FROM EDITOR
We will talk about biotechnological drugs' life cycle, certain aspects of biotechnological drugs' development, research and production.
The second part of the article contains materials on the further structuring of the domestic industry and the formation of trusts, the development of a classification of chemical industries and the organization of the Scientific and Technological Department of the Supreme Economic Council (NTO). The special attitude of the country's leadership towards the old personnel and organizations that ensure the operation of enterprises in this industry, as well as the government's concern for the education of young domestic chemists grown in Russia, is shown. A special place is occupied by the work on organizing the involvement of former owners of plants and factories in the restoration of their enterprises. On the initiative of VN Ipatiev, work began on the organization of a concession commission under the State Planning Committee. The second part contains materials on the further structuring of the domestic industry and the formation of trusts, the development of a classification of chemical industries and the organization of the Scientific and Technological Department of the Supreme Economic Council (NTO). The special attitude of the country's leadership towards the old personnel and organizations that ensure the operation of enterprises in this industry, as well as the government's concern for the education of young domestic chemists grown in Russia, is shown. A special place is occupied by the work on organizing the involvement of former owners of plants and factories in the restoration of their enterprises. On the initiative of VN Ipatiev, work began on the organization of a concession commission under the State Planning Committee.
Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Federal center of nuclear medicine projects design and development" of FMBA of Russia is the leading Russian manufacturer of therapeutic radiopharmaceutical preparations (RPP) is celebrating its 55th anniversary this year. The Enterprise was at the origin of the development of nuclear medicine in Russia and remains the largest manufacturer of therapeutic RPPs in our country. The account of the company's evolution is the story of the advancement of nuclear medicine in Russia. In the present article, we offer an analysis of the production experience the company accumulated over the years of operation as well as the major achievements and hardships the Enterprise dealt with. We put a special emphasis on the reciprocity of the Enterprise's background and progress with general trends in the development of nuclear medicine in Russia.
The particle size of vaccines has a considerable influence on their half-life in vivo, as well as on their uptake by antigen-presenting cells. The surface charge of particles is also suspected of influencing the same parameters. Here we use DLS and ELS to characterize respectively the particle size and zeta potential of two inactivated antiviral vaccines. A tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) vaccine displays a monomodal particle size distribution in the lower micrometer range, corresponding to the expected size of the aluminum salt adjuvant. A cell-based influenza vaccine, in contrast, is shown to contain both split viruses (ca. 30 nm) and larger aggregates (ca. 250 nm). Zeta potential measurements indicate that both vaccines consist of weakly anionic particles. Interestingly, we demonstrate that simulated cold chain disruptions (heat treatment, freeze-thawing) induce significant changes in the particle size distribution of both vaccines.
EVENTS
On March 17–18, Novosibirsk hosted an exhibition of equipment, raw materials, materials and services for the production of pharmaceuticals, perfumes and cosmetics and dietary supplements.
From April 19 to April 22, the 20th Anniversary International Exhibition of Laboratory Equipment and Chemical Reagents "Analitika Expo 2022" was held at the Crocus Expo IEC.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
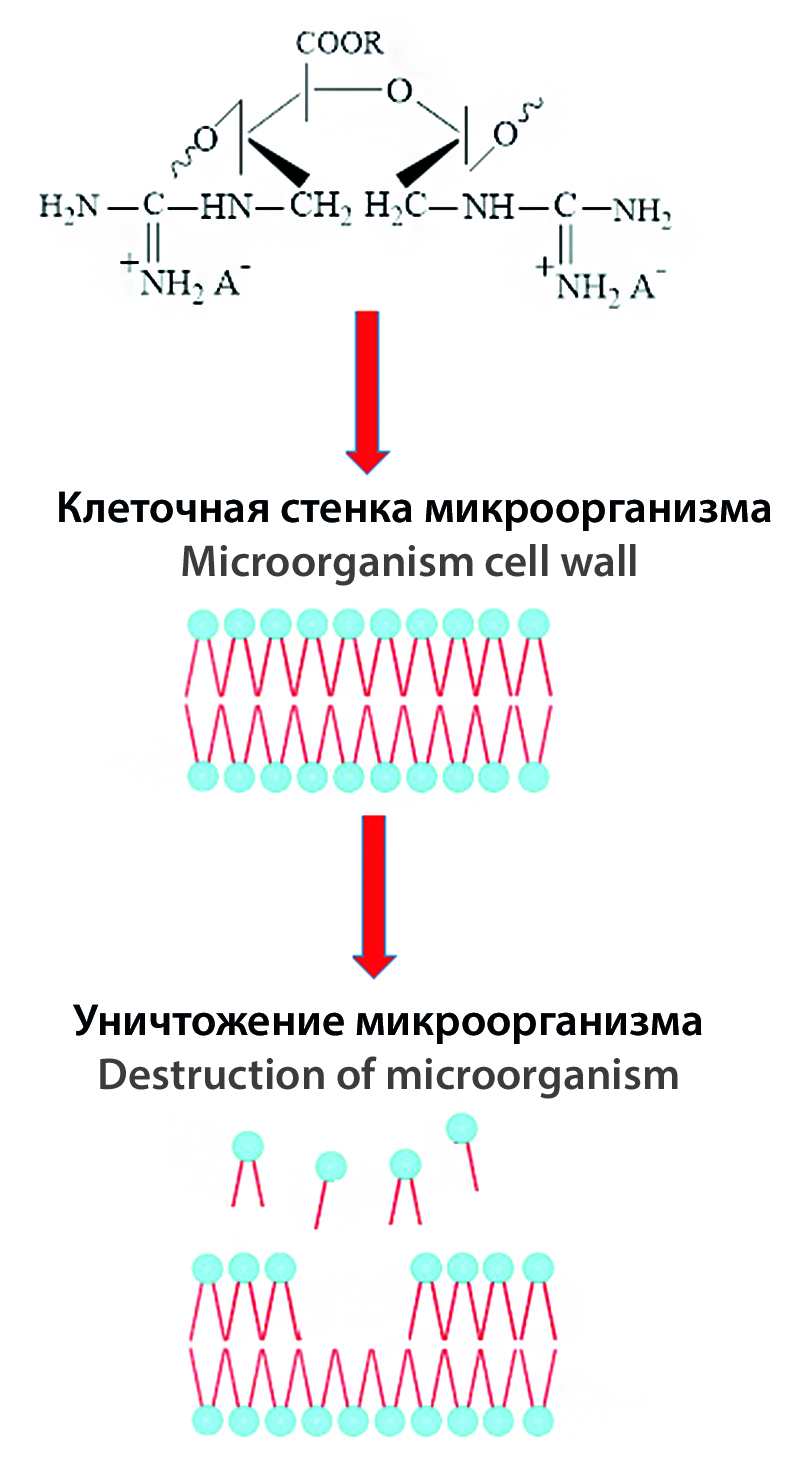
Introduction. Up to the present time, there are practically no studies on the relationship between the structural characteristics and biological activity of antimicrobial polymers synthesized by the chemical addition of guanidine groups to polysaccharide macromolecules. Therefore, there is a need to carry out the chemical modification of guanidine with natural polymers, in particular polyaldehyde pectin, and to conduct comparative studies of the antimicrobial activity of the obtained samples with different physicochemical characteristics.
Aim. To conduct the synthesis of guanidine-containing pectin derivatives. In addition, to determine the influence of structural variations in the obtained samples on exhibiting antimicrobial properties.
Materials and methods. The synthesis of guanidine-containing pectin derivatives consisted of the following stages: periodate oxidation of the polysaccharide, modification of guanidine using polyaldehyde pectin, and chemical reduction of azomethine bonds. The amount of guanidine in the obtained samples was calculated by acidimetric titration, the nitrogen content (N, %) was determined using a Eura EA (Italy) elemental analyzer. The рКα values of the synthesized compounds were found by the back titration method. Absorption spectra were analyzed on a "UV 1280" spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan) in the range λ = 180–400 nm. IR spectra were recorded on a Vector-22 spectrometer in the wavelength range of 400–4000 cm-1 in KBr tablets (3 mg sample / 300 mg KBr). The molecular weight characteristics of the synthesized derivatives were determined by high-performance gel permeation chromatography on an Agilent 1260 Infiniti liquid chromatograph. The acute toxicity of guanidine-containing pectin derivatives was calculated by the Prozorovsky method. Comparative assessment of antimicrobial activity was conducted by agar diffusion method.
Results and discussion. By varying the oxidation level of polyaldehyde pectin, synthesized compounds differ in the degree of substitution, guanidine content, molecular weight, and pKα value. It was found that the levels of the antibacterial and antifungal activity of the studied samples depend on the degree of substitution and the nature of the counterion. The antimicrobial effect increases with an increase in the quantitative content of guanidine groups in the macromolecular chain of pectin. Moreover, it was found that the change of low molecular weight Cl–, NO3– , F–, I– counterions by carboxylate anions leads to a sharp decrease in antimicrobial properties. Upon oral injection of the synthesized compounds to mice, it was found that all samples belong to the category of practically non-toxic substances (V-class).
Conclusion. Comparative analysis of guanidine-containing pectin derivatives with different characteristics showed that the severity of the antimicrobial action of the synthesized compounds against bacteria and fungi of the genus Candida depends on the quantitative content of cationic groups and the nature of the counterion.
Introduction. At the rate of World health organization from 1 to 4 million people annually get infected with cholera, and around 143 000 people become a victim of this infection. At this point of seventh pandemic WHO and its partners actively evaluate new methods of treatment and prevention of cholera in addition to existing traditional methods. Today enterosorbents are widely used for treatment and prevention of number of infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Previously reported about results of construction of specific enterosorbent, which having a neutralizing effect regard to choleric enterotoxin. For toxin-neutralizing activity of components and finalized product control applied Craig dermal test method, which have significant disadvantages: duration of analysis, using expensive biomodels, etc. Ethical side of in vivo methods is also important, which dictating necessity of experiment humanization and replacing mammals to less evolved living objects, using physicochemical and immunochemical systems.
Aim. Methodical approach improvement of definition activity of semi-finalized and completed enterosorbent product in indirect in dot-immunoanalysis (DIA) with using non-enzymatic diagnosticum based on colloidal gold nanoparticles.
Materials and methods. Were used antitoxic rabbit immunoglobulins and experimental series of anicholeraic immunoenterosorbent. Definition of toxin-neutralizing activity carried out by Craig test on adult rabbits. In indirect DIA were used hydrosol gold, connected with staphylococcus protein A by sorption and stabilized with solution PEG-20000.
Results and discussion. In indirect DIA identified titers of specific antibody in product component samples composed from 1 : 6400 to 1 : 12800, while in copleted enterosorbent the titers composed from 1 : 6400 to 1 : 25600. Specificity of test is confirmed by negative results with standard rabbit immunoglobulins. Comparative analysis of toxin-neutralizing activity level of antitoxin immunoglobulins and anicholeraic enterosorbent, determined in Craig dermal test and DIA was performed: the correlation coefficient composed 0,93 and 0,97 respectively.
Conclusion. Developed methodical approaches to indirect DIA conduction with S. aureus protein A based diagnosticum and colloidal gold nanoparticles can be used for determination of antitoxic activity level of immunoglobulins and experimental immunoenterosorbent. Correlation of in vitro and in vivo tests allows to recommend indirect DIA on control stages during specific anticholeraic enterosorbent production.
Introduction. Currently, research is being actively conducted to find new biological objects as sources of biologically active substances. This is necessary in order to obtain producers who will be profitable in cultivating, maintaining their vital activity and obtaining at the output a sufficient number and high quality of the target products. Micro-and macroalgae can be one of these sources.
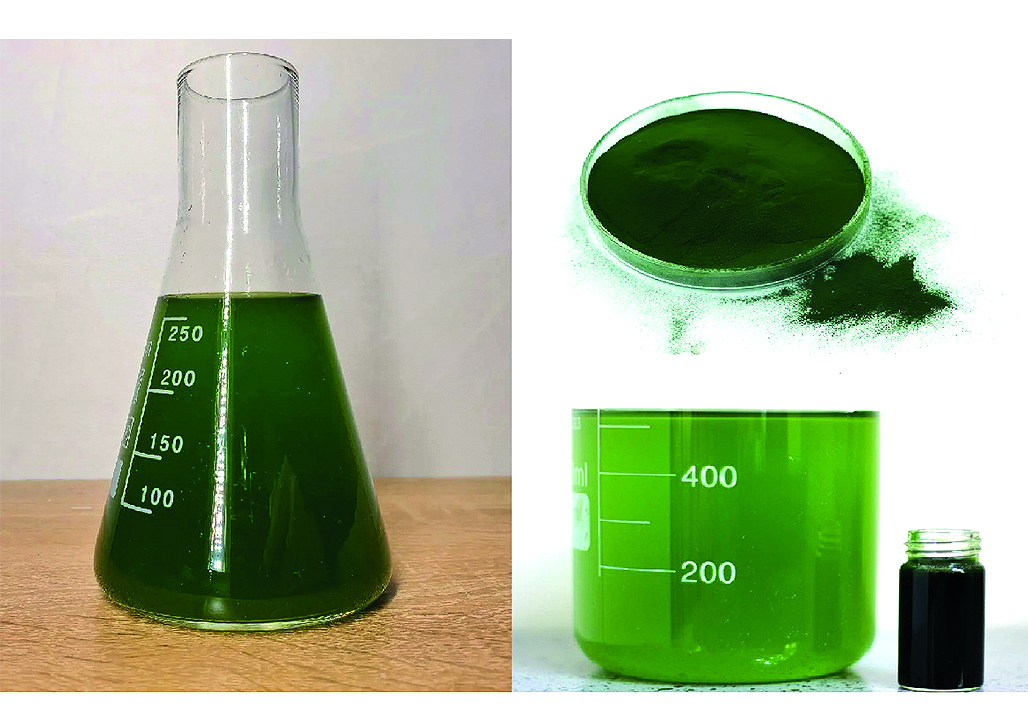
Aim. The aim of this study is to conduct a phytochemical analysis to confirm the presence of a wide range of BAC, as well as studies on the selection of optimal parameters for extracting chlorella C-2019 biomass in order to obtain extracts with a high content of BAC that have an antibacterial effect (pigments, flavonoids).
Materials and methods. The object of the study was the biomass of the strain Chlorella vulgaris Beyerinck IPPAS C-2019. The fractional composition, humidity, ash content, and extractive substances were determined according to GF XIV, 2018. The work uses spectrophotometric, GLC methods, as well as the method of drip electrophoresis.
Results and discussions. As a result of phytochemical analysis, the main BAC of chlorella biomass of strain C-2019 were determined. The presence of proteins (64 %), fatty acids (7 %), phenolic compounds (1.56 %), pigments (2.46 %), macro – microelements has been proven. The optimal raw material-extractant ratio is 1 : 50. Increasing the temperature and duration of extraction increased the yield of the main BAС.
Conclusion. The phytochemical composition of promising plant raw materials is determined. The optimal conditions for the extraction of chlorella biomass in the preparation of the extract are established: the ratio of raw materials:extractant 1 : 50, extractant ethyl alcohol 95 %, extraction temperature 60–80 °C, triple extraction for 60, 60, 60 minutes.
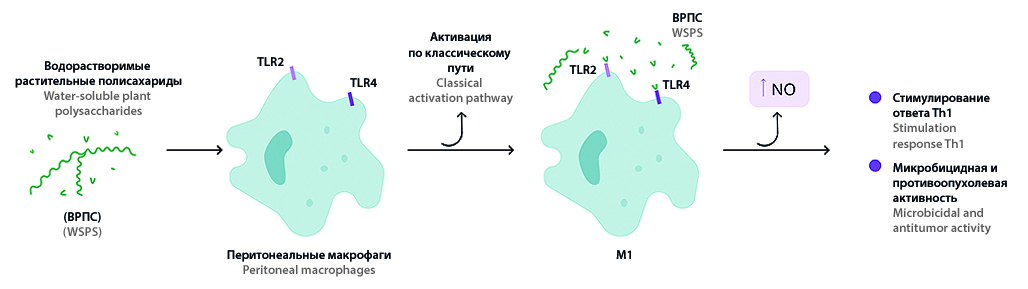
Introduction. The nitric oxide molecule is one of the most versatile, multifunctional mediators of biological reactions in the body. NO participates in the formation of innate and specific immunity, the inflammatory process and protection against infectious pathogens. It is known that polysaccharides of higher plants are widely used to activate pro- and anti-inflammatory reactions. Previous studies have shown the promise of a more detailed research in the immunomodulatory properties of plant polysaccharides of the genus Saussurea DC, the mechanisms of their immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory action depending on the origin and conditions of extraction.
Aim. The aim of present research was to evaluate the dependence of the affection of the extraction parameters of water-soluble polysaccharides (WSPS) from the aerial parts of S. salicifolia (L.) DC., S. controversa DС., S. frolovii Lebeb. on NO synthase activity and peritoneal macrophages proliferation.
Materials and methods. Chemical methods for the isolation of water-soluble polysaccharides, cultural and biochemical methods for assessing biological activity were used.
Results and discussion. Water-soluble polysaccharides (WSPS) from plants S. salicifolia (L.) DC., S. controversa DС., S. frolovii Ledeb. obtained with different extraction parameters have the ability to enhance production of nitrites antigen-presenting cells in the same way as standard macrophage activator liposaccharide. Polysaccharides from S. controversa and S. frolovii at acidic extractant are free of endotoxin impurities. All water-soluble polysaccharide samples obtained using neutral and alkaline extractants contain endotoxin impurities. Samples from the S. controversa contained this impurity after extraction in an acidic extractant. Polysaccharide samples are not cytotoxic.
Conclusion. It was stated that water-soluble polysaccharides from plants of the Saussurea genus using an acidic extractant do not possess cytotoxic properties, do not contain endotoxin impurities and significantly enhance the production of nitric oxide by macrophages. These samples used in a detailed study of the immunomodulatory properties and further development on their basis of new treatment methods various diseases that require correction and regulation of the functional activity of immune cells, including macrophages.
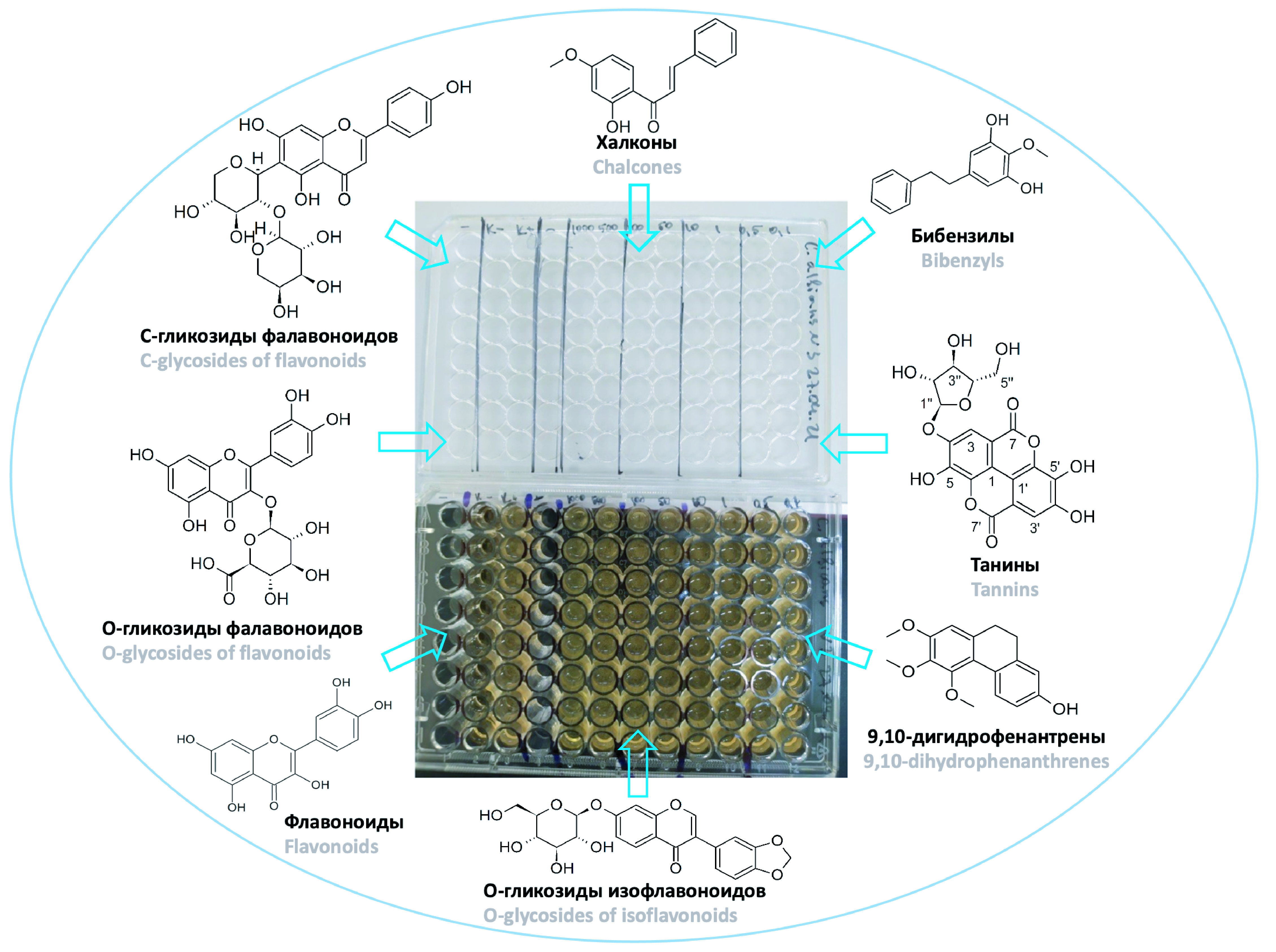
Introduction. The emergence of new strains of microorganisms with multidrug resistance (MDR) is one of the most pressing problems of modern medicine. Currently, to combat MDR, active attempts are being made to obtain new biologically active substances of natural (microbial, plant, animal) origin. Earlier, 32 individual compounds were isolated by the authors from the aerial part of Iris laclea Pall., Rubus chameamorus L. leaves, Empetrum nigrum L. shoots, Ononis arvensis L. aerial part and Solidago canadensis L. aerial part, and 2 more compounds were synthesized according to previously published methods. The study of the antimicrobial activity of compounds of these classes is an urgent problem for finding potential agents for combating MDR.
Aim. Studying of the antimicrobial activity of the isolated and synthesized substances in an individual form against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans.
Materials and methods. To test the antimicrobial activity, substances of 34 compounds were used, which were obtained as a result of previous research, the structure of which were established using NMR spectroscopy and high-resolution mass spectrometry. The antifungal and antibacterial activity of the compounds were determined through the micromethod of two-fold serial dilutions in liquid nutrient medium in 96-well plates in duplicate. Screening for antimicrobial activity was carried out against reference (type) strains of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Candida albicans NCTC 885-653.
Results and discussion. In the group of flavonoids and O-, C-glycosides, the antifungal activity of all studied compounds did not differ significantly, but it should be noted that the antibacterial activity of apigenin C-glycosides and isoflavonoid O-glycosides was slightly greater in comparison to O-glycosides of flavonols. The greatest antimicrobial activity among the group of chalcones was shown directly by the chalcones themselves – chalcone, 2’, 4’-dihydroxychalcone, and 2’-hydroxy-4’-methoxychalcone. Among the dihydrochalcones, the highest antimicrobial activity was found for 2‘, 4’-dihydroxyhydrochalcone, which was comparable in magnitude to the antimicrobial activity of the chalcones themselves. An interesting feature of dihydrochalcones is that methylation of phenolic hydroxyl groups in the 2‘ and 4’ positions decreases the antimicrobial activity. The antimicrobial activity of 9,10-dihydrophenanthrenes, as in the case of dihydrochalcones, depended on the number of methoxy groups in the molecule. The lowest MIC values were exhibited by 4,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene containing only two methoxy groups. For bibenzyls, an inverse dependence of antimicrobial activity on the number of methoxy groups was observed – the best activity among bibenzyls against the studied strains was shown by 1-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethane, which contains two methoxy groups in its structure.
Conclusion. Polyphenolic secondary metabolites of plant origin belonging to the studied groups: flavonoids and O-, C-glycosides, chalcones, 9,10-dihydrophenanthrenes and bibenzyls did not show significant antimicrobial activity against the studied strains of microorganisms – S. aureus (6538 EP ATCC), E. coli (25922 ATCC) and C. albicans (885-653 NCTC). Despite this fact, a certain variation in antimicrobial activity was revealed depending on the structure of the tested substances.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. Infectious otitis externa and middle ear can cause hearing loss, which significantly reduces the quality of life of patients. The main causative agents of acute bacterial otitis media are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. This article is devoted to the development and study of a novel dosage form for treatment of infectious diseases of the external ear containing bacteriophages that lyse bacterial strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ear drops were considered as a promising dosage form for instillation into the ear canal.
Aim. The aim of the work is to develop a dosage form of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages for the local treatment of infectious otitis media.
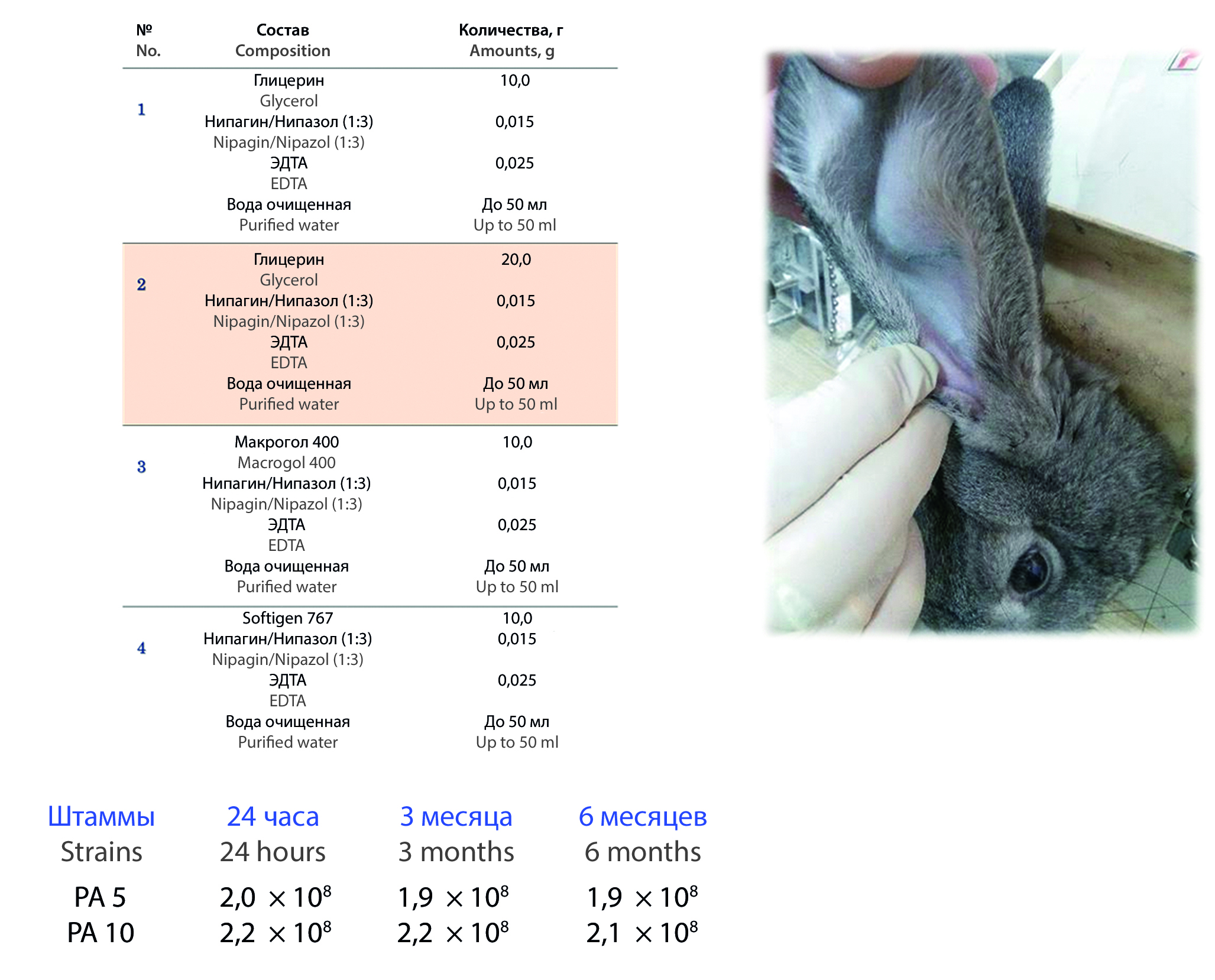
Materials and Methods. The active substances of the developed drug are bacteriophages that lyse bacterial strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: PA5 and PA10, which were obtained by growing on a solid growth medium in mattress flasks with subsequent sterilizing filtration through a membrane filter (0,22 µm) and elimination of endotoxins on a chromatographic column. To obtain experimental compositions, excipients that do not cause a drop in the titer of bacteriophages were used – purified water as the solvent, viscosity modifiers: glycerol (CHIMMED, Russia) and a mix of macrogol 6 and glyceryl caprilocaprate brand Softigen 767 (Cremer, Germany), antioxidant Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), preservatives nipagin and nipazole. The obtained samples were standardized according to pharmacopoeial indicators, recommended for the dosage form "drops" – density, pH, viscosity. For all experimental compositions, the stability of the titer of bacteriophages was studied by the Gratia method for 6 months. The local irritation and systemic effects were also studied on five chinchilla male rabbits.
Results and discussion. As a result of the conducted research, four experimental compositions of ear drops with a cocktail of bacteriophages PA5 and PA10 were obtained. The optimal technological characteristics were observed in the composition containing glycerol as a viscosity modifier at a concentration of 10,0 %. For optimal composition, the stability of the bacteriophages cocktail titer, local irritating and systemic effects were analyzed. The study revealed stability of the bacteriophages PA5 and PA10 titers in the composition of dosage form, and absence of local irritating and systemic effects of ear drops.
Conclusion. The dosage form can be recommended for preclinical studies.
Introduction. Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug that has been widely used in veterinary medicine. Parasitic diseases of farm animals cause great economic damage and pose the risk of human infection. Prolonged dosage forms of ivermectin are effective against them. The first step in the creation of such a drug was the preparation and study of polymeric microparticles of polycaprolactone with encapsulated ivermectin.
Aim. Obtaining polymeric microparticles of polycaprolactone with encapsulated ivermectin using a continuous flow-through unit.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was microparticles of polycaprolactone with encapsulated ivermectin obtained on a continuous flow-through unit. Determination of the average particle size and size distribution was carried out by the method of laser diffraction. Microscopy was used to visually assess the shape and size of the microparticles. UV – spectrophotometry was use to quantitative determination of ivermectin.
Results and discussion. Polymeric microparticles of polycaprolactone with encapsulated ivermectin was obtained and had an average size of 126.63 ± 42.67 μm and contained 32,73–62,00 % of ivermectin. Suspensions prepared from the obtained microparticles were passed through a 20G injection needle without noticeable resistance, which indicates the possibility of their use as the basis of an injectable preparation.
Conclusion. Obtained results confirm the possibility of using flow-through dispersion using a device developed by us for obtaining polycaprolactone microparticles with encapsulated ivermectin, which are suitable for injection. Thus, the results obtained make it possible to continue studies of microparticles and create a drug based on them.
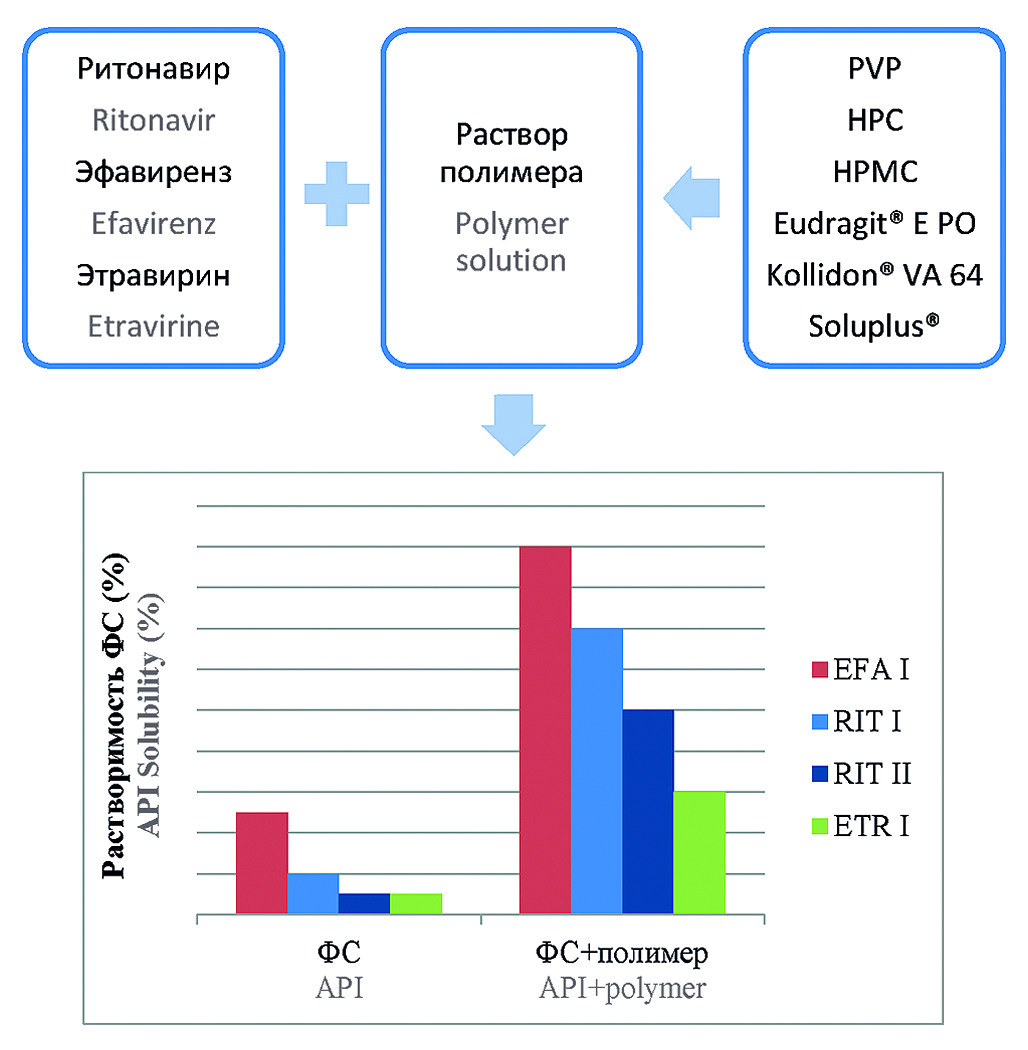
Introduction. Many of new active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) have low solubility that can affect bioavailability negatively and therefore therapeutically efficacy as well. These APIs include the following antiretroviral substances: ritonavir, efavirenz, etravirine. There are various approaches to increase the dissolution of the APIs, for example, the preparation of solid dispersion systems (SDS), in which polymer is used as a drug carrier, and the other one is usage of surfactants. However, the techniques used to obtain SDS have a number of disadvantages: high temperatures, organic solvents and expensive equipment. In turn, surfactants affect the work of internal organs, have an irritating effect. Instead of these methods, they use pharmaceutical acceptable polymers, which are safer in comparison with low-molecular-weight surfactants and still act as surface-active agents.
Aim. Study of the pharmaceutical grade polymers effect on the dissolution of practically insoluble antiretroviral substances: ritonavir, efavirenz, etravirine.
Materials and methods. APIs: efavirenz form І (LLC "AMEDART", Russia, batch 010520); efavirenz reference standard (USP No. R09740); ritonavir form I (LLC "AMEDART", Russia, batch 010320); ritonavir form II (LLC "AMEDART", Russia, batch 010320); ritonavir reference standard
(USP No. H0M427); etravirine form І (LLC “AMEDART”, Russia, batch 010720); etravirine reference standard (MSN, India, batch ETV/A312/6/01). The dissolution of substances in polymer solutions was studied using the Paddle apparatus under the conditions recommended by the FDA for the drugs.
Results and discussion. The nature of the effect, which is, as defined, influenced by the type of polymer, the concentration of the polymer solution and the pH of the medium, is ambivalent. Both a substance dissolution increase and a decrease are possible. Polymers, such as hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, Eudragit® E PO, can significantly increase the dissolution of substances, while polyvinylpyrrolidone can block it in certain cases. The greatest increase in dissolution of ritonavir, efavirenz and etravirine was found in Eudragit®
E PO solutions.
Conclusion. The results of the study showed the feasibility of determining the bioavailability of dosage forms of practically insoluble APIs with the inclusion of polymer excipients in their formulations.
Introduction. The use of a combined herbal extract of chamomile flowers, calendula flowers and yarrow herb (patent RU 1 561 262 C) can be effective against various microbial strains, including those causing inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. The article presents the results of a comparative pharmaceutical and technological study of an adsorbed liquid plant extract on sorbents of various nature for subsequent introduction into the composition of orodispersible tablets.
Aim. To select the optimal sorbent of liquid plant extract of chamomile flowers, calendula and yarrow herb ensuring the suitability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient for direct compression, by analyzing using the SeDeM expert system method.
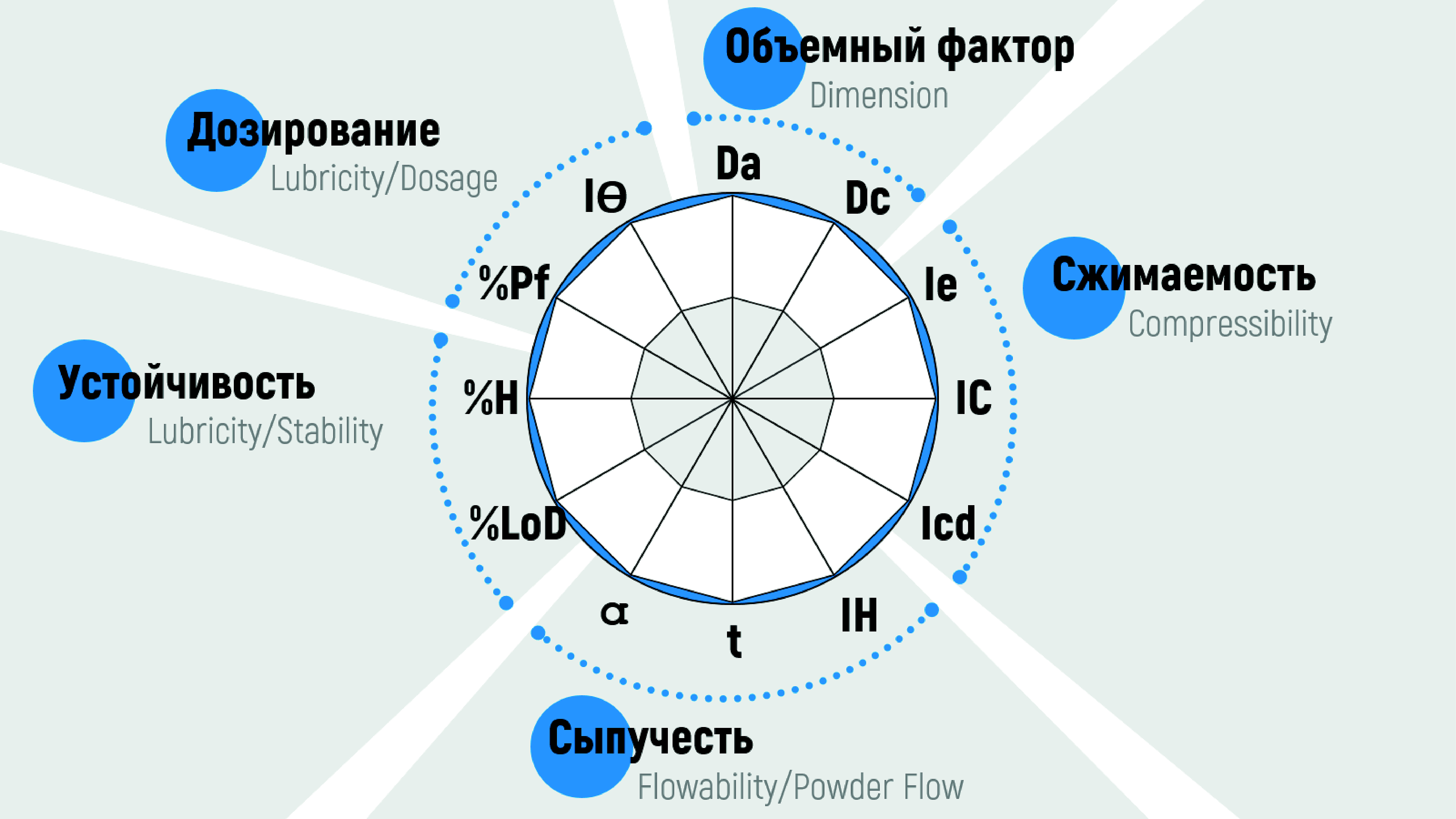
Materials and methods. Active pharmaceutical ingredient was adsorbed on organic (microcrystalline celluloses of various brands) and inorganic (colloidal silicon dioxide of various brands) sorbents, a liquid combined plant extract of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial action of chamomile flowers, calendula flowers and yarrow herb. Pharmaceutical-technological analysis included the study of such technological parameters as: Bulk Density (Da = m/Va), Tapped Density (Dc = m/Vc), Inter-particle Porosity (Ie = (Dc – Da)/(Dc · Da)), Carr index (IC = (Dc – Da)/(Dc · 100)), Cohesion Index (Icd), Hausner Index ratio (IH = Dc/Da), Angle of Repose (Tgα = h/r), Powder Flow (t), Loss of Drying (%LoD), Hygroscopicity (%H), Particles <50 μm (%Pf), Homogeneity Index (IΘ = Fm/100 + ∆Fmna).
Results and discussion. A comprehensive pharmaceutical-technological study of sorbents of liquid plant extract before and after adsorption was carried out, the results of which were processed and presented by the SeDeM expert system method. It was found that the adsorption of the extract has a positive effect on the Dimension (ID = (Da · Dc)/2) of all studied sorbents which may be related to change in the fractional composition due to the aggregation of small particles during adsorption and destruction of large ones when sifting the finished mixtures through a sieve with a mesh diameter of 200 μm (recommended insoluble particle size for use in the oral cavity). A negative effect on the Stability (IS = (%LoD · %H)/2) was also recorded for all samples, regardless of their nature, which is probably explained by residual moisture after drying and high hygroscopicity of adsorbed plant bioactive substances. Changes in the Compressibility (IC = (Ie · IC · Icd)/3), Flowability (IF = (IH · α · t)/3) and Dosage (IDos = (%Pf · IΘ)/2) are individual.
Conclusion. The SeDeM expert system method makes it possible to characterize bulk materials from the point of view of suitability for direct compression, to establish the factors that need to be primarily corrected by the introduction of auxiliary substances. As a result of the conducted studies, Aeroperl 300 (inorganic sorbent) and Pharmacel 112 (organic sorbent) can be recommended for the introduction of liquid plant extract of chamomile flowers, calendula flowers and yarrow herb into the composition of orodispersible tablets.
Introduction. Gramicidin S is a peptide antibiotic that has been widely used for more than 70 years. Gramicidin S is available in the form of tablets with a low dosage, which leads to possible deviations in the "Uniformity of dosage" parameter during manufacturing. Another limitation is the presence of lactose and sucrose in the formulation, which limits the drug application by patients demonstrating intolerance. As an alternative, we propose inclusion complexes of gramicidin S with β-cyclodextrin.
Aim. The work aims to describe the influence of the methodology to prepare the inclusion complex on the characteristics and properties of the final product.
Materials and methods. The gramicidin S – β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex has been prepared by dry mixing, paste complexation, co-precipitation and fluid-bed complexation. The complex formation has been confirmed by 1H NMR spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetry while the morphology and size by scanning electron microscopy for the solid and dynamic light scattering for the solution. The flowability, slope angle, bulk density of the obtained powders were estimated using the methods described in Russian Pharmacopoeia of the XIV edition.
Results and discussion. In the present work, we prepared a set of gramicidin S and β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes by various approaches. The thermal analysis demonstrated a significant change in the peak referring to phase transition of the substances, indicating the interaction between the components. The 1H NMR spectroscopy reveals that the L-ornithine amino group is the part of gramicidin S involved in the complexation. Evaluating the technological properties of gramicidin S and β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes significant variability, which is associated with the particle morphology. Complexes obtained using co-precipitation and fluid-bed complexation methods are more suitable for producing gramicidin S tablet production by direct compression technology.
Conclusion. Herein, we demonstrate that the formation of the gramicidin S and β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex occurs through the L-ornithine amino group in the gramicidin S. In addition, depending on the method significant differences in the particle size and shape have been observed. The obtained results could provide valuable information for the development of new gramicidin S buccal formulations, which are more consistent in the "Uniformity of dosage" and allow to avoid the use of lactose and sucrose as excipients.
Introduction. Enteric coat have a wide range of functions: from protecting the API from the adverse effects of the acidic environment of the stomach to targeted delivery to certain parts of the intestine in order to increase the effectiveness of the drug. When developing such dosage forms, special attention is paid to the type of film-forming polymer in the coating composition, its solubility and ability to withstand passage through the stomach.
Aim. Development of enteric-coated tablets based on sodium 4,4'-(prpoandiamido)dibenzoate.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were sodium 4,4'-(propanediamido)dibenzoate 60 mg core tablets and compositions for enteric coatings. The uniformity of distribution of coatings over tablets was determined by the method developed at the Department of Technology of Medicinal Forms of SPCPU on the basis of the Fokker–Planck equation. The dissolution kinetics of enteric-coated tablets was studied using an Erweka DT 626 tablet dissolution tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany). The amount of the substance that passed into the dissolution medium was determined using an SF-2000 spectrophotometer (LLC "OKB Spektr", Russia).
Results and discussion. It has been established that all the studied coatings are evenly distributed over the tablets. When studying the kinetics of tablet dissolution, it was found that all coatings are resistant to acidic environments (0.1 M hydrochloric acid solution), however, in a phosphate buffer solution, the highest rate of release of the substance from tablets is achieved using a coating based on a copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate of the type B.
Conclusion. Tablets based on sodium 4,4'-(propanediamido)dibenzoate, enteric-coated AquaPolish® P white 712.06E were developed.
Introduction. In recent decades, the role of X-ray endovascular methods has been progressing in the treatment of oncology. It became possible to perform embolization not only to stop bleeding from a tumor, but also for the purpose of targeted delivery of chemotherapy drugs. However, of particular interest is the development of new combined drugs that combine cytostatic action, embolization of blood vessels that feed the tumor, and analgesia.
Aim. The aim of the study is to develop the composition and technology of a combined drug for parenteral administration, including lyophilized polymer microspheres saturated with doxorubicin hydrochloride and an injection solution of comenic acid.
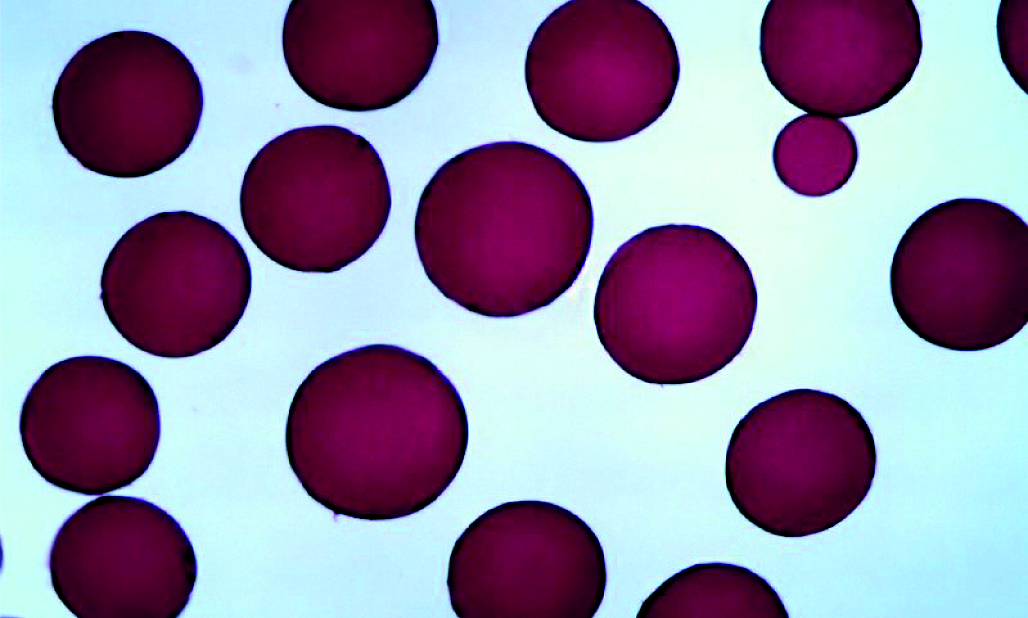
Materials and methods. The study of the sorption of comenic acid by polymeric microspheres was carried out using the HPLC method. Analysis of the appearance of polymeric microspheres and obtaining their photographic images was carried out by microscopy using a microscope with a digital camera.
Results and discussion. The study made it possible to determine that comenic acid, unlike doxorubicin hydrochloride, is practically not sorbed by polymer microspheres, which justifies the expediency of including a solution of comenic acid in the composition of the finished dosage form in the form of a separate injection solution. It has been established that when obtaining lyophilized polymer microspheres saturated with doxorubicin hydrochloride, it is necessary to use water for injection as a solvent for doxorubicin hydrochloride lyophilisate. A combined medicinal product has been developed for use in the field of X-ray surgery, containing: a bottle with a lyophilizate of polymeric microspheres saturated with doxorubicin hydrochloride in a ratio of 1 : 2, intended for chemoembolization; an ampoule with a solution containing 20 mg/ml of comenic acid, intended for intravenous administration in order to relieve pain.
Conclusion. As a result of the study, the possibility of sorption of comenic acid by polymeric microspheres was studied. A technology has been developed for obtaining polymeric microspheres saturated with doxorubicin hydrochloride. A combined drug intended for use in the field of X-ray surgery has been developed.
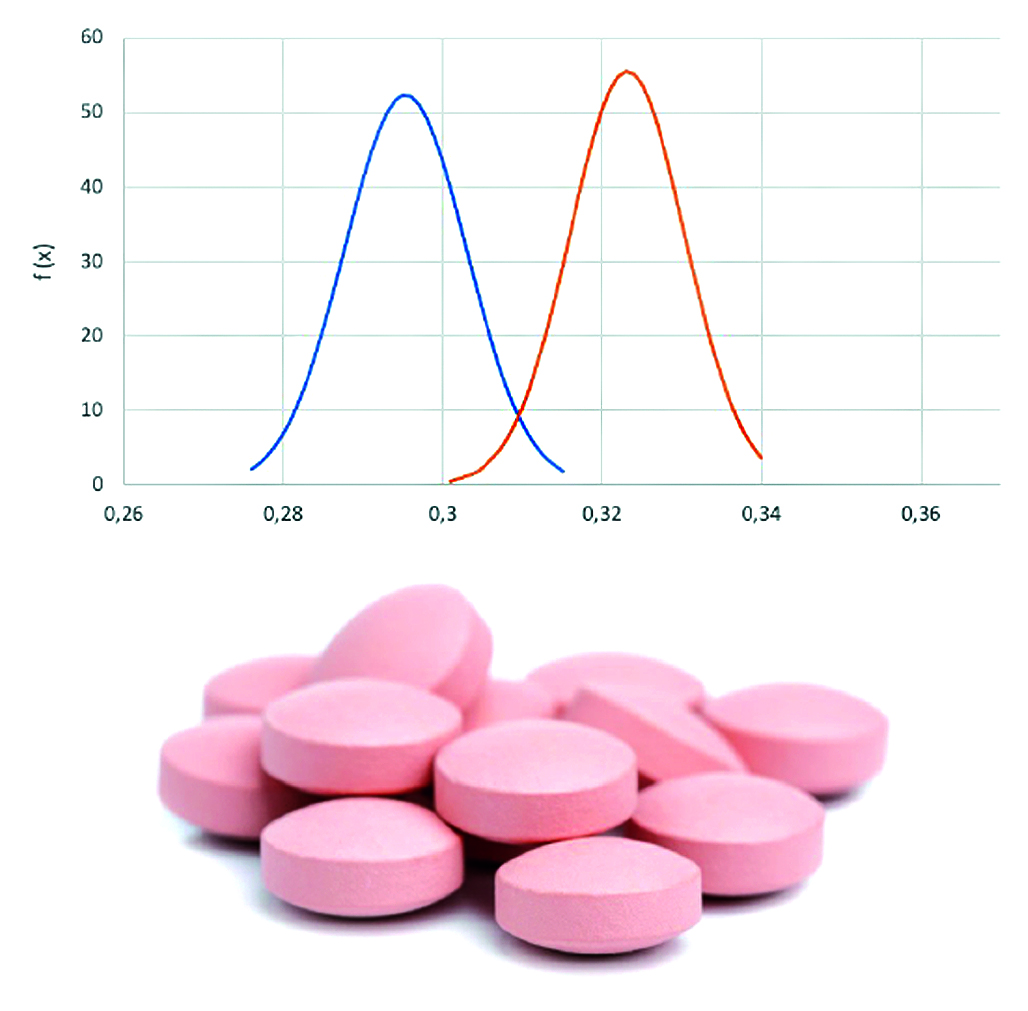
Introduction. Dihydroquercetin is a flavonoid from the group of flavanonols with a wide spectrum of pharmacological activity. Its positive therapeutic profile was established for chronic venous insufficiency, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchial asthma, for the prevention of stroke. Its use leads to an improvement in the course of atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. In addition, it is characterized by radio-protective, antidote, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, reparative, hepatoprotective effects. Currently, there are no drugs containing dihydroquercetin on the domestic pharmaceutical market. However, the pronounced therapeutic potential of dihydroquercetin, the economic and technological availability of its substance indicate the relevance of the development of dosage forms based on this molecule.
Aim. Development of the optimal composition and technology of tablets based on dihydroquercetin and assessment of their physico-chemical properties, general toxic effect and safety.
Materials and methods. The tablets were obtained by direct compression on a laboratory rotary XS press (Robert Bosch GmbH, Germany). The flowability and bulk density of the powders were checked by tester ERWEKA GT (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany). Tablets hardness and geometric dimensions were checked by tester SOTAX HT1 (SOTAX AG, Switzerland), the friability of the tablets was checked by tester SOTAX F2 (SOTAX AG, Switzerland), disintegration time was checked by tester DISI-A touch (CHARLES ISCHI AG, Switzerland). Pharmaceutical substance dihydroquercetin of the company "Khimiya Drevesiny" was used as an active pharmaceutical substance. Silicated cellulose for direct compression, aerosil 200, sodium starch glycolate and magnesium stearate were used as a excipients. The qualitative and quantitative content of dihydroquercetin in tablets was determined using HPLC-UV (Agilent 1260 Infinity II). The tablets were dissolved in a certain volume of the mobile phase, and then the solution was filtered (0.22 microns PTFE syringe filters, VWR, USA). The following reagents were used: acetonitrile for chromatography and concentrated phosphoric acid, "BDA", Russian Pharmacopoeia XIV, OFS.1.3.0001.15 "Reagents. Indicators". Determination of acute, subacute toxicity and local irritant effect was carried out according to the generally accepted method according to Russian Pharmacopoeia XIV on mature male and female white mice and rats in the laboratory of Pathomorphology and Drug toxicology of the Central Research Laboratory (REC) of the RUDN. The study was performed on 36 healthy sexually mature outbred mice with a body weight of 18–20 g and on 30 healthy sexually mature outbred rats with a body weight of 180–200 g. The drug is administered to animals once intragastrically with the help of an atraumatic probe in the form of a suspension prepared from crushed DQV tablets on 1 % starch gel. The comparison preparation was 1 % starch gel. The duration of observation of laboratory animals is 14 days for the study of acute toxicity and 30 days for the assessment of subacute. Daily clinical examination of the animals was performed, physiological parameters were evaluated, and the condition was recorded. The choice of doses was carried out according to the already available data on toxicity requirements described in the OESD regulatory documentation No. 425. A detailed clinical examination of the animal is carried out in the holding cage, in the hands and in the open area. Note the manifestation and expression, where acceptable, of signs of intoxication. The frequency of the examination depends on the severity of the intoxication pattern, but not less often than on the 2nd, 7th and 14th day of the experiment. Body weight is recorded immediately, on the 2nd, 7th day, and immediately before euthanasia. Deviations in the consumption of feed and water by the animals in the group planting cages are recorded visually on a daily basis. Food deprivation is performed the night before euthanasia. Animals are deprived of food, but not water. The animals are subjected to euthanasia by being placed in an ether-containing desiccation chamber 14 days after the administration of the study drug and the reference drug.
Results and discussion. The technological characteristics of the substance of dihydroquercetin for the implementation of the technological process of making tablets based on it have been determined. It has been found that the substance dihydroquercetin has very poor flowability. Four types of excipients were used to improve the technological properties of the active substance. In the course of tabletting, the pressing modes were selected. The optimal pressing force was 5 kN. The depth of filling was – 7 kN. The optimal distance between of the punches was 2.5 mm. The rotor speed was constant at 15 rpm. The speed of the feeder is 25 rpm. Chromatography conditions were selected for the determination of dihydroquercetin in tablets by HPLC-UV method. The lethal dose for a single administration was determined, and the toxic effects of repeated repeated administration of the drug dihydroquercentin in the dosage form of an oral tablet were evaluated. The local irritant effect of the drug during oral administration was evaluated in laboratory animals. In the course of the conducted experiments, the absence of a local irritant effect was established when using tablets based on dihydroquercetin, when determining the toxicity class, the drug is assigned to the III class of "Moderately toxic" substances.
Conclusion. The formulation and technology of tablets based on dihydroquercetin have been developed. It was found that the optimal composition for the manufacture of tablets with dihydroquercetin by direct compression should contain a filler silicated cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, aerosilglidant and a sliding agent – magnesium stearate. The HPLC-UV technique for identification and determination of the quantitative content of dihydroquercetin in tablets has been developed and validated. It is shown that in addition to the main peak, the peaks of bioflavones of eriodictyol and quercetin are determined on the chromatogram of tablets. This may contribute to the expansion of the spectrum of pharmacological activity of the tablets obtained. On the basis of the developed composition and production technology of tablets based on dihydroquercetin, an assessment of the general toxic effect and safety of the preparation based on bioflavonoids of the Daurian leaflet was carried out. The average lethal dose of the drug (LD50) was established, which, when administered orally to mice, corresponded to 159 mg/kg. During the study, the clinical picture of intoxication was evaluated. With intragastric administration of the drug, at a dose of 159 mg/kg, the death of 50 % of the animals in the experimental group was observed.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. The bitter wormwood herbs (Artemisia absinthium L.) is used to reflexively enhance gastric juice secretion, increase appetite, and increase bile secretion. These pharmacological effects are due to the rich chemical composition of the feedstock, of which essential oil is an important component. The study of the peculiarities of accumulation of this group of compounds is relevant.
Aim. The aim of this study the features of the accumulation of essential oil in bitter wormwood herbs, collected in agro- and urbo-cenoses of the Voronezh region.
Materials and methods. In the Voronezh region, 13 raw material harvesting points were chosen to study the content of essential oil in it, which was carried out according to the methodology of the FS "Bitter wormwood herbs." Correlation coefficients were analyzed to examine in detail the effect of basic pollutants (heavy metals and arsenic) on the accumulation of essential oil.
Results and discussion. All analyzed vegetable raw materials are considered benign in terms of essential oil content. The maximum amount of essential oil (2.04 %) is noted in a sample of bitter wormwood herbs growing on the territory of the Khopersky Reserve. The minimum amount of essential oil was noted in a sample collected on the street of the city of Voronezh (0.63 %). In general, for samples of control territories and agrobiocenoses, a higher content of essential oil can be noted than in samples of urbobiocenoses. Thus, the content of essential oil in the herb of bitter wormwood collected in territories deprived of human economic activity amounted to 1.85–2.04 %, near agricultural land – 1.61–1.85 %. In a number of urbanized territories, samples of bitter wormwood herbs with a much lower content of essential oil were harvested – less than 1 % – on the streets of the cities of Voronezh, Ostrogozhsk, Borisoglebsk, along the M4 highway in Ramonsky and Pavlovsky districts, along the railway. The calculated values of correlation coefficients showed a strong negative effect of lead, cadmium, nickel, cobalt, zinc on the accumulation of essential oil bitter wormwood herb.
Conclusion. The lowest content of essential oil was found in samples harvested on the streets of large cities of the region, along road routes and the railway. This makes it possible to conclude that the anthropogenic load has a negative effect on the accumulation of this group of compounds in bitter wormwood herbs.
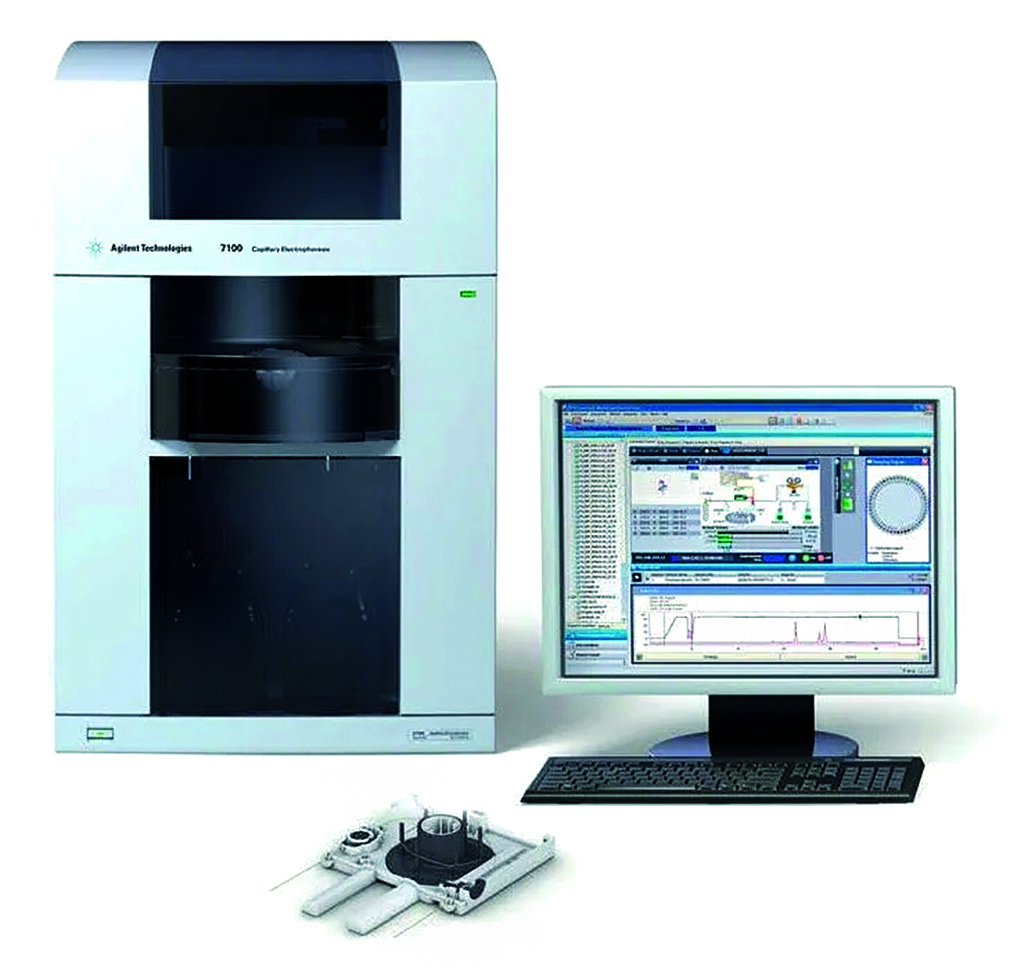
Introduction. Curcuminoids are natural polyphenolic colorants with a wide spectrum of pharmacological activity. Modern hybrid and classical methods are used for the determination of curcuminoids. However, the problem of the analysis of curcuminoids in the composition of plant and medicinal objects remains relevant. In this work, capillary electrophoresis (HPCE) in the variant of micellar electrokinetic chromatography with diode array detection (MEKC/DAD) was used as such a method.
Aim. The purpose of this analysis is the choice of optimal conditions for the separation of curcuminoids using capillary electrophoresis in the form of micellar electrokinetic chromatography.
Materials and methods. Separation of curcuminoids was carried out on an Agilent 7100 CE capillary electrophoresis instrument with a diode array detector and an Agilent Chem Station monitoring and data acquisition system. Borate buffer (20 mM, pH 9.3) with the addition of sodium dodecyl sulfate – SDS (30 mM) in ratios of 1 : 1 was used like the electrolyte. The sample was injected hydrodynamically – 50 mbar/3 sec, electrode voltage is +25 kV, quartz capillary – total capillary length/effective capillary length = 30/40 cm, ID = 50 µm, capillary temperature +20 °С. The output of curcuminoids was monitored at the wavelength of the diode-matrix detector – λmax = 425 nm/4 nm, the refereed wavelength is 360 nm/100 nm.
Results and discussion. Curcuminoids in a borate buffer solution with the addition of SDS are practically not separated, which is associated with a high activity of the electroosmotic flow, to suppress which 95 % ethyl alcohol was added. In the course of research, it was found that the addition of ethyl alcohol in an amount of 20 % relative to the buffer solution makes it possible to separate the mixture of curcuminoids.
Conclusion. Thus, the conditions for the separation of the total curcuminoids by the HPCE method in the variant of micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) were selected. It has been established that for the separation of curcuminoids by this method, it is necessary to use an electrolyte consisting of a mixture of equal volumes of borate buffer (20 mM) and sodium dodecisulfate (30 mM) and ethyl alcohol in an amount of 20 % of the electrolyte volume. A further increase in the concentration of ethyl alcohol in the electrolyte is unreasonable, since it can adversely affect the stability of micelles.
Introduction. Hygienic monitoring of air pollution at the pharmaceutical enterprise required by the law of the Russian Federation (orders, standards, methodological guidelines and guidelines). This requirement follows from the need to protect the personnel of the pharmaceutical plant from the adverse air conditions of the working area, which may contain suspended solids of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Despite the use of breathing equipment by staff and occupational safety requirements, the risk to workers should be minimized by regular assessment of air pollution.
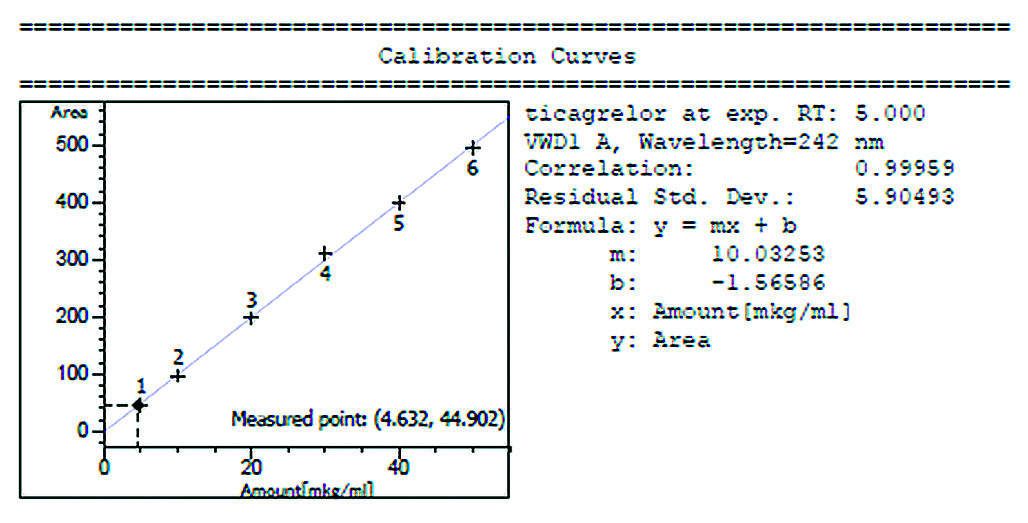
Aim. The purpose of the stady is to carry out hygienic monitoring of working area air tikagrelor – API of the medicinal preparation Brilinta®.
Materials and methods. The subject of this research is API ticagrelor including air and flush samples from the surface of LLC «AstraZenica Industries», collected during the production of the consignment of Brilinta® (MNN – ticagrelor). Air samples of the working area were collected using air intake systems of type "IOM Sampler", using both personal and stationary systems. Flushing from the surface is done by template v printing using cotton swaps. Sampling points selected to cover. All stages of the production cycle. Subsequently, the quantification of ticagrelor in samples was carried out by the method of high-efficiency liquid chromatography with UV detection (HPLC-UV).
Results and discussions. The quantitative determination showed that 4 air samples and 25 surface fluxes exceeding the allowable content of ticagrelor. Each sample was related to the time and place of sampling, and assumptions were made as to why the sample points exceeded the standard values.
Conclusion. At the pharmaceutical enterprise we have carried out hygienic monitoring of the working area air for the content of API ticagrelor. The results of the measurements were obtained and processed, on the basis of which measures were proposed to reduce the concentration of ticagrelor in the air in order to protect personnel from the adverse effects of the work area. These measures include optimization of process operations and/or training of personnel in new approaches to the operation and cleaning of equipment.
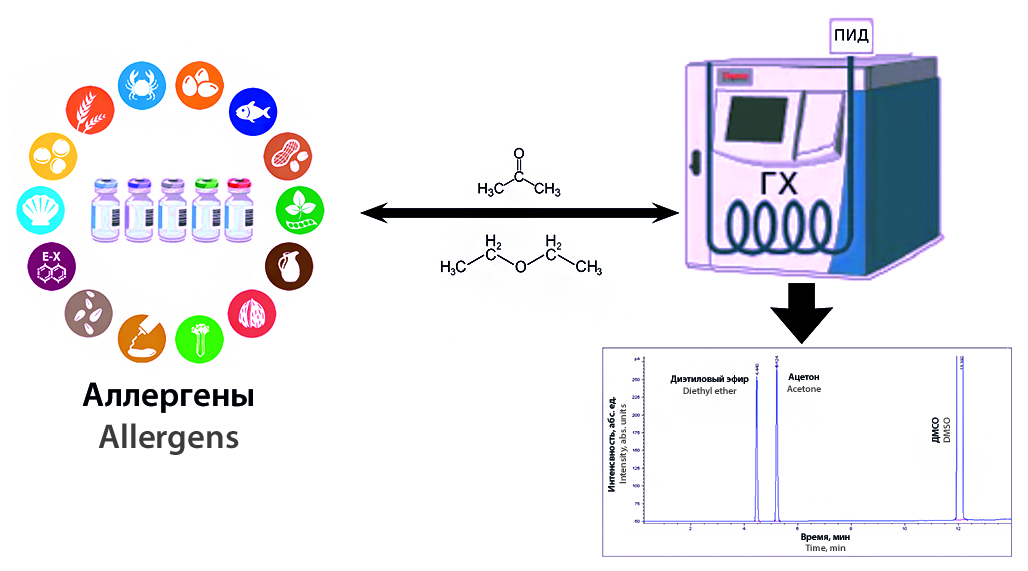
Introduction. One of the requirements for the quality of pharmaceuticals, including allergens, is the determination of residual organic solvents in them. In the production of allergen preparations, in a number of cases in the technological process, organic solvents of the third toxicity class are used, diethyl ether and acetone, which are solvents of low toxicity and their maximum content is allowed up to 0.5 % (5000 ppm). Since diethyl ether or acetone, and in some cases both solvents can be used simultaneously in the production process of allergen preparations for degreasing and cleaning, it is therefore advisable to develop and use a unified technique to determine them.
Aim. The aim of the study was to develop and validate a method for the quantitative determination of residual organic solvents in allergen preparations.
Materials and methods. The studies were carried out by gas-liquid chromatography with a flame ionization detector with injection of the test samples using an autosampler on a Zebron ZB-624 capillary quartz column (G43, 6 % cyanopropylphenyl / 94 % dimethylpoly siloxane).
Results and discussion. The conditions for the chromatographic separation of acetone and diethyl ether on a capillary quartz column were selected. The parameters of the suitability of the chromatographic system have been determined. The developed method was validated according to the following characteristics: specificity, linearity, limit of quantitative determination, correctness and precision at the level of repeatability and intra-laboratory precision. The content of acetone and diethyl ether in 26 preparations of allergens was determined. The results of the quantitative determination of diethyl ether and acetone in allergen preparations, in the technological process of which OOP are used, are in the range of 0.0053–0.0524 % for diethyl ether and 0.0029–0.0994 % for acetone. Thus, the content of diethyl ether and acetone in all tested allergen preparations was below the established norm (less than 0.5 %).
Conclusion. An analytical method has been developed for determining the quantitative content of diethyl ether and acetone in allergen preparations using the GLC method; the method has been validated according to characteristics that meet the requirements of General Pharmacopoeia Monograph 1.1.0012.15 "Validation of analytical methods". The analysis of allergen preparations was carried out in accordance with the methodology. In all preparations, the content of diethyl ether and acetone was no more than 0.5 %.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
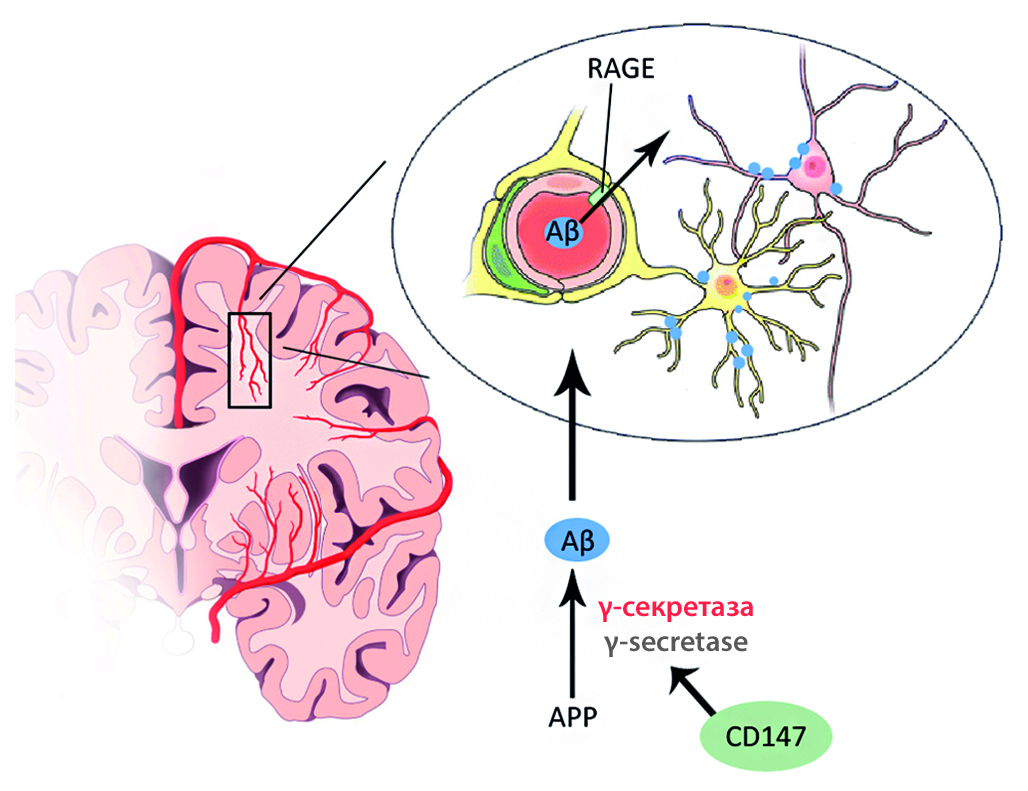
Introduction. In the study of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the cause-and-effect relationship between neurodegenerative changes and the accompanying amyloid angiopathy is becoming increasingly important. The accumulated clinical data indicates that an important contribution to the pathogenesis of AD is made by neurovascular unit dysfunction, including disruption in permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), microcirculation, and metabolic coupling of cells.
Aim. To study the molecular mechanisms of disturbed brain microcirculation and the structural and functional integrity of the BBB in experimental models of AD in vitro under the modulation of CD147 and RAGE.
Materials and methods. The study was carried out on C57BL/6 mice. First, we formed an AD model in animals of the experimental group. Then, we isolated and cultured primary cells of the brain, modulated the activity of CD147 and RAGE in endothelial cells using siRNA CD147, siRNA RAGE, cyclophilin A and Aβ1-42, and formed a BBB model in vitro. Further, we assessed transendothelial electrical resistance in the BBB model in vitro, registered the marker molecules of angiogenesis and analyzed the expression of APP in endothelial cells. Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out using the methods of nonparametric statistics: the Mann – Whitney U test for comparing independent samples and the Wilcoxon test for comparing dependent samples. The level of statistical significance of differences was p ≤ 0.05.
Results and discussion. Knockdown of RAGE led to a statistically significant increase in TEER, an intensification of neoangiogenesis, and a decrease in the level of APP expression. At the same time, although CD147 knockdown led to an increase in TEER, it also led to controversial effects on angiogenesis and an increase in APP expression.
Conclusion. Analyzing the data obtained, it can be concluded that RAGE and CD147 silencing in the cells of cerebral microvessels can become a promising method for reducing their pathological permeability.
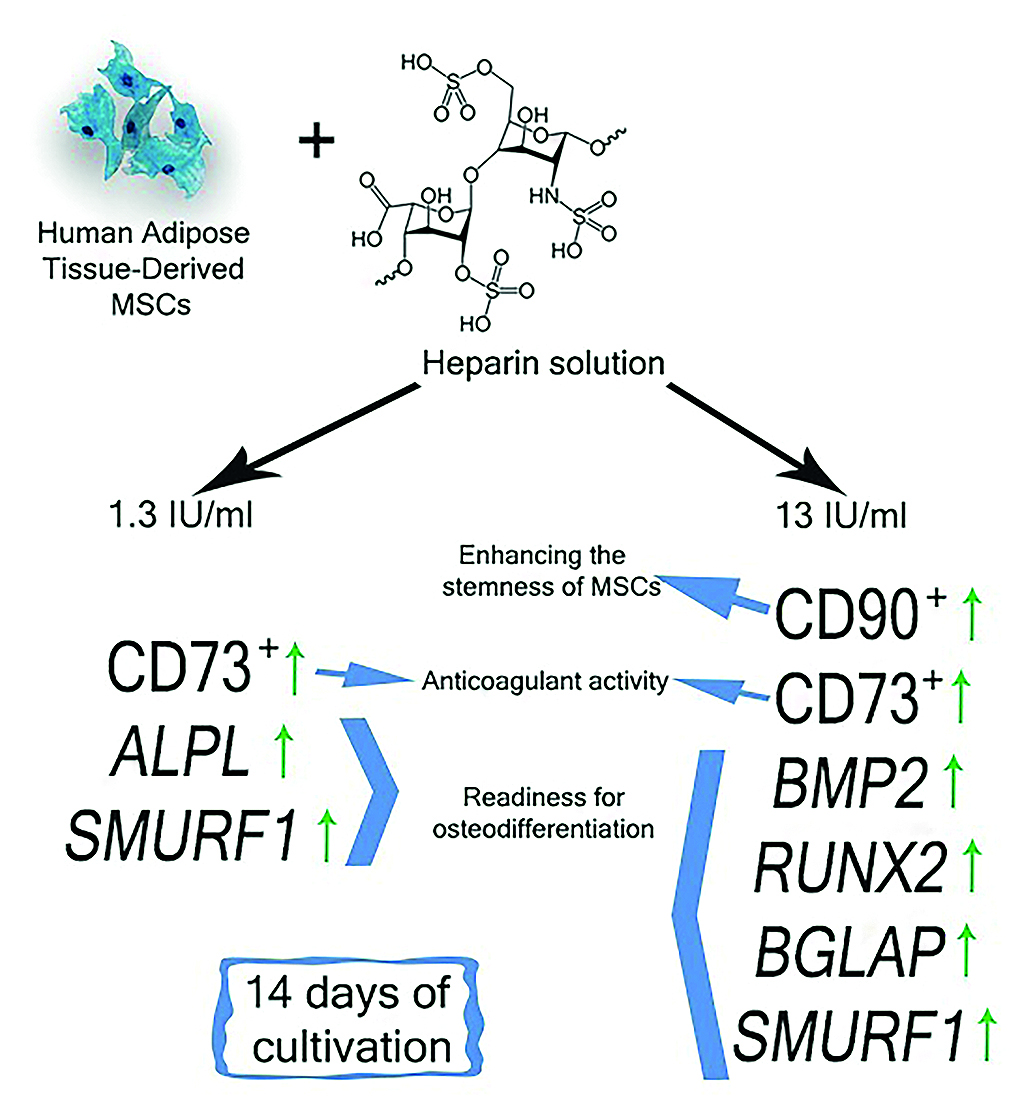
Introduction. Artificial materials used in regenerative medicine induce a balanced inflammatory response after implantation, which is an important step for effective regeneration of damaged bone tissue. The contact of the implant with tissues and biological fluids is accompanied by the deposition of blood proteins on its surface, which contributes to the activation of the complement system and initiates blood clotting, leading to the formation of a fibrin clot. On the surface of the implant, fibrin ensures the adhesion of stem cells and their maturation into fibroblasts that produce collagen and its derivatives. The formed extracellular matrix is the basis for the formation of a tissue structure (callus). To prevent the development of postoperative pathological conditions caused by hypercoagulatory syndrome, therapeutic strategies with anticoagulants such as heparin are used. However, their use limits the formation of a fibrin clot in vivo, which may slow down the migration of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and the subsequent formation of callus.
Aim. To investigate of the effect of heparin at pharmacological concentrations on stemness and the ability of MSCs from human adipose tissue to undergo osteogenic differentiation under conditions of in vitro cultivation.
Materials and methods. To assess the morphofunctional state of cells cultured in the presence of heparin, 2 experimental groups were formed: 1) MSCs in the presence of heparin at a therapeutic concentration (1.3 IU/ml); 2) MSCs in the presence of heparin at a toxic concentration (13 IU/ml).
Results and discussion. Flow cytometry results showed that the addition of heparin at both concentrations used in the study to MSC culture leads to an increase in the number of cells expressing the surface markers CD73 and CD90, indicating the maintenance of their stem state. On the other hand, a stimulatory effect of heparin at both concentrations used on the transcription of mRNA of osteogenic genes (BMP2, BMP6, ALPL, RUNX2, BGLAP and SMURF1) in MSCs was also observed, which may indicate the osteogenic potential of heparin for the cell culture studied.
Conclusion. The results of the study are useful for regenerative medicine related to the use of MSCs in clinical practice; they may serve as a prerequisite for the development of new therapeutic strategies for orthopedic and traumatologic patients at high risk of postoperative thrombosis after endoprosthetics surgery and osteosynthesis.
Introduction. Coronavirus infection is an acute viral disease with a predominant lesion of the upper respiratory tract caused by an RNA-containing virus of the Coronaviridae family. However, it is known that neutralizing antibodies play an important role in antiviral therapy because they effectively inhibit the reproduction of viruses and reduce the severity of the disease. Polyclonal antibodies contained in convalescent plasma are usually used as emergency therapy for emerging infectious diseases. In this aspect, the use of a human immunoglobulin G preparation containing specific antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 ("COVID-globulin") appears to be safer and more effective.
Aim. The aim is pharmacokinetics study of drug "COVID-globulin" (specific human immunoglobulin against COVID-19, solution for infusions, not less than 160 anti-COVID units/mL (ACU/mL), JSC "NPO Microgen", owner of the registration certificate of JSC "Natsibio", Russia), in addition to standard therapy for the treatment of patients with middle-grade COVID-19.
Materials and methods. The clinical and analytical stages of the study of the pharmacokinetics of drug "COVID-globulin", as well as the analysis of the safety and parameters of pharmacokinetics were carried as part of a clinical study of the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the drug immunoglobulin ("COVID-globulin"), not less than 160 anti-COVID units/mL (ACU/mL), JSC "NPO Microgen", owner of the registration certificate of JSC "Natsibio", Russia. Quantitative determination of antibody concentrations against SARS-CoV-2 was carried out by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using spectrophotometric detection in the visible range of the spectrum on an automatic plate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analyzer Lazurite (Dynex Technologies Inc., USA). The calculation of pharmacokinetic parameters was carried out using the Microsoft Excel package with an extension for pharmacokinetic analysis Boomer (Department of Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism, Allergan, Irvine, CA 92606, USA).
Results and discussion. No serious adverse events were reported in the study, and the only adverse event that resulted in a volunteer withdrawing from the study was not related to the use of the drug. The pharmacokinetic parameters of the drug "COVID-globulin" were calculated for two batches of drugs. The pharmacokinetics of the "COVID-globulin" (the content of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 – 330 ACU/ml) was assessed on a sample of 8 volunteers. The maximum concentration of specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus was 25.46 ± 8.71 ACU/ml (Mean ± SD, where Mean is the arithmetic mean, SD is the standard deviation). The median value of the time to maximum concentration of specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus was 0.25 hours. Specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus were eliminated from blood plasma with a half-life value 266.89 ± 59.92 hours. The pharmacokinetics of the "COVID-globulin" (the content of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 – 250 ACU/ml) was assessed on a sample of 15 volunteers. The maximum concentration of specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus was 20.93 ± 3.82 ACU/ml. The median value of the time to maximum concentration of specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus was 0.25 hours. Specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus were eliminated from blood plasma with a half-life value 295.56 ± 50.68 hours.
Conclusion. According to the results of the study, the safety profile of the drug "COVID-globulin" is assessed as favorable. Based on the concentrations of specific IgG antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 virus obtained during the analytical stage of the study, the main pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated, and the average pharmacokinetic profiles of the test drug "COVID-globulin" were plotted after a single injection. The results obtained were the basis for the subsequent phases of clinical trials of the drug "COVID-globulin".
Introduction. Deferasirox is one of the most well-known complexing drugs chelators and is successfully used in chelating therapy for the treatment of excess iron in the human body. Deferasirox is also included in the list of vital and essential medicines, which indicates the importance of this drug for Russian healthcare. In this document, there are drugs only from a foreign manufacturer, therefore, within the framework of the trend towards import substitution, the development of deferasirox preparations of domestic production is a necessary and promising direction. In this connection, there is a need to develop a method that allows quantifying deferasirox in human blood plasma with minimal time and resource costs as part of a pharmacokinetic study.
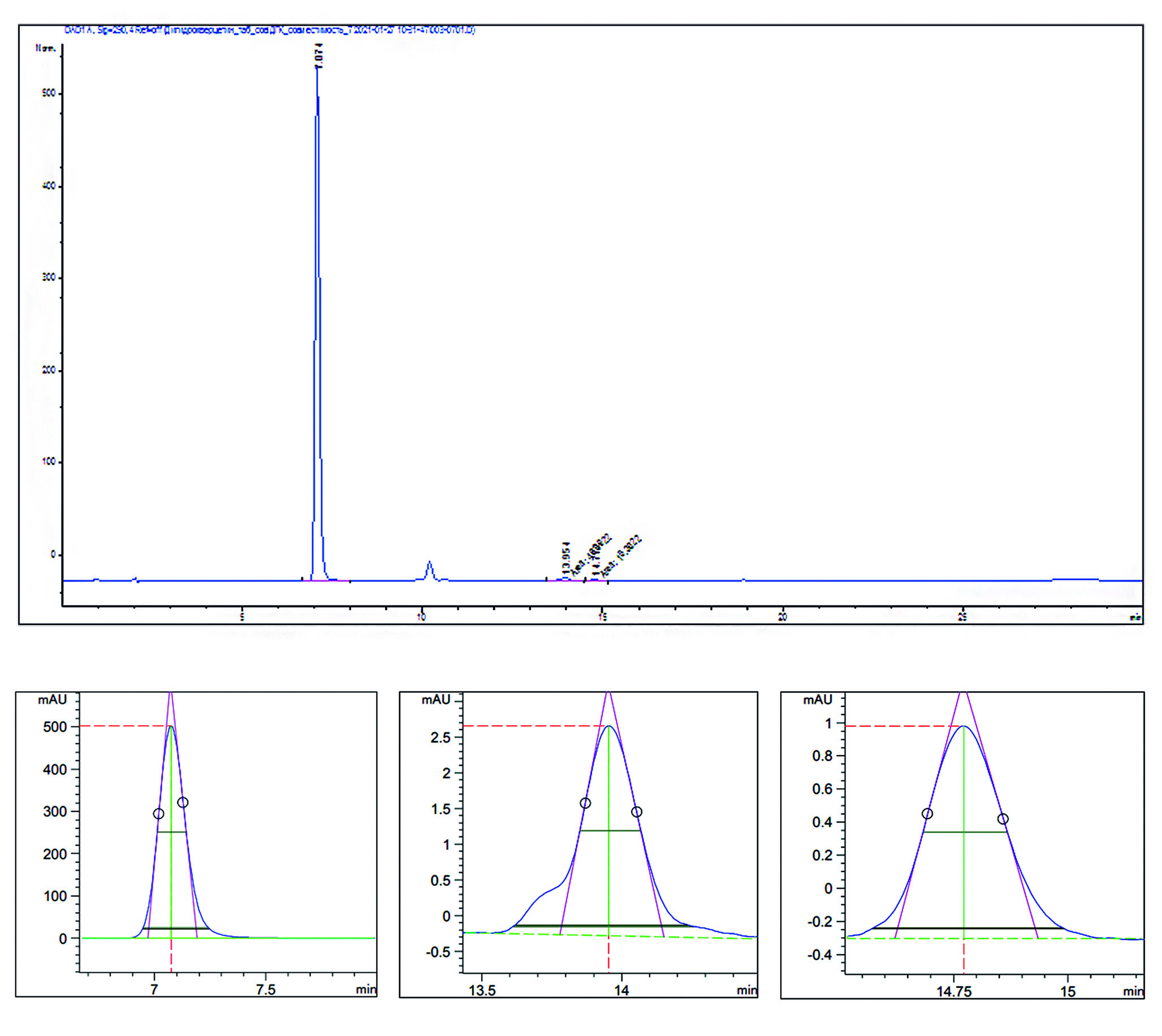
Aim. The aim of this study is to develop a method for quantitative determination of deferasirox in human blood plasma by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with ultraviolet detection (HPLC-UV) for further bioequivalence studies.
Materials and methods. Determination of the deferasirox in human blood plasma was carried out by HPLC-UV. The method of proteins precipitation by acetonitrile was used as a sample preparation. Erlotinib solution was used as an internal standard. Mobile phase: 0.3 % solution of orthophosphoric acid in water, brought to pH 3.0 (eluent A) and 0.1 % solution of formic acid in acetonitrile (eluent B). Column was Symmetry®, 75 × 4,6 mm (Waters, США). Analytical range of the technique for deferasirox was 0.25–70.00 µg/ml in human blood plasma. Detection was carried out using a UV detector at an absorption wavelength of 299 ± 2 nm.
Results and discussion. This method was validated by selectivity, calibration curve, accuracy, precision, spike recovery, the lower limit of quantification, carry-over effect and stability.
Conclusion. A method of quantitative determination of deferasirox in human blood plasma was developed and validated by HPLC-UV. The analytical range was 0.25–70.00 µg/ml in human blood plasma. This method was used as part of a study of the pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of deferasirox drugs.
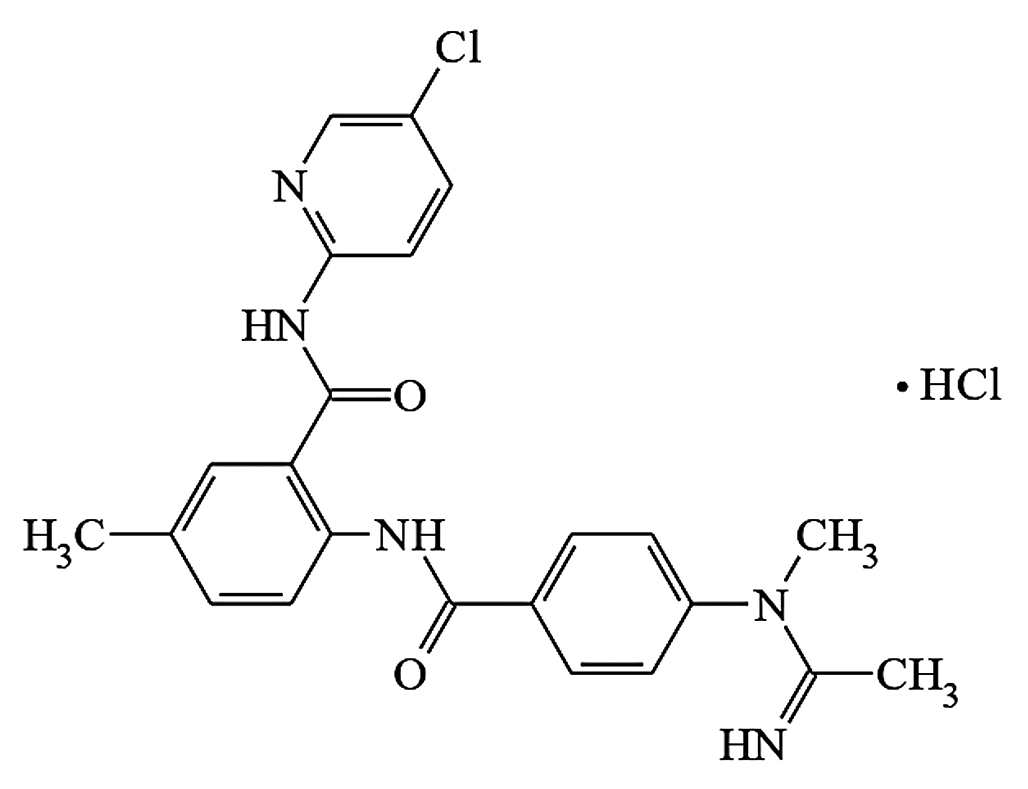
Introduction. Nowadays, discovery and development of innovative drugs represent a relevant goal for the pharmaceutical market. One of such drugs is N-(5-chloropyridine-2-yl)-2-({4-[ethanimidoyl(methyl)benzoyl}amino)-5-methylbenzamide hydrochloride (hereinafter DD217), an innovative drug that belongs to the class of anticoagulants, namely factor Xa inhibitors.
Aim. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a method for DD217 determination in rat plasma by means of high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) to carry out pharmacokinetic studies.
Materials and methods. Outbred Wistar rats were used in the study. Rats received a single dose of DD217 substance solution intragastrically at a dose of 5, 15, 30 mg/kg. The validated HPLC-MS/MS method was employed for DD217 determination in rat plasma. Nebivolol was chosen as the internal standard of the method. Chromatographic separation involved the use of Phenomenex Luna С8 column (3 µm, 50 × 4.6 mm) and gradient elution with water-acetonitrile solution containing 0.1 % formic acid. The total run time of each sample was equal to 2.0 min. DD217 and nebivolol were detected in positive electrospray ionization mode, the ion transitions monitored were m/z 436,1 → 119,9 and 406,0 → 151,0, respectively. Pharmacokinetic parameters and descriptive statistics were calculated through model-independent method in IBM SPSS Statistics v27 and Julia v1.6.0 (MixedModels v3.8.0, ClinicalTrialUtilities v0.5.1) software.
Results and discussion. Method was validated by linearity, lower limit of quantification, selectivity, accuracy and precision, dilution integrity, matrix effect, recovery, carry-over, and stability. The lower limit of quantification of DD217 in rat plasma was 2.0 ng/mL. The method was successfully applied for establishing the pharmacokinetic parameters of DD217 substance in rat plasma after intragastric administration at a dose of 5, 15, 30 mg/kg.
Conclusion. HPLC-MS/MS method for DD217 determination in plasma was developed, validated and applied in order to evaluate pharmacokinetic parameters of DD217 substance in rat plasma.
ANNIVERSARIES
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)