phase.
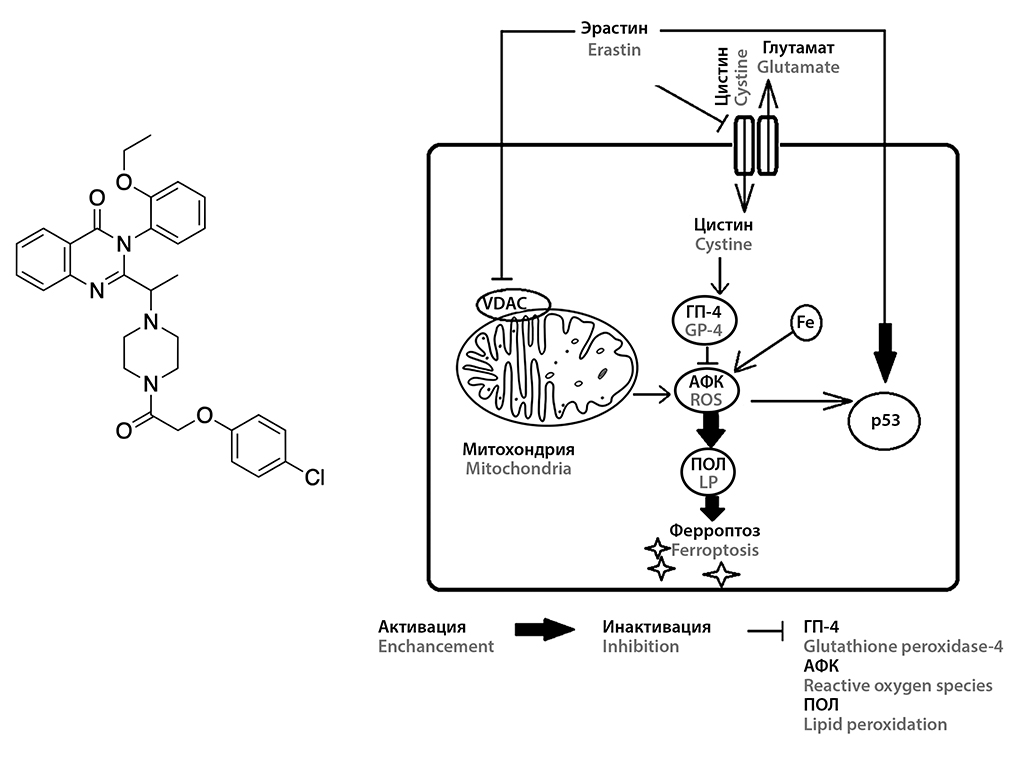
Introduction. Improving the efficacy of chemotherapy is a non-trivial task of modern oncology. Its successful solution requires knowledge in many fields, including physiology, pathology, clinical oncology, pharmacology and others. The search for small molecules that selectively kill tumor cells led to the accidental discovery of erastin.
Text. Erastin is a unique molecule that has a quinazoline fragment in its structure. Not so long ago it became known that the antitumour effect of this compound is due to the induction of ferroptosis – an iron-dependent form of cell death caused by lipid peroxidation. Erastin is able to induce ferroptosis through various biochemical pathways, including blocking of cystine-glutamate transport channel of cell membrane and potential-dependent anion channel of mitochondria, as well as activation of p53 protein.
Conclusion. Pharmacological induction of ferroptosis by erastin and its analogues represents a promising direction in cancer chemotherapy. In addition, erastin and its analogues are able to increase sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which allows us to talk about the possibility of their use in the combined treatment of malignant neoplasms.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. Medicines of natural origin have advantages over synthetic drugs and occupy a significant share in the assortment of pharmacies. Filipendula ulmaria (L.) Maxim., characterized by a chemical composition rich in phenolic compounds and various types of biological activity has the potential in terms of the development of new herbal medicines. In an in vivo experiment, F. ulmaria extract showed immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, osteogenic activity and effectively stimulated myelopoiesis in conditions of microbial damage of bone tissue.
Aim. Development of an optimal technology for obtaining dry extract of F. ulmaria by remaceration and investigation of its аcute toxicity.
Materials and methods. The technology of extract was developed in a laboratory reactor equipped with a water heater jacket and a stirrer. The content of flavonoids was determined by differential spectrometry. Flowability was determined on a flowability tester for powders and granules, bulk density was determined on a bulk density tester for powders and granules, moisture content was developed on a moisture content analyzer. Acute toxicity was determined on Wistar rats.
Results and discussion. The dry extract of F. ulmaria, obtained using 70 % ethanol by remaceration, is effective in conditions of microbial damage of bone tissue and bone marrow, which determined the choice of extragent and the type of extract. The optimal parameters for obtaining the extract were determined (three-fold maceration at a water jacket temperature of 80 °C, the ratio of raw materials to extragent 1 : 14, time 30 min), its main technological characteristics were determined and a wet granulation method for improving them was proposed. In the study of acute toxicity of the extract, according to the results of toxicometry for 14 days after administration and necropsy data, the studied extract was classified as low-toxic substance.
Conclusion. The dry extract of F. ulmaria, obtained by remaceration using 70 % ethanol, has specific activity in conditions of microbial damage to bone tissue. Optimal extraction parameters allow to increase the yield of target components, it is advisable to improve the technological parameters of the extract by wet granulation. The assessment of the safety profile of the dry extract from F. ulmaria, along with its high biological activity, provides a perspective for its further study and implementation into medical practice.
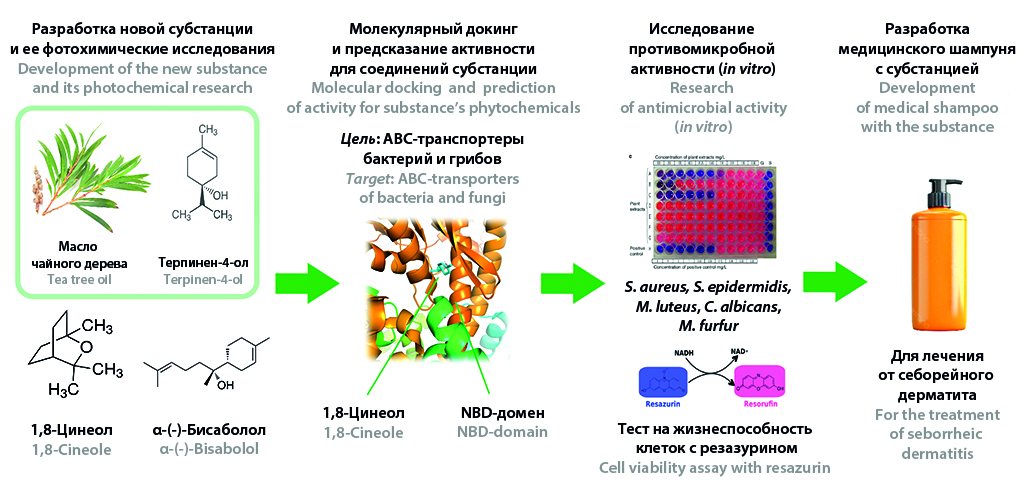
Introduction. Despite the proven clinical efficacy of antifungal and anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, the search for new targets and the development of new substances with a beneficial effect on the scalp microflora, with a low risk of antimicrobial resistance and adverse effects, are relevant.
Aim. Development of the antimicrobial multicomponent pharmaceutical substance of plant origin in stages: from a literature search for promising substances, analysis of their composition by GC-MS, in silico evaluation of the affinity of individual components to pathogenetic targets, selection of the optimal composition of a multicomponent substance based on the results of in vitro research of antimicrobial action and the making of a medical dosage form based on it – a medicinal shampoo for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis.
Materials and methods. Objects of research: tea tree essential oil, 1,8-cineole, α-(-)-bisabolol and the multicomponent substance based on them. Methods: molecular docking (AutoDock version 4.2), prediction of pharmacological activity (Phyto4Health), TLC, GC-MS, study of antimicrobial activity in vitro.
Results and discussion. Based on the results of a literature search, 3 promising substances were selected for the development of a multicomponent plant-based substance: tea tree essential oil, 1,8-cineole and α-(-)-bisabolol. Molecular docking predicted the targeted activity of the phytochemicals of tea tree essential oil, 1,8-cineole and α-(-)-bisabolol on the domains of ABC-transporters of microorganisms involved in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis and justified the possibility of use for therapy. The multicomponent substance has been developed based on tea tree essential oil, 1,8-cineole and α-(-)-bisabolol in a mass ratio of 1 : 1 : 1. The qualitative composition of the substance was assessed by TLC and GC-MS methods, and 15 terpenes were quantitatively identified in its composition with a predominance of terpinen-4-ol (16.98 %), 1,8-cineole (25.63 %) and α-(-)-bisabolol (27.67 %). The synergistic antimicrobial activity of the substance has been established against S. epidermidis, S. aureus, C. albicans and M. furfur in comparison with benzalkonium chloride, ketoconazole and climbazole. The composition of a new medical shampoo based on the investigated substance has been developed, which has a pronounced antifungal effect (more than 99.0 %) against M. furfur without visible suppression of normal microflora. For the novel substance of plant origin and medical shampoo, quality parameters were assessed in accordance with the Russian Pharmacopoeia of XIV edition.
Conclusion. A substance of plant origin with synergistic and targeted antimicrobial activity has been developed. It has an interest for further study as a drug and API for new products for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
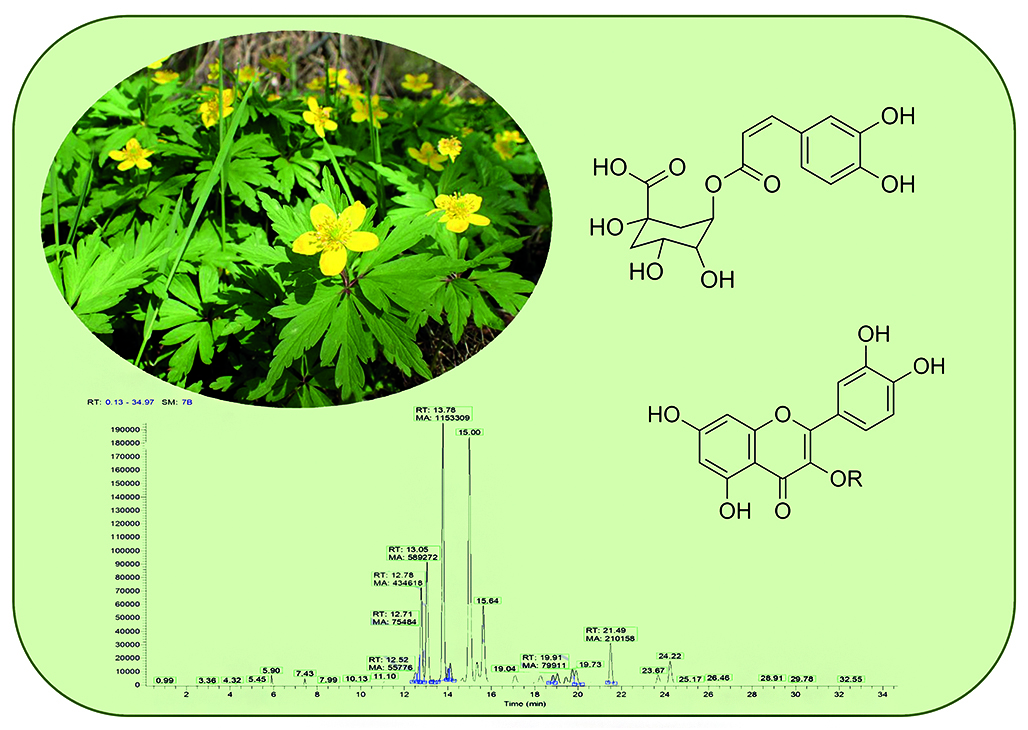
Introduction. Yellow wood anemone (Anemone ranunculoides L.) is a herbaceous perennial. This plant grows in the European parts of Russia, Ciscaucasia, Siberia, Central Europe and other regions. It has many different pharmacological activities: immunomodulatory, sedative, anti-inflammatory, antitoxic, diuretic, antibacterial, antioxidant, antitumor and antirheumatic activity. These various effects are due to their biologically active compounds, which include ephemeroids, protoanemonin, saponins, tannins, resins, ascorbic acid, ranunculin, oils lipids and triterpene glycosides. As to phenolic compounds, currently there is no sufficient information on flavonoids and hydroxycinnamic acids (HCAs) profiles in different species of genus Anemone. Because these groups of compounds are quite specific for yellow wood anemone, their detailed study seems to be relevant.
Aim. The objective of this research is to identify and quantify flavonoids, HCAs, and their conjugates in Yellow wood anemone leaves, flowers and rhizomes with roots.
Materials and methods. The identification was carried out by using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometric detection (UHPLC–DAD–ESI-MS) with quantification of individual compounds by external calibration method.
Results and discussion. Among the 47 compounds, 30 flavonoids and 17 derivatives of HCAs were detected. Quercetin glycosides were found to be the major flavonoids in aerial parts whereas chalcone glycosides – in underground parts. The major HCA in rhizomes with roots was feruloyltartaric acid (1.18 mg/g) whereas chlorogenic acid was predominant in leaves and flowers (8.68 mg/g and 2.62 mg/g accordingly). The total content of phenolic compounds was estimated at 60 mg/g on a dry weight basis.
Conclusion. As a result of the research a detailed profile of flavonoids and HCAs acids of anemon was described. The data obtained can serve to identify this species in the standardization of medicinal plant materials and taxonomic studies.
Introduction. Virgin grape (maiden grape, Virginia grape, virgin grape, Parthenocissus quinquefolia (L.) Planch.) is currently used primarily for decorative purposes, but is also beginning to attract scientists from different countries as a promising source of important compounds such as anthocyanins, flavonoids, organic acids, macro- and microelements. To introduce a plant into medical practice, one of the first steps is the need to develop regulatory documentation that allows for quality assessment and standardization of plant materials, and the first stage of this process is the assessment of the characteristics of the authenticity of the object.
Aim. Establish the morphological characteristics of the leaf and petiole of the virgin grape (Parthenocissus quinquefolia (L.) Planch.).
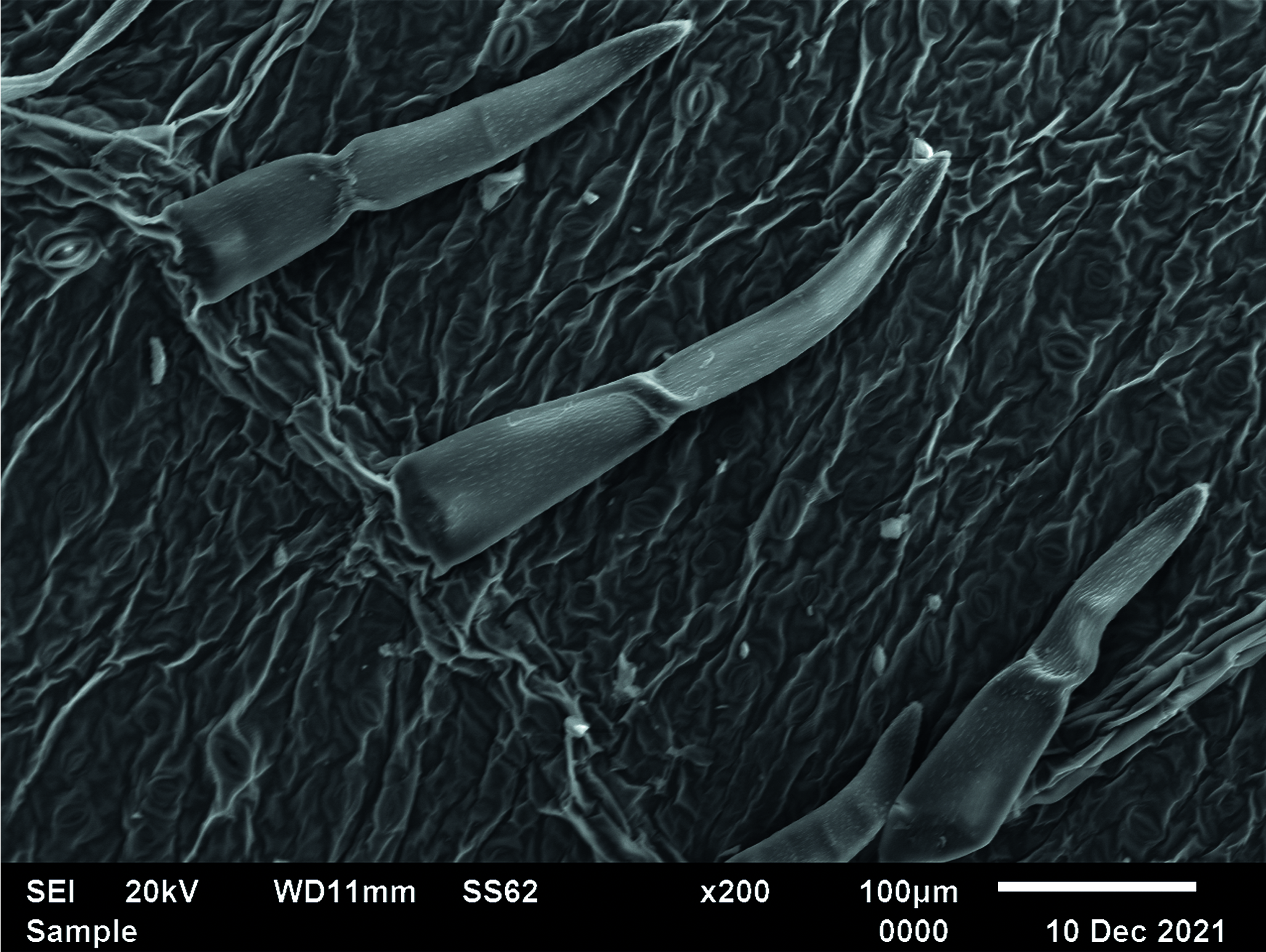
Materials and methods. The object of the study was developed leaves of the virgin grape, harvested in the Voronezh region in the summer of 2022 and dried in the shade. To carry out the experiment, a JSM-6510LV electron microscope was used; the analysis was carried out after sputtering a thin film of gold onto the sample.
Results and discussion. For the first time, the main structural features of various morphological features of the leaf blade of the virgin grape were identified, differences in the morphological picture of the upper and lower sides of the leaf were established, and structural features of the surface of the petiole were identified. Using micro-X-ray analysis, it was revealed that calcium and potassium are present in large quantities in the leaves and petiole of virgin grapes. The least amount of the studied elements in the study object contains magnesium. It has been shown that the leaves contain a small amount of chlorine, and the cellular contents of the petiole include a small amount of sodium.
Conclusion. For the first time, a study of the morphology of the surface of the leaf blade and petiole of the virgin grape was carried out using scanning electron microscopy. The main diagnostic features of plant raw materials have been identified and visualized. Micro-X-ray structural analysis made it possible to establish the composition of the elements of the leaf blade and petiole of virgin grapes and revealed the ability to concentrate calcium, potassium, and phosphorus.
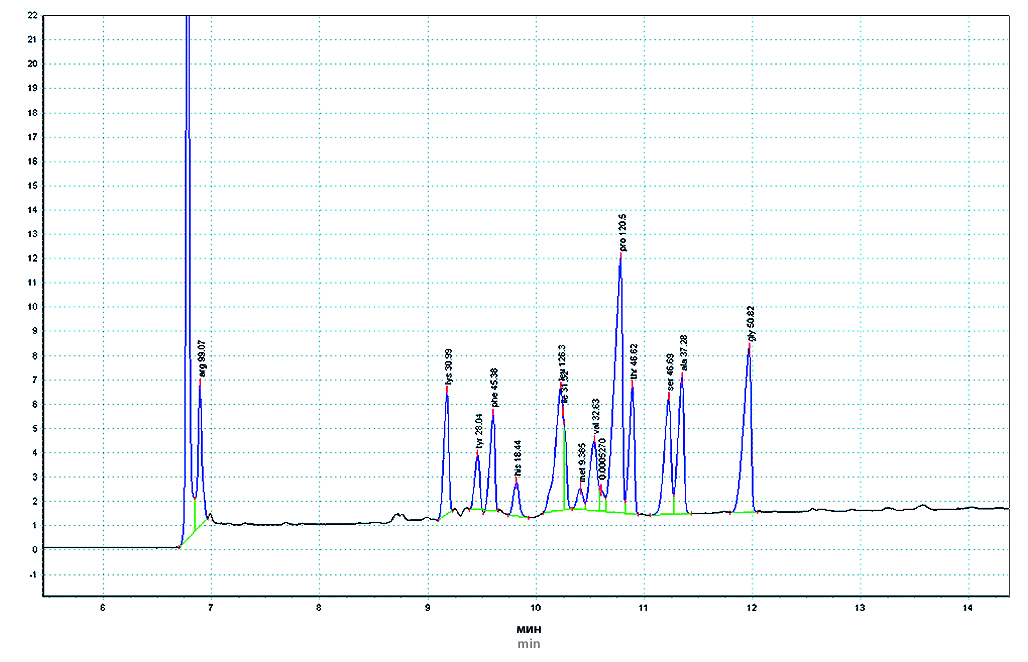
Introduction. Currently, there is an increasing trend towards assessing the full spectrum of chemical compounds in plant materials. One of the first steps in the formation of secondary metabolites of complex structure, participating in biochemical processes in the plant body, which have their own effect on the human and animal body, are organic acids (OA) and amino acids (AA). However, due attention is not always given to these compounds when studying the component composition of plant raw materials.
Aim. The purpose of the work was to study the profile and quantitative assessment of the content of organic acids and amino acids of Aesculus hippocastanum L. flowers.
Materials and methods. The object of the study were horse chestnut flowers, collected during flowering in the Voronezh region in 2021 and dried by air-shade method. Quantitative assessment of the amount of TC in terms of malic acid and ascorbic acid was carried out titrimetrically according to the methods presented in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XIV edition. The composition of the OA and AA profiles of horse chestnut flowers was determined using the capillary electrophoresis method ("Kapel®-105/105M", Group of Companies "Lumex", Russia).
Results and discussion. The method of capillary electrophoresis revealed the presence of 12 compounds of the OA group in a total amount of 4.7 % (in terms of absolutely dry raw materials). The rationality of recalculating the content of the sum of OA to the major component – citric acid, which amounted to 1.65 ± 0.04 %, was shown. The content of ascorbic acid was low (0.033 ± 0.007) %. Using the TLC method, the presence of 5 zones of compounds belonging to the AA class was established in the aqueous extract of horse chestnut flowers. The quantitative content of the sum of free AA in terms of glutamine, determined by the spectrophotometric method, was 2.25 ± 0.07 % (n = 5). The presence of 17 AA was determined by capillary electrophoresis, which amounted to 7.13 %. Glutamic acid is present in the greatest quantity in horse chestnut flowers (1.19 %). Essential amino acids amounted to 2.27 %; leucine was present in the predominant amount (0.58 %).
Conclusion. A study was carried out of the qualitative composition and quantitative content of organic acids and amino acids of horse chestnut flowers. The composition of the profile and the quantitative content of organic acids and amino acids have been established. It was revealed that citric acid prevails in the total organic acids; glutamic, aspartic acid, arginine and proline are found in greater quantities in the total amino acids.
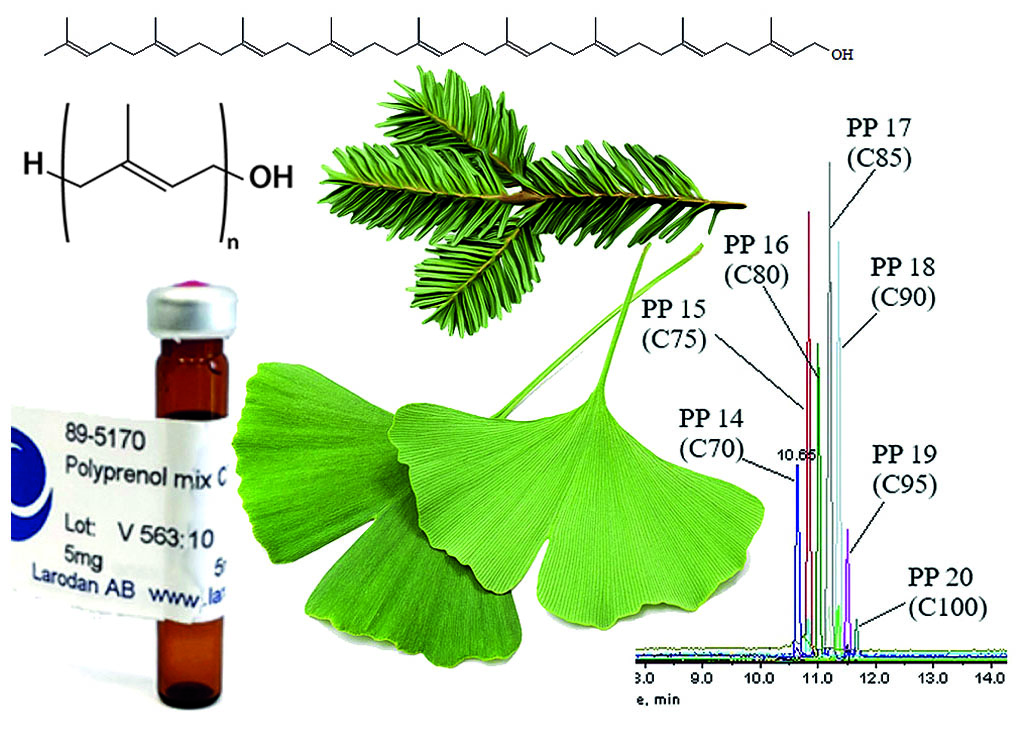
Introduction. Polyprenols are known as a class of natural long-chain isoprenoid alcohols, which are natural bioregulators that directly participate in the synthesis of cell membrane glycoproteins. Their hepatoprotective activity is proven, as well other types of their pharmacological effects are known, which is the reason of significant interest in these substances as a promising medicinal product. It is non-trivial task to determine the sum of polyprenols in extracts as include design and implementation of accurate reproducible analytical methods, which will subsequently be used in standardization.
Aim. Development and validation of the chromatographic-mass spectrometric technique for polyprenols identification and their quantitative assessment.
Materials and methods. Chromatographic separation of polyprenols was performed by using an HPLC Agilent 1260 Infinity II (Agilent Technologies, США); with the mixture of methanol, n-hexane, propanol-2, and aqueous ammonium acetate solution as eluent in gradient mode. An AB Sciex QTrap® 3200MD (AB Sciex Pte. Ltd., Singapore) triple quadrupole mass spectrometer was used as a detector, with the registration of polyprenols adducts.
Results and discussion. The conditions for chromatographic separation and detection of polyprenols were identified. The developed technique was validated for the following characteristics: specificity, limit of detection, limit of quantification, linearity, accuracy, precision, range of application, and stability.
Conclusion. It was determined the content of polyprenols in the substance recieved from Ginkgo biloba L. and Picea abies L. The developed technique can be used in the future to assess the content of polyprenols in drug products or pharmaceutical substances.
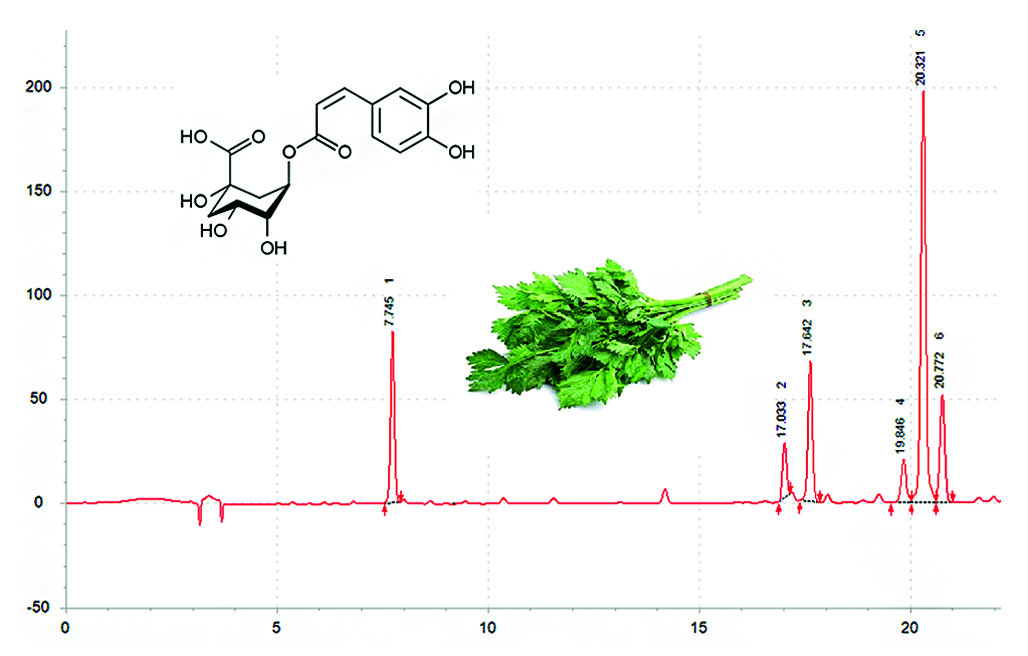
Introduction. Special studies on the benefits of agricultural crops – current research regarding the prospects for the development of their products based on functional and specialized nutrition. Substances with a phenolic profile carry out various types of pharmacological activity aimed at treating metabolic and other socially significant phenomena, which allows them to be positioned as generally accepted main ingredients. The leafy botanical form of celery is a rich source of phenolic compounds.
Aim. Development and validation of a method for the quantitative analysis of chlorogenic acid to assess the varietal advantages of Apium graveolens L. raw materials using HPLC.
Materials and methods. For the analysis, we used leaf celery grass of different varieties grown at two sites (the village of Lembolovo and SNT "Ruchey"). Sample preparation of raw materials was carried out by extraction in an ultrasonic bath. Chromatography conditions: column Luna 5 μm C 18(100) Å LC Column 250 × 4.6 mm, thermostat temperature 40 °C, detection wavelength 327 nm. PF A 0.05 % TFA, PF B acetonitrile. Elution mode: 0 min 12 % B, 20 min 30 % PF B, 23 min 12 % PF B.
Results and discussion. According to the data obtained, the accumulation of chlorogenic acid in celery raw materials depends on both the plant variety and the cultivation conditions. However, the difference in the quantitative content of the target component correlates between varieties grown on different sites. The highest content of chlorogenic acid was noted in the variety Nezhny (SNT "Ruchey") and amounted to 0.464 ± 0.012. The variety Summer Boom can be distinguished as the best variety.
Conclusion. The results of the study can be used in the development and quality control of functional and specialized nutrition based on the leafy botanical form of odorous celery due to the high content of phenolic substances.
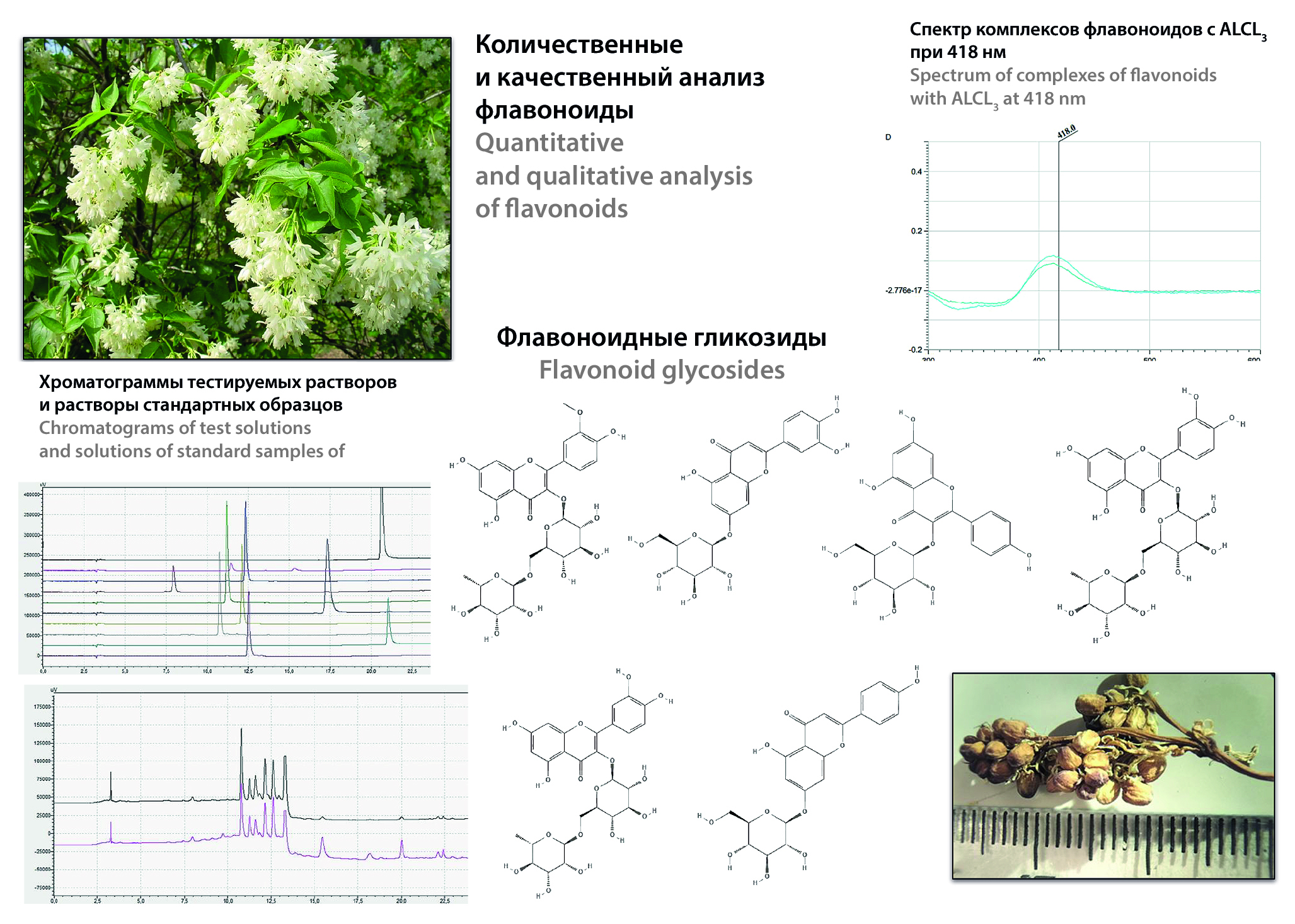
Introduction. Search for new plant species containing biologically active substances (hereinafter – BAS) is one of the leading tasks of pharmacognosy as a science. The search for flavonoid glycosides in plant raw materials is especially relevant, since they have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunostimulating, as well as weak fungicidal and bacteriostatic action. Staphylea pinnata L. is an endemic plant of the Caucasus, cultivated not only in Georgia, but also in the Russian Federation in the Northern and Northwestern Caucasus. In foreign literature there are studies of antioxidant, antiproliferative and cytotoxic activity of leaf extracts of several species of S. pinnata L., as well as inhibitory activity of COX-1, COX-2 and LTB4 formation. Meanwhile, no serious Russian-language scientific studies on either the chemical composition or pharmacological action of generative organs of S. pinnata were found in the literature. This work is part of a comprehensive phytochemical study of S. pinnata. The aim of the work is to study the qualitative and quantitative composition of flavonoids in the studied object.
Aim. To isolate, identify and quantify flavonoids in flowers and buds of Staphylea pinnata L.
Materials and methods. Alcohol-water extracts from dried generative organs of the studied plant were used as analyzed solutions. Solutions were analyzed on a spectrophotometer SF-2000 (LLC "OKB Spectr", Russia) after sample preparation with aluminum chloride and on an HPLC Nexera-i LC-2040 (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan) equipped with a column and sample thermostat, degasser and autosampler using an individually selected elution gradient of the mobile phase (0.1 % orthophosphoric acid/acetonitrile solution). The primary data were processed using LabSolutions Single LC software (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). Compounds from the flavonoid group were identified by retention times. Detection was carried out using a UV detector with an absorption wavelength of 365 ± 2 nm.
Result and discussion. Alcohol-water extracts from flowers and buds of S. pinnata L. were obtained. Quantitative evaluation by spectrophotometry for flavonoid content was carried out. A gradient elution mode for HPLC was selected for simultaneous determination of 7 flavonoid glycosides. These chromatographic conditions allowed the identification and quantification of astragaline, cynaroside, cosmosiin, narcissin and rutin in flowers and buds of Staphylea pinnata L. Flavonoid glycosides: raponticin and kaempferol were not detected.
Conclusion. Flavonoid glycosides were isolated from the generative organs of S. pinnata L., a technique for quantitative determination of flavonoid glycosides in alcohol-water extracts was developed, astragalin, cynaroside, cosmosiin, narcissin and rutin were detected and quantified.
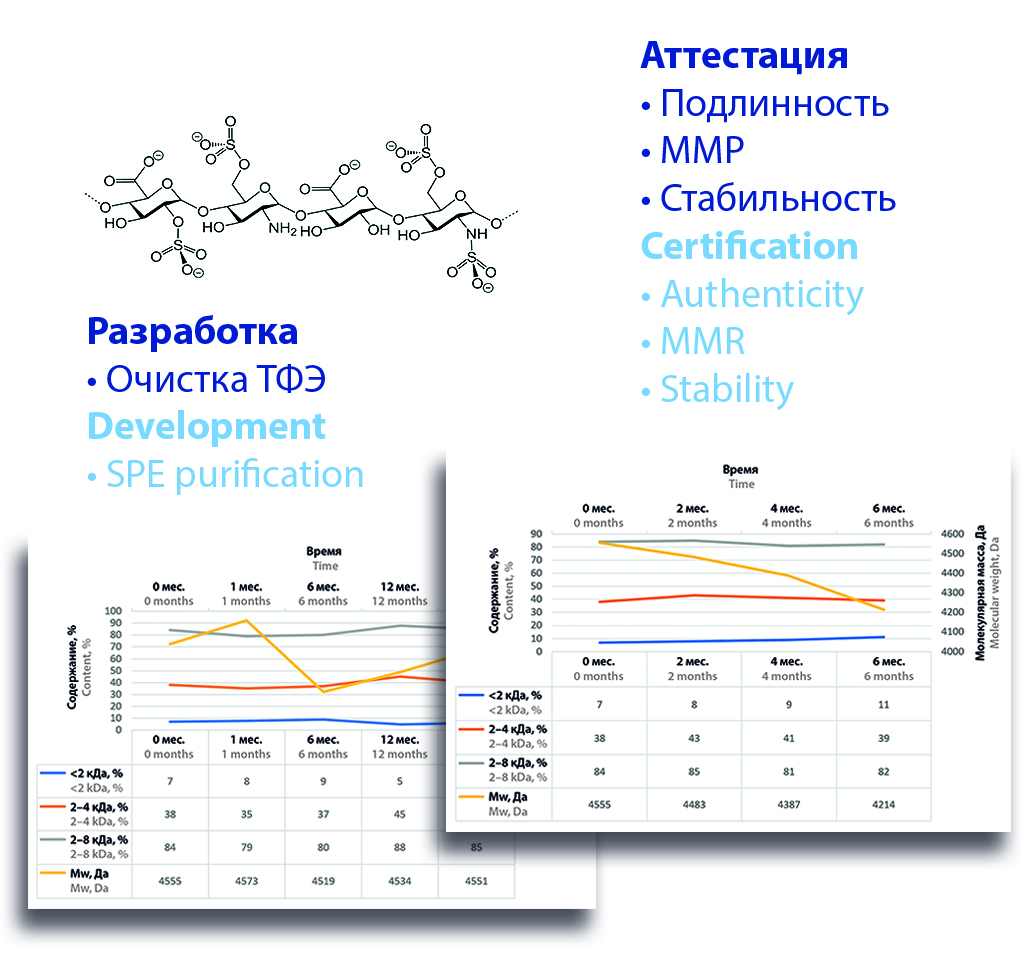
Introduction. The widespread use of heparin preparations for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolic complications is known. One of the low molecular weight heparin drugs successfully used in clinical practice is calcium nadroparin. The modern approach to assessing the quality of medicines involves the use of standards, in comparison with which the quality control of the drug is carried out – standard samples (SS). The most important specific parameter in assessing the authenticity of low molecular weight heparins is the characteristic of the fractional composition.
Aim. The aim of the work was to develop, attestation and determine the stability during the shelf life of a secondary standard sample to determine the authenticity of calcium nadroparin as part of improving the quality control system of the enterprise with the prospect of creating a domestic pharmacopoeia standard sample.
Materials and methods. The object of development and attestation was the standard sample of the enterprise – low molecular weight heparin, obtained on the basis of the Technology implementation center of Siberian state medical university. The certified standard sample was obtained by purification of calcium nadroparin by solid-phase extraction. The completeness of the purification was confirmed by comparing the chromatograms of the purified samples with the chromatograms of the international standard sample. The characteristics of the molecular weight distribution were determined chromatographically. The stability of the certified SSE (the standard sample of the enterprise) was studied under two storage conditions – at a temperature below 8 °C in a dry state for 16 months and in solution at –40 °C for 6 months by evaluating trends in molecular weight distribution.
Results and discussion. For each batch of the certified standard sample, the molecular weight and molecular weight characteristics are calculated in 2 parallel definitions, and a representative chromatogram is presented. The values of the relative standard deviation of the molecular weight of the samples and the content of the controlled fractions did not exceed 2.5 %. A detailed analysis of the molecular weight distribution showed the "classical" dependence of RSD (relative standard deviation) from the average value with a significant increase up to 30 % for small fraction values (less than 0.5 %). It was found that during 16 months at a storage temperature below 8 ºC, the molecular weight and molecular weight characteristics of standard samples of low molecular weight heparin did not significantly change. However, in the SSE solution at a storage temperature of minus 40 °C for 6 months, they degraded by more than 10 %.
Conclusion. According to the results of the study, a protocol has been developed for obtaining a standard sample of low-molecular-weight heparin for the standardization of the calcium nadroparin substance according to the indicator "molecular weight distribution". The established shelf life of the sample is at least 16 months at temperatures below 8 °C. The stability of solutions of the standard sample at a storage temperature of –40 °C for 3 months is shown.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
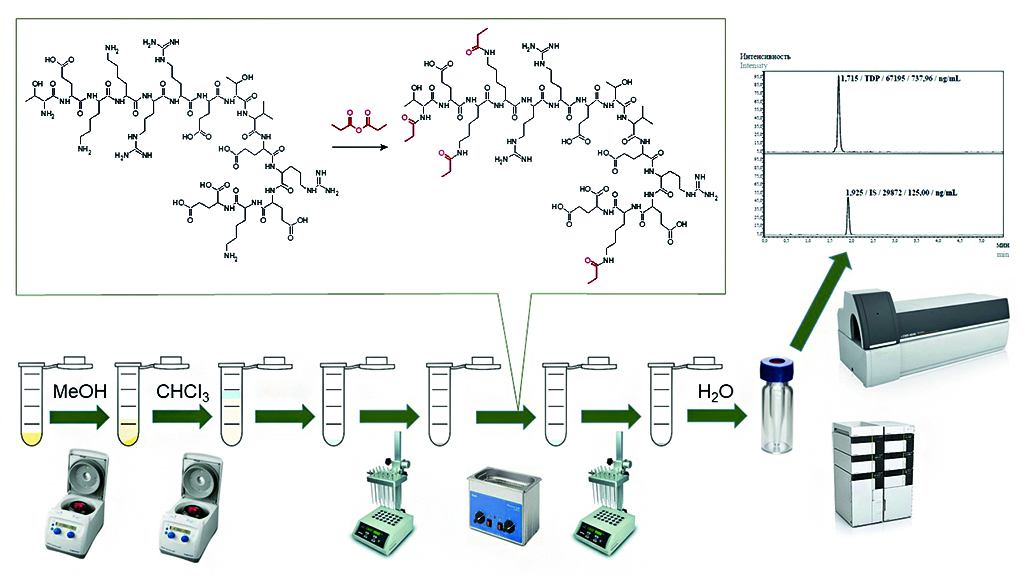
Introduction. The number of peptide drugs being developed and registered has increased in recent years. Therefore, modern analytical approaches and methods are required to determine these substances in biological matrices during pharmacokinetic studies. Peptides are structurally intermediate between small molecules and biopolymers, making it difficult to develop methods for determining them using High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Peptide derivatization can help achieve optimal chromatographic separation and increase method sensitivity.
Aim. To develop and validate a method for the determination of the tetradecapeptide (TDP) threonyl-glutamyl-lysyl-lysyl-arginyl-arginyl-glutamayl-threonyl-valyl-glutamyl-arginyl-glutamyl-lysyl-glutamate in human plasma by HPLC-MS/MS.
Materials and methods. The determination of TDP in human plasma was performed by HPLC-MS/MS. Sample preparation included a combination of blood plasma protein precipitation with propionic acid solution in methanol, liquid-liquid extraction with chloroform, and peptide derivatization with propionic anhydride. Internal standard (IS) was threonyl-glutamyl-lysyl-lysyl-arginyl-arginyl-glutamayl-threonyl-leucyl-glutamyl-arginyl-glutamyl-lysyl-glutamate. Chromatographic separation was performed in gradient mode, eluent A was 0.1 % formic acid solution in water, eluent B was 0.1 % formic acid in acetonitrile. Column: Waters XBridge C18, 4.6 × 50 mm, 5 µm. Ionization source was electrospray in positive mode. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions for 4-substituted TDP propionate were: 681.30 → 73.95 m/z, 681.30 → 84.00 m/z, 681.30 → 101.90 m/z, 681.30 → 140.10 m/z, and for 4-substituted IS propionate: 686.00 → 74.10 m/z, 686.00 → 84.05 m/z, 686.00 → 102.00 m/z, 686.00 → 140.00 m/z.
Results and discussion. Validation of the developed method was carried out in accordance with the requirements of Eurasian Economic Union and the following parameters were determined: selectivity, matrix effect, calibration curve, accuracy and precision, recovery, lower limit of quantification, sample carryover, stability.
Conclusion. The method for the determination of TDP in human blood plasma by HPLC-MS/MS was developed and validated. The analytical range was 5.00–1000.00 ng/mL, allowing the method to be used to study TDP pharmacokinetics.
Introduction. One of the reasons for the development of many diseases primarily malignant is the increased expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Bevacizumab is a drug that neutralizes the biological activity of VEGF. The molecular structure of bevacizumab is a recombinant humanized antibody. Its use reduces vascularization in the foci of increased VEGF expression which slows down tumor growth and also helps restore vision in a number of ophthalmic diseases. To determine the concentration of bevacizumab in human biological fluids a test system based on Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is presented.
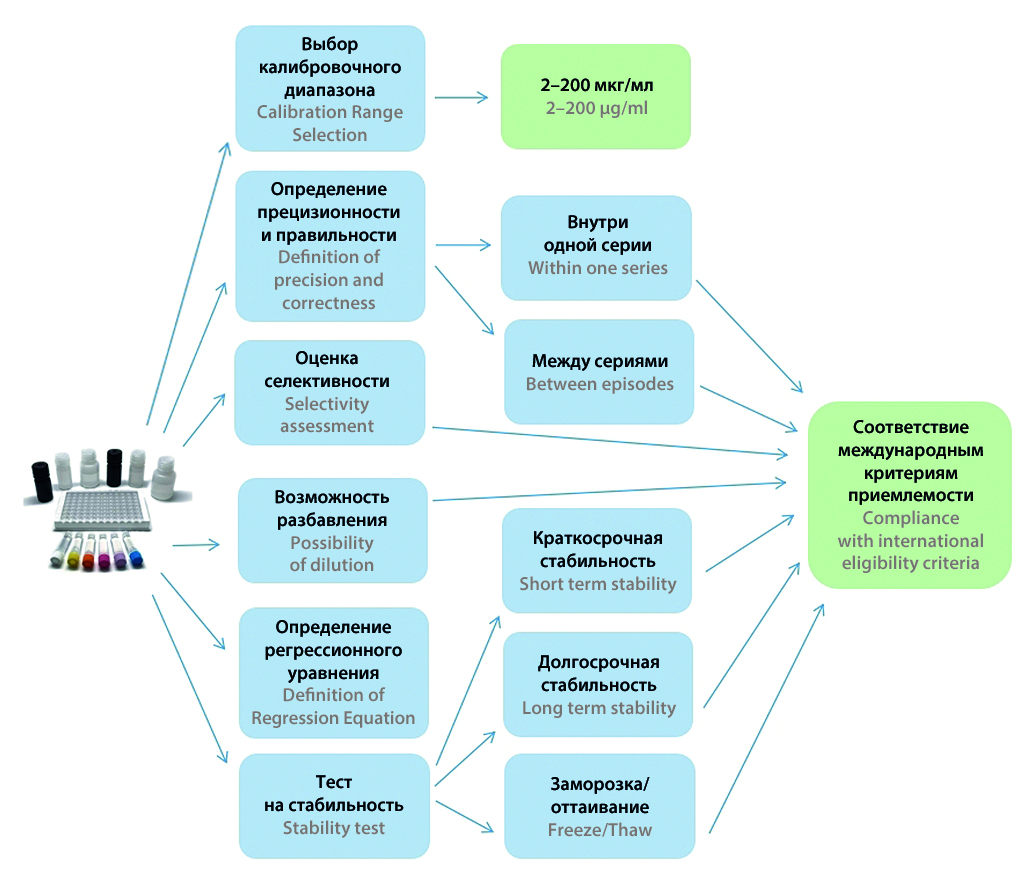
Aim. Aim of this study is the validation of this test system.
Materials and methods. Blank sera of volunteers, bevacizumab solution, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, solid-phase sandwich ELISA kit, microplate photometer.
Results and discussion. The following characteristics of the test system were determined: the lower limit of quantification is 2.0 mcg/ml, the upper calibration range is up to 200 mcg/ml, the accuracy and precision within one series and between series does not exceed 20 %, and the total error of the method – 30 %, short-term stability for samples at room temperature – 6 hours, long-term stability – 14 days at –20 °C, the ability to freeze/thaw of samples is up to three times, the ability to determine samples with a concentration above the upper calibrator after diluting in 2 times.
Conclusion. The results obtained fully comply with international acceptance criteria and allow the use of the ELISA test system manufactured by LLC "Probiotek" for use in the field of clinical laboratory diagnostics.
Introduction. The naïve Bayes classifier combined with principal component analysis allows to distinguish the effects of antipsychotic agents effectively as well as evaluate their dose-dependency based on their impact on electroencephalogram parameters in rats. Further development of this method requires its validation as an instrument for the screening of new understudied molecules. Valproic acid derivatives appear to be a promising neuropharmacological group as they exhibit not only antiepileptic activity but also mood-stabilizing, antimigraine, neuroprotective and analgesic effects.
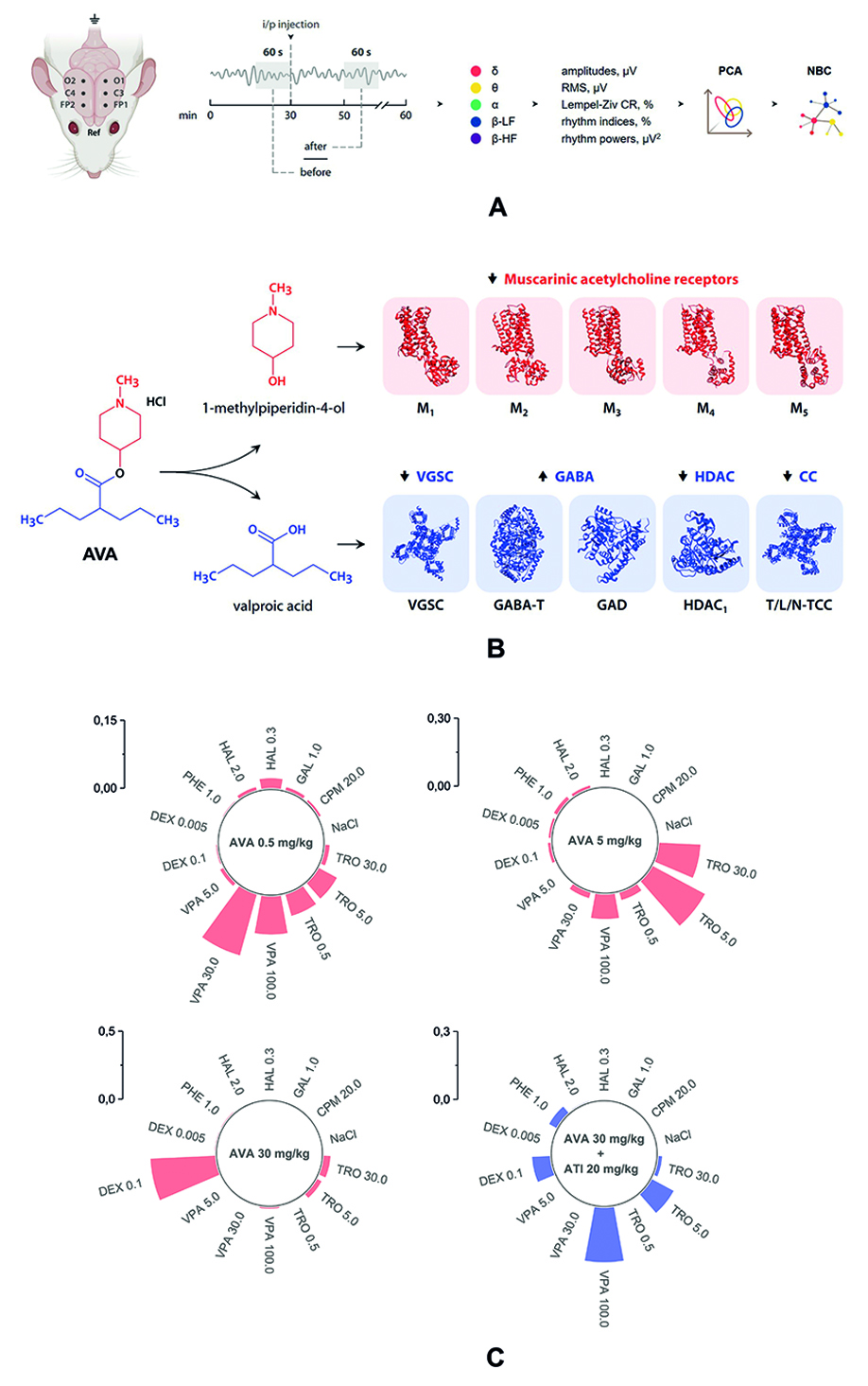
Aim. This work was carried out to perform the pharmacological screening of a valproic acid aminoester (AVA) that exhibits antidote properties in case of poisoning with anticholinesterase agents.
Materials and methods. The experiments were conducted in white outbred rats with chronically implanted electrocorticographic electrodes. AVA was administered at doses of 0,5, 5 and 30 mg/kg. The training set, used as a reference to determine the pharmacological effects of each dose of the investigated substance, included matrixes of effects of 7 drugs: the antiepileptic agent sodium valproate, the D2-dopamine receptor blocker haloperidol, the M-cholinergic receptor blocker tropicamide, the H1-histamine receptor blocker chloropyramine, the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor galantamine, the sedative dexmedetomidine, and the anxiolytic phenazepam.
Results and discussion. AVA at the dose of 0,5 mg/kg showed effects similar to those of sodium valproate, while a tenfold dose increase led to the predominance of an atropine-like effect. When administered at the dose of 30 mg/kg, the compound exhibited dexmedetomidine-like action. The central M-anticholinergic effect of AVA was confirmed by an arecoline test in mice, in which the substance at a dose of 88 mg/kg completely abolished the onset of tremor. Dexmedetomidine-like action was cancelled by the administration of atipamezole in equimolar quantities, which may indicate the potential сapability of AVA to activate α2-adrenergic receptors at a high dose. The results of molecular docking suggest that this effect is related specifically to the original aminoester molecule and not to its presumable active metabolites.
Сonclusion. The obtained results confirm the effectiveness of the naïve Bayes classifier as an instrument for the prediction of the pharmacological activity of compounds based on their impact on electroencephalogram parameters in rats. Identification of new pharmacological effects of understudied compounds may widen the potential range of their clinical application as well as reveal probable adverse effects.
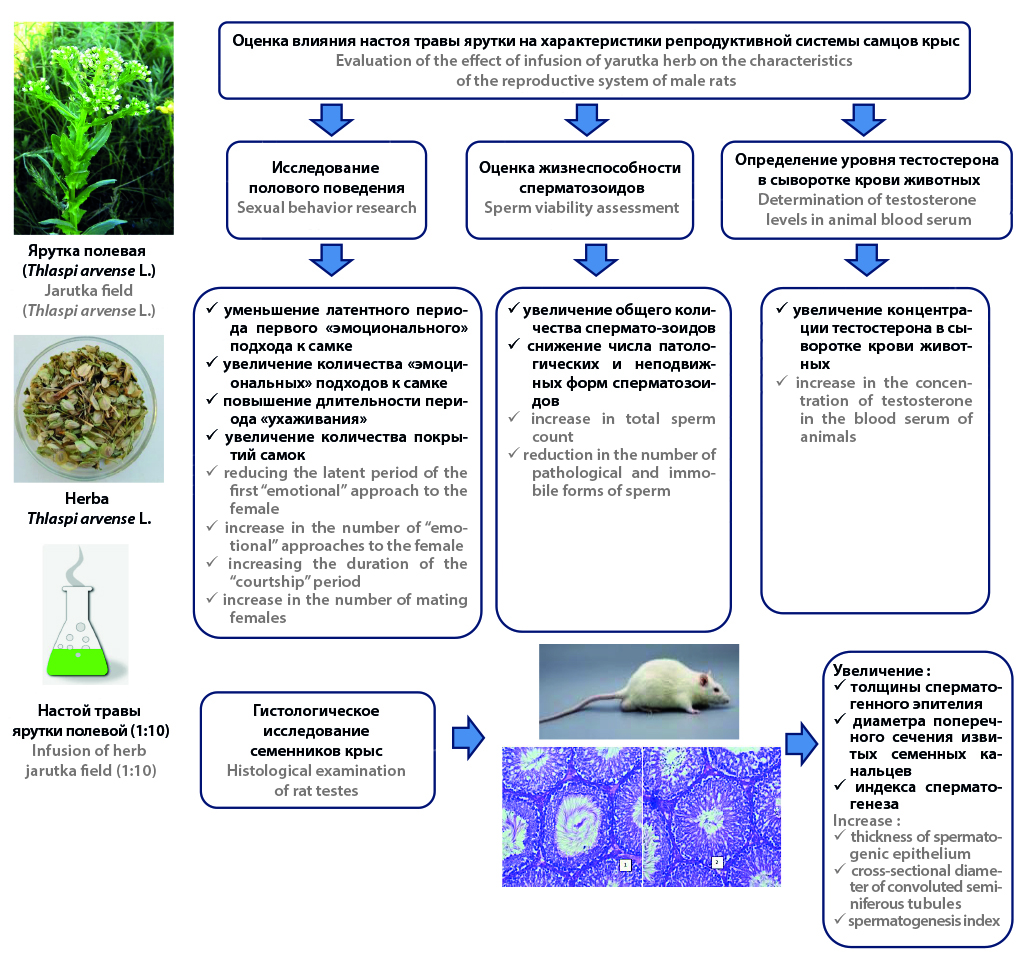
Introduction. The development of new effective and safe herbal medicines capable of having a positive effect on reproductive status is an urgent task of domestic pharmacy. Medicinal plants are considered as alternative therapies aimed at increasing testosterone levels and fertility in men. The arsenal of medicinal plants used in traditional medicine for the treatment of diseases in men is mainly represented by phytoadaptogens, most of which have a small resource potential in Russia, therefore, it is relevant to search for plants with a sufficient raw material base and with the potential for cultivation. Thlaspi arvense L. is a promising medicinal plant, as it is widely used in folk medicine as a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, diaphoretic, antihistamine, hemostatic, astringent, has a positive effect on the processes of spermatogenesis and is widely distributed in our country. However, information on the chemical composition and biological activity of Thlaspi arvense L. they are insufficient, which shows the relevance of its further more detailed study in order to substantiate the possibility of application in practical medicine and solutions to the issues of standardization of medicinal plant raw materials.
Aim. The study of the influence of Thlaspi arvense L. on the characteristics of the reproductive system of male rats.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was an infusion of herbа Thlaspi arvense L. The features of the reproductive behavior of male rats after 21-day administration of the infusion of grass yarutka field were studied using tests that allow quantifying the severity of sexual motivation and sexual activity of males. The viability of spermatozoa in the ejaculate of rats was assessed, the total number of spermatozoa (ACS, million), degenerative and immobile forms (%) was calculated. Morphophysiological parameters of spermatogenesis of rats of control and experimental groups of animals were studied using classical histological methods. The concentration of testosterone in the blood serum of experimental groups of animals was determined by the enzyme immunoassay.
Results and discussion. The results obtained allow us to conclude that the fertility of rats has increased against the background of the course administration of the infusion of herbа Thlaspi arvense L., as evidenced by an increase in the testosterone content in the blood, improvement of spermogram indicators and morphophysiological characteristics of spermatogenesis in the testicles of rats. The use of the infusion of herbа Thlaspi arvense L. has a protective effect on spermatogenesis. An increase in the thickness of the spermatogenic epithelium, the diameter of the cross-section of the convoluted seminal tubules and the index of spermatogenesis compared with the control group of animals was revealed. The positive effect of Thlaspi arvense L. on indicators of sexual motivation and sexual activity of male rats is shown.
Conclusion. Thlaspi arvense L. is a promising medicinal plant, as it is able to have a positive effect on libido, the number and mobility of spermatozoa, the production of sex hormones, spermatogenesis, as well as on the pituitary-gonadal axis, which is associated with the content of a complex of biologically active substances in it.
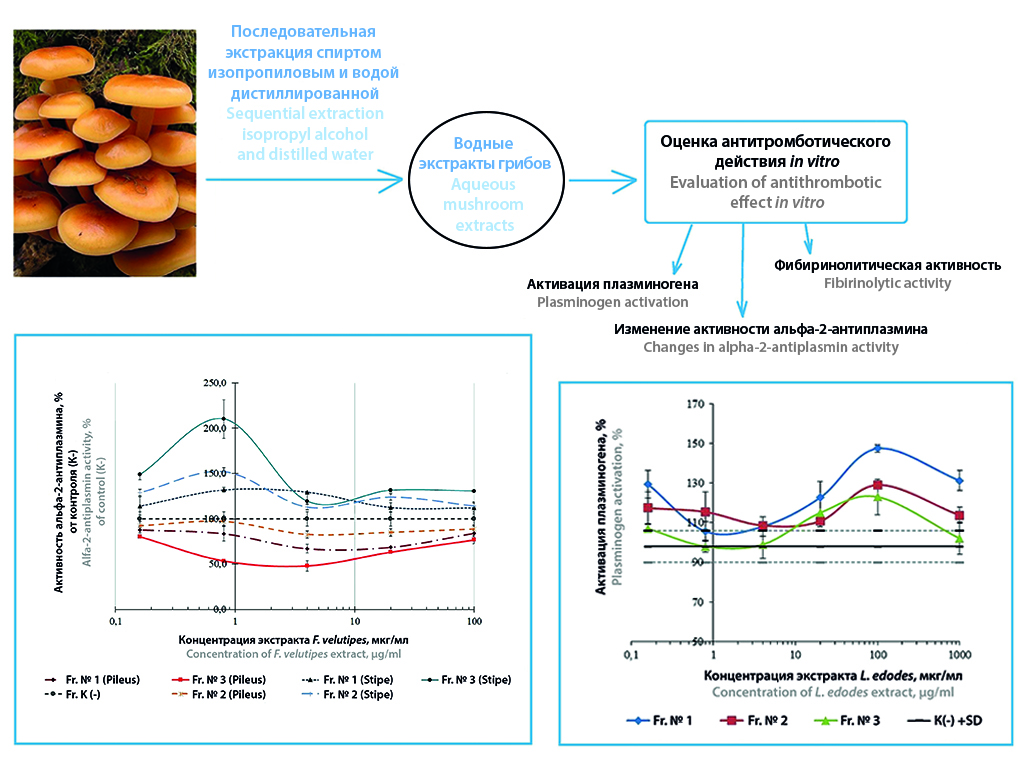
Introduction. Various compounds of mushroom extracts are of interest as a source of new active pharmaceutical substances with antithrombotic activity.
Aim. The aim of the work is to determine the potential antithrombotic activity in vitro of aqueous extracts of xylotrophic mushrooms: Lentinula edodes, Pholiota squarrosa, Flammulina velutipes (Curtis) Signer, Kuehneromyces mutabilis, Armillaria cepistipes, Armillaria borealis, Hypholoma capnoides, Lentinellus cochleatus, Léccinum aurantíacum, Pleurotus ostreatus.
Materials and methods. The study of fibrinolytic activity of water extracts of mushrooms in vitro was carried out. The effect of test objects on plasminogen activation, on the activity of enzyms of the fibrinolysis system α2-antiplasmin, on the time of euglobulin clot lysis and on the concentration of fibrinogen was evaluated. For the analysis we used reagent kits of SPD «RENAM» and LLC Company «Тechnology-Standard» (Russia).
Results and discussion. Pronounced antithrombotic activity is demonstrated by an aqueous extract of L. edodes and fractions of aqueous extract. Extracts of L. edodes affect all studied parameters of fibrinolysis to varying degrees. Caps and stems of P. squarrosa, K. mutabilis, and F. velutipes aqueous extracts and fractions of aqueous extracts also demonstrate antithrombotic (fibrinolytic) activity in vitro, having a statistically significant effect on various parameters of fibrinolysis. A less pronounced effect on fibrinolysis parameters in comparison with the above samples is observed when using an aqueous extract of L. cochleatus marked. A. cepistipes, A. borealis, H. capnoides, L. aurantiacum, P. ostreatus fruiting bodies aqueous extracts do not affect the studied parameters of fibrinolysis and the concentration of fibrinogen.
Conclusion. The data obtained make it possible to recommend extracts from L. edodes, F. velutipes, P. squarrosa and K. mutabilis for further study, for example, in order to develop functional food products for cardiovascular diseases or to create antithrombotic drugs.
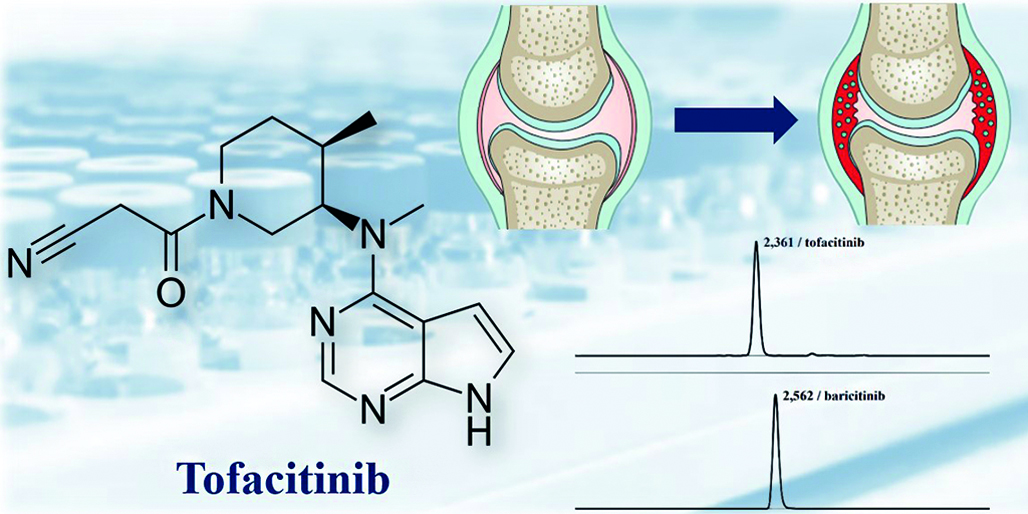
Introduction. The use of tofacitinib as a pharmacological treatment for rheumatoid arthritis remains relevant in the light of the predicted increase in prevalence of the disease. At the same time, due to the withdrawal of several foreign pharmaceutical companies from the Russian pharmaceutical market, there has been a heightened demand for domestically produced medications, including generic formulations of tofacitinib. Registration of generic drugs necessitates the conduct of bioanalytical studies. Development and validation of a method for quantifying the analyte in biosamples remains to be a crucial part of the bioequivalence studies.
Aim. The aim of this research is to develop and validate a method for the quantitative determination of tofacitinib in human plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography as the separation system coupled with a tandem mass spectrometer for detection purposes.
Materials and methods. Biosample preparation was based on plasma proteins precipitation using acetonitrile. Baricitinib was selected as an internal standard. The analytical range of the method was 1.00 to 200.00 ng/mL and was further expanded to 0.30 to 200.00 ng/mL during the analytical phase of the study. The mobile phase consisted of water and acetonitrile, both acidified with formic acid (0.1 % v/v). The stationary phase was a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 column [100 × 3.0 mm, with a particle size of 5 µm (Phenomenex, USA)]. Sample separation and detection were carried out using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS), operating in positive ion mode. The multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions selected for the analyte and the internal standard were 313.30 to 173.00 m/z and 371.90 to 186.00 m/z, respectively.
Results and discussion. The developed assay was validated in accordance with the current requirements of regulatory documentation from the EAEU (Eurasian Economic Union), FDA (US Food and Drug Administration), and EMA (European Medicines Agency) with the following parameters being evaluated: selectivity, specificity, carry-over, matrix effect, recovery, calibration curve, lower limit of quantitation, accuracy, precision, stability. The validated method was applied in the analytical part of a bioequivalence study of domestically produced generic tofacitinib.
Conclusion. A method for the quantitative determination of tofacitinib in human blood plasma with an analytical range of 0.30–200.00 ng/mL was developed and validated. Application of the assay during the analytical phase of bioequivalence study of generic tofacitinib confirms the possibility of using the method in similar bioanalytical investigations.
REGULATORY ISSUES
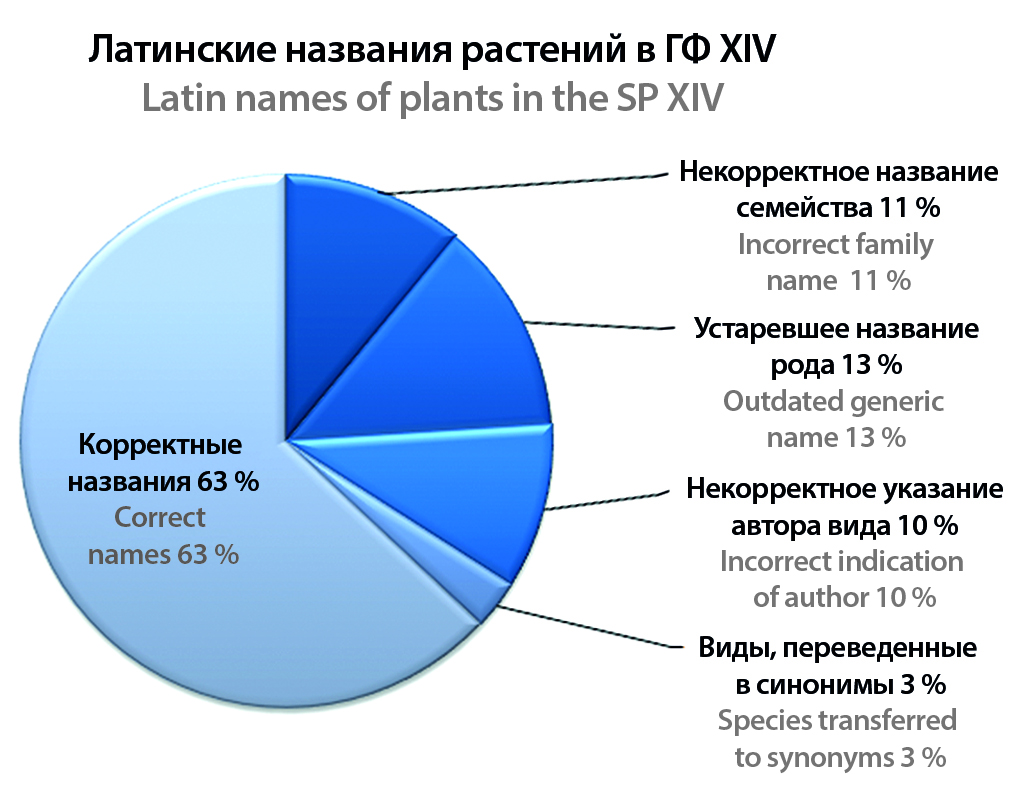
Introduction. The State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XIV-th edition (SP XIV), includes 107 monographs devoted to medicinal plant materials. The purpose of the study was to identify incorrect Latin names of medicinal plants in the monographs of the XIV edition, study the officially accepted Latin names and taxonomic position of medicinal plants in accordance with the contemporary system of flowering plants, and justify the need to make changes in subsequent editions of the pharmacopoeia.
Text. 44 cases of incorrect Latin names were found. This is explained by the fact that when developing new pharmacopoeia monographs, either Latin names historically established in Russian pharmacognosy were used, or names that were legal at the time of the last edition of the Pharmacopoeia. The bulk of nomenclatural changes are associated with the adoption of the new APG system of flowering plants, based on molecular genetic data. The paper contains lists of plants for which the State Pharmacopoeia XIV contains an incorrect name of the genus, species, family or author, indicating the correct name, as well as comments on the rules of modern botanical nomenclature.
Conclusion. In connection with the prospects for processing monographs on medicinal plant raw materials for the State Pharmacopoeia XV-th edition, as well as the EAEU Pharmacopoeia, the harmonization of the nomenclature of pharmacopoeial plants with modern international requirements becomes especially relevant.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)