Research and production peer-reviewed journal «Drug development & registration» (Razrabotka i registraciâ lekarstvennyh sredstv) is an up-to-date free application publication and information portal for Professionals involved in the circulation of medicines.
Journal is designed for pharmaceutical manufacturers and their employees from the departments of development, quality control, registration, production and development; employees of laboratory centers, contract research organizations, scientific and educational institutions. It is included in the VAK list of peer-reviewed scientific journals, in which the main scientific results of dissertations for the degree of candidate of science, for the degree of doctor of science should be published.
The main five thematic sections of the journal «Drug development & registration» (Razrabotka i registraciâ lekarstvennyh sredstv) include the development cycle of a medicinal product from its creation to obtaining a marketing authorization. The first section is devoted to the research and development of new medicines, the second provides information about pharmaceutical technology, pharmaceutical ingredients, and equipment for drug development. The third section describes analytical quality control methods; the fourth section is devoted to approaches to evaluating the efficacy and safety of medicines, conducting clinical and preclinical studies. The fifth section deals with the validation of methods, preparation of the registration dossier, the life cycle of the drug product in the GxP environment.
Current issue
FROM EDITOR
February 17–18, 2026, Moscow will host the annual two-day congress "Drug development and registration". The congress's topics traditionally cover all key stages of a drug's life cycle, from development to post-registration studies.
As part of the 10th Pan-Russian GMP Conference, a session was held dedicated to regulatory science issues in the field of high-tech pharmaceuticals in the Russian Federation.
An open discussion on the localization of CAR-T cell therapy drugs in the Russian Federation was held with the participation of representatives of the State Duma, federal executive bodies, the expert community, the pharmaceutical industry, and leading medical centers. It took place on October 6–7 as part of the BIOPROM: Industry and Technology for Humans conference.
In a new interview from the "Leadership Opinion" series, we spoke with Maria B. Verbitskaya, Commercial Director of AICS LAB, and Dr. Parag Gadkari, Chief Scientific Advisor of Electrolab India Pvt Ltd. and Igor Shokhin, General Director of the Center of Pharmaceutical Analytics.
The article provides facts about the state of the USSR's vitamin industry in the pre-war years of the Great Patriotic War. It lists the research and production organizations involved in the study and production of vitamin products. The article presents the results of experiments on working with medicinal plant raw materials and stabilizing aqueous solutions with vitamin C. It also describes a method for purifying solutions of ascorbic acid obtained from pine needles. The article examines the vitamin C content in various types of medicinal plants of the rosehip genus during the ripening process. The article describes methods for enriching fish oil with vitamin A from zander liver and extracting carotene from waste products of ascorbic acid production. It also presents the history of the discussion and approval of domestic vitamin K at a meeting of the Pharmacological Committee of the USSR Ministry of Health.
PHARM-AKTIV PRO provides a comprehensive approach to equipping pharmaceutical and laboratory facilities. We understand supply as a full cycle, from design and selection of optimal solutions to commissioning, qualification, and support throughout the entire lifecycle. All in accordance with drug registration requirements, process validity, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
EVENTS
On September 19, 2025, a landmark event for pharmaceutical industry specialists took place at the Kalibr Technopark: a master class dedicated to current aspects of drug development and registration. The event will focus on master classes from experts at the Center for Pharmaceutical Analytics, focusing on issues related to conducting registration laboratory studies.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
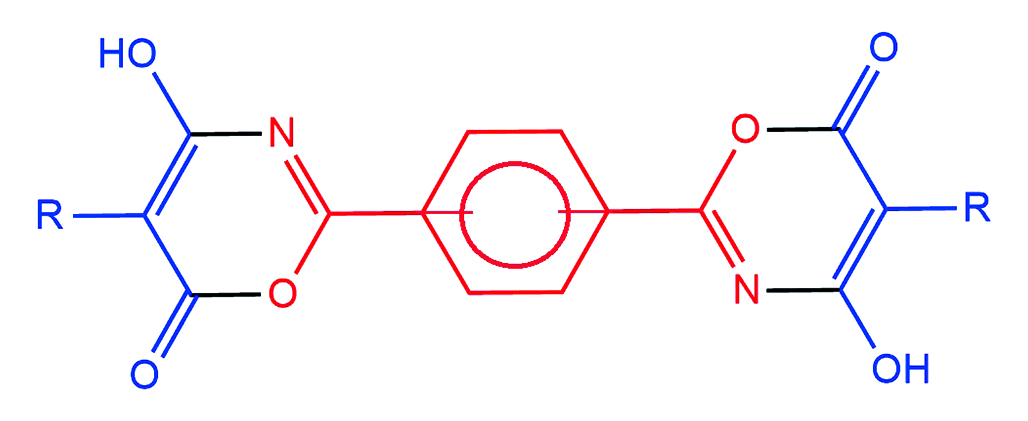
Introduction. The study of 1,3-oxazine derivatives plays a crucial role in the field of heterocyclic chemistry. However, there is a lack of systematized information in the literature regarding the synthesis methods of bis-derivatives of 1,3-oxazin-6-ones. The development of efficient methods for obtaining these oxazines, as well as the study of their structure, properties, and biological activity, represents a promising direction for both medicinal chemistry and the pharmaceutical industry.
Aim. To develop a laboratory method for the synthesis of bis(4-hydroxy-6H-1,3-oxazin-6-ones) based on the reaction of benzene-1,3-dicarboxamide and benzene-1,4-dicarboxamide with substituted malonyl chlorides, and to confirm their structure using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy on 1H and 13C nuclei.
Material and methods. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AM-600 spectrometer in deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6), and their processing was carried out using ACD/Labs software. The progress of the reactions was monitored using thin-layer chromatography on plates coated with silica gel TLC Silicagel 60 F254 using ethyl acetate as the eluent and detection in ultraviolet (UV) light. The synthesis procedure included suspending 1 mmol of terephthalic or isophthalic acid diamide in absolute 1,2-dichloroethane, adding 2,4 mmol of substituted malonyl chloride and refluxing the mixture for 15 hours. The end of the reaction was determined by the absence of the initial diamides in the reaction mass by thin-layer chromatography.
Results and discussion. As a result of the study a laboratory method of the synthesis of bis(4-hydroxy-6H-1,3-oxazine-6-ones) with phenylene bridges between heterocyclic fragments was developed. The use of absolute 1,2-dichloroethane as a solvent made it possible to increase the yield of the target compounds by 5–7 % and reduce the synthesis time by 5 hours compared to absolute benzene. The structure of the obtained compounds was proved by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy on 1H and 13C nuclei. The spectra of the obtained compounds contain all the characteristic signals corresponding to bis(4-hydroxy-6H-1,3-oxazine-6-ones).
Conclusion. A laboratory method for the synthesis of bis(4-hydroxy-6H-1,3-oxazin-6-ones) has been developed, implemented, and optimized based on the reaction of benzene-1,3-dicarboxamide and benzene-1,4-dicarboxamide with monosubstituted malonyl chlorides. The target compounds were obtained in absolute 1,2-dichloroethane with yields close to quantitative, confirming the efficiency of the developed approach. The structure of all obtained bis(4-hydroxy-6H-1,3-oxazin-6-ones) was reliably established using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy on 1H and 13C nuclei.
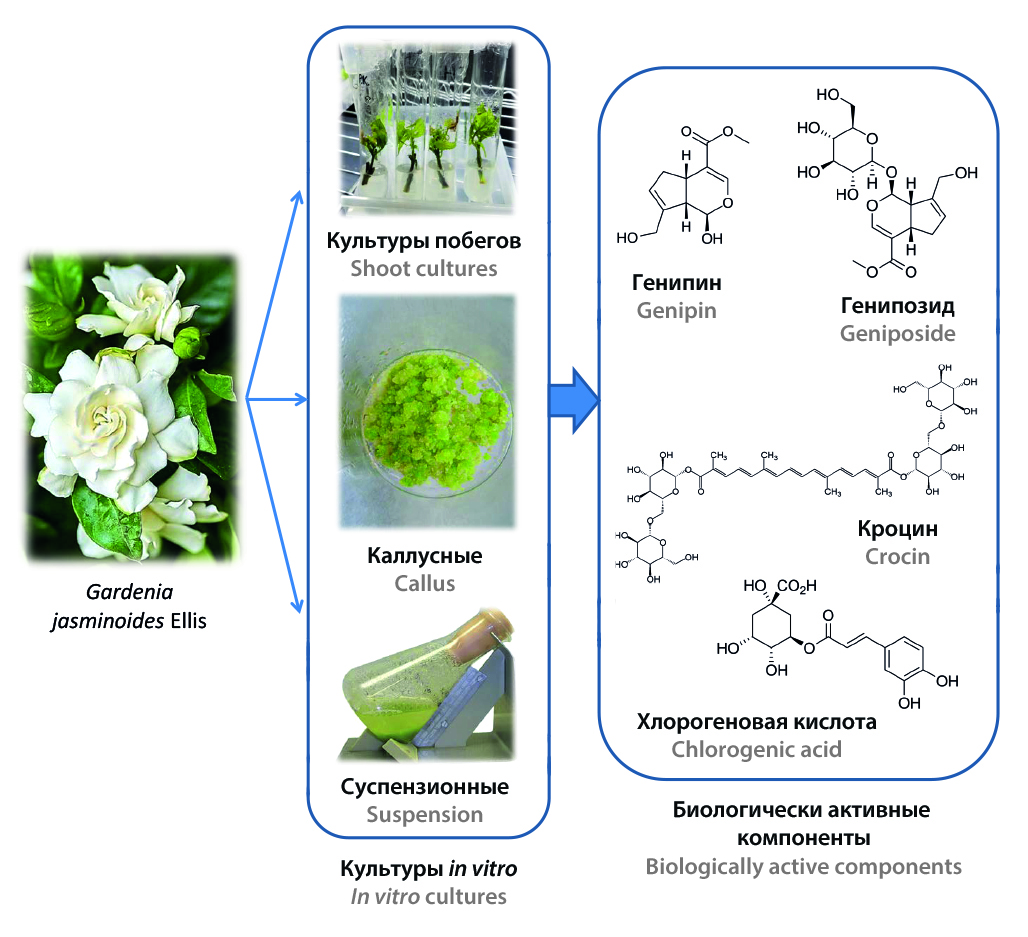
Introduction. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis is an evergreen shrub of the Rubiaceae family, naturally growing in China and Japan, and cultivated as an ornamental plant in many regions of the world. This review presents data on the results of studies of the accumulation of biologically active substances in various in vitro cultures, the possibility of inducing their biosynthesis, and the biological activity of substances isolated from Gardenia jasminoides cell cultures.
Text. To date, about 162 compounds have been isolated and identified from G. jasminoides, including flavonoids, iridoid glycosides, gardenia yellow pigment, monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, triterpenoids, organic acids and their derivatives. The most important biologically active constituents of G. jasminoides are iridoid glycosides and yellow pigments – crocin derivatives. The use of plant cell cultures is one of the most promising approaches to obtaining biologically active substances of plant origin, since this method is characterized by less dependence on climatic and environmental factors, provides more precise process control and allows for a shorter production cycle, which contributes to the effective scaling of production. A number of researchers have obtained callus and suspension cultures, as well as shoot and modified root cultures of G. jasminoides. In order to increase the production of the main classes of biologically active substances – iridoid glycosides, polyphenolic compounds and carotenoids in callus, suspension and shoot cultures of G. jasminoides, a number of studies were conducted on the introduction of specific additives into nutrient media. It was shown that G. jasminoides cell cultures have high antioxidant activity due to phenolic compounds such as ferulic and chlorogenic acids. Callus culture extracts showed significantly greater superoxide dismutase activity than leaf extracts. At the same time, only callus culture extracts exhibited antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus.
Conclusion. A review of the literature data allows us to conclude that in vitro G. jasminoides cultures provide stable and enhanced production of valuable secondary metabolites (iridoid glycosides, polyphenols, carotenoids), exceeding the indicators of intact plants, which opens up prospects for the industrial production of biologically active substances and phytopreparations.
Introduction. In recent years, the use of medicinal plants in therapeutic and prophylactic preparations capable of regulating adaptive modifications aimed at maintaining human mental and physical functions in the face of constantly changing natural and social factors has become increasingly important. One interesting plant for medicinal use is Rhodiola rosea L., a member of the Crassulaceae family. This species is highly polymorphic both morphologically and chemically. The main raw material sources are the mountains of southern Siberia (Altai, Sayan), Tuva, and Transbaikalia. However, domestic raw material sources are insufficient, making it necessary to expand them and identify phenotypes with high levels of biologically active substances among cultivated populations.
Aim. To establish the morphometric characteristics of different phenotypes of Rhodiola rosea cultivated in Northwest Russia and to conduct a comparative analysis of secondary metabolites in samples of underground organs of Rhodiola rosea of different phenotypes using high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC).
Materials and methods. The study subjects were 24 samples of Rhodiola rosea rhizomes and roots of various phenotypes, collected in 2024 during the flowering and fruiting phases at the medicinal plant nursery of the St. Petersburg Chemical and Pharmaceutical University (Leningrad Region, Vsevolozhsk District, 38 km of Priozerskoye Highway). Extracts from the raw materials were obtained using a Sapphire-4.0-TTC ultrasonic bath (Russia). 70 % ethyl alcohol was used as the extractant. HPTLC analysis was performed on a CAMAG instrument (Switzerland) using MERCK HPTLC plates silica gel 60 F 254 (20 × 10 cm).
Results and discussion. 70 % ethyl alcohol was used as the extractant. The resulting solutions were analyzed by HPTLC in a solvent system of chloroform, 96 % alcohol, and water (25 : 16 : 1). After scanning densitometry at 254 nm, the densitograms of individual tracks were compared to identify Rhodiola rosea phenotypes with higher levels of biologically active compounds. A comparison of the tracks of 24 Rhodiola rosea underground organ samples revealed female samples (No. 1, 7, 8 and 14) and male (No. 15, 18, 21, 23 and 24) samples, ranging in height from 23 to 41 cm, were proposed as promising for further study and cultivation.
Conclusion. Morphometric characteristics of various phenotypes of Rhodiola rosea cultivated in the north-west of Russia were established. HPTLC analysis of alcohol extracts from Rhodiola rosea rhizomes and roots of different phenotypes revealed both female and male samples had higher levels of secondary metabolites (phenylpropanoids and simple phenols). The height of the plants ranged from 23 to 41 cm.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
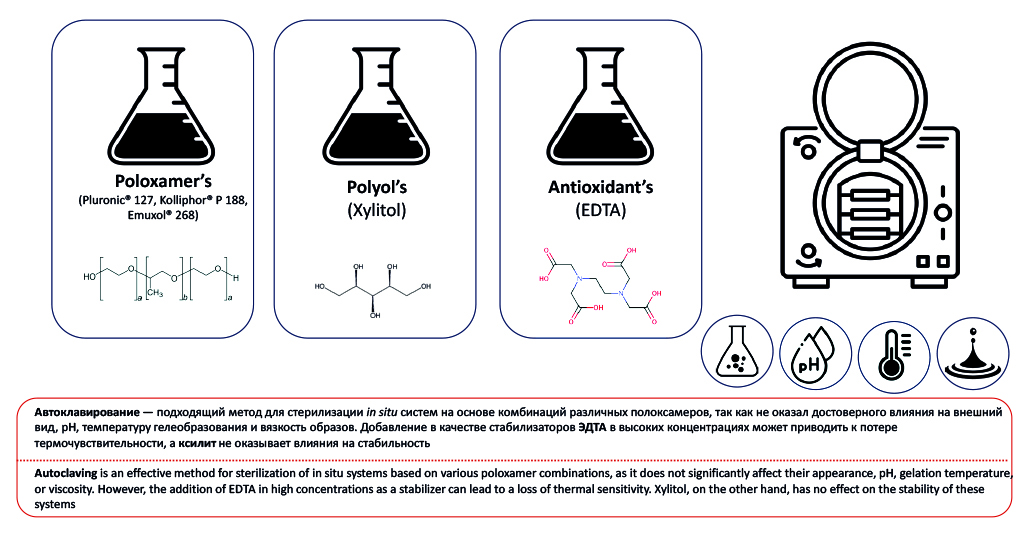
Introduction. Parenteral and ophthalmic in situ systems must be sterile. The selection of sterilization method is a key step in the development of sterile stimuli-sensitive systems, as an inappropriate method can lead to the degradation of the gel-forming polymer and the API, resulting in a loss of activity. Unfortunately, the stability of poloxamer-based thermosensitive systems during sterilization, as well as methods for their stabilization using protective agents, remains insufficiently studied.
Aim. The aim of the study was to investigate the stability of poloxamer-based systems during autoclaving and to develop methods for protecting them from the adverse effects of sterilization.
Materials and methods. Poloxamers used in the experiment included Kolliphor® P 407, Kolliphor® P 188, Kolliphor® P 338, and Kollisolv® P 124 (BASF, USA), as well as Emuxol-268 and Proxanol-168, provided by JSC "NIOPIK" (Russia). Disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (LLC PCF "KhimAvangard", Russia) and xylitol ("Sladkiy Mir" LTD, Russia) were selected as protective agents. The samples were autoclaved at 121 °C for 20 minutes. Stability was evaluated based on the following parameters: appearance, pH, kinematic viscosity, and sol-gel transition temperature.
Results and discussion. Autoclaving of various combinations of poloxamers had a negligible effect on the stability parameters of the formulations. The addition of EDTA at high concentrations led to an increase in viscosity, as well as a decrease in pH and gel-forming ability of the formulations. After sterilization, gel precipitation was observed in all samples containing EDTA, but the original appearance of the formulations was restored within 5 days. The other parameters remained stable after autoclaving. The addition of xylitol had a negligible effect on the initial properties of the poloxamers, and the formulations retained stability after sterilization.
Conclusion. The results of the experiments showed that autoclaving is a suitable method for sterilization of systems based on various combinations of poloxamers. The addition of EDTA, especially at high concentrations, should be avoided due to its negative impact on the key parameters of in situ systems and the risk of gel precipitation during autoclaving. Xylitol does not affect the stability of poloxamers during sterilization. However, further research is needed to evaluate the potential of EDTA and xylitol as protective agents for the stabilization of other stimuli-sensitive systems.
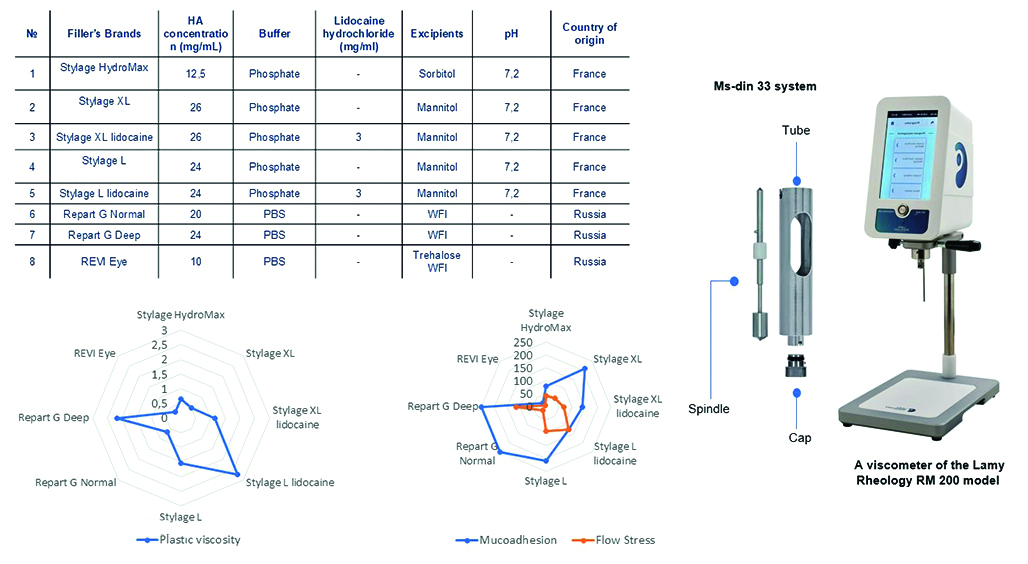
Introduction. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a polysaccharide belonging to glycosaminoglycans. Due to its high biocompatibility and ability to retain moisture, HA is widely used in cosmetology and medicine. The popularity of HA-based gels is growing, especially in injection cosmetology for the correction of age-related changes, making up a significant part of aesthetic procedures. As a result of the departure of foreign manufacturers from the Russian market, there is a need to develop domestic analogues. The study of the rheological properties of gels helps to optimize formulations for medical use, ensuring the effectiveness and safety of new products.
Aim. To study how the concentration of HA and excipients affect the rheological properties of gels. The study is also aimed at identifying the relationship between these properties and clinical effectiveness.
Materials and methods. Objects of study: fillers of the Stylage® line – Stylage® HydroMax, Stylage® L, Stylage® L lidocaine, Stylage® XL, Stylage® XL lidocaine, and Repаrt® Ġ line – Repart G Normal, Repart G Deep. The samples were examined by rotational viscometry.
Results and discussion. We established a relationship between the clinical characteristics of liquid implants and their rheological properties. In the course of the studies, we determined the following optimal ranges: mucoadhesion – from 100 to 200 Pa, plastic viscosity – from 0,2 to 1,0 Pa ∙ s at a shear rate of 0–100 s–1 at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C, flow stress – from 50 to 150 Pa at a shear rate of 0–100 s–1 at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C, thixotropy – complete.
Conclusion. As a result, the study showed that viscosity is important for injection and distribution of the drug in tissues. High mucoadhesion in gynecology and urology determines the fixation of the implant in the tissues. However, excessive mucoadhesion can cause the formation of subcutaneous agglomerates, which limits the use of such products on the face. The relationship between the flow stress and the quality characteristics of the implants was not established.
Introduction. In vitro equivalence dissolution test is one of the main tests in drug development. In vitro equivalence dissolution test models the bioavailability of the active substance under the conditions of its use, allowing to assess the bioequivalence of drugs. The article describes an approach in which the results of in vitro equivalence dissolution test are used as a basis for obtaining a drug that differs in pharmaceutical dosage form and composition from the referent drug.
Aim. To select a composition of vaginal tablets that would be equivalent to suppositories on a lipophilic base according to in vitro equivalence dissolution test.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are vaginal tablets and suppositories on a lipophilic base containing natamycin. The study was conducted using dissolution tester (the "Basket" apparatus) and a UV spectrophotometer to calculate the amount of released natamycin.
Results and discussion. The authors proposed an approach in which the development of a new dosage form of natamycin (vaginal tablets) is based on the development of similar to lipophilic base vaginal suppositories registered in the EAEU release profiles. For carrying out in vitro equivalence dissolution test, the authors developed samples of vaginal tablet formulations. The composition was selected to obtain a set of results with different release profiles and select the most optimal one both in terms of profile equivalence with the reference drug and the technological effectiveness (ease of introduction into production and cost-effectiveness of drug production) of the resulting composition. The formulations were selected to provide a set of release profiles that could be further compared with the reference. The objects of study were analyzed using a «Dissolution» test («Basket» apparatus), the released natamycin was monitored by UV spectrophotometry.
Conclusion. In vitro equivalence dissolution test was carried out for vaginal tablets containing natamycin, and the most promising formulation that meets the stated requirements for equivalence of release profiles was selected.
Introduction. Hepatoprotectors are one of the broad drug groups used in complex therapy at different stages of liver damage. In clinical practice, hepatoprotective agents are used in form of individual or combined drugs. A combined drug is defined as a preparation containing two or more active biological substances that act together in the human body to prevent and treat diseases or to restore and maintain health. Combined drugs are used to increase the treatment effectiveness, reduce side effects, simplify medication intake, or help to treat multiple symptoms at the same time. Often the following well-known hepatotropic agents are most studied and used in combinations: essential phospholipids, glycyrrhizic acid, ursodeoxycholic acid and silymarin. It should be noted that although the pharmacological action of ursodeoxycholic acid and milk thistle preparations has been well studied, no technological research has been conducted to create combined medicines based on them.
Aim. Development of a technology for a combined hepatoprotective agent in form of solid enteric-soluble gelatin capsules with granules containing ursodeoxycholic acid and milk thistle dry extract in form of a solid dispersion system as active substances.
Material and methods. Ursodeoxycholic acid and the solid dispersion system of milk thistle dry extract are included as substances in the formulation of the combined hepatoprotective drug. Solid intestinal-soluble gelatin capsules were filled with granules containing a solid dispersion system of milk thistle dry extract and ursodeoxycholic acid using a ProFiller 3600 desktop manual capsule filling machine, capsule size "2". 3 series of solid gelatin capsules with granules were developed. The capsules standardization was carried out in accordance with the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV edition. The following indicators were determined: description, authenticity, quantitative content of the amount of flavolignans in terms of silybin, quantitative content of ursodeoxycholic acid, mass uniformity of dosage forms, disintegration and dissolution.
Results and discussion. The granules formulation was developed by wet granulation, microcrystalline cellulose as disintegrator, magnesium stearate as lubricant, and 5 % aqueous solution of potato starch were used as excipients. The obtained formulations were compared in terms of quality and technological properties. It was found that granules containing microcrystalline cellulose have the best technological properties, such as weight loss during drying, hygroscopicity, bulk density, Carr index, Hausner coefficient, flowability. For capsules with granules, quality indicators were determined and standardized according to the POA (pharmacopeia official article) "Capsules" in terms of quality indicators: description, authenticity, quantitative content of the amount of flavonoids in terms of silybin, quantitative content of ursodeoxycholic acid, mass uniformity of dosage forms, disintegration and dissolution. When performing the "Dissolution" test, the release of silybin and UDCA was determined in 30, 45 and 60 minutes. The release of silybin was monitored by spectroscopy at a wavelength of λ = 289 nm and the release of ursodeoxycholic acid by high–performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in accordance with the US pharmacopoeia, USP 44 – NF 39. It was determined that 89.0 ± 0.5 % of silybin was released in 45 minutes, during which time 97.0 ± 0.3 % of ursodeoxycholic acid was released.
Conclusion. The granules formulation with a solid dispersion system of milk thistle dry extract and ursodeoxycholic acid has been developed. Microcrystalline cellulose is used as disintegrant, magnesium stearate as lubricant, and 5% aqueous solution of potato starch as binder. The technological properties of the granules and quality indicators are determined. The technology of intestinal-soluble capsules filled with granules has been developed. The quality indicators were determined and standardized according to quality indicators: description, authenticity, quantitative content of the amount of flavonoids in terms of silybin (by UV spectroscopy), quantitative content of ursodeoxycholic acid (by HPLC), mass uniformity of dosage forms, disintegration and dissolution. The releasing profiles of the active pharmaceutical substance from enteric capsules were studied and it was found that 89.0 ± 0.5 % of the amount of flavolignans in terms of silybin and 97.0 ± 0.3 % of ursodeoxycholic acid were released by 45 minutes, respectively, which meets the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV edition.
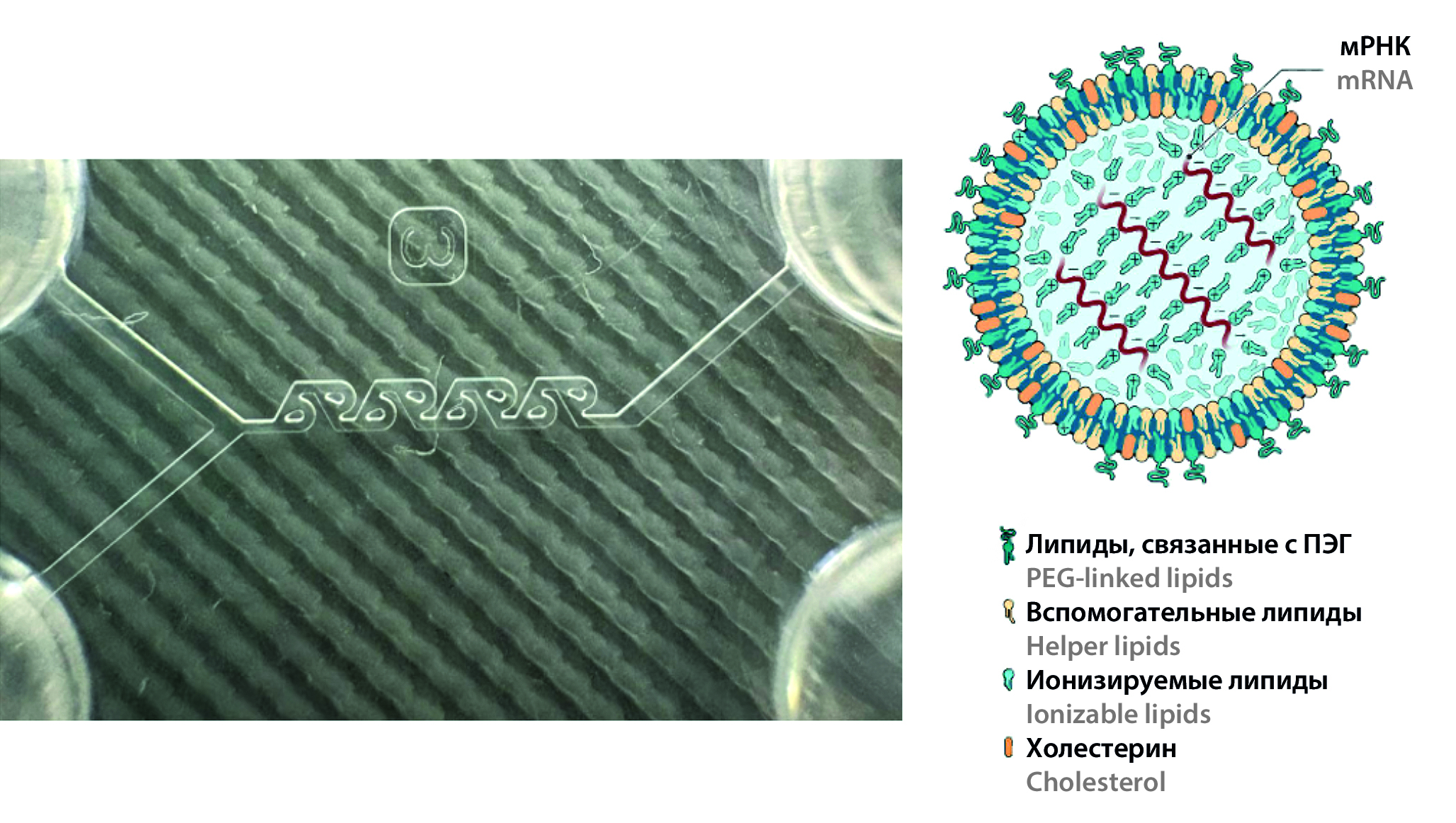
Introduction. Gene therapy is actively developing through the use of mRNA agents for the treatment and prevention of various diseases. To manifest a therapeutic effect, it is necessary to deliver mRNA to target cells and induce the synthesis of target proteins. Key challenges include developing safe and efficient delivery systems. The critical quality attributes for lipid nanoparticles are average particle size, polydispersity index, and ζ potential.
Aim. To study and optimize the assembly conditions of lipid nanoparticles to control their basic characteristics.
Materials and methods. Ionizable lipid heptadecan-9yl(Z)-N-((4-dimethylamino)butyl)thio)carbonyl)-N-(2-(non-2-en-1-yloxy)-2-oxoethyl)glycinate (IL) and helper lipids – dipalmitoylglierophosphate (DPPC), cholesterol, and a-(3"-[1,2-di (myristyloxy) propanoxy]carbonylamino}propyl)-w-methoxypolyoxyethylene (DMG-PEG2000). Solvents: absolute alcohol, purified water. Buffer solutions: acetate buffer solution (pH 4.5), phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.4). Equipment: microfluidic installation Dolomite (Dolomite Microfluidics, Великобритания), Y-shaped polymer microfluidic chip with passive micromixer type "tesla coil", Nanosizer Zeta Pro nanoscale particle analyzer (LLC "Microtrack", Russia).
Results and discussion. The study examined the effects of TFR and FRR parameters on LNF properties. Characteristics such as hydrodynamic diameter (Z-average), average particle diameter (D50), polydispersity index (PDI) and ζ potential were analyzed. The study confirms that with increasing FRR, the average hydrodynamic and median particle sizes decrease. Increasing TFR also decreases Z-average and D50 through hydrodynamic focusing, but at TFR = 3200 μl/min, particle size increases due to decreased nanoemulsion stability and fine particle aggregation. The study did not reveal a direct relationship between FRR and PDI. Nanoemulsions with FRRs of 1 : 3 and 1 : 4 showed the greatest homogeneity. As TFR increases, the polydispersity of the nanoparticles decreases. In the study, the dependence of the ζ potential of lipid nanoparticles on the estimated process parameters was not found. However, as TFR increases, the ζ potential tends to increase.
Conclusion. In the study, the conditions for assembling lipid nanoparticles (LNP) using the microfluidic method were optimized. Mathematical models are proposed to control characteristics of nanoparticles. Optimal conditions for producing LNP: FRR = 1 : 3; 1 : 4; TFR 2000 to 3000 µL/min. If FRR = 1 : 5 and/or TFR > 3000 µL/min are used, the values may be outside the optimal range, which requires additional risk assessment.
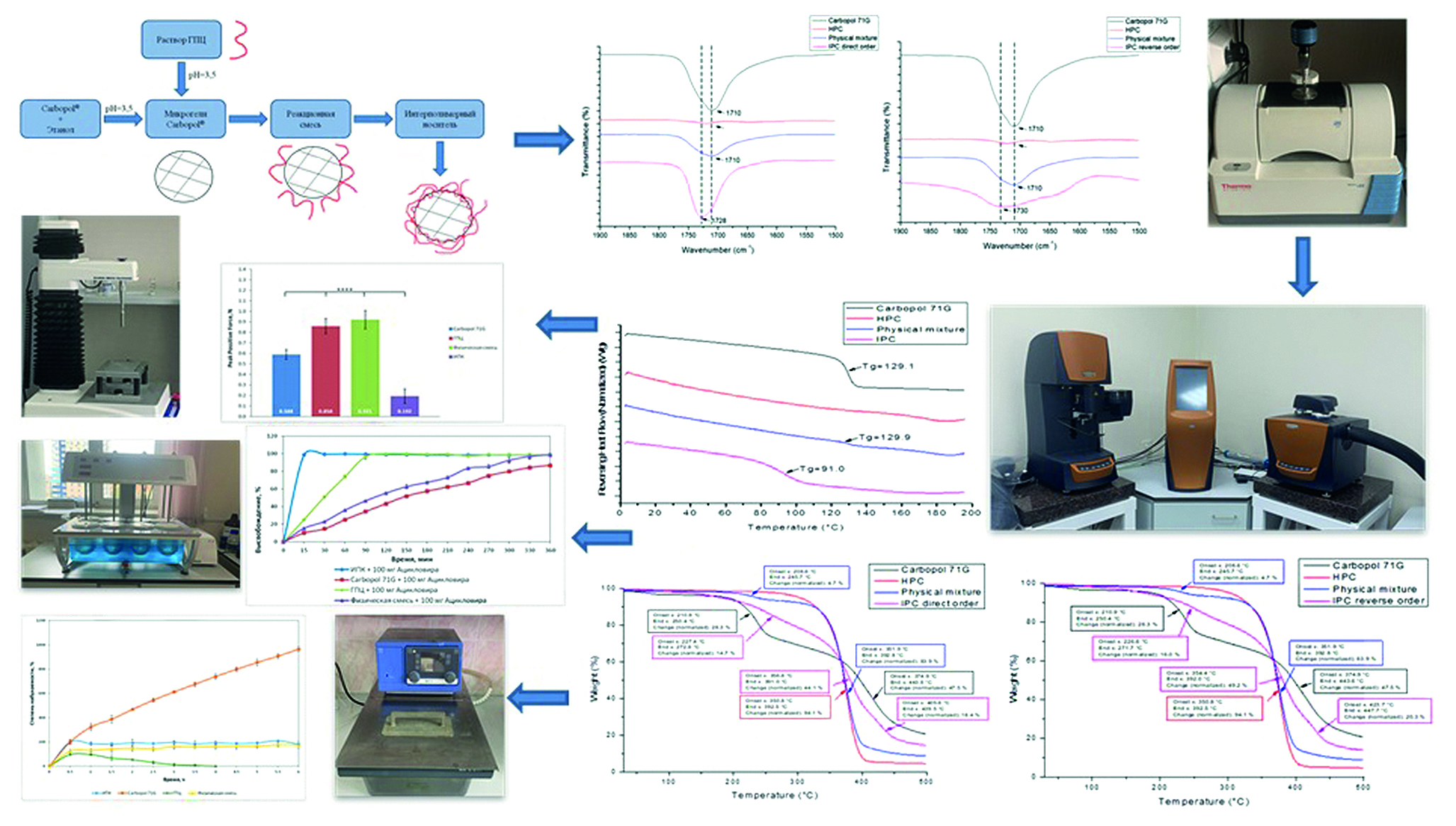
Introduction. As a result of the study, the process of formation of interpolymer complex (IPC) between pairs of polymers was studied between hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and different brands of Carbopol® 71G, 971, 974 at two mixing orders in 95 % ethanol at pH = 3,5 (acidified with 0,1 M HCl) by turbidimetry, IR-spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The performed experiments confirmed the formation of an interpolymer complex (IPC) between these pairs of polymers. According to the research results, the prospective ratio of a pair of HPC and Carbopol® 71G was selected in a stoichiometric equimolar ratio regardless of the mixing order. The compatibility of the studied polymers in the composition of the resulting polycomplex was confirmed, using the method of modulated differential scanning calorimetry (mDSC). The obtained IPC had a stoichiometric composition of Carbopol® 71G / HPC 2 : 1 (by moles), according to the elemental analysis. Swelling of matrices based on the synthesized IPC, as well as matrices from individual polymers and their physical mixture (PM), was carried out in a medium simulating stomach acid in comparison with the original polymers. The analysis of the of acyclovir release from the produced carriers was also carried out in a 0.1 M HCl media and showed the prospects of the developed system for creating a carrier with targeted release of drugs into a model environment simulating an empty stomach. The IPC samples showed low mucoadhesive properties compared to individual polymers and their physical mixture. The development of new carriers for drug delivery is one of the key areas of pharmaceutical technology. In this regard, special attention is paid to polymeric substances, carriers based on which provide a reduction in side effects, increased bioavailability and prolongation of the drug action. Gastroretentive delivery systems are of interest in the development of new dosage forms that allow regulating the rate of release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in the stomach.
Aim. Development of a polycomplex carrier based on hydroxypropyl cellulose with Carbopol® for gastroretentive delivery of acyclovir.
Materials and methods. The selection of IPC – formation conditions was carried out using the methods of turbidimetry, IR-spectroscopy, and TGA. The obtained optimal polycomplex carrier composition was characterized using modulated differential scanning calorimetry (mDSC) and IR-spectroscopy. The swelling of the matrices based on the synthesized polycomplex was studied in an environment that imitating stomach acid. The acyclovir release from the resulting matrices was studied in modeling media using method 1 (USP I) "basket method". Mucoadhesion was studied using a TA.XTplus texture analyzer (Stable Micro Systems, Surrey, UK) on mucin compacts.
Results and discussion. The formation of IPC occurs through the formation of hydrogen bonds between the —OH groups of macromolecular units of linear HPC and —COOH groups of rare-crosslinked polyacrylic acid (rPAA) in the composition of the used brands of Carbopol’s. The leftward shift of the characteristic band to 1730 cm–1 in the FTIR spectra of the polycomplexes confirms the formation of IPCs. The IPCs are characterised by a single glass transition temperature (Tg = 91,0 ± 2,1 ºC). Elemental analysis revealed a two-fold molar excess of the rare cross-linked polymer (Carbopol® 71G) over the linear one (HPC). Throughout the entire experiment to study the kinetics of swelling, the compacted matrices retain their shape, increasing in size. Monitoring of possible structural transformations was carried out, using thermal analysis of samples of polycomplex matrices in the process of assessing their swelling, to confirm the stability of the polycomplex in an acidic environment. According to the results of the model API release kinetics, the maximum concentration of acyclovir released into the media is observed at 30 minutes of the experiment and equal 98.5 %. Whereas for HPC matrices, the maximum concentration is achieved after 2 hours, and for matrices based on Carbopol® 71G and their PM only in the final part of the experiment. The synthesized IPC was characterized by low mucoadhesion capacity on mucin compacts compared to individual polymers and the PM.
Conclusion. As a result of the study, optimal conditions for IPC – formation between pairs of polymers HPC and different brands of Carbopol® (71G, 971 and 974) were selected. Turbidimetry, IR-spectroscopy and TGA methods proved the formation of polycomplexes based on HPC and various brands of Carbopol®. The IPC HPC / Carbopol® 71G of stoichiometric composition, confirmed by elemental analysis, was characterized using thermal and spectral methods. The study of the release of acyclovir from the obtained matrices has shown the promise of using the developed systems for oral gastroretentive delivery.
Introduction. Due to its broad spectrum of biological activity, trans-resveratrol is a promising candidate for the development of pharmaceuticals. However, its low aqueous solubility and chemical instability when administered orally limit its clinical use. Therefore, alternative delivery methods that limit the first-pass effect through the liver are promising.
Aim. Development and pharmacotechnological evaluation of resveratrol transdermal patches.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was the substance trans-resveratrol (DSM, Switzerland). Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) of various molecular weights (K-17, K-30, K-90, USP, Dalian Sinobio Chemistry Co., Ltd., China) and a copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate (BASF, Germany) were considered as carrier polymers that ensured the adhesion of the patches. Polyethyleneglycol-400 (PEG-400) (LLC GC "Ruskhim", Russia) served as a plasticizer. Sodium metabisulfite (Yantai Sodium Metabisulfite Co., Ltd, China) was used as an antioxidant, and ethyl alcohol 95 % (Pharmacopoeial Monograph 2.1.0036, Р N003960/01, ROSBIO LLC, Russia) served as a solvent for the matrix components. A 20-μm-thick polyethylene terephthalate film formed the outer coating layer (backing), and anti-adhesive siliconized paper protected the matrices. Patches were prepared using the casting method and dried in an HPP110 climatic chamber (Memmert, Germany). As part of the quality control of the finished TTS, shear resistance was assessed in accordance with the requirements of the FTM 8 methodology of the FINAT International Association Guidelines, and adhesion was assessed in accordance with the "Methods of Adhesion Testing" monograph of the 18th edition of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. The Nicorette® transdermal patch (LTS Lohmann Therapy-Systems AG, Germany) served as the reference drug. An ERWEKA DT 626 dissolution tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany) with a holder disk was used to study the biopharmaceutical properties of the developed formulations. The hygroscopicity of the matrices was assessed using a BINDER FED 53 drying oven (BINDER GmbH, Germany). The test results were processed using elementary statistical methods in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation. To compare adhesion indices between groups, a one-way analysis of variance was performed (One-way ANOVA, GraphPad Prism 8.0.2, USA) at p < 0,0001.
Results and discussion. A comparative assessment of shear strength revealed that increasing matrix thickness leads to an increase in the number of shear layers, which reduces its cohesive strength. The introduction of high-molecular-weight PVP K-30 and K-90 into the PVP K-17 formulation provides a concentration-dependent increase in the composition's internal strength and enhances its resistance to shear deformations, but has a negative impact on the release of the active ingredient from the polymer matrix. The composition, based on a copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate, demonstrates an optimal combination of adhesive and biopharmaceutical properties.
Conclusion. The study confirms that developing a TTS is a complex, multi-step process that requires a balanced approach to formulation optimization. A critical aspect is the need for a comprehensive assessment of several key quality indicators, as modifying the formulation to improve some characteristics may degrade others. For further development of resveratrol patches, it is promising to use a matrix based on a copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate, and to consider optimizing the PVP K-17-based formulation to improve its adhesion properties.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
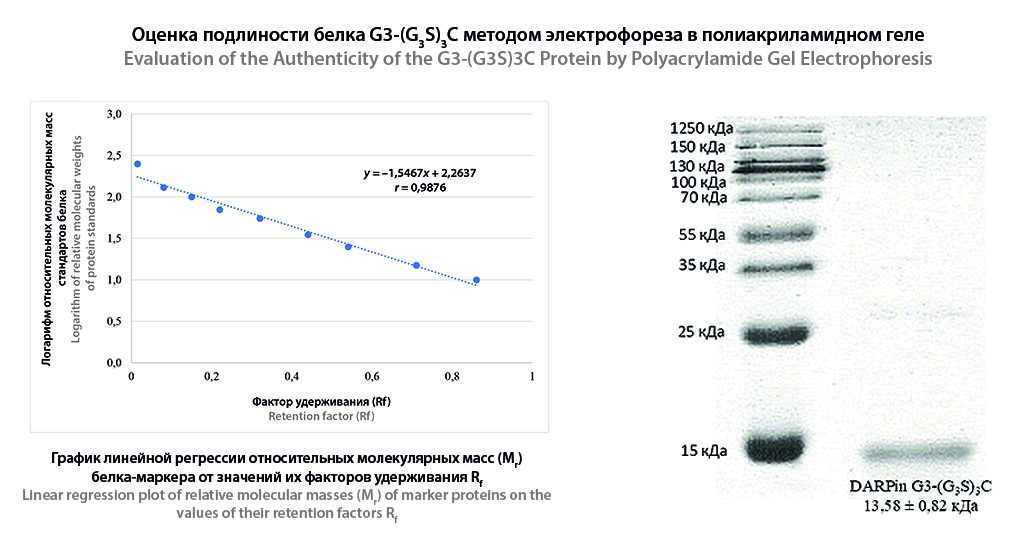
Introduction. Overexpression of the HER2 receptor is associated with aggressive cancer progression and poor prognosis. Traditional immunohistochemical diagnostics have a number of limitations, including invasiveness, inability to assess tumor heterogeneity, and total spread of the process. A promising alternative is radionuclide imaging using targeted scaffold DARPin G3 proteins. Based on the results of preclinical studies, the drug 99mTc[Tc]-G3-(G3S)3C has been proposed for Phase I clinical trials. The experimental drug is a sterile lyophilizate of a chemical precursor in a single vial and must comply with the requirements of OFS 1.11.0005 "Chemical Precursors for Radiopharmaceuticals" and OFS 1.7.1.0007.15 "Medicinal Products Obtained by Recombinant DNA Methods."
Aim. The aim of the present study was to develop approaches and techniques for quality control of DARPin G3-(G3S)3C protein included in the developed composition of chemical precursor lyophilizate lyophilizate for preparation of 99mTc-containing preparation for radionuclide imaging of HER2 overexpression in malignant tumors
Materials and methods. A lyophilizate containing DARPin G3-(G3S)3C with excipients was prepared for quality control. HPLC with a tandem mass spectrometer equipped with an electrospray ionization source was used to record mass spectra. Vertical electrophoresis with SDS in a heterogeneous buffer system was carried out in a polyacrylamide gel with an acrylamide concentration of 15 % at 110 V for 2 hours. Coomassie B-250 solution was used as the dye solution. Peptide mapping was performed using an HPLC system with a mass spectrometer via a nano-electrospray source. When correlating the amino acid sequence, carbamidomethylation of Cys, deamidation of Asn/Gln and oxidation of Met were counted as variable modifications. UV spectrophotometry was performed to determine the Quantification index at a wavelength of 280 nm. Validation evaluation of the developed method was carried out in accordance with the requirements of OFS.1.1.0012 "Validation of analytical methods".
Results and discussion. The authenticity and purity of DARPin G3-(G3S)3C was confirmed using HPLC-MS. The purity of the protein was close to 100 %. Application of 2 μg of protein for electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel showed a distinct stain allowing the authenticity of DARPin G3-(G3S)3C to be established. To determine the homodimer impurity, 10 μg of protein should be applied. The purity of the protein established by the peptide mapping method is 98 %. More than 700 variations of peptide fragments were identified by protein hydrolysate analysis. The value of –10LogP was more than 20. The developed UV-visible spectrophotometry technique meets the validation requirements and allows the quantification of DARPin G3-(G3S)3C protein in the lyophilizer ±10 % of the nominal content.
Conclusion. To determine the "Genuineness" of a new chemical precursor of DARPin G3-(G3S)3C protein in the lyophilizate for the preparation of 99mTc-containing preparation for radionuclide imaging of HER2 overexpression in malignant tumors the following methods were proposed: mass spectrometry, peptide mapping, electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel. For the indicator "Related impurities" – the technique of electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel. For the indicator "Quantitative determination" the method of UV-spectrophotometry.
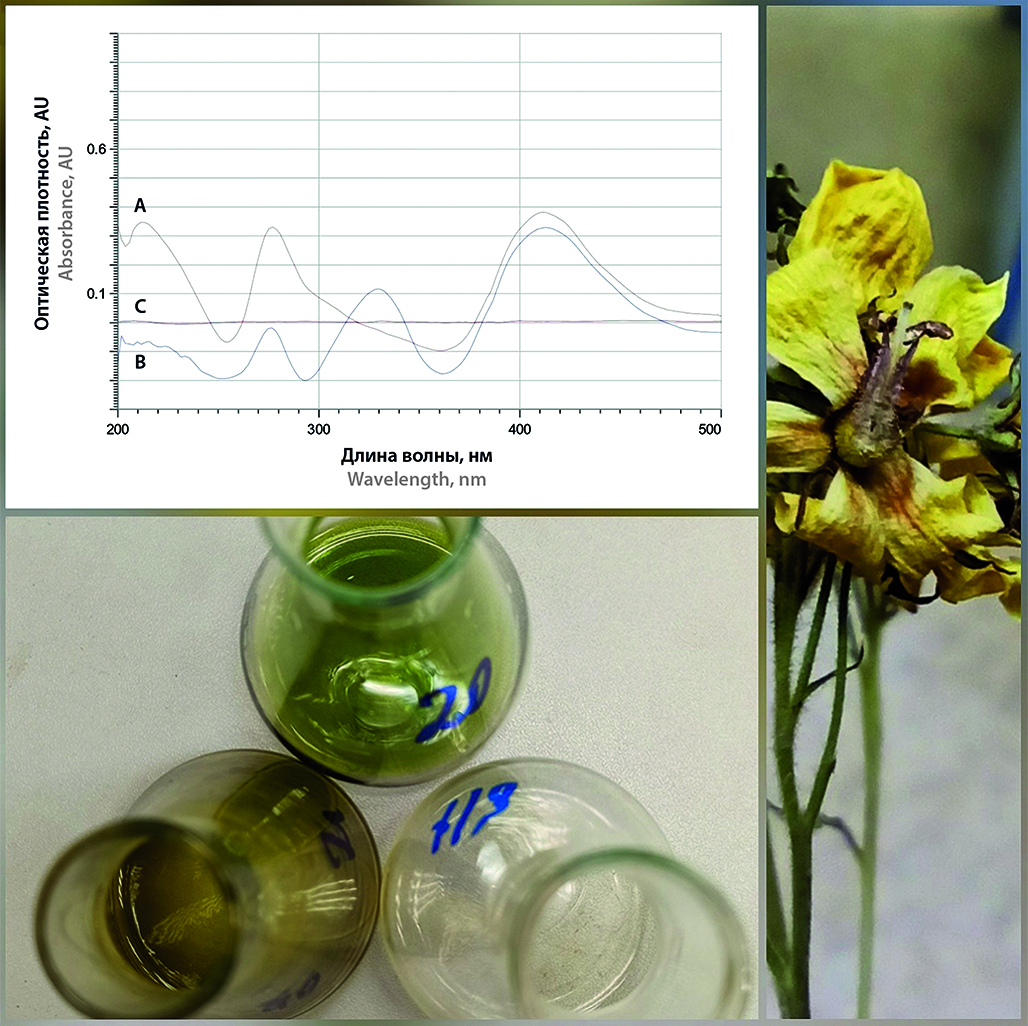
Introduction. The study of the qualitative and quantitative composition of plants and the identification of promising medicinal species is one of the most important tasks of modern pharmacognosy. Yellow loosestrife (Lysimachia vulgaris L.) of the Primulaceae family is a perennial herbaceous plant. The main group of active substances in the herb of L. vulgaris are phenolic compounds. L. vulgaris is widely distributed in Russia, is known in traditional medicine, its biological activities have been examined in vitro and in vivo experiments. A search of scientific literature in the Russian segment did not reveal sufficient information on the quantitative content of biologically active substances.
Aim. Development and validation of an analytical procedure for assessing the quantitative content of flavonoids in the herb of yellow loosestrife (L. vulgaris) in terms of rutin using spectrophotometry.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was alcohol extracts from the aerial part of L. vulgaris, harvested during the flowering period in the Leningrad region. Quantitative determination was carried out by spectrophotometry. The proposed analytical procedure was validated in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia XV in terms of specificity, linearity, range, repeatability (intra-assay precision), precision and accuracy (trueness).
Results and discussion. For the proposed analytical procedure, rutin was proposed as a standard sample. It was found that the maximum extraction of flavonoids from the herb of L. vulgaris is achieved by using a single extraction with 70 % ethyl alcohol for 30 min at a raw material : extractant ratio of 1 : 100 and a raw material grinding of 2–1 mm. A 1 % alcohol solution of aluminum chloride was proposed as a complexing agent, and the complexation conditions were selected (aliquot of aluminum chloride 1 % solution 2 ml, complexation time 30 min). The analytical procedure meets the requirements of the validation characteristics. According to the developed method, it was found that the amount of flavonoids in the herb of L. vulgaris, harvested in the Leningrad region, is 2,97 ± 0,05 % expressed in rutin.
Conclusion. A method for the quantitative determination of the flavonoid content in the herb of yellow loosestrife (L. vulgaris) by spectrophotometry expressed in rutin has been developed and validated.
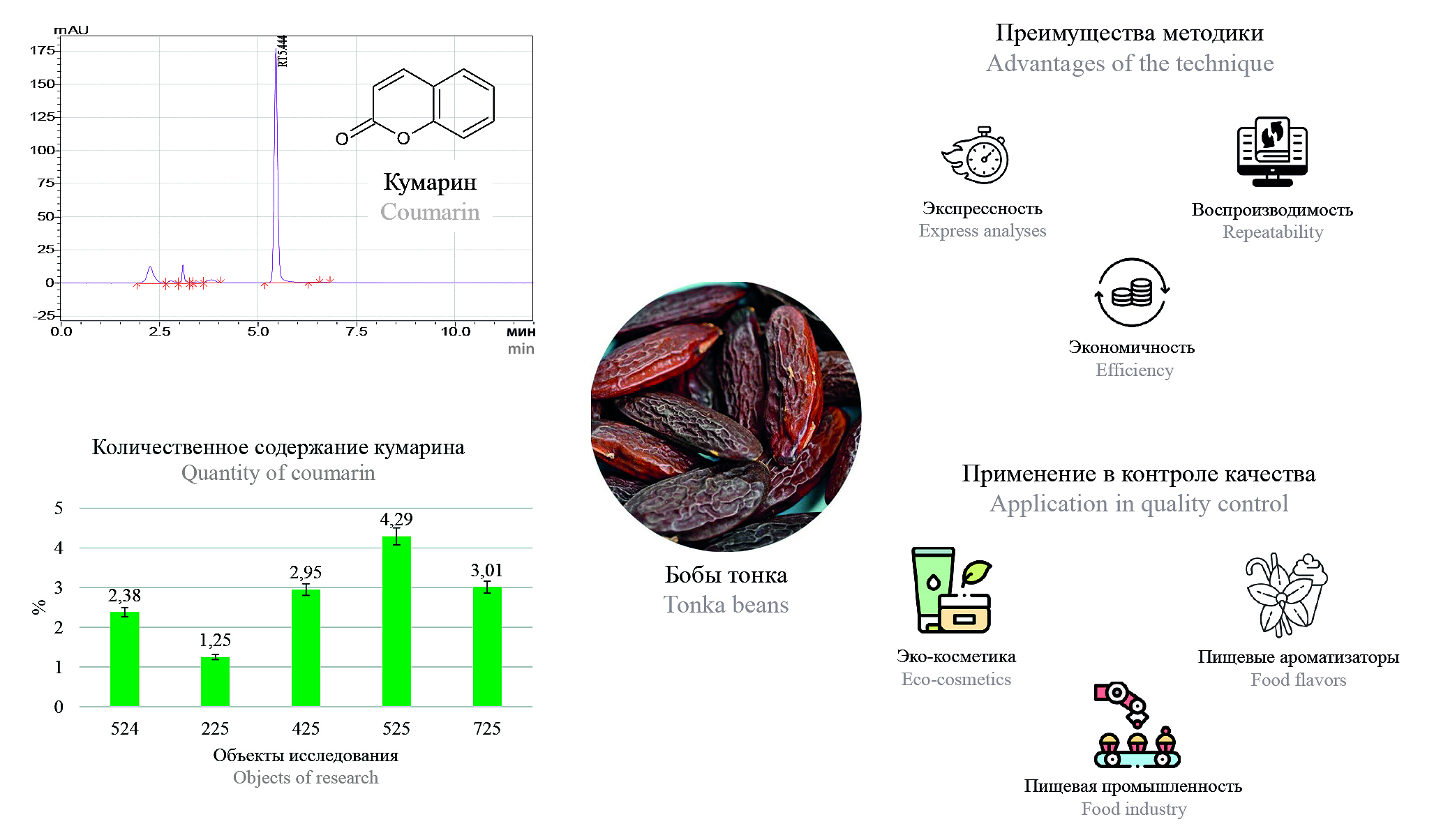
Introduction. The tonka beans (seeds of Dipteryx odorata, family Fabaceae) is a valuable source of coumarin used in the food, perfume and cosmetic industries thanks to its rich aroma. Despite its pharmacological value (anticoagulant, antioxidant activity), coumarin has a proven hepatotoxicity and haematotoxicity, which limits its use in a number of countries. Despite the control of synthetic coumarin in aromatics, the natural analog of tunica beans does not have clear rules, although it has identical activity. Growing demand for organic products has increased the popularity of tonka beans, but lack of scientific data on their safety and methods of analysis makes quality control difficult. The development of validated techniques, such as HVACR, is an urgent task to ensure the safety of its application in industry.
Aim. Development of a HPLC-method for the quantitative determination of coumarin in beans and its validation with further testing on several batches of the studied object.
Materials and methods. Five batches of Tonka beans from different producing countries were purchased as research objects, for sample preparation was used US-bath. Chromatography conditions: Luna 5 μm C18(100) Å LC Column 250 × 4.6 mm, thermostat temperature – 40 °C, detection wavelength – 275 nm. Mobile phase A – acetonitrile, mobile phase B – water. Elution mode: isocratic mobile phase B – 50 % for 12 minutes.
Results and discussion. The method meets the criteria of suitability of the chromatographic system, specificity, linearity (range 0.001–0.1 mg/ml) and precision. Its advantages are expressiveness and economy, which simplifies the quality control of raw materials. The quantitative content of coumarin in the studied object ranges from 1.25 ± 0.07 % to 4.29 ± 0.12 %.
Conclusion. Developed and validated by HPLC-methodology for the quantitative determination of coumarin in tonka beans. The developed methodology can be used to standardize this promising raw material in various industries, ensuring the necessary level of safety in its application.
Introduction. Coumarin and its derivatives are biologically active substances (BAS) of plant origin that exhibit a range of pharmacological activities as well as toxicological effects. The adverse effects of coumarin derivative drugs, along with poisonings caused by the use of rodenticides, coumarin-containing plants, and other related factors, justify the relevance of developing a rapid analytical method for the detection of coumarin derivatives.
Aim. To develop a rapid semi-quantitative method for the determination of coumarin derivatives using paper chromatography, perform validation tests, and apply the method to plant-based samples.
Materials and methods. For the development of the method were used substances coumarin and sodium hydroxide, filter paper brand FS and UV-lamp (365 nm). The technique includes impregnating paper bars with NaOH solutions (5–30 %), sample preparation with water or ethanol extraction followed by filtration, and visual fluorescence detection. Validation was performed using standard samples of phenolic compounds (coumarin derivatives, hydroxycorium derivatives, benzoic acids and flavonoids).
Results and discussion. As a result of the studies, the optimal conditions of the technique were established: concentration of the impregnating solution of sodium hydroxide – 10 %, use of SF-mark paper and detection time of 20 seconds. It is shown that the method has selectivity to coumarin derivatives when performing a number of tests, which are reflected in the «decision tree». Confirmed the possibility of semi-quantitative determination with detection limit 1 · 10–6 mg/ml and testing on synthetic and plant objects.
Conclusion. A rapid semi-quantitative method for the determination of coumarin derivatives has been developed, based on their alkaline hydrolysis on a paper substrate with subsequent fluorescence detection. The method is characterized by simplicity, high sensitivity (limit of detection 1 · 10–6 mg/mL), and was successfully tested on medicinal products, plant materials, and other objects. The proposed methodology is recommended as an effective tool for preliminary screening in laboratory practice.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
Introduction. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modelling is a method that allows predicting the distribution of drugs in the body based on anatomical and physiological parameters. This approach has become widespread only with the development of computing technologies. Today PBPK is actively used by regulatory agencies to optimize clinical trials and reduce the number of animal experiments.
Text. PBPK models represent the body as a system of interconnected compartments corresponding to organs and tissues. Three main types of models are described: Full PBPK, which maximizes accuracy at the expense of detail; Reduced PBPK, which reduces computational complexity; Hybrid PBPK, which combines both approaches to balance accuracy and efficiency. Key parameters for model building are discussed in detail: physicochemical properties of substances (LogP, pKa, solubility), physiological parameters (organ volumes, blood flow, enzyme activity and membrane transport proteins) and pharmacokinetic parameters (volume of distribution, clearance). Special attention is given to the Gordon Amidon absorption and transit model (CAT/ACAT) and its integration into PBPK modeling. Procedures for model reliability are given calibration (parameter tuning), validation (assessment of predictive ability), qualification (confirmation of fitness for purpose), and verification (verification of mathematical correctness). Statistical metrics for assessing accuracy are described. An overview of popular PBPK modeling software such as GastroPlus, Simcyp, PK-Sim, SimBiology, and Mrgsolve is presented, highlighting their main advantages and applications in the pharmaceutical industry and academic research.
Conclusion. PBPK modeling is on the threshold of a new era where its application will go beyond traditional pharmacokinetics, becoming an integral part of digital medicine, biotechnology and precision therapeutics. In the future, such technologies will not only be able to predict the behavior of drugs in the body, but also become the basis for virtual clinical trials, which will fundamentally change the approach to drug development and application.
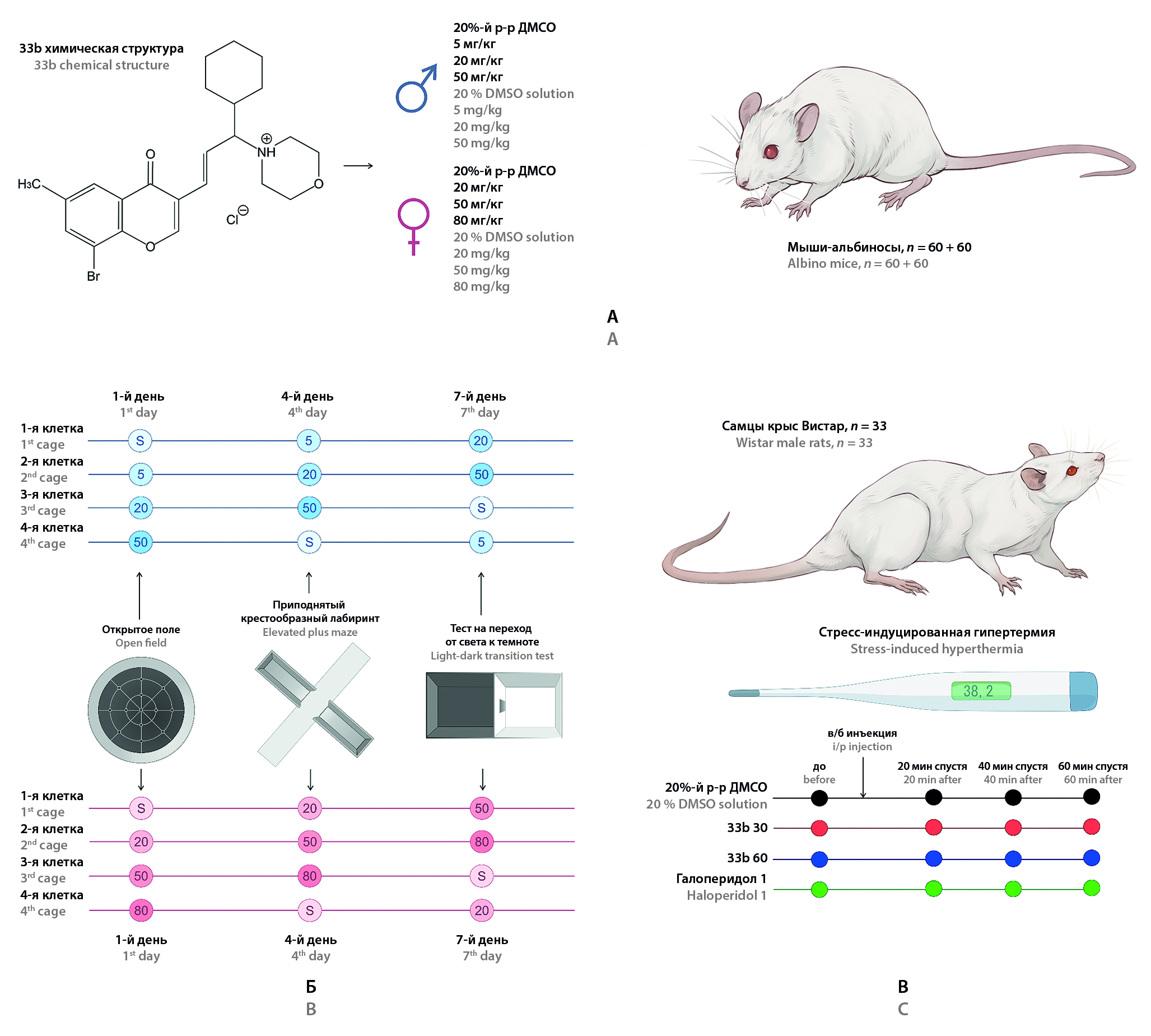
Introduction. Chromone-containing allylmorpholine derivatives (PAMs) are a new group of biologically active compounds with putative psychotropic activity. In a series of experiments on Danio rerio, PAMs demonstrated a pronounced dose-dependent sedative effect, and compound 33a at low doses exerted anxiolytic effects in the Novel tank test. Screening by pharmacoencephalography of another molecule from the PAM series, 33b, demonstrated similarity of its effects on EEG with the dopamine blocker sulpiride and the antihistamine agent chloropyramine. Based on the results of this prediction, the molecule can be hypothesized to have sedative and antipsychotic effects.
Aim. To study the pharmacological activity of compound 33b in tests for exploratory and anxiety behavior in mice, as well as in the test "Stress-induced hyperthermia" in rats.
Materials and methods. The pharmacological activity of 33b was evaluated in the Open Field (OF), Elevated Plus Maze (EPM), Light-Dark Box test (LDB) tests in male and female mice, as well as in the Stress-Induced Hyperthermia test in male Wistar rats.
Results and discussion. In the OF, EPM and LDB tests, the studied compound 33b at doses of 50 and 80 mg/kg resulted in a persistent decrease in the number of stance in both females and males. The decrease in locomotor activity in the OF test remained at trend level without statistical significance. Suppression of vertical activity in males occurred when lower doses of 33b were administered than in females. No data on the anxiolytic action of the molecule in these tests were obtained. In the test "Stress-induced hyperthermia" a pronounced decrease in body temperature was observed in rats when 33b was administered at a dose of 60 mg/kg.
Conclusion. The data obtained demonstrated a moderate sedative effect of compound 33b, while the sensitivity of males to the action of the molecule was higher. In the test on rats for the studied PAM was shown hypothermic action under stress conditions, which may be a confirmation of its dopamine-blocking action. This allows us to consider substance 33b from the group of chromone-containing allylmorpholines as a promising compound for further studies as a potential antipsychotic agent.
Introduction. Hedysarum semenowii Regel & Herder of the genus Hedysarum L., possess a rich phyto-chemical profile and hold promise as a foundation for developing novel pharmaceuticals. Despite the recognized pharmacological activities of various Hedysarum L. species, their safety profiles have not been sufficiently studied, necessitating further investigation to evaluate their toxicity and potential adverse effects. To address this gap, a study was conducted to assess the subacute toxicity, local irritant effects, and allergenicity of Hedysarum semenowii extract, with the aim of determining its safety and therapeutic potential.
Aim. Determination of subacute toxicity, local irritant effect and allergenicity of the Hedysarum semenowii Regel & Herder extract.
Materials and methods. The subacute toxicity study was performed using outbred rats, with the extract from aerial part of the plant administered orally at doses of 500, 2000, and 5000 mg/kg over a 28-day period. The condition of the animals was monitored throughout the study. At the conclusion of the subacute toxicity evaluation, pathological changes in the liver and kidneys of the experimental animals were examined. Local irritant and allergenic effects were assessed in rats and guinea pigs, respectively, employing visual inspection and the Draize scoring system.
Results and discussion. The 28-day subacute toxicity study revealed no significant toxicity, mortality, or behavioral changes in the animals. Body weight, food consumption, and water intake remained stable across all groups. According to the results of macroscopic and microscopic examination, minor physiological changes were noted in the liver and kidneys, the severity of which correlated with the administered doses of the extract. Furthermore, the extract did not induce skin irritation or allergenic reactions in tests involving rats and guinea pigs.
Conclusion. Hedysarum semenowii extract exhibited low toxicity and an absence of irritant and allergenic effects, affirming its safety and potential for further exploration as a therapeutic agent.
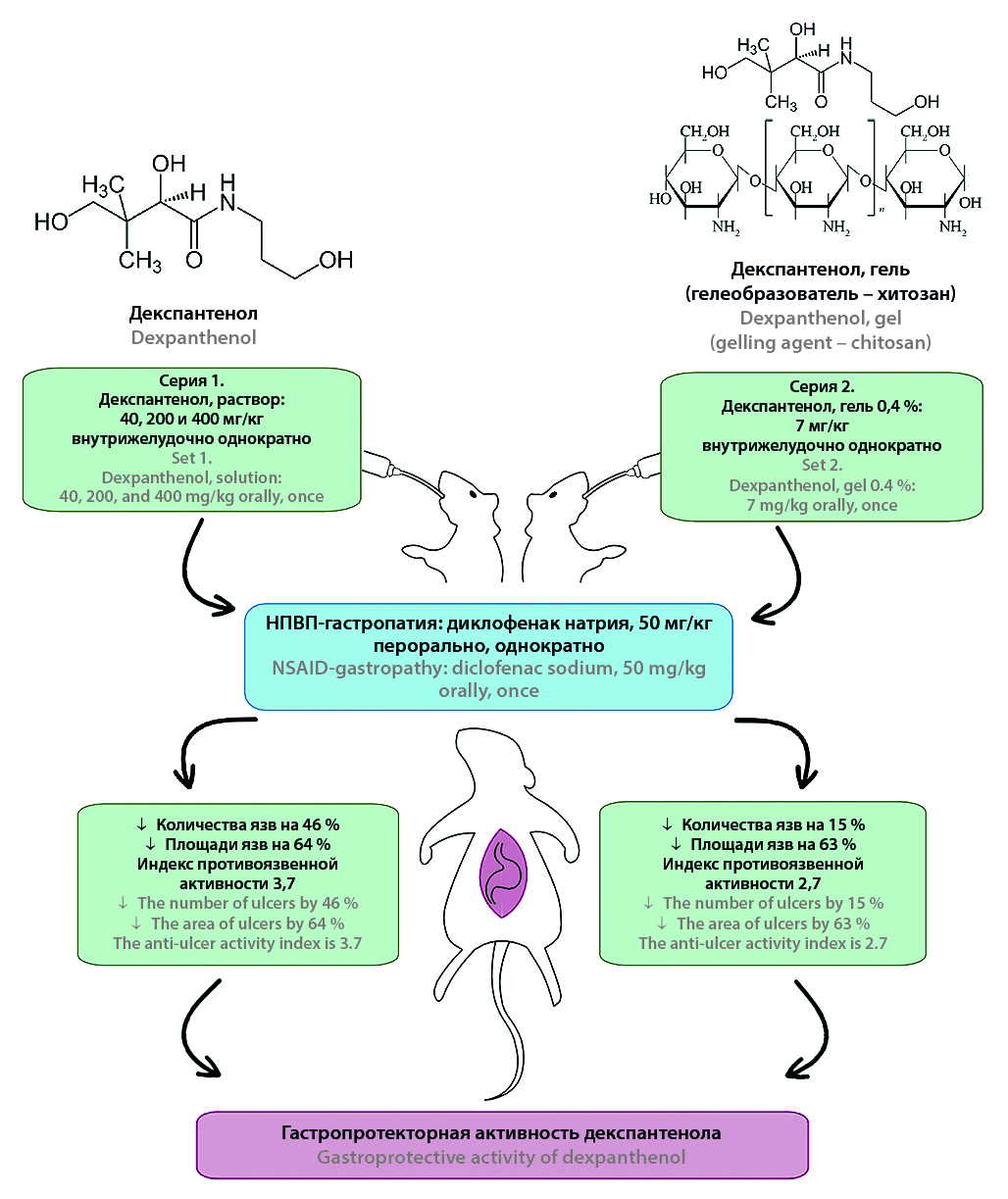
Introduction. The search for new gastroprotectors remains relevant, one of which could be dexpanthenol – a precursor of pantothenic acid that is non-toxic when taken orally. In Russia, systemic dexpanthenol preparations are not registered, and their use for treating acid-related diseases (ARDs) of the gastrointestinal tract isn’t known, and studying its gastroprotective properties when administered orally is promising.
Aim. Study of gastroprotective properties of dexpanthenol in oral administration using a model of gastropathy caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID-induced gastropathy) in preclinical research.
Materials and methods. The studies were conducted on 142 male outbred white rats weighing 220–280 g. The model used was NSAID-induced gastropathy with ulcerogenic agent sodium diclofenac, administered orally in a single dose of 50 mg/kg, euthanasia was performed 3 hours after administration via an overdose of chloroform anesthesia. Dexpanthenol was administered 1 hour before sodium diclofenac in a single oral dose in the form of an aqueous solution at doses of 400, 200, 40 mg/kg, and in the form of a developed 0.4 % gel (using high-viscosity chitosan as a gelling agent) at a dose of 7 mg/kg. Comparative drugs: dioxomethyltetrahydropyrimidine (syn. methyluracil) at a dose of 42 mg/kg, bismuth tripotassium dicitrate at a dose of 17 mg/kg. Both drugs were administered orally 1 hour before sodium diclofenac in a single dose. Evaluation criteria: number of animals with ulcers, number and area of ulcers on the gastric mucosa (GM) – determined using developed software written in Python with a graphical user interface (GUI). Calculation of the Pauls index and antiulcer activity index using known formulas, conducted histological examinations of the gastric mucosa with hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Results and discussion. It has been established that dexpanthenol provides a dose-dependent statistically significant reduction in the number and area of ulcers on the gastric mucosa, maximally by 2.7 times (at a dose of 40 mg/kg, 1,0 % aqueous solution, single oral administration) compared to the control group, and antiulcer activity index is 3.7, which exceeds the effectiveness of methyluracil. The 0,4 % dexpanthenol gel at a dose of 7 mg/kg demonstrated a significant reduction in ulcer area by 63 %, with an antiulcer activity index of 2.7, surpassing the effectiveness of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate. This is confirmed by signs of reduced inflammation intensity and activation of regeneration processes according to histological studies. The observed effects are likely attributed not only to dexpanthenol’s intrinsic activity but also to synergistic interactions with chitosan and the gastroprotective mucoadhesive properties of the gel formulation. The revealed gastroprotective activity of dexpanthenol aligns with its known mechanisms of action, including preservation of phospholipid bilayer integrity, modulation of mucin and tight junction (TJ) protein synthesis, regulation of nuclear transcription and apoptosis factors, growth factors, cytokines, and inflammatory mediators, cell division and cell differentiation.
Conclusion. For the first time, it has been proven that dexpanthenol, when administered orally in a single dose on the NSAID-gastropathy model, exhibit gastroprotective activity. It provides a significant statistically significant reduction in the number and area of ulcers compared to the control group. The antiulcer activity index is 3.7 (at a dose of 40 mg/kg, 1.0 % aqueous solution) surpassing the efficacy of methyluracil, 2,7 – when administered as a 0,4 % gel at 7 mg/kg (with chitosan as the gelling agent), these results were confirmed by histological examination and demonstrated superior effectiveness compared to bismuth tripotassium dicitrate.
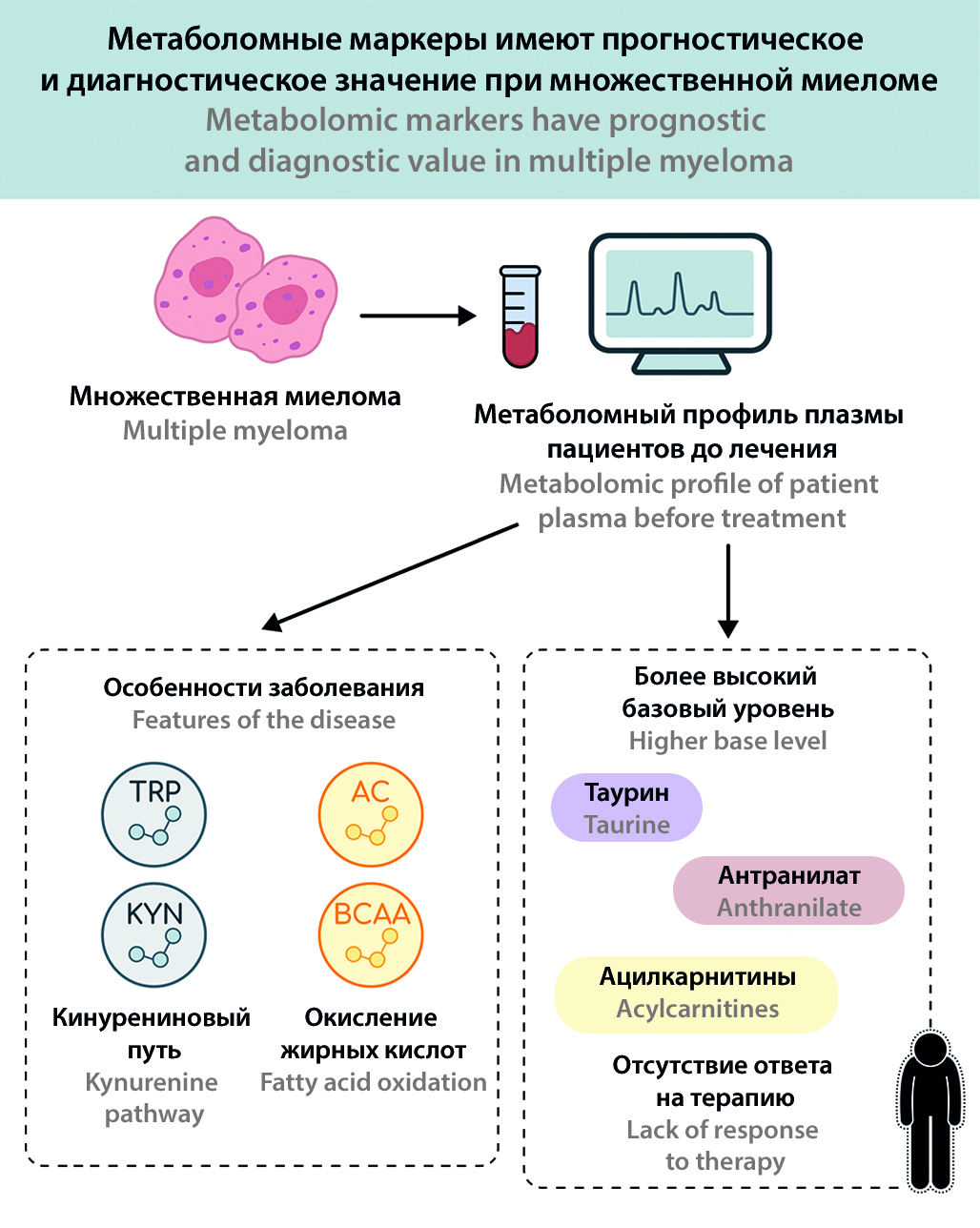
Introduction. Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant disease of plasma cells characterized by marked heterogeneity of the clinical course and variability in response to treatment. Metabolomic analysis, which reflects the totality of small molecules in biological fluids, opens up new possibilities for the search for diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers.
Aim. To evaluate metabolomic profiles of patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and to identify metabolic markers associated with the efficacy of polychemotherapy.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted from September 2022 to May 2025 at the Department of Hospital Therapy No. 1 of Sechenov University. We performed targeted analysis of plasma metabolites in 29 pre-treatment MM patients and 30 healthy volunteers (controls). Patients were divided into response and no response groups based on the results of therapy with VCD protocol after three courses.
Results and discussion. Significant differences in metabolomic profiles of MM patients compared to controls were found. MM patients showed increased tryptophan catabolism via the kynurenine pathway (~41 % increase in kynurenine/tryptophan ratio, ~80 % decrease in serotonin levels), changes in urea and nitric oxide cycle metabolites (~28 % decrease in arginine, ~5.3-fold increase in asymmetric dimethylarginine), and amino acid imbalances (decrease in serine, aspartate, BCAA) and a significant increase in total acylcarnitines (~1.4-fold higher than control). The baseline metabolic profile also differed between patients with different treatment outcomes: before treatment, patients who subsequently showed a clinical response had lower levels of several acylcarnitines and tryptophan breakdown products (e.g. anthranilic acid), whereas patients without response showed decreased levels of 5-hydroxytryptophan, indole-3-lactic acid and histidine.
Conclusions. Metabolomic analysis revealed characteristic metabolic alterations in MM reflecting activation of immunometabolic pathways (tryptophan kynurenine pathway, arginine metabolism) and impaired energy and amino acid regulation. The results indicate the potential prognostic significance of metabolites: a number of biomarkers (e.g. tryptophan derivatives, acylcarnitines) may be associated with chemotherapy sensitivity. The findings open the prospects for further research on metabolic approaches in MM monitoring and therapy.
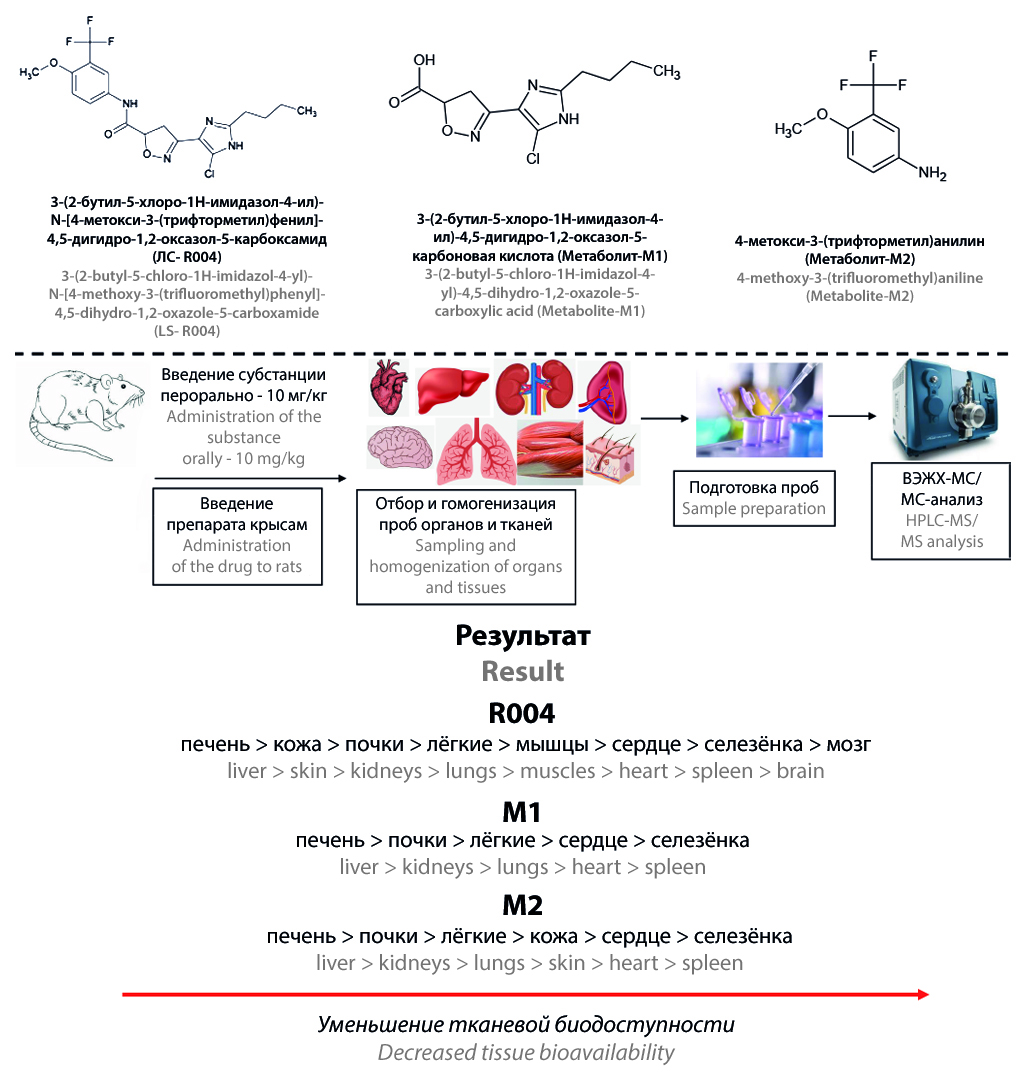
Introduction. The new pharmacologically active substance 3-(2-butyl-5-chloro-1H-imidazole-4-yl)-N-[4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxamide (R004) is a new PAR-2 receptor inhibitor for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. This compound is at the stage of preclinical trail. The distribution study of R004 and its metabolites by organs and tissues has not been performed before.
Aim. The investigation of distribution of R004 and its metabolites in rat organs after a single oral administration of the active substance.
Materials and methods. The study was carried out on 50 male Wistar rats. Substance of R004 was administered orally at a therapeutic dosage of 10 mg/kg. Sampling of liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, spleen, brain, skin and muscles was performed 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 24 h after administration of the drug. Organs were immediately homogenized using acetonitrile and frozen. Further sample preparation was carried out by addition an acetonitrile solution of internal standards to the homogenates. Quantification of R004 and its metabolites 3-(2-butyl-5-chloro-1H-imidazole-4-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylic acid (M1) and 4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline (M2) was performed by HPLC-MS/MS.
Results and discussion. The developed method for quantification of R004, M1 and M2 in organs has been successfully validated in the analytical ranges of 2–2000 ng/g for R004 and 1–1000 ng/g for M1 and M2. R004 is distributed by all studied biological objects. The tissue bioavailability of R004 decreases in the following sequence: liver > skin > kidneys > lungs > muscles > heart > spleen > brain. M1 and M2 was detected in large quantities in liver and kidneys. Metabolites penetrated into the heart, lungs and spleen in much lower concentrations. In skin tissues only M2 was identified. M1 and M2 were not found in brain and muscles.
Conclusions. The validated bioanalytical method has been successfully used for distribution study of R004 substance. The drug is well distributed throughout the studied organs and has a high tissue bioavailability. The highest concentrations of metabolites were observed in liver and kidneys.
Introduction. Intermittent hypoxia (IH) promotes oxygen free radical oxidation, which may precede many diseases. Decreased physical activity, ischaemic processes in organs and disturbances at the cellular level, may be a consequence of intermittent hypoxia. It is important to search for potential drugs to correct this process.
Aim. Comparative study of the efficacy of the active metabolite of ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate (EMHPS), ethylmethylsulfapyridine (EMSP), with a native molecule in a model of IG in mice.
Materials and methods. Test subjects were administered intraperitoneally for 14 days – EMSP was administered at a dose of 85 mg/kg, Mexidol® – at a dose of 100 mg/kg. Prolonged intermittent hypoxia was reproduced by placing animals in a membrane hypoxifier. The following conditions have been set for 14 days: 6 % – oxygen content in the hypoxic chamber, duration – 6 hours. The effect of the drug on dynamic load (grip strength test), respiratory parameters (plethysmograph parameters), behavioral and cognitive parameters (open field and elevated plus maze tests), heart rate and venous oxygen saturation were evaluated, and the potential mechanism of action was studied by real-time PCR.
Results and discussion. It was found that EMSP was effective in terms of plethysmography parameters, in particular, it helped the body adapt to chronic hypoxic effects, which resulted in significant differences in inhalation and exhalation parameters from the control group. The study of behavioral and cognitive states revealed the presence of anxiety, decreased exploratory activity and increased mobility of animals in all groups. These parameters were less pronounced for animals treated with EMSP and Mexidol® than in the control group. There was a tendency to increase the expression of a gene affecting the ubiquinol-cytochrome c-reductase complex, which is a part of mitochondrial respiration.
Conclusion. According to the results of the study, EMSP showed comparable protective properties with a native molecule EMHPS. There was also a tendency to increase the stimulation of UQCRC2 gene against the background of EMSP administration compared with EMHPS.
Introduction. Chronic heart failure (CHF) often leads to progressive renal dysfunction; however, pharmacological protection strategies aimed at correcting metabolic and oxidative disturbances in renal tissue remain underdeveloped. In this regard, it seems relevant to study the effect of new compounds, such as malonic acid derivatives, including 4-[(3-ethoxy-3-oxopropanoyl) amino]benzoic acid (etmaben), on the expression of genes encoding key enzymes of metabolic and antioxidant pathways in the kidneys in CHF. Previously, a more pronounced nephroprotective effect was detected for etmaben than for another malonate, maloben.
Aim. To evaluate the effect of 4-[(3-ethoxy-3-oxopropanoyl)amino]benzoic acid on the expression of genes regulating enzymatic pathways in the kidneys of rats with experimental CHF.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted on 30 outbred white male rats (300–350 g) housed under standard conditions (12-hour light/dark cycle, temperature 22 ± 2 °C, humidity 50–60 %, with ad libitum access to food and water). The animals were divided into three groups. Group 1 (Control–) consisted of healthy animals (n = 10) that received purified water (1 mL/kg/day, intragastrically). Group 2 (CHF–) included animals with chronic heart failure (CHF, n = 10) that were administered purified water (1 mL/kg/day, intragastrically) starting from day 30 after the surgery. Group 3 (CHF+) was composed of animals with CHF (n = 10) that received etmaben (60 mg/kg/day, intragastrically) starting from day 30 after the surgery. CHF was modeled by ligation of the left coronary artery. Successful model induction was confirmed echocardiographically (ejection fraction <40 %). Operated animals were randomized using a random selection method. Etmaben or water was administered daily for 30 days, starting from day 30 after surgery. On day 61, the animals were euthanized, and kidney tissues were homogenized in Lira reagent (LLC "Biolabmix", Russia). RNA was extracted using chloroform, isopropanol, and NaOAc, and purified with LiCl. RNA concentration was measured on a Nanophotometer N60, and quality was assessed by gel electrophoresis. Reverse transcription was performed from 1 µg of RNA (MMLV-RT-Kit, Eurogen). Real-time PCR was run on a QuantStudio 5 with SYBR Green (Eurogen), analyzing the genes Gpx1, Nrf2, Nox1, Glud1, Hes1, mTOR, Txnrd1, Hif1a, Cpt1b, and B2M (reference). Statistical analysis was performed in R-Studio (version 4.3.3) using the RQdeltaCT package. One-way ANOVA, the Kruskal – Wallis test, post-hoc Tukey and Dunn tests, as well as odds ratio analysis and logistic regression were applied. Gene expression analysis was performed using the 2–ddCt method with normalization to the reference gene B2M.
Results and discussion. It was found that CHF led to significant activation of the transcription factor Nrf2; however, the expression level of its target gene, GPx1, remained unchanged both in CHF and after etmaben treatment, indicating impaired functioning of this signaling pathway. Administration of 4-[(3-ethoxy-3-oxopropanoyl)amino]benzoic acid caused a statistically significant increase in the expression of the Cpt1b gene (p < 0.05), suggesting a shift in cellular metabolism towards fatty acid β-oxidation. Furthermore, significant suppression of the pro-oxidant enzyme Nox1 and activation of the thioredoxin reductase 1 (Txnrd1) gene (p < 0.05) were recorded in the treatment groups. The Notch signaling pathway was activated by etmaben, as evidenced by increased expression of the Hes1 gene (p < 0.05), while no significant effect on the expression of the mTOR gene was detected.
Conclusion. Etmaben functions as a metabolic modulator and redox regulator. Its action is not associated with direct antioxidant activity but is due to the activation of adaptive mechanisms: reducing the demand for antioxidant defense by suppressing sources of reactive oxygen species (Nox1), activating a key regulator of the antioxidant response (Nrf2), and altering energy metabolism through the induction of Cpt1b and Glud1.
Introduction. Maloben is a new drug for the treatment of liver diseases with previously unstudied pharmacokinetics in humans.
Aim. To determine the pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters of Maloben tablets (SPCPU, Russia) after single and multiple administrations in healthy volunteers as part of a phase I clinical trial.
Materials and methods. The phase I clinical trial was conducted in two stages. Stage I involved 24 volunteers divided into 3 cohorts of 8 volunteers each: cohort 1 received a single 60 mg dose of maloben, cohort 2 a single 120 mg dose, and cohort 3 a single 180 mg dose. Stage II included healthy volunteers who completed the previous stage: cohort 4 received a daily dose of 60 mg, cohort 5 a daily dose of 120 mg, and cohort 6 a daily dose of 180 mg. To determine maloben concentrations in plasma, high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection (HPLC-MS/MS) was used. Based on plasma concentrations obtained during the analytical phase after single and multiple oral administrations, pharmacokinetic parameters of maloben were evaluated.
Results and discussion. Pharmacokinetic parameters of maloben were evaluated in 6 cohorts of 8 volunteers each. Mean Cmax values were 18.09 ± 8.06, 41.36 ± 5.63, and 51.81 ± 11.05 ng/mL after single dosing in cohorts 1–3, and 37.93 ± 20.98, 70.83 ± 37.37, and 78.98 ± 37.03 ng/mL after multiple dosing in cohorts 4–6. Mean AUC(0–t) values were 348.59 ± 200.65, 938.32 ± 344.95, and 1177.13 ± 221.81 ng · h/L after single dosing in cohorts 1–3, and 3142.22 ± 2091.08, 5714.73 ± 2482.56, and 7799.02 ± 3829.67 ng · h/L after multiple dosing in cohorts 4–6. Mean AUC(0–∞) values were 623.05 ± 390.08, 1171.68 ± 471.89, and 1666.93 ± 596.25 ng · h/L after single dosing in cohorts 1–3, and 3228.41 ± 2141.08, 5789.32 ± 2539.34, and 8970.72 ± 5143.42 ng · h/L after multiple dosing in cohorts 4–6. Dose proportionality (linear PK) was established for PK parameters Cmax, AUC(0–t), and AUC(0–∞) after single dosing, and for AUC(0–t) and AUC(0–∞) after multiple dosing.
Conclusion. For the first time, the pharmacokinetics of maloben under various dosing regimens in volunteers were investigated, as well as the assessment of changes in PK parameters.
REGULATORY ISSUES
Introduction. The quality assurance of research work is a key factor in scientific discoveries, as well as the emergence of innovative high-margin products on the market. Due to the specific nature of the scientific research field, there are currently no uniform rules for organizing and conducting research that meet the needs of both scientific groups and businesses interested in the commercialization of developments, including drug developments, and individual approaches are only being formed. The set of established approaches and concepts, according to the existing system of good practices (GxP), is called "Good Research Practice" or GRP.
Аim. Generalization of existing global trends in the field of Good Research Practice and description of the implementation of GRP principles using the example of the quality management system of the Sirius University Laboratory Facility.
Materials and methods. The methods of GRP principles implementation in the Laboratory Complex are based on the requirements of ISO 9001 and ICH recommendations in such areas as document and record management, personnel and training management, audit and inspection management, risk management, analysis and evaluation of performance and efficiency.
Results and discussion. The current principles of GRP, formed within the framework of national scientific communities, individual universities and state programs, are analyzed. Using the example of the Laboratory Facility of the Sirius University, the possibilities and examples of complex implementation of GRP in such areas of the quality management system as document and record management, personnel and training management, audit and inspection management, risk management, conducting periodic analysis and assessment of the effectiveness and efficiency of activities are considered.
Conclusion. The approach to conducting scientific research work described in the article, based on the integrated implementation of GRP, is a tool for ensuring the quality of research, necessary both for purely scientific activities and for successful scientific and applied interaction between the academic environment and pharmaceutical companies in order to accelerate the launch of new drugs to the market and meet patient demand.
Introduction. Bringing medicines for medical use to the market is an extremely expensive and resource-intensive process associated with long-term development, high risks, quality assurance of the final product, safety and efficiency, while limited by strict regulatory requirements. The key goals of the pharmaceutical industry development are to promote the conditions for guaranteeing the safety of the Russian Federation in the field of drug provision to the population and drug availability in all segments, ensuring an advanced level of scientific, technical and technological development of the pharmaceutical industry, creating an export-oriented potential, the presence of competencies in research and development, full-cycle production, implementation in clinical practice and export of medicines. The development of the pharmaceutical and medical industry of the Russian Federation involves not only a consistently pursued import substitution policy, but also the task of realizing the export potential to ensure comprehensive support for the stability of the national pharmaceutical market.
Text. The article demonstrates data on the export of Russian medicines, suggests possible methods and tools for reducing barriers to entering foreign markets and supporting the export activities of domestic manufacturers.
Conclusion. The main areas of implementation of the Strategy for the Development of the Pharmaceutical Industry of the Russian Federation until 2030 provide for support for the export of Russian pharmaceutical products. The application of the system for assessing the levels of readiness of export potential will allow it to be used as a tool for reducing barriers to entry into foreign markets and strengthening the positions of Russian manufacturers, including ensuring harmonization of regulation with the best international practices.
ANNIVERSARY
Market news (in Russ.)
2025-12-23
Pharmtech & Ingredients 2025: Вдохновляющие результаты и новые перспективы
 | В Москве с успехом завершилась 27-я Международная выставка оборудования, сырья и технологий для фармацевтического производства Pharmtech & Ingredients 2025, подтвердив свой статус ключевого события для всей индустрии. Мероприятие продемонстрировало беспрецедентный масштаб и установило новые рекорды по посещаемости, став мощным стимулом для развития фармацевтической промышленности и биотехнологий. |
2025-12-19
«Биннофарм Групп» создает логистический хаб в Китае для усиления присутствия в Азии
 | «Биннофарм Групп» запускает логистическое направление в Китае на базе дочерней компании «Шанхай Биннофа Кемикл Ко., Лтд». Собственные складские мощности и работа с китайскими перевозчиками позволила оптимизировать стоимость перевозок и сократить сроки поставки сырья и материалов. |
2025-12-19
ГЕРОФАРМ получил в Узбекистане регистрационное удостоверение на Семавик
 | Компания ГЕРОФАРМ зарегистрировала в Узбекистане препарат Семавик с действующим веществом семаглутид, предназначенный для лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа и ожирения. Семавик стал первым зарегистрированным в стране аналогом датского препарата Оземпик и уже доступен для пациентов. |
| More Events... |
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)