FROM EDITOR
We present to your attention a new interview as part of the Leaders' Opinion series. The first guest of the series was the General Director of CFA LLC, editor-in-chief of the journal Development and Registration of Medicines, Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences Igor Evgenievich Shokhin.
The Labconcept Group is the official distributor of leading manufacturers of analytical and general laboratory equipment. Labconcept offers comprehensive solutions for equipping laboratories of various fields, including for the pharmaceutical industry. The pharmaceutical industry in Russia continues to develop and expand the volumes of manufactured medicines, which inevitably entails the need to create new and expand existing laboratories for quality control of manufactured drugs. Under the conditions of sanctions pressure, many familiar manufacturers of analytical equipment have left the market. At the same time, there is a growing need for reliable and efficient analytical and testing equipment. The Labconcept Group offers solutions that have been tested in own laboratory, in particular, dissolution testers from Haosoo Instruments (Hanon Group) and total organic carbon analyzers under its own OEM brand SILab. Both lines of devices comply with the requirements of the US Pharmacopoeia, the European Pharmacopoeia and the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
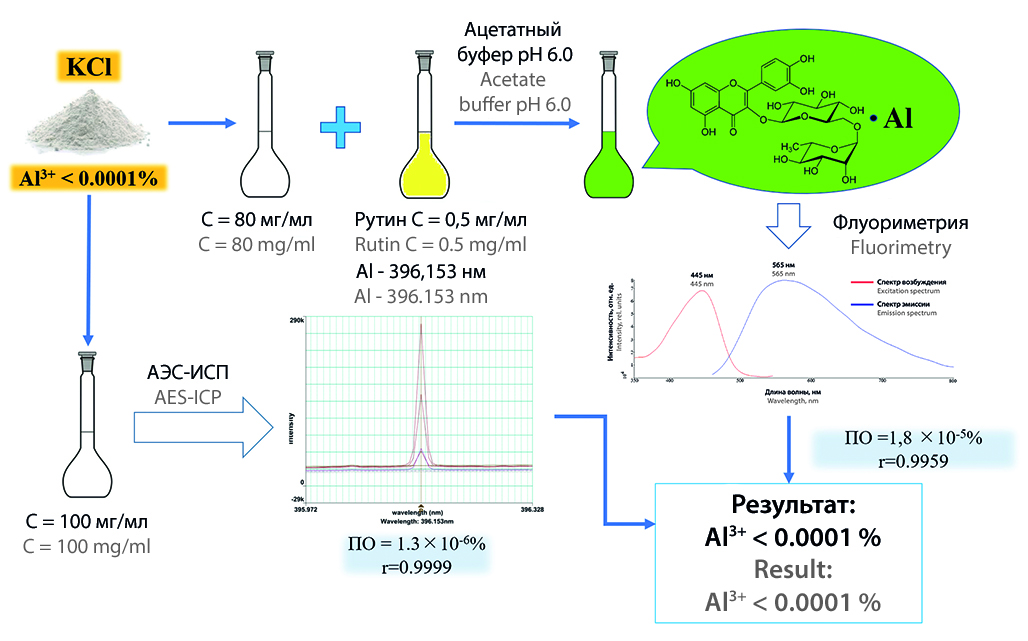
Introduction. Evaluation of the content of impurities is the most important step in confirming the safety and efficacy in the quality control of the medicinal product. Aluminum, being an acceptable impurity in a number of pharmaceutical substances, can adversely affect the human body, as a result of which its content is normalized. The admixture of aluminum in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XV is determined by the spectrofluorimetric method using the ligand – 8-hydroxyquinoline in chloroform. In the present work, it is proposed to replace 8-hydroxyquinoline with the more accessible rutin, which also forms fluorescent complexes with metals. This approach involves the exclusion of the stage of extraction of the aluminum complex into chloroform from sample preparation, which improves the accuracy of the technique, and the replacement of chloroform has a positive effect on safety.
Aim. To create an alternative approach for the spectrofluorimetric determination of aluminum impurities using rutin and "potassium chloride" as an active pharmaceutical ingredient.
Materials and methods. The following substances and reagents were used as research materials: CRS of aluminum ion 1 mg/ml (LLC "EKROSHIM", Russia), CRS of iron ion (II) 1 mg/ml (LLC "EKROSHIM", Russia), CRS of zinc ion 1 mg/ml (LLC "EKROSHIM", Russia), CRS of lead-ion 1 mg/ml (LLC "EKROSHIM", Russia), CRS nickel-ion 1 mg/ml (LLC "EKROSHIM", Russia), CRS copper-ion 1 mg/ml (LLC "EKROSHIM", Russia), chromium (III) cation standard 1 mg/ml (imp., Sigma-Aldrich, USA) rutin (imp., Sichuan Guangsong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), ammonium acetic acid (imp., Molekula GmbH, Germany), glacial acetic acid (chemically pure, JSC "Base No. 1 Himreaktivov", Russia), potassium chloride (pharmaceutical substance, LLC "MZHR", Russia). The spectrofluorimetric study was carried out on an FL 6500 instrument (PerkinElmer Inc., USA). The aluminum impurity content was also evaluated using an Optima 8000 inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP AES) (PerkinElmer Inc., USA) and a Multi-Element Solution standard sample (PerkinElmer Inc., USA).
Results and discussion. The approach given in the article eliminates the use of 8-hydroxyquinoline in chloroform and replaces it with rutin in 70 % ethyl alcohol. The aluminum-rutin complex has an excitation wavelength at 445 nm and an emission wavelength at 565 nm. The proposed method was tested on the substance "Potassium chloride" to assess the indicator "Aluminum", the content of which should not exceed 0.0001 %. Method validation was carried out according to three parameters "Specificity", "Linearity" and "Limit of detection". Comparison of the data obtained was carried out using atomic emission spectroscopy, during which the relevance of the technique was proved.
Conclusion. An ergonomic approach has been developed for the spectrofluorimetric determination of aluminum impurities using rutin with approbation on the substance "Potassium chloride". The results obtained during the experiment were confirmed by the ICP AES method.
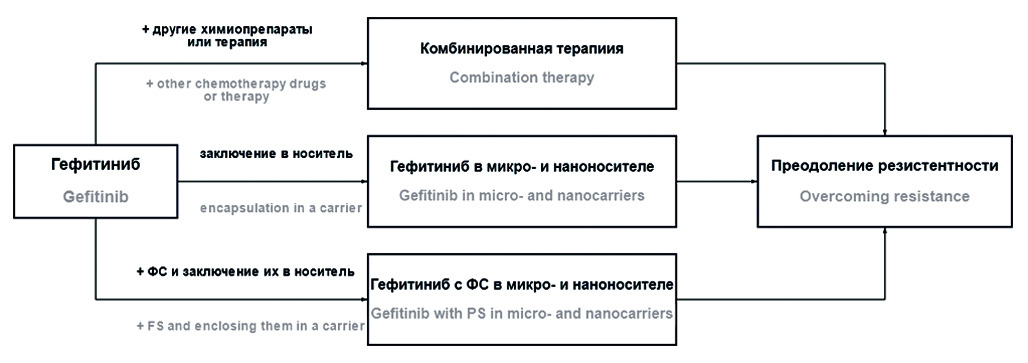
Introduction. The search for new methods of therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is an urgent task of modern science. Gefitinib is a targeted drug widely used in the treatment of NSCLC in patients with a mutation in the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain. However, using of gefitinib and other drugs from the group of tyrosine kinase inhibitors is to limited by rapidly developing resistance, for this reason finding of a ways overcome drug resistance is actual part of research interests.
Text. The review is devoted to the use of gefitinib in modern developments: introduction to various targeted delivery systems (liposomes, micelles, microspheres, etc.), studying it in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, as well as in combination with photo- or thermosensitive compounds in various micro- and nanostructured complexes.
Conclusion. As a result of the analysis of literature data, it was shown that, despite the fact that gefitinib is a first-generation drug, foreign and Russian researchers consider it quite promising for further use in the treatment of NSCLC. At the same time, developments are being carried out both in the field of expanding combination therapy and in the field of creating complex structures of targeted action, into which, in addition to gefitinib, photosensitizers or other compounds with photo- or thermosensitive effects are introduced.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. In modern medicine, the requirements for the quality of used materials are getting stricter. There is serious concern about bacterial and fungal contamination related to the use of silicone polymeric products, especially those that are in direct contact with human tissues and body fluids. In this regard, the issue of impregnating silicone medical products with various biologically active substances (BAS), particularly with antimicrobial properties, appears relevant.
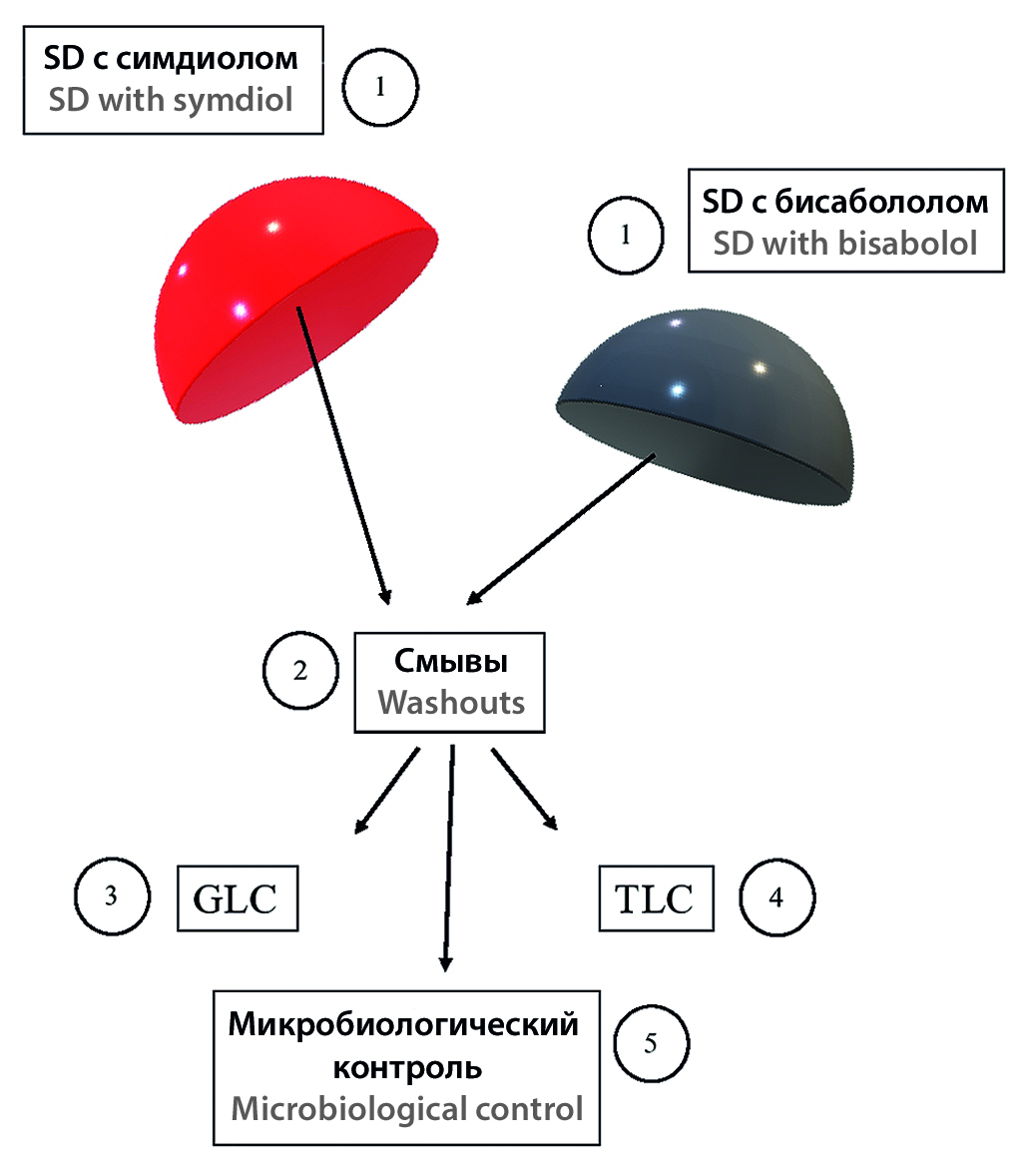
Aim. The research studies the relevance of adding BAS into silicone medical devices to improve their quality and prevent negative consequences of their use. The authors of the article aimed at proving prolonged release of the chosen BAS from silicone products during their contact with skin and the bacteriostatic effect emerging as a result of the BAS release. That required verifying the existence of BAS in the washouts from silicone disks, which, in turn, proves the fact that BAS initially distributed evenly in the volume of a silicone disk are capable of diffusing to the surface and then releasing from it under mechanical action, as well as when treating it with alcohol or alcohol-containing solutions.
Materials and methods. Symdiol and bisabolol were selected as the BAS for this study due to their proved antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties. Bisabolol and symdiol were used in the form of Dragosantol 100 and SymDiol 68T preparations correspondingly. Silicone disks (SDs), impregnated with BAS (0,2 % of the volume) were used as a simulation model of silicone liners. The BAS release from silicone liner models was assessed using highly sensitive chromatographic methods of thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatography.
Results and discussion. The method of impregnating SDs with BAS was worked out, the optimal concentration of these substances to add them into the silicone base was selected. The release of the impregnated additives, as well as prolonged stable releasing effect, were confirmed. The data obtained during the experiment allows saying with confidence that the impregnated preparation (symdiol and bisabolol) releases from a SD even upon short and low-intensity mechanical contact with skin, which produces stable bacteriostatic effect on a wide range of microorganisms. The process of BAS release from SDs is also facilitated when treating the product periodically with alcohol-containing solutions, which is necessary according to the operating rules. The obtained results of the chromatographic research quite correlate with the data of the previous microbiological experiments regarding the studied topic. Release of the studied BAS from polymer products during their contact with the skin within the period of not less than 3 months justifies feasibility of adding these BAS into the silicone base.
Conclusions. The study confirmed the release of biologically active substances from silicone medical products. Adding BAS into silicone liners undoubtedly improves the quality of these medical products, which can be applied in prosthetics and orthoses.
Introduction. Medical clays are polymineral sorbents with a predominance of the underlying clay mineral, the concentration of which determines the quality of mineral raw materials and its adsorption activity. One of the methods of improving the quality of mineral raw materials is its activation by means of ultrasonic treatment.
Aim. To study the effect of ultrasound on the activation and adsorption activity of mineral sorbents.
Materials and methods. Clinoptilolite mineral raw materials of the Kholinsky deposit, montmorillonite mineral raw materials of the Belgorod deposit and kaolinite mineral raw materials of the Eleninsky deposit were used as objects of research. A high-frequency UZDN-1 unit was used for ultrasonic treatment. Determination of adsorption activity was carried out by methylene blue.
Results and discussion. The effect of ultrasound on the activation of mineral sorbents at an ultrasonic wave frequency of 40 kHz for five minutes has been studied. It was found that the average content of Clinoptilolite, taking into account all fractions in the clay of the Kholinsky deposit, increases by 20 %, the average content of Montmorillonite, taking into account all fractions in the clay of the Belgorod deposit, increases by 14 %, the average content of Kaolinite, taking into account all fractions in the clay of the Eleninsky deposit, increases by 18 %. The effect of ultrasound on the adsorption activity of mineral sorbents has been investigated. The use of ultrasonic treatment increases the adsorption activity of mineral sorbents by 12–19 %.
Conclusion. The developed method of activation of mineral sorbents by ultrasonic treatment can be used to activate mineral sorbents by increasing the concentration of the underlying mineral (Clinoptilolite, Montmorillonite, Kaolinite), as well as increasing their adsorption activity.
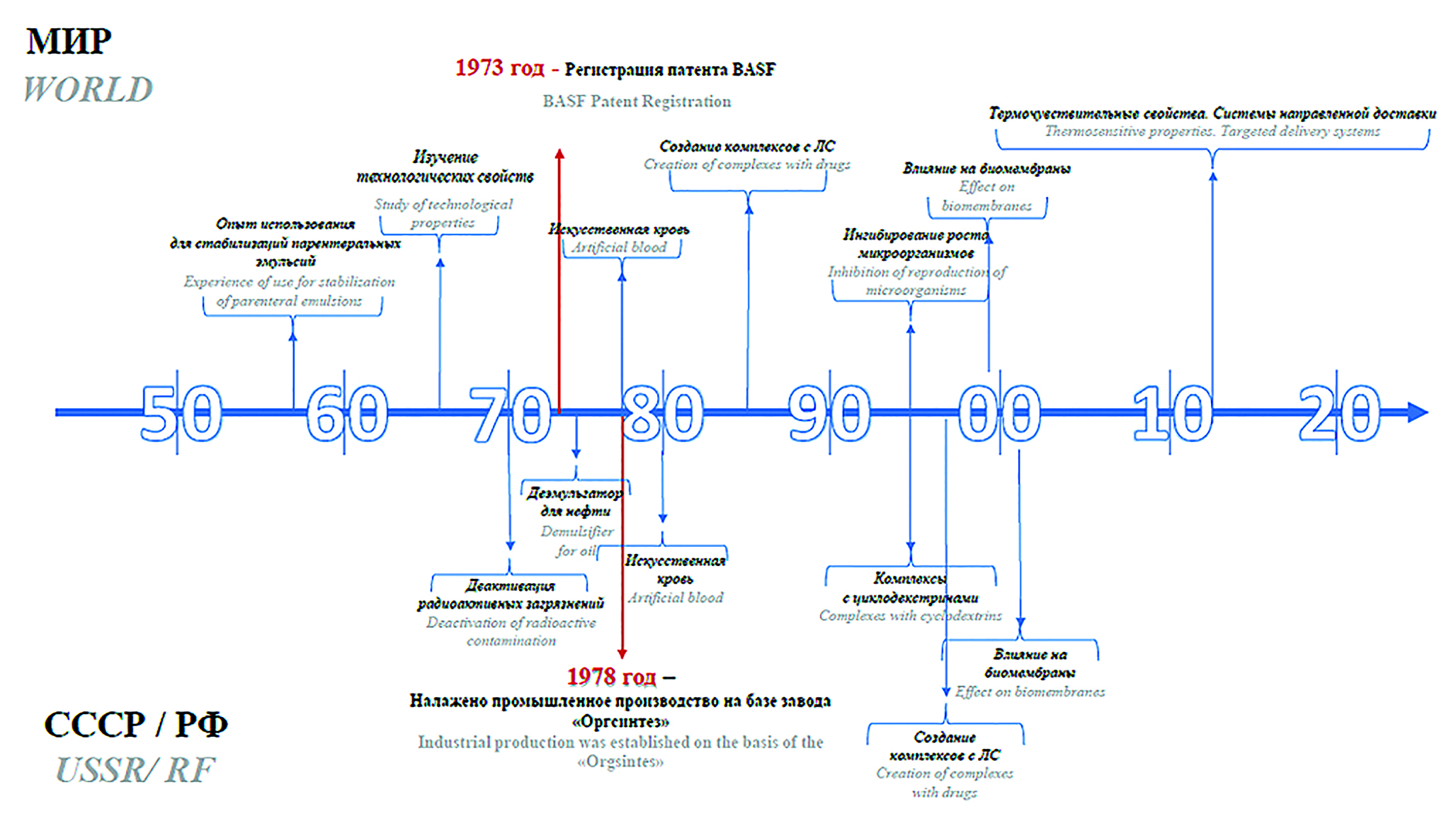
Introduction. Nowadays block copolymers of PEO and PPO (poloxamers, pluronics, proxanols) are among the most popular polymers in the pharmaceutical and biotechnological industries. They can be applied as effective nonionic surfactants, biological membrane stabilizers, elements of targeted delivery systems, solubilizers, as well as excipients in the technology of traditional dosage forms – gelling agents, lubricants, etc. For the past fifty years, the world's largest manufacturer of poloxamers has been the German chemical concern BASF. However, today in the Russian Federation there is a risk of defects, which defines the relevance of import substitution of this excipient.
Text. The purpose of this review is to highlight the experience of production and implementation of PEO and PPO block copolymers into novel Russian scientists’ developments, comparing them with the experience of foreign research groups, which is necessary to assess the potential for import substitution. PEO and PPO block copolymers have been known in the Soviet Union since the late 60s as far as they are mentioned in textbooks of 1964 and 1973. Domestic block copolymers of PEO and PPO have been used in the oil refining industry, as well as in some branches of light industry and in the decontamination of radioactive waste. The unique domestic synthesis of PEO and PPO block copolymers was established in 1978 on the basis of the "Orgsintez" factory. Soviet poloxamers were produced under the brand name "proxanol" in a wide range of ratios of EO and PO units and molecular weights. It should be noted that today in the Russian Federation, industrial batches of the solubilizer Emuxol 268, which is close in its properties to the well-known poloxamer 188, are still produced, and block copolymers with other ratios of EO and PO units are synthesized to order.
Conclusion. According to the retrospective analysis, the modern Russian industry has enough experience and resources to establish the synthesis of PEO and PPO block copolymers necessary to produce drugs and to develop innovative delivery systems and drugs. Based on the materials of the systematic review, the most complete register of known brands of PEO and PPO block copolymers synthesized over the past 50 years in our country and in the world was compiled for the first time, with a detailed description of their physicochemical properties.
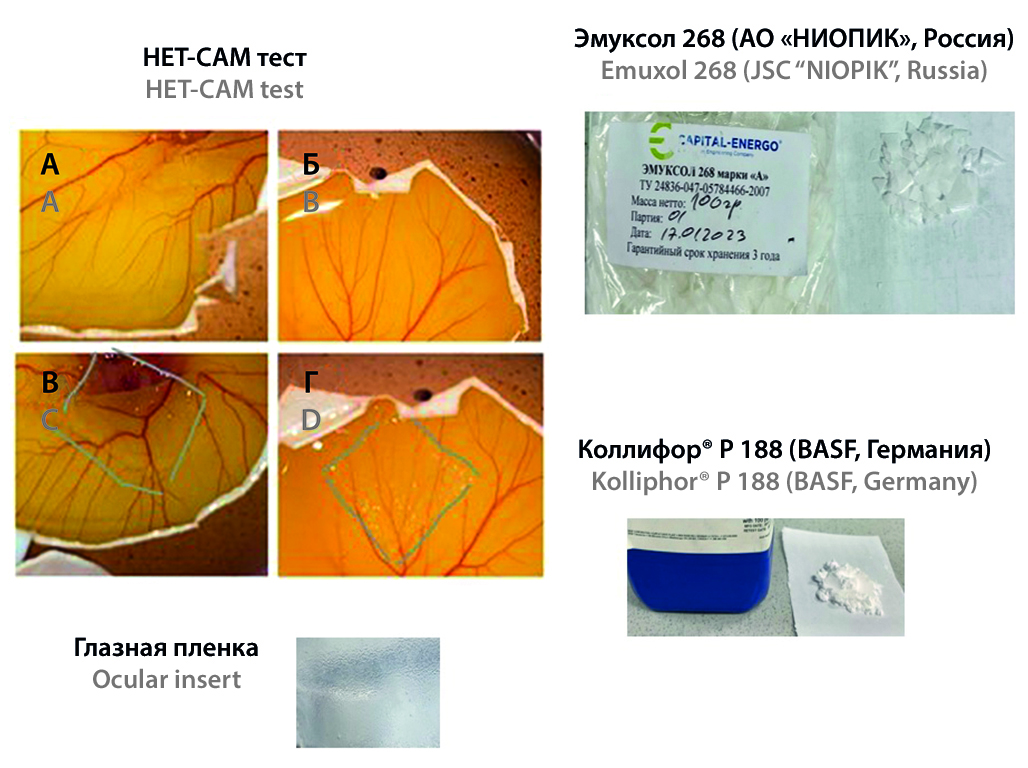
Introduction. Emuxol-268 (JSC "NIOPIK", Russia) is a block copolymer produced in Russia with similar in physicochemical and biological properties to poloxamer Kolliphor® P 188 (Pluronic F68) manufactured by BASF, USA. However, a comparison of the properties of natural polymers to assess the prospects of their dosage forms has not been carried out before.
Aim. The aim of the study was to demonstrate the interchangeability of auxiliary components using the example of the development of an ophthalmic drug insert by comparing the results of testing the dosage form in terms of such quality parameters as elasticity, thickness, mucoadhesion, pH, biodegradation time and irritation test (hen’s egg-chorioallantoic membrane test, HET-CAM test).
Materials and methods. Poloxamers Emuxol 268 (JSC "NIOPIK", Russia) and Kolliphor® P 188 (BASF, Germany), hydroxyethyl cellulose (Natrosol™ 250 HHX, Ashland Global Holdings Inc., USA), and glycerol (LLC "Tulskaya Pharmfabrika", Russia) were used in the experiment. Elasticity, thickness, mucoadhesion, pH, biodegradation time, HET-CAM test were used as screening methods to identify the benefits of the composition.
Results and discussion. Experiment results proved that the use of a domestic analogue makes it possible to create an ocular insert with improved quality parameters. The difference in the elasticity index of the inserts differs by 1.3 times, mucoadhesion – 1.7 times, biodegradation time – 2.5 times. In this connection, it can be assumed that an insert based on a domestic polymer contributes to an increase in the time of contact with the eye surface, thereby providing a prolonged effect of the drug and improving its bioavailability. The results obtained may be due to the difference in the average molecular weight of the hydrophobic polyoxypropylene part, which is 2600 Da for Emuxol 268 and 1800 Da for Kolliphor 188. The HET-CAM method showed the same results of the two compositions, both compositions do not have an irritating effect.
Conclusion. Summing up, the only analogue of Kolliphor® P 188 available on the Russian pharmaceutical market – Emuxol-268 of JSC NIOPIK is a promising substance for replacement in the development of ophthalmic dosage forms. Despite the differences in physicochemical properties of the domestic block copolymer in comparison with the replaced poloxamer 188, its introduction into placebo inserts gave improved results in terms of quality indicators, which was revealed during a biopharmaceutical analysis.
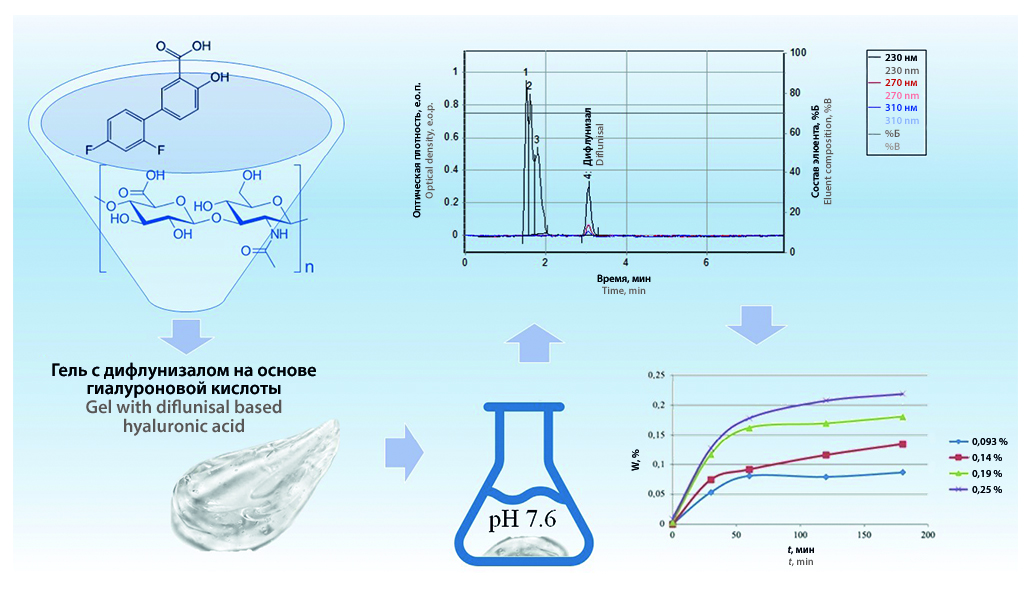
Introduction. The effectiveness of diflunisal in the treatment of cardiac amyloidosis has been clinically proven. Currently, only tablet forms of diflunisal are registered in the world, however, long-term use of NSAIDs leads to characteristic side effects. Therefore, delivery systems for diflunisal (including a form for external use) are now being actively developed to reduce side effects and improve its bioavailability.
Aim. Research of the dynamics of release of the active substance diflunisal from the polymer matrix of hyaluronic acid.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study are diflunisal gels in hyaluronic acid with a concentration of the main substance of 0.093, 0.14, 0.19 and 0.25 %. Quantitative determination was carried out by reverse-phase HPLC using a Prontosil C18, 120-5, 75 × 2 mm chromatographic column, thermostatically controlled at 40 °C. Eluent: phosphate buffer solution (PBS) with pH 3.0 and acetonitrile (30 : 70), flow rate 0.1 ml/min. Eluates were detected at wavelengths of 230, 270, 310 nm.
Results and discussion. During the work, a method (HPLC) was selected and a method for determining diflunisal in a HA matrix was developed. The delivery system under study significantly increases the solubility of diflunisal in an aqueous solution compared to the dissolution of the substance. The release of the active substance from the matrices was carried out in a phosphate buffer solution with pH 7.6. The release rate for all samples exceeded 90 % after 3 hours after the start of the experiment, with most of the active substance released within an hour.
Conclusion. The data obtained suggest that the release profile is characteristic of biodegradable matrices and diffusion-controlled delivery systems. Complete extraction of diflunisal from HA was achieved using PBS with pH 7.6 as a dissolution medium.
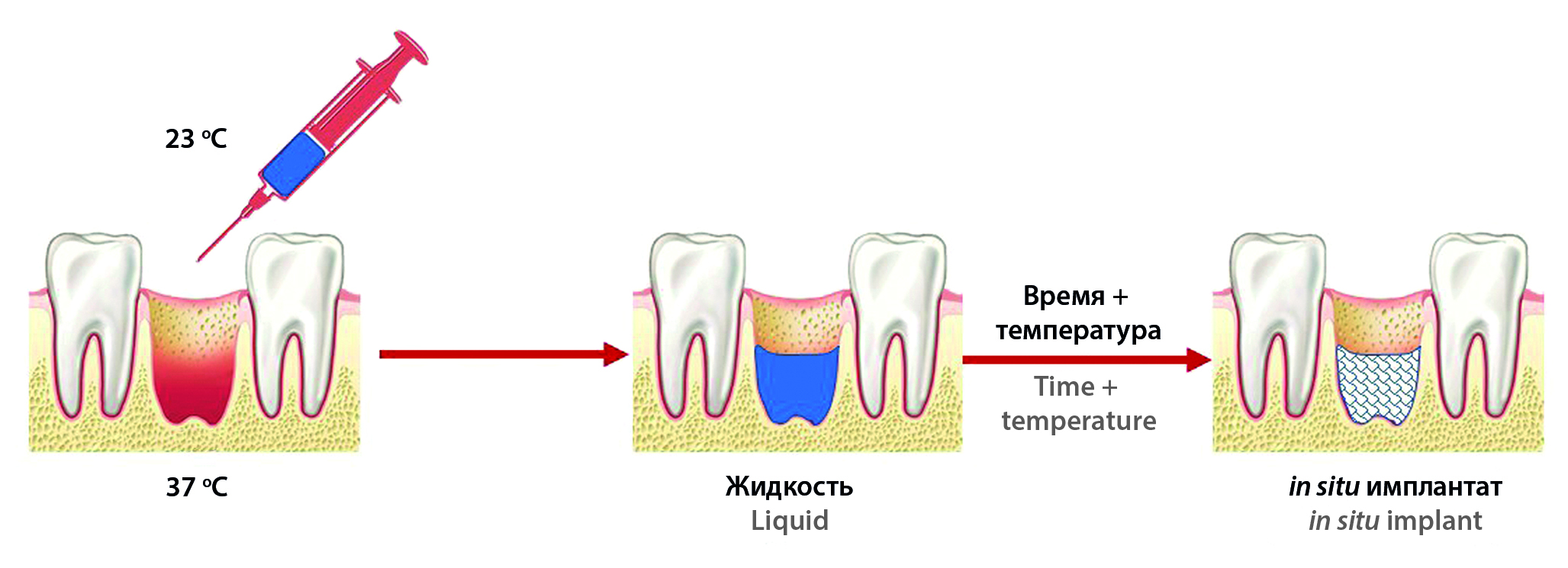
Introduction. The problem of pain relief after surgery is relevant in modern dentistry, as pain control is an important part of treatment. In addition to anesthesia, there are other problems of post-resection therapy such as bleeding from the wound and inflammation. Modern dental practice does not have a targeted delivery system or a medical product with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anesthetic or hemostatic action, which ensures high adherence of patients to the ongoing post-resection therapy.
Text. To solve this problem, it can be proposed to develop an in situ implant – a dosage form that is formed directly at the injection site, in the alveolar socket. Targeted delivery system has advantages: no need to use a medical dressing material; no risk of secondary contamination; dosing accuracy and target delivery to the lesion locus; high mucoadhesion to the site of application; the duration of the active ingredient release and others. The purpose of the review is to substantiate the possibility and relevance of developing a new in situ implant system for use in dental post-resection practice. The study was conducted on the main databases of publications (Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed and others), and patent search database on materials published from 2000 to the present. The study describes the currently existing in situ systems for dental problems, which could be a prototype of systems for delivering an anesthetic directly to the tooth socket, the polymers used to create them and the possibility of releasing drugs, and also characterizes existing drugs for the pain relief (applied both locally and for systemic action), in comparison with in situ systems, which have certain advantages and great potential for development.
Conclusion. Based on the results of the work, a conclusion about the possibility of pharmaceutical development of dental in situ implants was made, and the most promising polymers for phase transition in the alveolar socket were identified.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
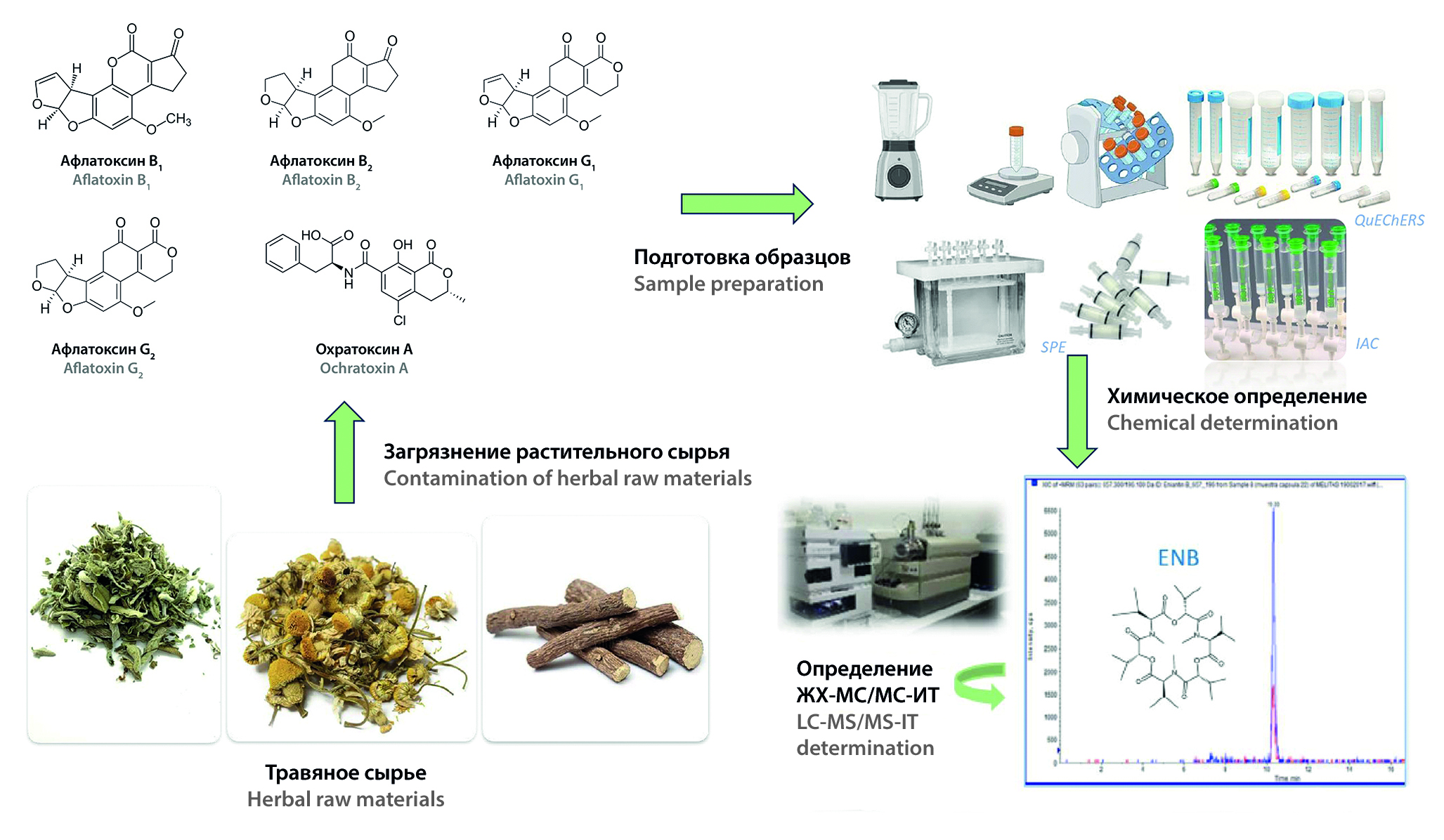
Introduction. Aflatoxins and ochratoxin A are secondary metabolites of microscopic mold fungi. They seriously threaten human and animal health. These toxins are carcinogenic, teratogenic, hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic substances. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified them as class IA and IIB carcinogens. The maximum permissible concentrations of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in the Russian Federation are currently regulated only in food products according to the Technical Regulation of the Customs Union 021 "On Food Safety". The content of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in medicinal plant raw materials is not regulated in any way. Harmful environmental and biological conditions such as temperature, humidity, air quality, insects and others during post-harvest handling can lead to contamination of medicinal raw materials with aflatoxins and ochratoxin A. Therefore, the detection of these toxins is one of the problems of raw materials quality control.
Text. The present review summarizes the following methods of sample purification, used at the sample preparation stage: solid-phase extraction, immunoaffin column and QuEChERS. This review also summarizes the following modern analysis methods for the identification of aflatoxin and ochratoxin A in medicinal plant raw materials: thin-layer chromatography, liquid chromatography, gas chromatography and screening methods.
Conclusion. The QuEChERS method has been identified as the most popular method for preparing samples for analysis. It is based on solid phase extraction technology. This method combines the variability of approaches to sample purification and allows people to study a wider range of toxins. The high-performance liquid chromatography method has been identified as the most popular method for qualitative and quantitative analysis. It has high selectivity, multicomponent analysis and low detection limits.
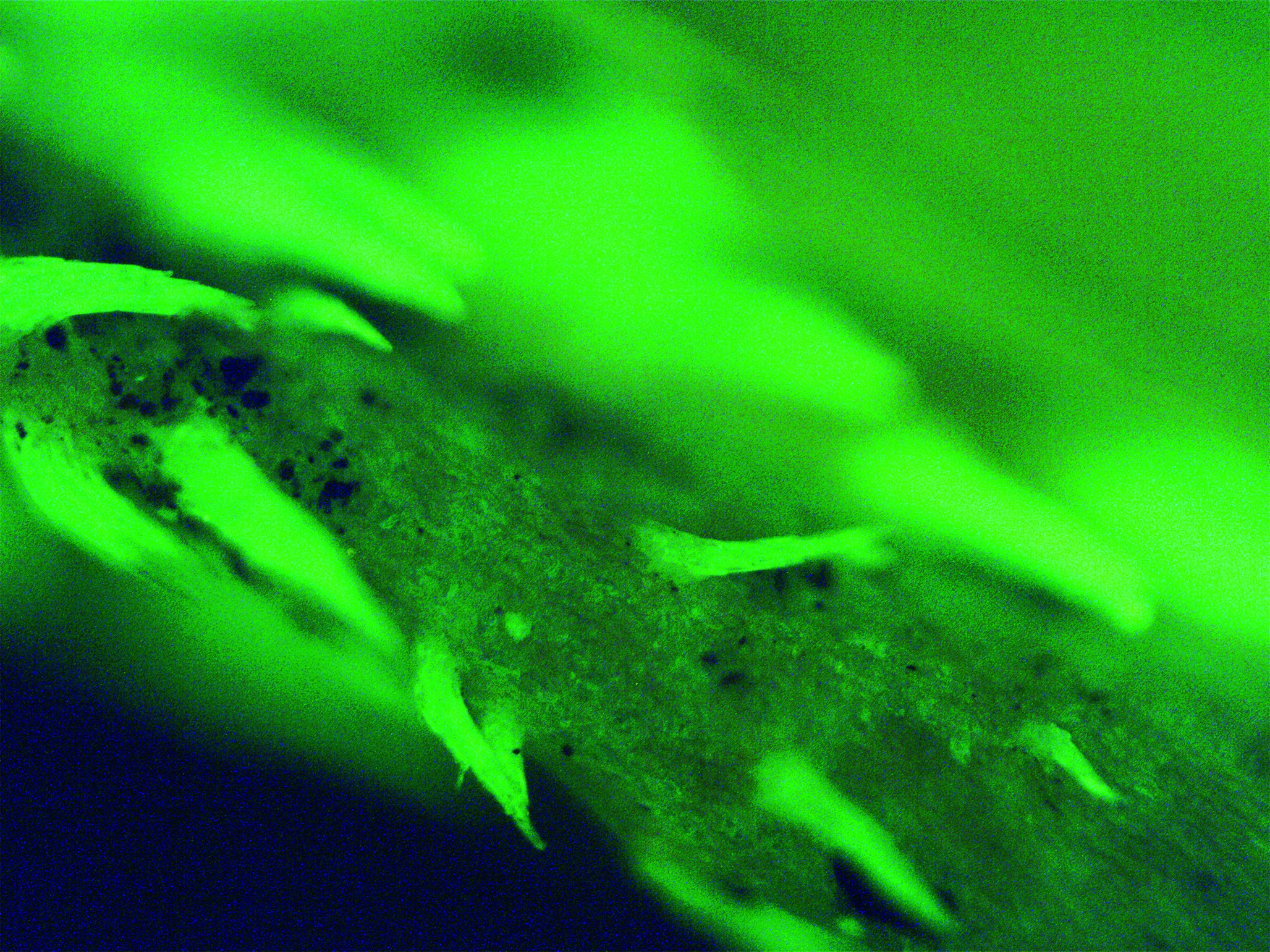
Introduction. The issue of standardization and quality assessment of medicinal plant materials is currently one of the most important. To do this, a number of parameters are evaluated, the primary of which is the assessment of the authenticity of the analyzed plant object. The problem of identifying official species in the presence of closely related species is typical for plants belonging to the genus Persicaria Mill., among which only two species are used in medical practice and there is regulatory documentation for the herbs of these plants. The similarity of morphological and anatomical features of plant species acceptable for medical use and impurities interprets the need to use additional modern methods of analysis. One of such selective methods for diagnosing plant materials, along with the well-known and used in pharmaceutical analysis, is luminescence microscopy.
Aim. The goal was to study the features of the luminescence of closely related species of the genus Persicaria Mill. to improve the process of their identification and standardization of official types of raw materials.
Materials and methods. For work, 10 species of the genus Persicaria Mill. were used from families Polygonaceae Juss., most common in the Central Chernozem region: P. maculosa Gray, P. tomentósa Bicknell, P. lapathifólia Delarbre, P. nodósa Opiz, P. scábra Moldenke, P. brittingeri Opiz, P. hydropiper Delarbre, P. minor Opiz, P. amphibia Delarbre, P. amphibia var. terrestris Munshi & Javeid. The plants were cut at a height of about 15 cm from the soil during mass flowering in the summer of 2020 in the Voronezh region, dried in the shade. Previously, before the study, the plants were divided into morphological components (stems, leaves, petioles, bells, flowers, fruits), for which herbarium samples were used in dried form and individual parts were examined, straightened on a glass slide. To assess the luminescence of objects, a Micromed-3 Lum microscope (Russia) with a luminescent nozzle housing was used.
Results and discussion. It was revealed that the intense fluorescence of large trichomes, the conducting system, guard cells of stomata, thickening of cell walls, and, in some species, the contents of receptacles and glands, is common to all studied species. A number of characteristic features of tissue luminescence for the studied species have been revealed: P. hydropiper has numerous brightly luminous receptacles and glands on all morphological parts. For P. maculosa, the presence of large receptacles along the veins was established for the first time. The perianth, glandules, and filiform hairs of the bell of P. brittingeri are clearly visible and have a yellowish-green luminescence. The leaf glands of P. tomentósa, unlike other species, do not have luminescence. The perianths of P. scábra and P. tomentósa have a yellowish-orange glow. The membranous trichomes are clearly visible in P. lapathifólia and stand out with a brownish tint. The largest number of long tufted trichomes with a bright greenish glow is characteristic of P. amphibia var. terrestris.
Conclusion. The method of luminescence microscopy was first applied to the analysis and identification of identification parameters, new diagnostic features were established and visualized, allowing the most accurate identification of species of the genus Persicaria.
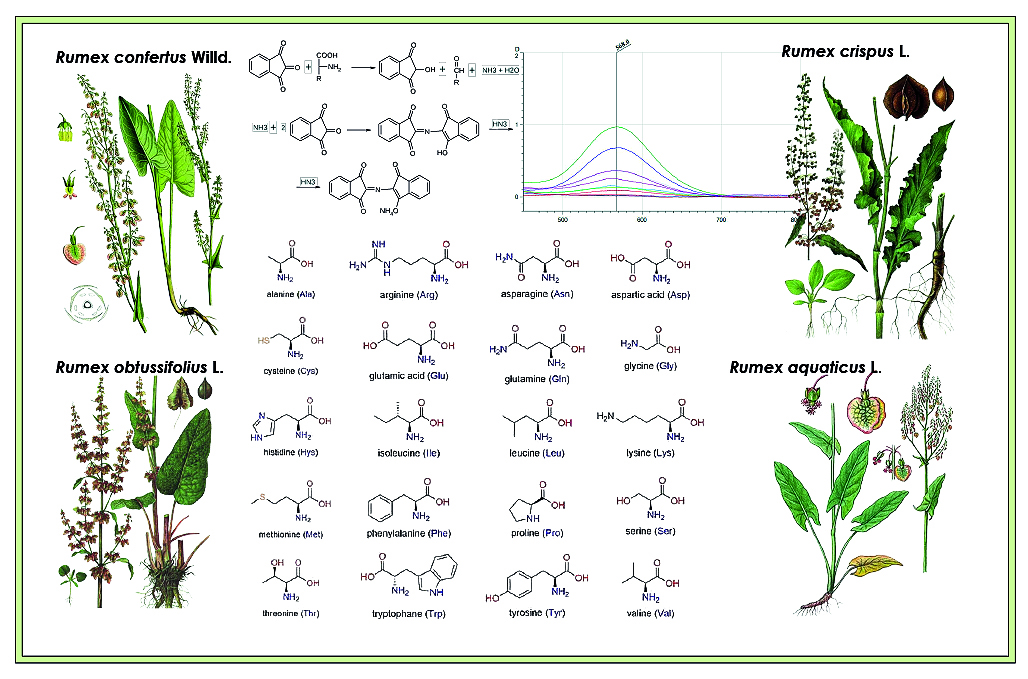
Introduction. Amino acids (AA), the primary metabolites in plants, play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including the synthesis of phenolic compounds. Drug products and dietary supplements made from medicinal plants can become a rich source of both nonessential and essential amino acids. High levels of free amino acids found in herbal raw material often indicate the presence of biotic and abiotic stress in the plants. Therefore, understanding the dynamics of bioactive compound accumulation in plants throughout their phenological phases of development is critical to optimizing their potential health benefits.
Aim. To compare qualitative composition and dynamics of AA accumulation in the underground organs of four representatives of the Rumex genus: R. confertus, R. crispus L., R. obtusifolius L., R. aquaticus L. of three different vegetative phases.
Materials and methods. Water extracts from underground organs of the studied plants were analyzed using two different methods for qualitative and quantitative analysis. Extracts were applied to the chromatographic plates TLS Silica gel 60 F254 (Merk, Germany) 20 × 20 cm with a micro-syringe (LLC "Tsvet", Russia). After elution, the plates were treated with a 2 % ninhydrin solution. Quantitative analysis was carried out using the SF-2000 spectrophotometer (LLC "OKB Spectr", Russia).
Results and discussion. The amino acid profile of the underground organs of R. confertus, R. crispus L., R. obtusifolius L., R. aquaticus L. during three vegetative phases was determined using the TLC method; the quantitative analysis performed using spectrophotometry.
Conclusion. The most diverse amino acid (AA) profiles were found in the withering phase in all Rumex species, with up to 9 amino adsorption zones. In contrast, the least diverse AA profiles were observed in the flowering phase, ranging from 2 to 4 adsorption zones. The quantitative content of AA was lowest in the flowering phase, increased during the regrowth phase, and peaked in the withering phase. However, R. crispus L. showed an unusual pattern, with the highest quantitative content of AA detected in the regrowth phase.
Introduction. One of the most promising types of immunosensors is quartz crystal microbalance immunosensors (QCM immunosensors). Single-use biosensors are financially demanding, thus rendering the regeneration of the biosensor surface a pertinent issue for QCM immunosensors. Regeneration plays a pivotal role in sustaining the functionality of the sensor and enabling its reusability. In this article, "immunosensor" and "immunobiosensor" are interchangeable terms and are used to denote the same type of biosensors operating based on immunochemical interactions between antigens and antibodies.
Text. This review discusses the features, operational principles, and applications of QCM immunosensors. Particular attention is directed toward the challenge of regenerating the biosensor surface as a key aspect ensuring their effective operation and the potential for multiple uses. Various regeneration methods and their advantages are examined. The reactivation of the biosensing layer on the QCM electrode secures its stability and functionality over extended periods, which is especially valuable in clinical and scientific research. The possibility of reusing the biosensor reduces material costs and waste production, aligning with ecological and economic concerns. Furthermore, the ability to analyze different analytes on the same surface fosters versatility in multiparametric investigations. It is essential to emphasize that the removal of residual analytes and the biosensor's regeneration process enhance reliability, selectivity, heightened sensitivity, and the potential for reproducible measurements.
Conclusion. An analysis of scientific literature underscores the pivotal role of biosensor regeneration in maintaining functionality and reusability. The strength of the antigen-antibody interaction determines the conditions, which must be tailored individually for each antigen-antibody pair. The review thoroughly explores three primary approaches to the regeneration of piezoelectric transducers, including the use of a chemical method, oxygen plasma-based techniques, and the application of Piranha solution.
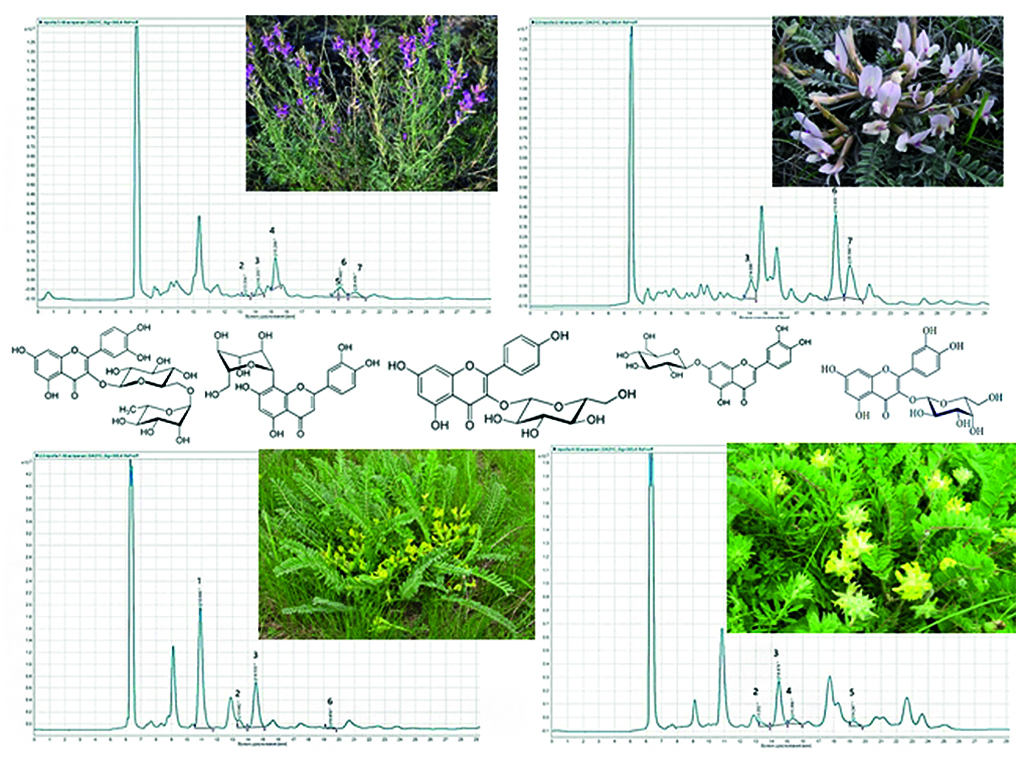
Introduction. The search for new promising sources of biologically active substances is one of the tasks of modern pharmacognosy. Among the huge variety of species of the genus Astragalus L., only a few of them have been studied. In addition, none of them is included in the current edition of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation. In our opinion, the study of four species of this genus of Astragalus L. (A. dasyanthus, A. varius, A. testiculatus, A. henningii) growing in the Volga region is of interest.
Aim. Study of the glycoside composition of flavonoids in the astragalus herb of four species (A. dasyanthus, A. varius, A. testiculatus, A. henningii) by HPLC-UV using external standards.
Materials and methods. The material was samples of astragalus grass (A. dasyanthus, A. varius, A. testiculatus, A. henningii), collected on the territory of the Saratov region in accordance with the basic rules of collection and preparation and dried to an air-dry state. Aqueous-alcoholic extracts (1 : 50) were analyzed. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of flavonoid glycosides was carried out on an Agilent 1260 chromatograph (Agilent Technologies, USA) equipped with a diode array detector, manual sample injection (Agilent G1328C manual injector, Agilent Technologies USA) and an Agilent Open Lab CDS system for collecting and processing chromatographic data. The elution gradient was selected individually using 0.1 % phosphoric acid/acetonitrile solution as solvents. Compounds were identified by retention times and UV spectra of reference standards (RS). The quantitative content of each detected component was expressed in mg/g of dry raw material. All studies were repeated five times, the results were statistically processed using MS Exсel 2010.
Results and discussion. The chromatographic profiles of aqueous-alcoholic extracts from the herbs of four types of astragalus were studied. Differences were found in both the qualitative composition and quantitative content of flavonoid glycosides in the grass of the analyzed species. The largest number of compounds was found in the herb of A. varius (6 compounds), 4 compounds were identified in the herb of A. dasyanthus and A. henningii, and 3 compounds were identified in the herb of A. testiculatus. The dominant components in the herb of A. henningii are orientin and rutin, in the herb of A. testiculatus and A. varius it is cynaroside, and in A. dasyanthus it is rutin.
Conclusion. A HPLC-UV method was developed for determining the quantitative content of flavonoid glycosides in extracts from the herbs of four species of astragalus (A. dasyanthus, A. varius, A. testiculatus, A. henningii) and the chromatographic profiles of the analyzed samples were studied.
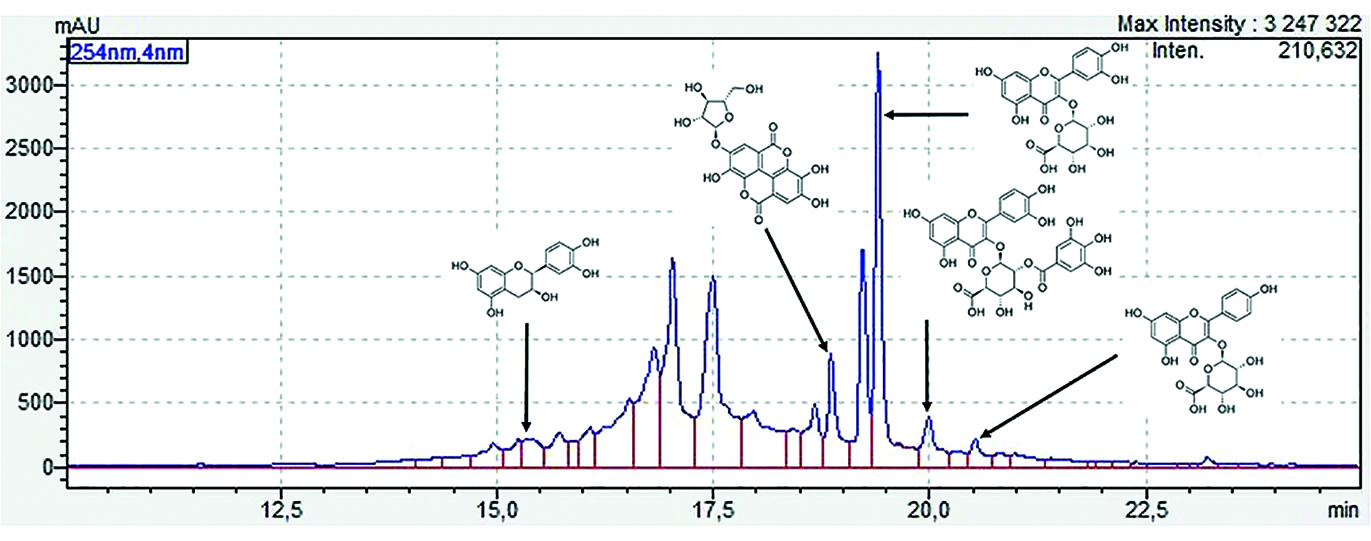
Introduction. One of the key tasks of the pharmaceutical industry is the search for new promising compounds – potential drug candidates. Natural objects, especially plants, have long been rich sources of new molecules and are widely used in the global food and pharmaceutical industries. Cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus L.) is a perennial herb from the Rosaceae family. The fruits and leaves of R. chamaemorus contain a wide variety of polyphenolic secondary metabolites – hydrolysable/condensed tannins and flavonoids. Extracts enriched by polyphenols showed significant antiproliferative activity and inhibition of cell growth, and also induce cell apoptosis. As a result of our previous phytochemical research of R. chamaemorus leaves, five polyphenolic secondary metabolites belonging to the classes of tannins and flavonoids were isolated and characterized.
Aim. Screening of previously isolated from R. chamaemorus individual compounds for the hemostasis system in vitro and identification of the most promising compounds for subsequent pharmaceutical development.
Materials and methods. Experiments under in vitro conditions were performed on the blood of healthy male donors. The research of the effect on platelet aggregation was carried out according to the Born method on an AT-02 aggregometer (LLC "SPF "Medtech", Russia). Determination of anticoagulant activity was carried out by conventional clotting tests on a Solar CGL 2110 turbidimetric hemocoagulometer (CJSC "SOLAR", Russia). Cytofluorimetric analysis was performed on a NovoCyte instrument (Agilent Technologies, USA).
Result and discussion. The influence of the isolated compounds 1–5 on the parameters of activation, platelet aggregation and the coagulation component of hemostasis was studied. At a concentration of 1.0 mg/ml, compounds 1–5 did not affect the fibrinogen concentration and prothrombin time. Compounds 1, 3 and 5 completely suppressed platelet activation at the studied concentrations. Compounds 1 and 3 showed antiaggregation activity comparible to the values of acetylsalicylic acid and are contained in all aqueous and alcoholic extracts of R. сhamaemorus leaves; their quantitative content varies depending on the extraction conditions.
Conclusion. Thus, as a result of the screening of individual compounds 1–5 isolated from the leaves of R. chamaemorus their antiaggregating and anticoagulation properties were established. Compounds 1 (4-O-α-L-arabinofuranosylellagic acid) and 3 (quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide) showed antiaggregation activity comparible to that of acetylsalicylic acid, and are the most promising of the studied series of compounds for the subsequent pharmaceutical development of new antiplatelet agents.
Introduction. Results of original research carried out by means of high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) of various plant samples (air-dry raw material) of Dioscoreaceae, Ranunculaceae, Fabaceae, Melanthiaceae, Scrophulariaceae families are presented in this article.
Aim. To carry out preliminary qualitative analysis by HPTLC method of steroidal sapogenins composition in hydrolyzed extracts, obtained from vegetative samples of above-ground and underground organs of some Dioscoreaceae, Ranunculaceae, Fabaceae, Melanthiaceae, Scrophulariaceae families.
Materials and methods. Extraction from pre-dehydrated raw materials was carried out with 50 % aqueous isopropanol (c.p.) in an ultrasonic bath, followed by acidic hydrolysis of O-glycoside bonds, evaporation and redissolution of dry residue in 99 % methanol (c.p.); purification from suspended solids by filtering through filters with 20 µm perforation diameter. HPTLC was performed on apparatus complex CAMAG (Switzerland) using HPTLC Aluminium sheets Silica gel 60 F254 plates 20 × 20 cm, which were cut to the size 20 × 10 cm.
Results and discussion. After scanning densitometry at 254 nm, we found that the separation of isopropanol extracts, followed by redissolution in strong methanol in this solvent system allows a fairly acceptable separation and identification of the compounds studied. Comparison of the tracks of plant extracts was performed with standard samples of steroid sapogenins, whose methanol solutions were applied to one stain-strobe of track 1, provided that they had different Rf indices and coloration after derivatization.
Conclusion. Diosgenin was identified in plant extracts of rhizomes and roots of Dioscorea nipponica and Dioscorea caucasica and in seeds of Trigonella foenum-graecum preliminarily. Sarsasapogenin was verified in extracts of fruits of Sophora japonica, tigogenin in extracts of seeds of Trigonella foenum-graecum, herb of Pulsatilla patens and herb of Veronica officinalis. Yamogenin was detected in extracts of seeds of Trigonella foenum-graecum and herb of Veronica officinalis. This work is exploratory in nature, assessing the presence of certain saponins by their sapogenins in selected extracts. We will optimize the HPLC separation procedure and choose other detection methods to unambiguously assess the co-presence of the studied sapogenins with approximately the same staining shades after derivatization and matching retention indices: there are pairs of steroidal sapogenins that have the same retention, we decided to group them in mixtures so that there would be separation within the group and subsequent comparison with the original extracts would make it possible to identify those or other sapogenins in such extracts.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
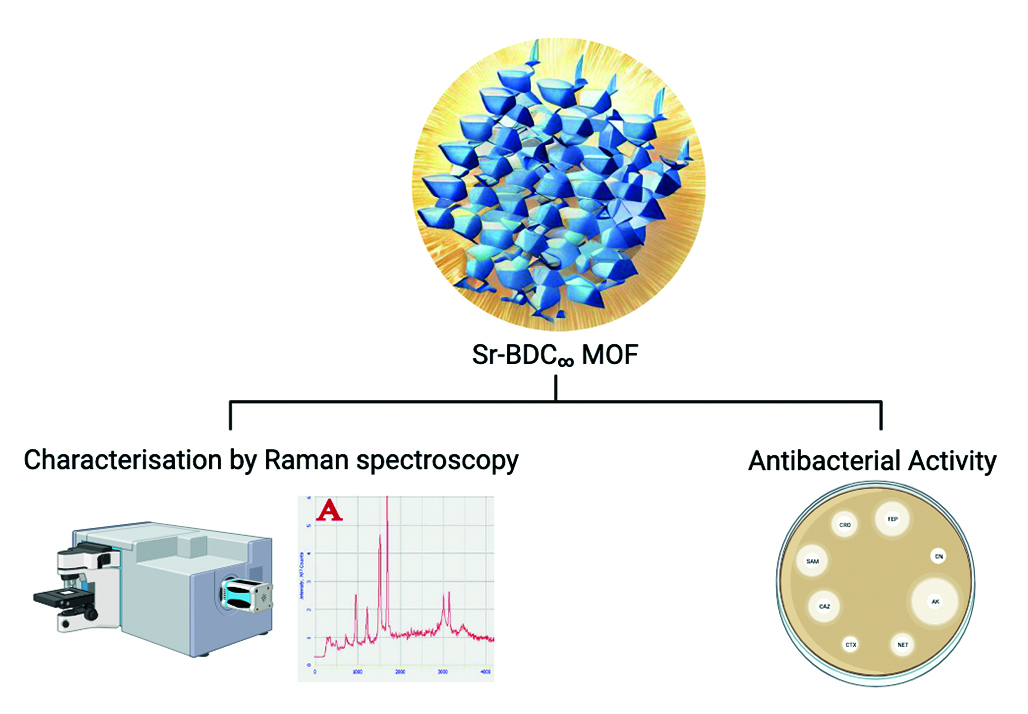
Introduction. In this work, Sr-BDC MOFs were obtained by a simple solvothermal process without the use of elevated pressure. This method is easily scalable and does not require any special equipment. In this work, the crystals obtained from the synthesis were studied by Raman spectroscopy. In addition, the obtained materials were analysed for antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and against Gram-negative bacteria.
Aim. During this work, the main objective was to comparatively evaluate the antibacterial properties of Sr-BDC MOFs activated by different methods (and without activation).
Materials and methods. In this work we used a solvothermal process using terephthalic acid, strontium nitrate and dimethylformamide. The peculiarity of this method is the absence of autoclaving in the synthesis process. Optical microscopy and Raman spectroscopy were used for characterization. Also, to study the antibacterial properties, a medium diffusion test was performed. The combination of these methods will help to establish the relationship between the method of activation and the biological activity of the resulting materials.
Results and discussion. In this work, the chemical structure of Sr-BDC MOFs was studied by Raman spectroscopy. The influence of the activation method on the chemical structure of MOFs was studied. It was found that the characteristic peaks of Raman spectroscopy can be used to confirm the removal of solvent (DMFA) from the crystal structure. In addition, tests on the manifestation of antibacterial activity were carried out for MOFs with different activation method. The MIC and MBC were established for each sample.
Conclusion. In the course of the work the effect of the activation method on the chemical structure of Sr-BDC MOFs was shown. We also found that the activation method could affect the biological activity of the obtained MOFs. It was also demonstrated that MOFs exhibit different antibacterial activities depending on the type of bacteria, which can be primarily related to the composition of the cell wall of microorganisms.
Introduction. Strokes remain the second leading cause of death and the third leading cause of disability. Additional serum biomarker testing should be used to better diagnose transient ischemic attack (TIA), but most neurospecific biomarkers have low prognostic specificity and sensitivity. Timely identification of TIA and differential diagnosis of stroke in the first hour will ensure a shorter period of patient recovery and reduce the risk of mortality and disability. Serum biomarker studies should be included to overcome the difficulty of diagnosing TIA.
Text. Neurospecific biomarkers such as S100B, GFAP, and NSE are used to diagnose acute ischemic damage to glial cells and neurons. S100B and GFAP are detected in astrocytes and NSE in neurons and cells of the neuroendocrine system. Elevated serum concentrations of these biomarkers are associated with various pathological conditions such as strokes and brain injuries and other central nervous system (CNS) lesions. Dynamic monitoring of biomarker concentrations makes it possible to evaluate the efficacy of the ongoing therapy and to identify predictors of patient deterioration for prompt correction of therapeutic procedures. To create a diagnostic panel it is necessary to study metabolic processes in ischemic tissue, taking into account concomitant diagnoses and results of neuroimaging, and to use breakthrough advances in machine learning and big data.
Conclusion. The review showed that none of the assessed biomarkers can be recommended for the diagnosis of cerebral circulation disorders, but the combination of several neurospecific biomarkers can significantly improve diagnostic efficiency and find application in the differential diagnosis of stroke, intracranial hematoma, and other brain lesions for the purpose of early pharmacotherapy of CNS lesions and as surrogate endpoints during clinical trials.
Introduction. Long-term use of anthracyclines during cancer chemotherapy has been associated with the development of potentially life-threatening cardiotoxicity. Despite researches ongoing since the middle of the last century, approaches to the choice of therapy remain limited.
Text. Doxorubicin currently is the most widely used chemotherapy. The leading side effect mechanism of the drug is the formation of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria with the mediated development of oxidative stress, which contributes to myocardial damage. However, despite the huge number of scientific papers devoted to various aspects of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, its prevention and treatment, this issue requires detailed investigation in order to develop more advanced methods for early diagnosis and timely cardioprotective therapy.
Conclusion. The current review discusses the pathogenetic mechanisms of cardiotoxicity associated with the use of doxorubicin chemotherapy. The pathogenesis of the cardiomyocytes death mechanism will provide an opportunity to develop new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in the clinical practice.
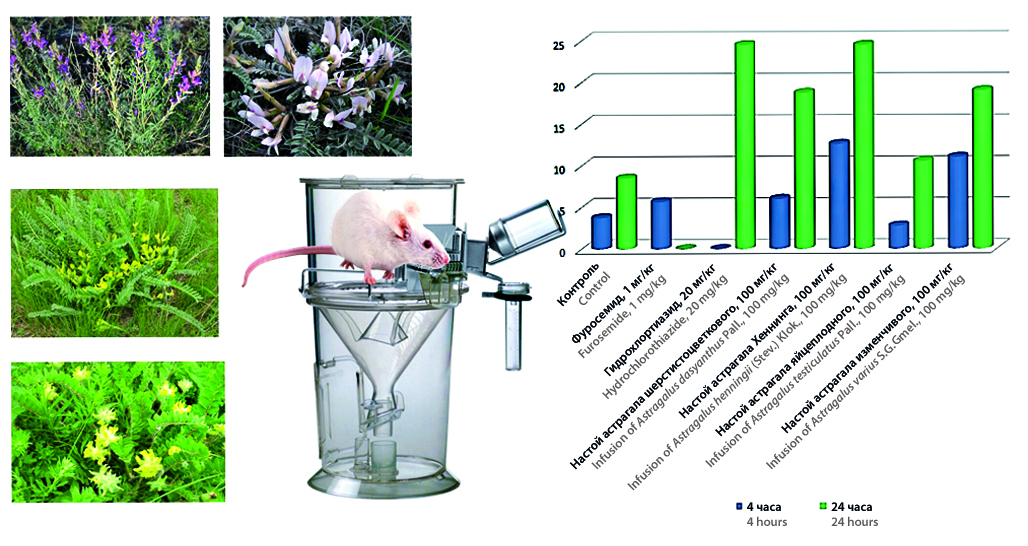
Introduction. Astragalus L. is the largest genus of the Fabaceae family and one of the largest genera of vascular plants on Earth. The official type of raw material included in the 7th edition of the European Pharmacopoeia is Radix Astragali – the dried root of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge and Astragalus mongholicus Bunge. Extracts obtained from astragalus root have anti-inflammatory, immunostimulatory, antioxidant, diuretic effects. In traditional medicine, the herb of Astragalus dasyanthus Pall. is actively used. An infusion of the herb of Astragali dasyanthi has sedative, hypotensive and diuretic effects. However, the raw material is not official and is not included in the list of plant raw materials of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation of the XIV edition. Promising species of the genus Astragalus L. can be not Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge and Astragalus dasyanthus Pall., but also other species, for example, Astragalus varius S.G. Gmel., Astragalus testiculatus Pall., Astragalus henningii (Stev.) Klok., which are widespread in the Saratov region. In view of the available data on the presence of the herb of Astragalus dasyanthus Pall. and Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge of the diuretic effect, it is of interest to study the diuresis of extracts from the herb of other species of the genus Astragalus L.
Aim. To study the diuretic activity of infusions from the herb of four types of astragalus: Astragalus dasyanthus, Astragalus varius, Astragalus testiculatus, Astragalus henningii in 4- and 24-hour experiments on male rats.
Materials and methods. The study of the diuretic activity of aqueous extracts from the herb of four types of Astragalus was performed on 42 white male rats, which were divided into 6 experimental and control groups of 6 animals. Aqueous extracts from Astragalus herb were prepared in the ratio of raw material-extractant 1:10, all obtained infusions met the requirements for these dosage forms according to the General Pharmacopoeia of the State Fund of the Russian Federation of the XIV edition. Aqueous extracts were administered to animals intragastrically through an umbrella at a dose of 100 mg/kg. During the experiment were collected 4-hour and 24-hour portions of urine. The comparison drug in the 4-hour experiment was furosemide at a dose of 1 mg/kg, and in the 24-hour experiment, hydrochlorothiazide at a dose of 20 mg/kg.
Results and discussion. As a result of the experiment, the diuretic effect of the infusion of the herb of Astragalus dasyanthus both in the 4-hour experiment and in the 24-hour experiment. Also in both experiments, the most pronounced diuretic effect was found in the infusion of the herb of Astragalus henningii at a dose of 100 mg/kg compared with herb infusions Astragalus dasyanthus, Astragalus varius. Diuretic effect Astragalus henningii exceeded the diuretic activity of furosemide at a dose of 1 mg/kg, while a comparable effect was observed with hydrochlorothiazide at a dose of 20 mg/kg. Diuretic effect of herbal infusion Astragalus varius in a 4-hour experiment exceeded the diuretic effect of herb infusion Astragalus dasyanthus and furosemide at a dose of 1 mg/kg, and in a 24-hour experiment comparable to the diuretic effect of herb infusion Astragalus dasyanthus, but lower than that of hydrochlorothiazide at a dose of 20 mg/kg and herb infusion Astragalus henningii. Diuretic effect of herbal infusion Astragalus testiculatus at a dose of 100 mg/kg was not detected both in the 4-hour and in the 24-hour period. The diuretic activity of the group that received the infusion of the herb of Astragalus testiculatus was at the level of the control group, compared with other experimental groups, a statistically significant decrease in diuresis was observed in animals.
Conclusion. The experiment confirmed the diuretic effect of the infusion of the herb of Astragalus dasyanthus and for the first time discovered the diuretic effect of the infusion of the herb of Astragalus varius and the infusion of the herb of Astragalus henningii. Among the studied infusions, the most pronounced diuretic effect was observed in Astragalus henningii herb infusion. The diuretic effect of Astragalus varius infusion is higher than that of Astragalus dasyanthus infusion. in a 4-hour experiment and did not differ in effectiveness from the infusion of the herb of Astragalus dasyanthus in a 24 hour experiment. The diuretic effect of the infusion of the herb astragalus oviparous was not revealed.
Introduction. Adalimumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody, is a tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) inactivator that is used against a number of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and other most common inflammatory arthropathies (ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis). Despite the proven efficacy of adalimumab treatment, there is a risk of adverse events, tied up with the formation of anti-drug antibodies, including neutralizing antibodies. Currently, the evaluation and characterization of neutralizing antibodies has become an important part of clinical trials in the development of new drugs and biosimilars.
Aim. The aim of this study is to develop and validate the cell-based functional method for neutralizing anti-adalimumab antibodies determination in human serum.
Materials and methods. For determination of neutralizing anti-adalimumab antibodies, the cell line L-929 has been employed. L-929 is a cell line sensitive to the TNFα-mediated apoptosis; the neutralizing antibodies interact with adalimumab that leads to TNFα-mediated cytotoxicity. Cytotoxicity was measured using resazurin, an aromatic compound that is a redox indicator.
Results and discussion. The developed method was validated for cut point, selectivity, sensitivity, precision, specificity and stability (short- and long-term). An important part of a method development for determining neutralizing antibodies is the selection of concentrations of TNFα (4 ng/ml) and adalimumab (250 ng/ml), as well as determining the minimum required dilution – this parameter is established as 1 : 20. Cut point was chosen as a «floating» cut point, and a correction factor (normalization factor) was determined equal to 0,86. The sensitivity of the developed method was estimated at 108,9 ng/ml of neutralizing anti-adalimumab antibodies.
Conclusion. The obtained results can be applied for determining anti-adalimumab neutralizing antibodies in the assessment of the adalimumab immunogenicity, including clinical trials.
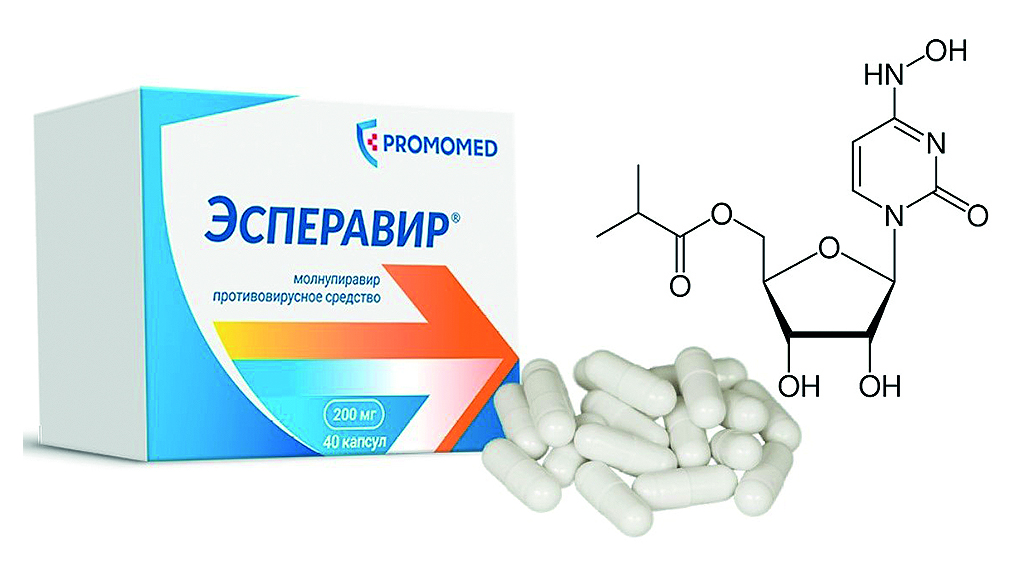
Introduction. The pandemic of the new coronavirus infection COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) was caused by a single-stranded RNA virus SARS-CoV-2 (Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2). Molnupiravir is an antiviral drug with activity against RNA viruses including SARS-CoV-2. Molnupiravir exerts the antiviral effect by introducing copy errors during viral RNA replication – by that the replication of SARS-CoV-2 inhibits. For oral administration of molnupiravir the drug Esperavir® has been registered in Russia.
Aim. The aim is pharmacokinetics study of Esperavir®, capsules 200 mg (the manufacturer is JSC "Biokhimic", LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia, as registration certificate holder) by a single dose (800 mg) and multiple doses oral administration (800 mg twice a day with a gap of 12 hours between doses) in healthy volunteers in a phase I pharmacokinetics study, comparison the obtained data of pharmacokinetic parameters with the literature data.
Materials and methods. The clinical and analytical phases of the pharmacokinetic study as well as pharmacokinetic analyses have been performed as a part of a clinical trial of the drug Esperavir®, capsules 200 mg (the manufacturer is JSC "Biokhimic", LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia, as registration certificate holder). Chromatographic separation and detection by Nexera XR high-performance liquid chromatograph with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry LCMS-8040 (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). The pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated with the Boomer pharmacokinetic analysis add-in for Microsoft Excel (Department of Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism, Allergan, Irvine, CA 92606, USA). Descriptive pharmacokinetic statistics were calculated with Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, USA).
Results and discussion. Pharmacokinetic parameters for cohort 1 (800 mg single dose of Esperavir®) and for cohort 2 (800 mg of Esperavir® twice a day with a gap of 12 hours between doses) were calculated. Averaged pharmacokinetic profiles of mean NHC concentrations over time in linear and log-linear scales were plotted. The geometric mean of Cmax and T1/2, the median, minimum and maximum of Tmax showed the comparability of the obtained data after a single dose administration of 800 mg of Esperavir® and the available literature data.
Conclusion. According to the concentrations from the analytical phase of the pharmacokinetic study the pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated, averaged pharmacokinetic profiles in linear and log-linear scales were plotted after a single dose and multiple doses of the drug Esperavir®, capsules (the manufacturer is JSC "Biokhimic", LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia, as registration certificate holder). The comparability of the obtained data and the available literature data was shown. The results justified the study of the subsequent phases of clinical trials of Esperavir®.
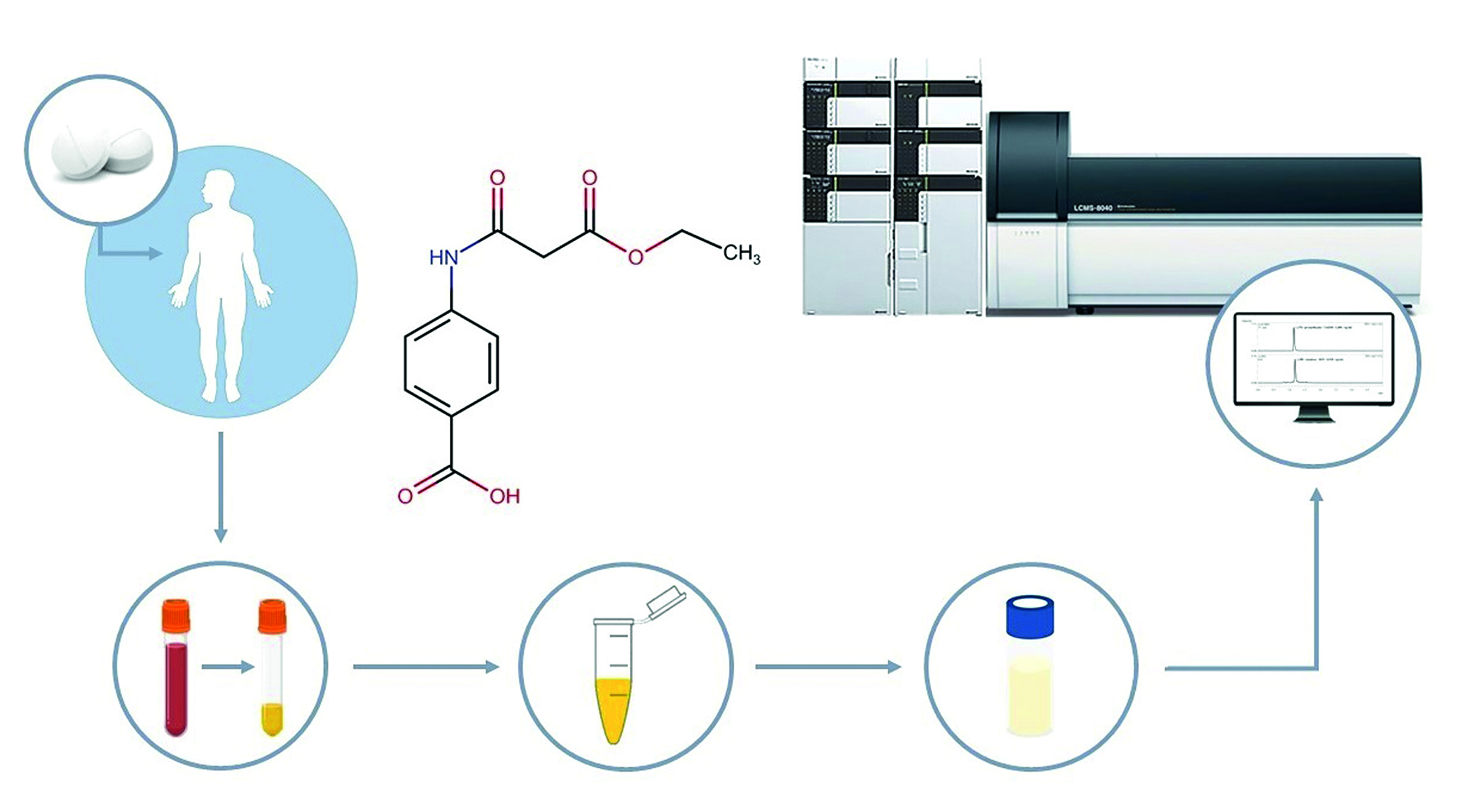
Introduction. Apixaban is an anticoagulant used in a number of thromboembolic diseases with an improved benefit-to-risk ratio, according to multiple clinical studies. Due to the prescription of apixaban as antithrombotic therapy in patients with COVID-19, an increase in its use has been observed. Thus, due to the widespread use of apixaban and the need to conduct pharmacokinetic and bioequivalence studies of the drug, it is important to develop and validate a simple and sensitive method for the quantitative determination of apixaban in human blood plasma.
Aim. The aim of the study is to develop and validate a method for the determination of apixaban in human blood plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass selective detection (HPLC-MS/MS) for the subsequent bioanalytical study.
Materials and methods. The determination of apixaban in human plasma was carried out by HPLC-MS/MS with rivaroxaban as an internal standard. The method of protein precipitation with acetonitrile was used as sample preparation. Mobile phase: 0.1 % solution of formic acid in water (eluent A); 0.1 % solution of formic acid in acetonitrile (eluent B). The total run time was 3.00 min. Column: Shim-pack Velox Biphenyl; 2.7 µm; 50 × 2.1 mm. Ionization source: electrospray with positive ionization mode. MRM transitions: 460.15 → 443.10 m/z (apixaban); 436.05 → 144.95 m/z (rivaroxaban).
Results and discussion. The developed method was validated in accordance with the EAEU requirements for the following parameters: selectivity, calibration curve, accuracy and precision, lower limit of quantitation, suitability of standard samples, matrix effect, recovery, stability, carry-over, dilution effects. The parameters met the acceptance criteria.
Conclusion. The confirmed analytical range of the developed and validated method was 1.00–300.00 ng/mL in blood plasma. The method for determining apixaban in blood plasma is simple and sensitive. This method was tested during the analytical part of the bioanalytical study and can be used to conduct other pharmacokinetic studies of apixaban drugs.
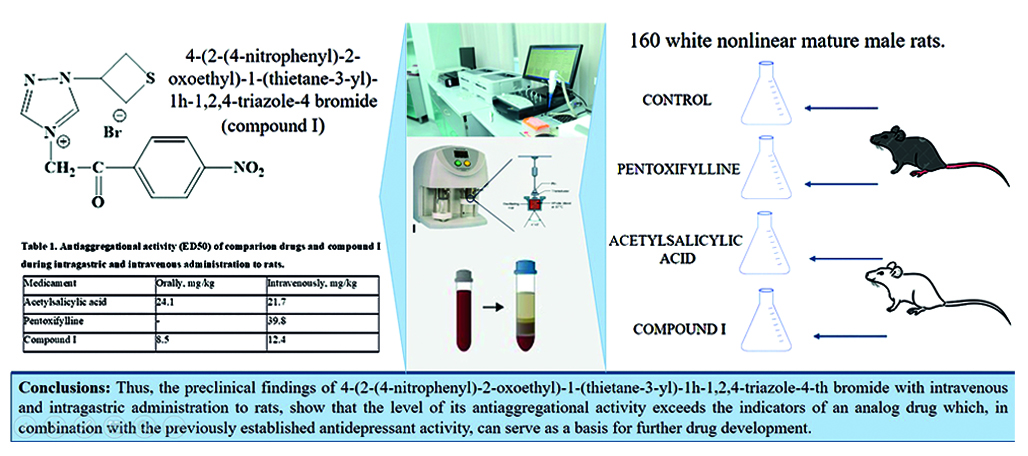
Introduction. A characteristic manifestation of vascular brain damage is depressive disorders that accompany both acute and chronic disorders of cerebral circulation. Depression not only reduces the patient's quality of life, but also complicates the treatment of basic vascular disease, increases the risk of stroke and death. Therefore, complex therapy of vascular depression includes not only antidepressants, but also basic means to correct the consequences of disorders of cerebral blood flow, including with antiplatelet activity. In this regard, the development of a new molecule based on thietane-containing heterocycles, combining the properties of an antidepressant and an antiplatelet agent.
Aim. To conduct a preclinical evaluation of 4-(2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1-(thietane-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4 bromide when administered to rats.
Materials and methods. A study was conducted of the effect of 4-(2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1-(thietan-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-bromide on the hemostasis system during intravenous and intragastric administration to healthy white non-linear sexually mature male rats (n = 160). Thromboelastography was performed on a TEG 5000 device, activated with a 0.2 M solution of calcium chloride, Born aggregometry and standard clotting tests to assess the coagulation component of hemostasis.
Result and discussion. The findings show that 4-(2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1-(thietane-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-4-th bromide with peroral administration exceeded acetylsalicylic acid by 2.8 times in terms of ED50, and by 1.8 times with intravenous way of administration accordingly. A similar effect of pentoxifylline in the intravenous route of administration was recorded at a concentration of 27.8 mg/kg versus 12.4 mg/kg of compound I. The results of a complex method to assess the state of the hemostasis system indicate a more pronounced antiaggregational effect of compound I compared with pentoxifylline and acetylsalicylic acid.
Conclusion. Preclinical studies of 4-(2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1-(thietane-3-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-4 bromide, was demonstrated that a combination of antidepressant and antiplatelet activity, which can serve as a basis for further drug development.
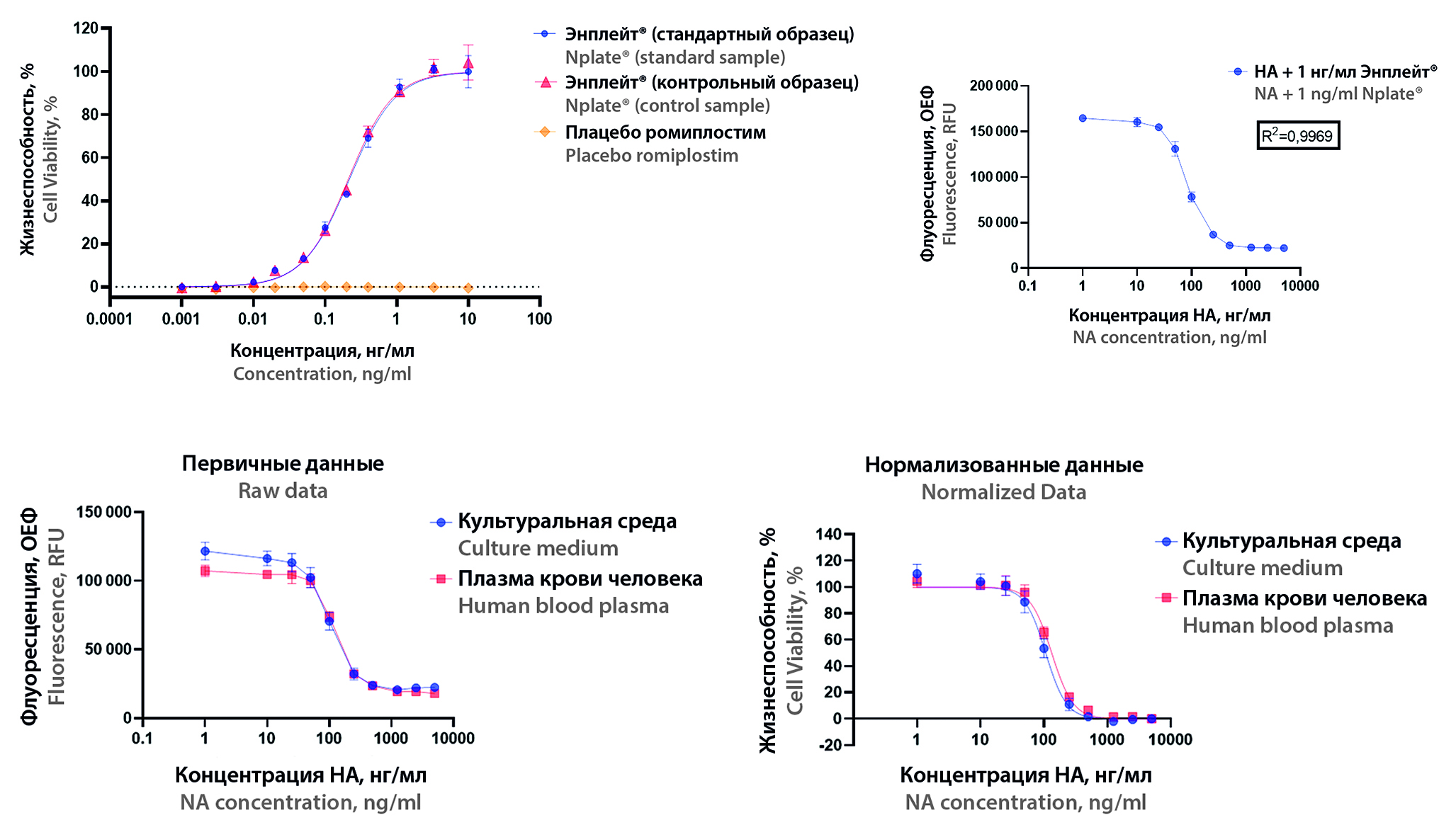
Introduction. Romiplostim is an analogue of the fusion protein peptide of thrombopoietin (TPO), which increases platelet count by binding and activating the human thrombopoietin receptor (TPO-R). It is used to treat thrombocytopenia associated with chronic immune thrombocytopenia. For romiplostim, one of the possible adverse reactions from the immune system is immunogenicity: the production of anti-drug antibodies to the medicinal product, including neutralising antibodies, which may affect the efficacy and safety profile of the medicinal product.
Aim. Validate the procedure for determining neutralising antibodies to romiplostim in human plasma for further clinical studies of immunogenicity.
Materials and methods. The study used rabbit polyclonal antibodies to romiplostim, Nplate® produced by Amgen Europe as a standard sample; a placebo produced by LLC "GEROPHARM", a cell line 32D-hTPOR clone 63 with stable expression of human TPO receptor and a chemiluminescence assay kit CellTiter-Glo® Luminescent Cell Viability Assay produced by Promega to assess specificity. The experiment was carried out on cell line 32D-hTPOR clone 63, which was seeded on the first day and the neutralizing antibody concentrations were titrated with a constant concentration of romiplostim, then the chemiluminescence was detected on the second day. Statistical processing of the results was carried out using Prism 9 software.
Result and discussion. The specificity of the procedure was demonstrated; at maximum concentration, the medicinal product differs from placebo by 309 times in the residual level of cell viability. The linearity of the procedure in terms of the coefficient determination is 0.9969. The precision of the procedure was determined: the repeatability was 1–9 %, the intermediate precision was 3–18 %. The coefficient of variation in selectivity of the procedure was 22 %. For the accuracy parameter, the values for recovery/spike were determined as 90–101 %. It was proven that there was no matrix effect.
Conclusion. It can be stated that the procedure is linear, specific, highly precise, correct, selective and with a proven absence of matrix effect, which allows it to be used to determine the immunogenicity of romiplostim medicinal products in clinical studies.
Introduction. Etmaben is a promising drug for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, widely studied in preclinical studies. In order to conduct phase I clinical trials, it is necessary to develop a bioanalytical method for the quantitative determination of etmaben in human blood plasma.
Aim. The aim of the study is to develop and validate a method for the quantitative determination of etmaben in human blood plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection (HPLC-MS/MS) for the pharmacokinetic study.
Materials and methods. The determination of etmaben in human blood plasma was carried out on a Nexera XR chromatograph with a mass-selective detector LCMS-8040 (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). Sample preparation: precipitation with acetonitrile. Internal standard: promethazine. Column: Luna C18, 100 Å, 50 × 2.00 mm, 5 µm. Elution in gradient mode at a flow rate of 1.00 mL/min. Mobile phase: 0.1 % formic acid solution in water (eluent A), 0.1 % formic acid solution in acetonitrile (eluent B). Retention time for etmaben and promethazine is approximately 1.18 min and 1.15 min, respectively. Total chromatogram registration time: 4.00 min. Ionization method and mode: electrospray; negative mode for etmaben, positive mode for promethazine. Detection was carried out in the mode of multiple reaction monitoring (MRM): 249.90 → 92.15 m/z; 249.90 → 160.20 m/z (etmaben); 284.95 → 197.95 m/z (promethazine).
Results and discussion. We have developed, for the first time, a method for determining etmaben and performed its full and partial validation according to current regulatory requirements.
Conclusion. The method for determining etmaben in human blood plasma with a confirmed analytical range of 0.250–30.000 µg/mL has been developed and validated. The confirmed analytical range of the method based on the results of the partial validation was 0.040–35.000 µg/mL. The method was successfully applied in phase I clinical trials and can be used for other pharmacokinetic studies of etmaben.
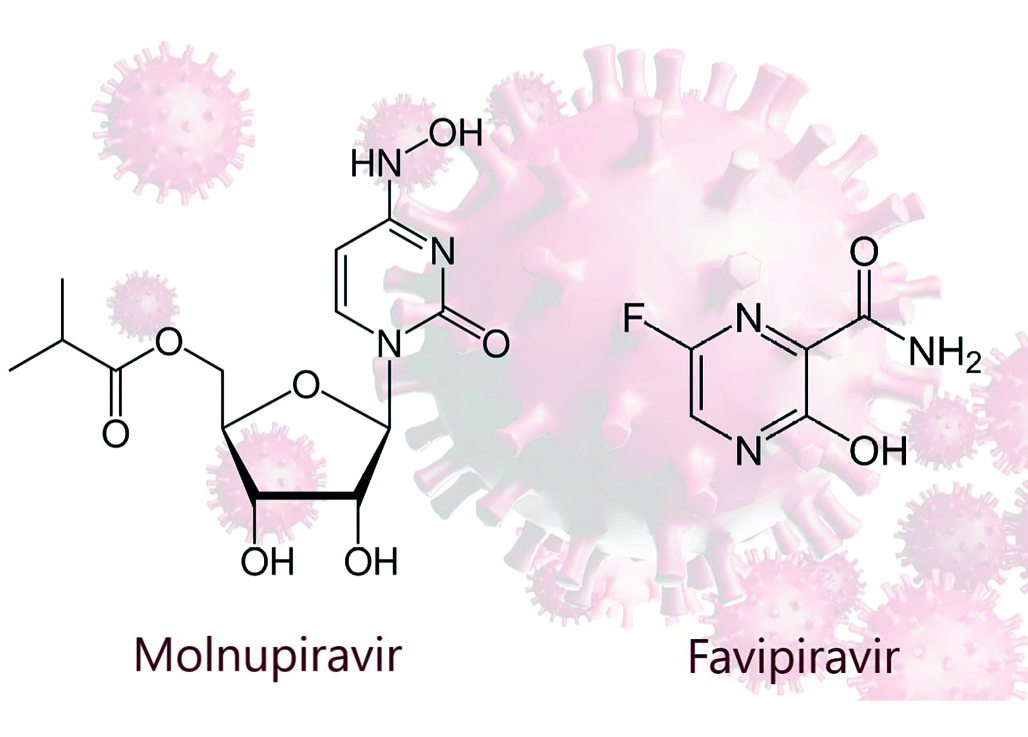
Introduction. COVID-19 (Coronavirus disease 2019) almost 4 years after he start of the pandemic is still a significant public health problem. SARS-CoV-2 (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) that causes COVID-19 continues to mutate and spread throughout the world. Molnupiravir and favipiravir have been shown to be efficacious against variety of RNA viruses including the SARS-CoV-2. The Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation approved the use of these drugs as a treatment of COVID-19. The developed drug contains the combination of two antiviral agents with different mechanisms of suppressing viral RNA replication, which suggests efficacy against the vast majority of ARVI pathogens found in the human population including SARS-CoV-2 and influenza.
Aim. The aim of the pharmacokinetics study is comparison between JTBC00301 (INN: molnupiravir + favipiravir), film-coated tablets (LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia), Esperavir® (INN: molnupiravir), capsules (LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia) and Areplivir® (INN: favipiravir), film-coated tablets (LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia) to evaluate the impact of monocomponents on each other's pharmacokinetics.
Materials and methods. The clinical and analytical phases as well as pharmacokinetic analyses have been performed as a part of a phase I, randomized, open-label, 3-period crossover study of drug JTBC00301 (INN: molnupiravir + favipiravir), film-coated tablets, 400 + 400 mg (LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia). The plasma concentration of β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine (NHC), the active metabolite of molnupiravir and favipiravir were determined in 42 healthy volunteers after taking the test drug JTBC00301 (1 tablet of 400 + 400 mg), the reference drug Esperavir® (2 capsules of 200 mg) and the reference drug Areplivir® (2 tablets of 200 mg). The descriptive statistics were calculated using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, USA). The pharmacokinetic parameters, analysis of variance (ANOVA), the intra-subject coefficient of variation (CVintra) and 90 % confidence intervals (90 % CI) were calculated by R Project 3.5.1 software (package «bear», version 2.8.3-2), originally created by Hsin-ya Lee and Yung-jin Lee, Taiwan.
Results and discussion. Pharmacokinetic parameters of NHC and favipiravir were determined, averaged pharmacokinetic profiles in linear and log-linear scales were plotted, analysis of variance was carried out. The 90% CIs for geometric mean ratios of Сmax and AUC(0–t) for NHC and favipiravir were all within the acceptance range of 80–125 % which means there is no effect of monocomponents on each other’s pharmacokinetics.
Conclusion. The development of the fixed-dose drug combination of molnupiravir and favipiravir has great potential as it may allow to increase the safety profile and improve the tolerability of therapy as well as increase the effectiveness of antiviral therapy. The results justified the study of the subsequent phases of clinical trials of JTBC00301 (INN: molnupiravir + favipiravir), film-coated tablets, 400 + 400 mg (LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia).
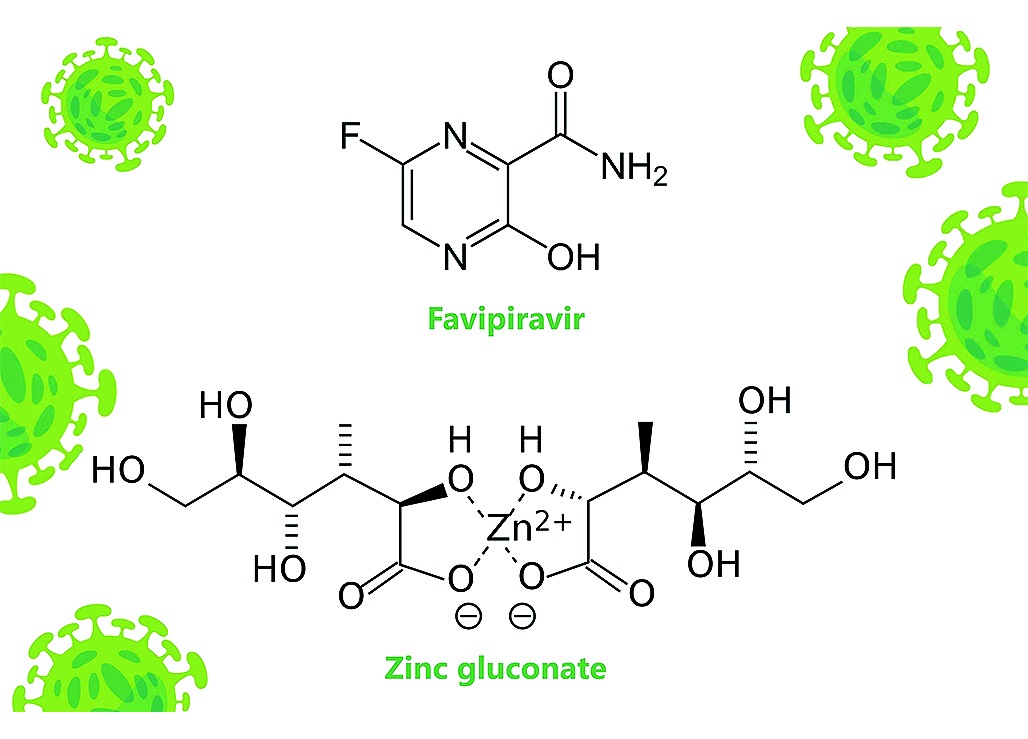
Introduction. Favipiravir is an antiviral compound that inhibits the RNA-dependent polymerase and possesses antiviral properties against RNA viruses, including SARS-CoV-2 (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2). The new drug Areplivir® Zinc as a combination of favipiravir (200 mg) and zinc gluconate (70 mg) in the form of film-coated tablets has been developed by LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia. This combination of favipiravir and zinc gluconate could provide more effective treatment of COVID-19.
Aim. The aim of the pharmacokinetics study is comparison between Areplivir® Zinc (INN: favipiravir + zinc gluconate), film-coated tablets (the manufacturer is JSC "Biokhimic", LLC "PROMOMED RUS" as registration certificate holder) and Areplivir® (INN: favipiravir), film-coated tablets (the manufacturer is JSC "Biokhimic", LLC "PROMOMED RUS" as registration certificate holder) to evaluate the effect of zinc on the favipiravir pharmacokinetics.
Materials and methods. The clinical and analytical phases as well as pharmacokinetic analyses have been performed as a part of a phase I clinical trial. Chromatographic separation and detection of favipiravir were performed by high-performance liquid chromatography – tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) method using Nexera XR high-performance liquid chromatograph with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometer LCMS-8040 (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). The validated analytical range of the method was 50.00–15 000.00 ng/mL in human plasma. The plasma zinc concentrations were measured by a biochemical method with the use of the kit «Zinc-Novo (50)» (JSC "Vector-Best", Russia). The descriptive statistics were calculated using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, USA). The pharmacokinetic parameters, analysis of variance (ANOVA), 90 % confidence intervals (90 % CIs) and the intra-subject variability (CVintra) were calculated by R Project 3.5.1 software (package «bear», version 2.8.3-2), originally created by Hsin-ya Lee and Yung-jin Lee, Taiwan.
Results and discussion. The 90 % confidence intervals of the ratios for Сmax and AUC(0–t) were 86.48–100.38 % and 103.77–119.47 %, respectively. The 90 % confidence intervals were all within the acceptance range of 80.00–125.00 % which means there is no effect of zinc on the favipiravir pharmacokinetics. The intra-subject variability (CVintra) of favipiravir for the pharmacokinetic parameters Cmax and AUC(0–t) were 15.06 % and 14.23 %.
Conclusion. The results justified the subsequent phases of clinical trials of Areplivir® Zinc (INN: favipiravir + zinc gluconate), film-coated tablets (LLC "PROMOMED RUS", Russia). This combination of favipiravir and zinc could expand the existing armamentarium of antiviral drugs for the treatment of COVID-19.
REGULATORY ISSUES
Introduction. A launch of larger number of pharmaceutical preparations based on recombinant products and biotechnologies leads to determine a strategy for protection of exclusive rights for subjects implemented into manufacturing process, including strains of microorganism-producers.
Aim. To define a possibility and a protection scope of microorganism strain as intellectual property subjects at a step of research, development and launch of pharmaceutical preparations, including biotechnological products.
Materials and methods. The materials of the study were available publications in peer-reviewed journals on thematic queries based on keywords of the selected topic, official websites, regulatory legal acts, regulating the procedure for patenting subjects in the Russian Federation and foreign countries.
Results and discussion. A brief review of regulatory acts on registration of a strain as an intellectual property subject is presented. It was defined features of a microorganism strain for patenting and for establishing an infringement of patent rights in the territory of Russian and foreign countries. A possible scope of patent rights for strains is indicated.
Conclusion. The problems raised upon protecting strains as intellectual property subjects as well as possibilities of strain registration as exclusive right subjects are defined.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)