FROM EDITOR
In February 2023, the opening of the laboratory complex of LLC "Center for Pharmaceutical Analytics" took place in the building at 8 Simferopol Boulevard. In connection with the relocation of the laboratory, the Russian federal television channel "NTV" released a report where the general director of LLC "CPHA" gave an interview about the current activities of the company and prospects.
The second part of the article presents the next steps of Peter the Great to improve the functioning of the pharmacy service in Russia. To improve the management of the nascent pharmacy service, the Emperor established the Main Pharmacy in the Pharmaceutical Prikaz (i.e. chamber) and appointed its head, endowed with clearly defined rights and responsibilities. The development of the pharmacy service in Russia was facilitated by the organization of hospitals, in which pharmacies were established. Usually, foreigners worked there, but they shared their pharmaceutical knowledge with young people of different social strata. At the same time, Peter the Great stimulated the emergence of chemical industries, issuing letters of commendation to Russian entrepreneurs to open chemical industries. To ensure the maintenance and financial sustainability of hospitals and pharmacies the Emperor issues a decree on a new tax (one kopeck from each ruble) for all military and civilian service people. Peter the Great paid special attention to the training of local people as personnel. So, at first, he invited specialists from abroad, but later, he constantly sent all young people to study literacy, arithmetic and geometry in schools by his Decrees. The most talented children of nobles, boyars and merchants were sent to study abroad. In the last year of his life, Peter the Great established the Academy of Sciences, which, according to his plans, should include the University, where medical and pharmaceutical sciences would be studied at the Faculty of Medicine. Thus, Peter the Great consistently and systematically formed the main directions of the domestic pharmacy service, which, while developing harmoniously, was supposed to ensure civil health.
The water treatment system is an essential part of the drug production cycle. The current regulatory documents normalize the composition and basic principles for the production, storage and distribution of water for injection and purified water. However, these recommendations are of a general nature, sometimes contradict each other, and, most importantly, do not contain specific technical recommendations that could be taken into account by engineers when designing equipment, manufacturers during production, and operating organizations during operation. Having a standard with the above content will provide technical support for the functioning of national legislation.
EVENTS
The Congress "Chemical and Biological Drugs: Pharmaceutical and Clinical Development in Accordance with the EAEU rules" will be held in Moscow on September 22 at the Sechenov University Congress Center. The theme of the event traditionally covers all life stages of a medicinal product, from development to post-registration studies of drugs.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
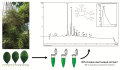
Introduction. Thymoquinone (2-Isopropyl-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone) is an organic compound of plant origin, which is formed as a result of the oxidation of thymohydroquinone. Thymoquinone is a component of the essential oil of black caraway seeds (Nigella sativa L.) and is known to possess a significant spectrum of pharmacological activity. Due to the lipophilicity of thymoquinone and its ability to accumulate in oils, we proposed a method to isolate thymoquinone from the fatty oil of caraway seeds in order to assess its selective accumulation and the possibility of using the oil as a source for the compounds production.
Aim. Method development for the isolation of thymoquinone as an individual compounds from black caraway (Nigella sativa L.) seed oil, to confirm its structure and determine the degree of purity of the obtained substance.
Materials and methods. To confirm the authenticity of the raw materials, analysis of key morphological and anatomical diagnostic features was performed. Quantitative assessment of thymoquinone content in black caraway seeds and control of the isolation process were performed though HPLC analysis. Sample preparation was carried out with methanol by: 1) triple extraction on a boiling water bath; 2) sonification; 3) maceration. The structure of the isolated compound was confirmed through the analysis spectral characteristics using IR spectroscopy by comparing the obtained IR spectrum with the data from the NIST database and one-dimensional NMR spectroscopy.
Results and discussion. As a result of the morphological and anatomical analysis, the authenticity of N. sativa seeds was confirmed. Extracts from black caraway seeds obtained by various sample preparation methods were analyzed with HPLC. As a result, it was noted that the method of obtaining the extract does not significantly affect the yield of thymoquinone, the content of which in black caraway seeds is 0.25 ± 0.02 %, which is sufficient for isolation purposes. Through the evaluation of various isolation methods for thymoquinone from black caraway seeds – maceration with alcohol and n-hexane from crushed seeds, liquid-liquid extraction from fatty oil, steam distillation of oil – showed that the best way to obtain thymoquinone is through the distillation of black caraway seed oil with water steam [oil : water ratio (1 : 1)] in a sand bath for 3 hours. The yield of thymoquinone from N. sativa oil is 398 mg from 150 ml of oil (0.26 %). The structure of thymoquinone was confirmed by spectral characteristics in comparison with the NIST database and literature data.
Conclusion. The possibility of isolating thymoquinone from Nigella sativa L. seed fatty oil with a chromatographic purity (HPLC) of more than 97 % along with the comparison of the isolated compounds spectral characteristics with literature data, which confirm the identity of the obtained compound, was shown. The proposed express and efficient method for the isolation of thymoquinone through steam distillation provides a yield of the target component of 0.26 %. This method can be applied at roduction sites that harvestand process of black caraway seeds to obtain natural thymoquinone.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. Degenerative retinal diseases, including glaucoma, are the main cause of vision loss in the adult population. The development and improvement of drug treatment of this group of diseases is an urgent problem.
Aim. Study of a new dosage form of methylethylpyridinol in the form of an ophthalmic gel.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were samples of eye gels containing methylethylpyridinol, for which mucoadhesion was studied by a combination of in vitro / ex vivo methods. Biodegradation and release kinetics of the active substance from the dosage form were studied using a dissolution tester in an artificial tear fluid medium. The shelf life of the dosage form was established in accordance with the stability study program. Determination of the local irritative action was carried out by conjunctival test in 10 rabbits of chinchilla breed weighing 3,6–4,1 kg.
Results and discussion. The article presents the results of the study of biopharmaceutical characteristics of the previously developed ophthalmic gel of methylpyridinol based on a nonionic polymer – hydroxyethylcellulose brand Natrosol™ 250 HHX. A comparative study of mucoadhesion by in vitro / ex vivo flow of ophthalmic gel samples in the range of hydroxyethylcellulose concentration in the gel of 1–1.5 % was performed. The sample with 1.5 % polymer content had the best adhesive characteristics because it had a minimum flow rate: in vitro 2.7 · 106 m/s and ex vivo 2.3 · 106 m/s. Dissolution kinetics and visual biodegradation of the sample after "Dissolution" test were studied, which indicates prolonged release of methyl ethyl pyridinol from the gel. The stability of the developed dosage form under long-term and stress conditions was shown. The local irritating effect was estimated by the conjunctival test.
Conclusion. The main biopharmaceutical characteristics of the developed ophthalmic gel methylpyridinol were determined and it was shown that it can be used as a delivery system for the treatment of degenerative retinal diseases because it possesses marked bioadhesive properties and prolonged release. The shelf life of the dosage form was determined, which was 2 years. Stress studies of methylethylpyridinol gel were carried out. The developed ophthalmic gel has no local irritating effect.
Introduction. Periprosthetic infections are a major problem in orthopedic surgery. The most optimal way to influence the bacterial film is to suppress the early stages of its formation. The use of hydrogel coatings for the prevention of periprosthetic infections is an effective measure, while the process of coating the implant can be simplified due to the use of in situ systems.
Aim. The purpose of the research is to develop and study antibacterial in situ coatings for preoperative treatment of implants.
Materials and methods. In the experiment we used poloxamers Kolliphor® P 407 and Kolliphor® P 188 (BASF, Germany), hyaluronic acid high-molecular PrincipHYAL® (1400–1800 kDa), low-molecular PrincipHYAL® (400–600 kDa), mixture of high, medium and low-molecular acids PrincipHYAL® Cube3 (ROELMI HPC Srl, Italy). As screening methods for identifying the optimal composition, we used gelation temperature measurements, pH measurements, studies of rheological properties, and microbiological tests.
Results and discussion. During the experiment, we found the optimal concentration of hyaluronic acid 1400–1800 kDa – 0.5 %, at which the studied composition at a temperature of 4.5 ± 0.5 °C was a homogeneous liquid, and it made a sol-gel transition when heated. It was revealed that hyaluronic acid had no significant effect on the gelling temperature, so we added poloxamer 188. We also established the influence of the hyaluronic acid molecular weight on the in situ systems characteristics. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid stabilized the viscosity values and improved the adhesive properties of the system, samples with medium and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid showed lower dynamic viscosity values at the phase gel-sol transition end. We tested the optimal composition (containing 18.0 % poloxamer 407, 2 % poloxamer 188, and 0.5 % hyaluronic acid (1400–1800 kDa) adhesion to the titanium plate. When exposed to the paddle stirrer (rotation speed 20 rpm) for 15 minutes and stored in the thermostat (37,0 ± 0,5 °C) for a week, the analyzed composition showed adhesion strength, which makes it possible to use it for coating.
Conclusion. By multistage screening a sample was selected for introduction of a model antibacterial component representing a cocktail of bacteriophages Klebsiella pneumonia, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli. Microbiological studies showed good compatibility of the immunobiological substance with excipients, which indicated the prospects for further preclinical studies.
Introduction. One of the promising strategies for the development of injectable formulations of poorly water-soluble drugs is the preparation of their nanosuspensions stabilized with albumin. A well-known example of the successful implementation of this technology is Abraxane® (nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel). In the present study, this approach is used for the development of the injectable formulation of a hydrophobic etoposide prodrug.
Aim. Development of the injectable formulation of a novel 4'-О-benzyloxycarbonyl derivative of etoposide (ETP-cbz) based on human serum albumin and evaluation of its cytotoxicity against breast carcinoma cells (BC).
Materials and methods. The structure of ETP-cbz was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy and elemental analysis; log P was calculated in silico using Molinspiration Cheminformatics. The ETP-cbz-HSA nanoparticles were prepared by high pressure homogenization. The particle size, size distribution, and disintegration concentration were evaluated by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The contents of ETP-cbz and albumin in the formulation were determined by HPLC. The conversion ETP-cbz-HSA to etoposide was studied in a model medium in the presence of esterase. The cytotoxicity of ETP-cbz-HSA compared to etoposide and free ETP-cbz was assessed on BC cells (HBL-100 and MCF-7) using a colorimetric MTT assay.
Results and discussion. ETP-cbz exhibited higher hydrophobicity as compared to the etoposide (log P 2.42 vs 0.7, respectively). Due to easy cleavage of the carbonate bond in the presence of esterase, ETP-cbz can be considered an etoposide prodrug. The ETP-cbz-containing HSA nanoparticles prepared by a high-pressure homogenization technique had the particle size of 110 ± 9 nm (DLS) and a low disintegration concentration of 3.0 ± 0.1 μg/mL. The drug content was 1.75 mg/mL. The nanoformulation demonstrated high cytotoxic activity in vitro against MCF-7 and HBL-100 cells that was comparable to the activity of substances etoposide and ETP-cbz.
Conclusion. The obtained nanoformulation of etoposide prodrug based on albumin, suitable for injection, showed high cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells in vitro and deserves further study to assess the possibility of its use in breast cancer chemotherapy.
Introduction. The manufacturing and application of enzyme preparations in the semisolid topical products has features associated with their lability. In previous studies, on the set of specifications the gel form was selected, containing aerosil and olive oil, in which the stabilization of collagenase from Paralithodes camtschaticus was ensured by lipophilic base. In the pharmaceutical development process, the drug critical quality attributes must be defined. Taking into account the lability of Paralithodes camtschaticus collagenase, the identification and minimizing risks аre relevant.
Aim. The aim was the risk factors assessment and minimization during the pharmaceutical development of the gel, containing Paralithodes camtschaticus collagenase within the QbD concept.
Materials and methods. The laboratory samples of gels, containing Paralithodes camtschaticus collagenase, were tested, using the analysis methods recommended by the SP RF 14th ed., as well as GOST 29188.3-91.
Results and discussion. Based on the potential critical characteristics of the material, the pharmaceutical substance Paralithodes camtschaticus collagenase (particle size) and excipients (concentration and sorption properties of aerosil, oxidation of olive oil) risk factors were assessed, and potential measures to reduce these risks are considered. It was revealed that the substance particle size in its origin exceeds the norm and requires preliminary grinding. The aerosil content factor was reveal as critical. The sorption properties of aerosil were not affected the proteolytic and collagenolytic activity of the collgenase gel. It was proved that chemical instability of oil refers to critical factors and the antioxidants (alpha-tocopherol or butylhydroxytoluene) content was justified.
Conclusion. In the course of the study, the Paralithodes camtschaticus collagenase gel the possible risks of pharmaceutical substances and excipients were theoretically justified in accordance with the QbD concept. An experimental assessment of their possible impact on the gel quality was given, which can improve the finished product quality during manufacturing manufacturing by eliminating the identified risks.
Introduction. Human performance depends on external and internal factors. Of a number of external factors, the environmental aspect is one of the leading ones. Internal factors are interrelated with external ones. The latter include the general condition of the human body, as well as the normal functioning of individual systems and organs. It must be noted that the use of herbal drugs in order to prevent the development of pathologies caused by internal factors is rational. A number of plants contain substances that can improve performance by strengthening the cardiovascular system, normalizing the liver, adjusting daily rhythms, reducing stress. In this regard, the development of the composition and technology of drugs based on substances of plant origin does not lose relevance.
Aim. Development of the composition of solid oral dosage form based on dry extract of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge containing saponins.
Materials and methods. As an object of research, a substance was used – dry extract of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, standardized in accordance with the requirements of SP XIV ed. Lactose monohydrate, calcium stearate, methylcellulose, corn starch, talc were used as excipients in the tablet technology. Under laboratory conditions, granulation was carried out by the wet mass extrusion method. A 3 % methylcellulose solution was used as the wetting reagent. Quality parameters of the final dosage form, tablets, were determined according to the methods described in SP XIV ed.
Results and discussion. As a result of the conducted research, the composition of a solid oral dosage form based on a dry extract of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge was proposed. The main quality indicators of the obtained dosage form are determined. A design quality specification has been developed for a drug.
Conclusion. The present study proposed technology dry extract for Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge herb. Quality index of the obtained plant substance are determined. The composition and technology of tablets based on the dry extract of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge herb have been developed. The main quality indicators of tablets based on the dry extract of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge herb were determined. A draft quality specification of the resulting dosage form has been developed.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. Innovative technologies, new approaches to the creation of medicines, a combination of classic technological methods with the latest trends makes pharmaceutical production a direction with positive dynamics of development. But along with the emergence of new synthetic drugs, as well as biotech products, the use of herbal raw materials for the production of medicines remains relevant. Phytopreparations have a number of undeniable advantages over synthetic drugs and are the drugs of choice in different age groups, including for preventive medicine. The flora of Kazakhstan is distinguished by the presence of endemic plants with a sufficient source of raw materials, which creates the prerequisites for their phytochemical profiling and the subsequent development of phytopreparations. In this regard, Ferula akitschkensis B. Fedtsch. ex Koso-Pol., which is widespread in Kazakhstan, is distinguished by the accumulation of various classes of biologically active substances (flavonoids, coumarins, essential oils) and has experience in folk medicine.
Aim. To study the component composition of ethanol extracts of Ferula akitschkensis roots by GC/MS using the Wiley 7th edition, NIST’02 library and to predict the pharmacological activity of identified compounds using the PASS Online web resource
Materials and methods. Ethanol extraction of roots was obtained by extraction of raw materials with 80 % ethanol in the ratio of raw materials : extractant 1 : 10 and under ultrasonic exposure at a frequency of 15–25 kHz for 10–20 min, followed by separation of the extract from the meal. The obtained extract was analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS) in full current scanning mode. The obtained mass spectra were interpreted using the Wiley 7th edition and NIST’02 libraries. To predict the biological activity of the identified compounds, the PASS Online web resource was used.
Results and discussion. The composition of the ethanol extract of the roots of Ferula akitschkensis B. Fedtsch. ex Koso-Pol. is characterized by a metabolomic profile of compounds that differs from other members of the Ferula genus. Thus, o-cymene, the oxygen derivative of p-cymene – thymol and 2,2'-methylenebis[6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methylphenol accumulate in the roots. These compounds can form a marker profile of the roots of Ferula akitschkensis and be used for species identification within the genus Ferula. The prognostic evaluation of the pharmacological activity of the identified compounds of Ferula akitschkensis showed the presence of an effect on metabolic and biochemical processes, in particular, the creation of a proton potential on the mitochondrial membrane, catalysis, redox processes, and stabilization of cell membranes. In addition, antispasmodic, fibrinolytic, and antioxidant activities can be predicted for the roots of Ferula akitschkensis. And in the focus of creating potential drugs based on the raw materials of this species of Ferula, it is advisable to consider the development of dermatological and carminative drugs.
Conclusion. Study of the phytochemical profile of ethanol extracts from the roots of Ferula akitschkensis B. Fedtsch. ex Koso-Pol. by GC-MS made it possible to establish the presence of o-cymene and p-cymene derivatives – thymol and 2,2'-methylenebis[6-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-methylphenol. These compounds make up the marker profile of the roots of Ferula akitschkensis and can be used to identify the species within the genus Ferula, since thymol is not the main component of the essential oil of other representatives of this genus. Prediction of the pharmacological activity of the identified compounds in silico showed the possibility of using Ferula akitschkensis raw materials in complex therapy as a means of improving tissue respiration in conditions accompanied by a violation of redox processes in the body. It has been shown that potential medicinal candidates based on the roots of Ferula akitschkensis will be characterized by antispasmodic, fibrinolytic and antioxidant effects. The development of dermatological drugs may also be in the focus of scientific groups due to the anti-eczematous activity of most compounds of the ethanolic extract of the roots of Ferula akitschkensis.
Introduction. Acca sellowiana, or feijoa belongs to the Myrtaceae family and it is an evergreen shrub or small tree 4–6 meters high. The phytochemical composition has been most thoroughly studied in the fruits of A. sellowiana. It has been shown that feijoa is rich in phenolic acids, hydrolysable and condensed tannins, steroidal saponins, and flavonoids. Hydrolysable tannins are known to have high biological activity.
Aim. To study the composition and content of hydrolysable tannins in the leaves of A. sellowiana.
Materials and methods. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detection and mass spectrometry.
Results and discussion. The results obtained showed the presence of 22 phenolic compounds in the extract of the A. sellowiana leaves. They have been classified as flavan-3-ols, flavonoids and hydrolysable tannins. Two compounds could not be identified. The total content of hydrolysable tannins was 44,28 mg/g (90 % of the total phenolic content). At the same time, ellagitannins were the main phenolic compounds of the extract (40,47 mg/g), while the amount of galloyl-glucose was only 3,81 mg/g.
Conclusions. Composition and content of hydrolysable tannins in the leaves of A. sellowiana introduced in the greenhouse of VILAR have been studied. The leaves accumulate mainly monomeric ellagitannins represented 92 % of the total content of hydrolysable tannins. The data obtained indicate that the leaves of A. sellowiana can be used as a raw material for obtaining extracts with a high content of ellagitannins and developing drugs based on them.
Introduction. Knotweed (curlytop knotweed (curly pea)) – Persicaria lapathifólia Delarbre belongs to the buckwheat family Polygonaceae Juss., the genus Persicaria Mill. For a long time, the Persicaria lapathifólia did not exist as a separate species since 1989, the sorrel-leaved mountaineer has become an independent species. This is an annual herbaceous plant, repeating the main features of the genus Persicaria, and, as the main differences, having larger leaves, most often whitish-green flowers collected in dense inflorescences, peduncles and perianth of which have a large number of yellowish glands and a specific sweet smell.
Text. Purpose of the work was to study the possible prospects for using the Persicaria lapathifólia as an official species. Currently, the plant is not used in medical practice and is considered an admixture in the collection of pharmacopoeial species of the genus Persicaria Mill. The plant is unpretentious to environmental conditions, is a weed, growing in absolutely all climatic zones, which indicates a rich procurement base. Despite the morphological similarity of the mountaineer sorrel with other species of the genus Persicaria, there is a sufficient amount of information in the literature regarding the identification of the object obtained as a result of a comprehensive morphological and anatomical assessment by microscopic methods (stereomicroscopy, luminescent microscopy, classical anatomy, petiolar anatomy), which allows a high the degree of reliability to eliminate errors in the procurement of raw materials and their further use. The chemical composition of Persicaria lapathifólia is represented by various classes of biologically active compounds, among which the most interesting are phenolic compounds (flavonoids), represented mainly by glycosides of quercetin and kaempferol. In addition, the plant is rich in vitamins, being a source of choline, organic and essential amino acids. Taking into account the peculiarities of the component composition of the mountaineer sorrel, the plant is considered as a source of phytopreparations with hemostatic, capillary-protective, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antifungal effects.
Conclusion. As a result of the generalization of the data available in the literature, the prospects of Persicaria lapathifólia to be introduced as a medicinal plant material and medicinal plant substance for the production of herbal medicines along with Persicaria maculosa and Persicaria hydropiper herb were revealed.
Introduction. Identity is an important quality attribute of products containing viable human cells, to be tested during the quality control. The verification of identity includes, among other things, determination of the proliferative activity of the cell lines included in such products. The Agilent xCELLigence real-time cell analysis (RTCA) DP (dual purpose) instrument (USA) for continuous, label-free in vitro analysis can be used to assess the cell proliferative activity.
Aim. Demonstration of reproducibility of the RTCA profiling technique as a test method for primary verification of the cell line identity.
Materials and methods. An xCELLigence RTCA DP cell analyzer (Agilent Technologies, USA) was used to obtain RTCA profiles of dermal fibroblast (DF-2) and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal (MSC AT_D122) cell lines. The experiment was carried out in triplicate after thawing three different vials from the same batch for each cell line.
Results and discussion. The RTCA profiles were obtained for DF-2 and MSC AT_D122 cell lines. The statistical processing of the results was carried out using the Friedman test, confidence intervals, and growth curve parameters obtained by the instrument (doubling time, proliferation rate, and maximum cell index). The obtained data demonstrate no differences in the RTCA profiles after parallel sampling of the contents from three vials for each cell line.
Conclusion. The RTCA profiling reproducibility was confirmed in order to assess the cell analyzer’s applicability to cell line identity.
Introduction. Expansion of the nomenclature of raw materials, including herbal substances, is one of the tasks of the development of the pharmaceutical industry. As an example of a potential and affordable medicinal plant raw material, we can offer the leaves of European dewberry with a proven anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antimicrobial activity. Medicinal plant – European dewberry (Rubus caesius L.) belongs to the genus Rubus L., which includes many species, often difficult to distinguish between each other. For complete pharmacognostic characteristics of medicinal plant raw materials, microscopic examination is necessary.
Aim. To carry out a comparative microscopic analysis of the leaves of R. caesius L., R. allegheniensis Porter and R. nessensis Hall to establish anatomical and diagnostic characters.
Materials and methods. Leaf samples were collected on the territory of Moscow and the Moscow region in 2021-2022. Microscopic structures were analyzed using a Leica DM1000 light microscope (Germany) with a 10x/20 eyepiece and 10x/0.25 and 40x/0.65 lenses.
Results and discussion. A comparative analysis of the anatomical and diagnostic structures of the leaves of the Rubus caesius L. (European dewberry) and its related species has been carried out. The size and frequency of occurrence per 1 mm2 of simple and glandular hairs and stomata were investigated, the type of stomatal apparatus was established, the shape of epidermal cells and crystalline inclusions in the mesophyll were considered.
Conclusion. As a result of the study, differences in the anatomical structures of the leaves of three types of blackberries were revealed. Anatomical and diagnostic characters of Rubus caesius L. leaves have been established, which are indicators of the identification of this raw material, including: the presence of simple one-celled fused at the base trichomes, abundant leaf pubescence (especially on the abaxial epiderm), a large number of stomata (106 ± 37 per 1 mm2), the sinuous shape of epidermal cells, cubic crystals of calcium oxalate in the mesophyll.
Introduction. Silicon-zinc-boron-containing glycerohydrogel substance is considered as a pharmaceutical substance for the new drugs creation with antimicrobial action for local, external and intravaginal use. Standardization and validation of the methods determining the quality parameters of the corresponding substances is one of the stages of introducing new pharmacologically active compounds into practice.
Aim. Determine the quality parameters of silicon-zinc-boron-containing glycerohydrogel, conduct their approbation. Develop a method for quantitative determination of silicon, zinc and boron. Perform statistical results processing of quantitative determination and provide a validation assessment of the chosen method.
Materials and methods. A silicon-zinc-boron-containing glycerohydrogel substance was synthesized at the Institute of Organic Synthesis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences and was used as the studying object. The studies were performed using a Nicolet 6700 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) spectrometer and an OPTIMA 4300 DV (PerkinElmer, США) optical emission spectrometer with inductively coupled plasma.
Results and discussion. The paper describes the results of new pharmacologically active silicon-zinc-boron-containing glycerohydrogel substance qualitative and quantitative tests. The data of statistical processing and validation assessment of the quantitative determination of silicon, zinc, and boron are presented.
Conclusion. The quality parameters of silicon-zinc-boron-containing glycerohydrogel were determined. A method of silicon, zinc and boron quantitative determination was developed. Standardization of the investigated pharmacologically active substance was carried out in accordance with the current requirements for pharmaceutical substances in the Russian Federation.
Introduction. It was found that in combination with radiation exposure, high doses of lithium salts have a depressing effect on tumor leukemia cells. The selection of the appropriate anionic component makes it possible to obtain pronounced radiosensitizing properties. The lithium salt of gamma-lactone 2,3-dehydro-L-gulonic acid is a promising compound for the creation of radiosensitizing drugs. It was found that this compound exhibits high antioxidant activity among other lithium salts, while showing a pronounced radiosensitizing effect. This radiosensitizing effect is dose-dependent and manifests itself in high concentrations in combination with photon or neutron irradiation. The potential antitumor effect, due to radiosensitization, is realized through the induction of oxidative stress, which implies, first of all, an increase in cytotoxic effects on rapidly proliferating tumor cells. The obtained results provide the necessary basis for the creation of drugs with radiosensitizing activity.
Aim. The aim of this work is to conduct an analytical assessment of the content of the active substance and establish the main indicators of the quality of the substance, regulated by the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. During the study, the following parameters were determined: solubility, authenticity, melting point, refractive index, specific rotation, transparency of the solution, color of the solution, pH of the solution, sulfate ash, heavy metals, impurities, water content, residual organic solvents, microbiological purity and a number of others.
Results and discussion. A draft specification for the pharmaceutical substance of the lithium salt gamma-lactone 2,3-dehydro-L-gulonic acid has been developed. The optimal parameters for the control of the composition and physico-chemical characteristics and quantitative determination of the pharmaceutical substance have been determined, which is the main task for the pharmaceutical development of the drug. The results obtained make it possible to conduct a comprehensive characterization of the FS and evaluate the quality parameters of the product, which creates the basis for obtaining a dosage form and further studying the properties for creating a drug with a radiosensitizing effect.
Conclusion. In the course of the work, experimental samples of the lithium salt gamma-lactone 2,3-dehydro-L-gulonic acid were synthesized and its standardization as a pharmaceutical substance was carried out in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation.
Introduction. The study of the dynamics of accumulation of biologically active substances (hereinafter – BAS) in relation to the phonological phases of plant development is of great scientific and practical interest. The quantitative content of aglycones and glycosides of flavonoids depends on the life cycle of the plant and its vegetation phase.
Aim. To identify and quantify flavonoids in the underground organs of Rumex confertus Willd., Rumex aquaticus L., Rumex crispus L. and Rumex obtusifolius L. harvested during different phases of vegetation.
Materials and methods. Extracts from the underground organs of the studied plants, obtained according to the method from the pharmacopoeial article on R. confertus, were analyzed. Chromatographic separation and detection were performed on a Nexera-i LC-2040 high-performance liquid chromatograph (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). The chromatograph was equipped with a column thermostat, chromatography column Grace HPLC-COLUMN 250 × 4.6mm platinum C8-EPS 5 mm (Grace, США) and Guard column Phenomenex SecurityGuardTM Cartridges Widepore C18 4 × 3,0 mm, a degasser, an autosampler (injection volume: 10 µl), and an ultraviolet detector. Detection was carried out at a wavelength λ = 365 ± 2 nm. Mobile phase contains 0.1 % phosphoric acid in water (v/v) (eluent A); acetonitrile (eluent B) with flow rate: 0.9 ml/min.
Results and discussion. All studied objects were analyzed. The authenticity of the substances contained were confirmed using the external standard, and their quantitative content was determined. The discovered and quantified substances were: 3-O-rutinoside of quercetin (rutin), 3-O-rutinoside of isorhamnetin (narcissin), 3-O-glucoside of kaempferol (astragalin), luteolin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin. 7-O-glucoside of luteolin (cynaroside) and 7-O-beta-D-glucoside apigenin (cosmosiin) were not found. The aglycone luteolin had the biggest share in the total quantitative content of flavonoids. It is noted that this aglycone is contained in larger quantities in relation to other flavonoids in all studied objects, regardless of the phase of vegetation.
Conclusion. In the process of the research, a method for the quantitative determination of flavonoids in alcohol-water extracts was developed. Aglycones and glycosides of flavonoids were identified and quantified in the underground organs of R. confertus Willd., R. aquaticus L., R. crispus L. and R. obtusifolius L. of three different vegetations.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
Introduction. Plant essential oils are supposed to be applied for local treatment of infectious focuses.
Aim. The aim of this study was evaluation of antimicrobial activity of essential oils of Thymus serpyllum L. and Thymus marschallianus Willd., widely distributed in the Saratov region.
Materials and methods. Antimicrobial activity of the essential oils was determined by a serial dilution test at the microbial number of 5 × 105 CFU/ml against 6 strains of Staphylococcus aureus, including S. aureus FDA 209P and five clinical, 2 strains of Escherichia coli – E. coli ATCC 25922 and one clinical, two strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa – P. aeruginosa ATCC 27835 and one clinical.
Results and discussion. The bactericidal minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of essential oil of T. serpyllum were determined for all strains of staphylococci (for 5 – 1097,5, for 1 – 2195 µg/ml). The bacteriostatic MICs were determined for 3 strains (for 2 – 548,75, for 1 – 1097,5 µg/ml). MICs of the T. marschallianus essential oil were bactericidal for all strains of S. aureus (120 for 5 and 480 µg/ml for 1 strain). For all test strains of gram-negative bacteria MICs of the essential oils of both species were bactericidal and amounted to 1097 and 960 µg/ml. Considering the chemical composition of the oils by thymol and its isomers, MIC50 of T. marschallianus and T. serpyllum for the test staphylococcal strains amounted 108,89 and 496,59, for the test strains of gram-negative bacteria 683,91 and 783,43 µg/ml respectively.
Conclusion. According to the values of MIC50 antistaphylococcal activity of the essential oils of T. marschallianus was significantly higher than this activity of the essential oils of T. serpyllum.
Introduction. Patient recruitment is one of the main quantitative and qualitative characteristics of a clinical trial. As a quantitative characteristic, the recruitment of patients is, first of all, the final figure necessary to answer the researcher's question; as a qualitative characteristic, the recruitment of patients is a process subject to influence. The recruitment of patients in the center is determined by the rate per month and allows you to gain the statistical power of the protocol, and if the recruitment of patients does not reach the planned capacity, then the capacity may not be gained and this leads to the failure of the clinical trial. Failures in patient recruitment reported in the literature lead to more than 80 % of failed clinical trials of all phases. Patient recruitment as a process is influenced by various factors, and the authors identify recruitment predictors, recruitment facilitators, and barriers to patient recruitment.
Aim. To consider the general features and patterns of recruitment of patients in clinical trials on the example of international multicenter clinical trials.
Materials and methods. We analyzed the quantitative characteristics of patient recruitment in 4 clinical trials with successful recruitment.
Results and discussion. Despite the uniqueness of each protocol, the set of patients has its own patterns common to all clinical studies. It was studied, in particular, that the integrative assessment of the preliminary recruitment of patients by the researcher of the clinical center is not associated with an objective pool of patients and affects the rate of patient recruitment and targeted patient recruitment. We found that the number of clinical centers not recruiting patients in each study is at least 30 % of all centers involved. Three patient recruitment rates have also been identified that need to be considered when planning a clinical trial.
Conclusion. We have identified patterns in patient recruitment that will help in planning clinical trials.
Introduction. It is known that the problem of regeneration of damaged peripheral nerves is one of the leading problems in traumatology and neurosurgery.
Aim. Aim of the study is to determine the features of the innervation of facial muscles when using allogeneic biomaterials.
Materials and methods. The experiment was performed on Chinchilla rabbits (n = 36). The facial nerve was cut in the animals. In the control group (n = 9), the wound was sewn up, in the 1st experimental group (n = 12), a fragment of their masticatory muscle was sewn together with a neurovascular bundle to the denervated buccal muscle. In the 2nd experimental group (n = 15), dispersed allogeneic biomaterials "Regeneration stimulator" and "Vasculogenesis stimulator" were injected into the muscle junction in the operation zone. Rabbits were withdrawn from the experiment for 10, 30, 60 and 180 days. Tissue pieces from the surgery area were examined by transmission electron microscopy.
Results and discussion. In the control and 1st experimental groups, the experiment ended with scarring of the operating area and contracture of facial muscles. In the 2nd experimental group, signs of tissue revascularization and axon germination to the buccal muscle with the restoration of individual neuromuscular synapses were revealed.
Conclusion. The use of allogeneic biomaterials in operations to restore damaged peripheral nerves accompanying muscles creates conditions not only for the restoration of muscle fibers, but also the vascular bed, as well as nerve elements with neuromuscular connections.
Introduction. Sea buckthorn leaves are a promising object for the development of new medicinal herbal preparations due to an extensive list of biologically active substances (tannins, flavonoids, organic acids, etc.). However, despite the active study of biologically active substances of buckthorn buckthorn leaves, their use in medicine is limited to obtaining an antiviral drug "Hyporamine" containing a dry purified extract from the leaves of this plant.
Aim. The aim of the work is to predict the pharmacological and toxic effects of decoction from buckthorn leaves in silico and to evaluate its anti-inflammatory activity in vivo in preclinical studies.
Materials and methods. With the help of the PASS-online Internet resource, the prediction of promising pharmacological and possible toxic effects for the main biologically active substances of the phenolic complex of sea buckthorn leaves in silico was carried out. In preclinical studies in vivo (white outbred conventional male rats, 21 individuals, 210–240 g, 3 groups of 7 individuals each) on a model of formalin paw edema of rats (3.0 % aqueous formalin solution, 0.1 ml subplantarly), the anti-inflammatory activity of decoction of sea buckthorn leaves was evaluated. Animals of the experimental groups were administered: a comparison drug – an infusion of chamomile flowers or a decoction of sea buckthorn leaves at a dose of 10 ml/kg intragastrically daily for 7 days.
Results and discussion. The analysis and systematization of data on the most likely pharmacological effects of the main biologically active substances of sea buckthorn leaves in silico using the PASS-online platform allow us to consider the most promising study of anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activity, which opens up prospects for further preclinical and clinical studies in order to expand the list of indications for the use of extracts from the leaves of sea buckthorn. The prediction of the toxic effects of the main biologically active substances of sea buckthorn leaves showed that the smallest number of probable toxic effects is predicted for narcissin and quercetin, the largest for the substance strictinin I (including neurotoxicity, hematotoxicity, negative effects on the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal toxicity, reproductive toxicity and carcinogenicity), which requires confirmations in preclinical toxicological studies. In preclinical studies in vivo on a model of rat paw edema, it was proved that a decoction of sea buckthorn leaves with a short-term oral course application of 7 days at a dose of 10 ml/kg (235 mg/kg based on the dry residue), it shows a sufficient anti-inflammatory effect, providing a significant, reliable decrease in the severity of rat paw edema, maximum 3 hours after phlogogen administration by 36.0 % compared with the control, which exceeds the effectiveness of the comparison drug (infusion of chamomile flowers).
Conclusion. The main types of pharmacological activity (anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral) and toxic effects (neurotoxicity, hematotoxicity, negative effect on cardiovascular activity and gastrointestinal tract) have been established. Pronounced anti-inflammatory activity was reliably detected.
Introduction. The development of safe and effective drugs with antimicrobial activity is currently a priority task of modern pharmacology. The need to obtain new antimicrobial agents is associated with the presence of problems, the main of which is the development of polyresistance of the pathogenic pathogen to existing antibacterial drugs. Of particular interest as a basis for the creation of drugs are pyrimidine compounds, which have a wide range of pharmacological effects, namely psycho- and neurotropic, metabolic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, immunotropic, etc. Also, the advantage of pyrimidines is the simplicity of the synthesis of new compounds based on them by attaching various functional groups to the heterocycle.
Aim. Evaluation of antistaphylococcal activity of a new pyrimidine derivative in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and methods. Antistaphylococcal activity of pyrimidine derivative 2-Methyl-3-(2-phenyl-2-oxoethyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-oh (VMA-13-13) was studied in vitro using a test culture of a strain of Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) using the method of serial dilutions. St. aureus was isolated from the sputum of patients treated in inpatient conditions of GBUZ JSC "City Clinical Hospital No. 3 named after S. M. Kirov" (Astrakhan). The minimum suppressive concentration (MPC) of 2-Methyl-3-(2-phenyl-2-oxoethyl) was determined in the studyquinazoline-4(3H)-oh in relation to St. aureus. In vivo, antimicrobial activity studies were conducted on a model of generalized infection caused by intraperitoneal administration of 1 ml of St. aureus drug containing 1 × 108 CFU/ml to mice. Laboratory animals were divided into several groups: control I – animals receiving an equivalent volume of water for injection; control II – animals infected with St. aureus; experimental groups – receiving the comparison drug ceftriaxone (Biosynthesis JSC, Russia) at an average therapeutic dose of 50 mg/kg; and mice treated with a pyrimidine derivative mixed with water for injection, at a dose of 1/10 of the molecular weight of 27 mg/kg, starting from the day of infection for 7 days. The study evaluated the effect of pyrimidine derivative on animal survival. At the end of the experiment, the index of contamination of blood, spleen, liver and lungs was calculated.
Results and discussion. In the study, it was found that the MPC of ceftriaxone, in which this drug had bacteriostatic activity against the St. aureus strain, corresponded to 1 mcg/ml, whereas for the pyrimidine derivative VMA-13-13, the MPC was 16 mcg/ml; the bactericidal effect of the comparison drug was caused at a minimum concentration of 32 mcg/ml, and the substance under study is in a concentration of 64 micrograms/ml. The formation of generalized staphylococcal infection led to a decrease in the survival rate of animals in the untreated control group up to 30 %; with the introduction of ceftriaxone and pyrimidine derivative – up to 80 % compared with the intact control. When evaluating the antistaphylococcal activity of pyrimidine derivative in the untreated control group, in comparison with the intact control, an increase in the index of bacterial contamination of internal organs and blood was observed. The introduction of ceftriaxone and the compound VMA-13-13 led to a decrease in this indicator in the lungs and blood by 6.6 (p ≤ 0.01) times compared with the infected group of animals; staphylococcus was not sown in the liver and spleen.
Conclusion. Thus, it was established that the compound of pyrimidine nature is 2-Methyl-3-(2-phenyl-2-oxoethyl)quinazoline-4(3H)-it has a bactericidal effect against Staphylococcus aureus and helps to increase the survival rate of laboratory animals in conditions of generalized staphylococcal infection.
Introduction. The available information on the elemental composition of medicinal plant raw materials of the Voronezh region showed that studies are carried out mainly on several elements, which does not allow determining the complete mineral complex of medicinal plants and describing the specifics of the accumulation of individual elements in them.
Aim. The purpose of the study is to study the macro- and microelement composition of medicinal plant raw materials of the Voronezh region on the example of a protected area.
Materials and methods. Pharmacopoeic types of medicinal vegetal raw materials were used as subjects of investigation: nettle leaves dioecious (Urtica dioica L.), plantain leaves large (Plantago major L.), common pajma flowers (Tanacetum vulgare L.), heart-shaped linden flowers (Tilia cordata Mill.), herb of five-lobed dumplings (Leonurus quinquelobatus Gilib.), grass of bitter wormwood (Artemisia absinthium L.), common millennium grass (Achillea millefolium L.), bird mountain grass (Polygonum aviculare L.), roots of the common bladder (Arctium lappa L.), roots of the dandelion drug (Taraxacum officinale F.H. Wigg). Raw material harvesting was carried out in accordance with pharmacopoeic rules in natural thickets in the Voronezh State Natural Biosphere Reserve named after V. M. Peskov in the Ramonsky district. The microelement composition of the samples was studied mass-spectroscopically on an ELAN DRC device (PerkinElmer Instruments, USA) after acid-microwave decomposition.
Results and discussion. In each plant sample, 59 elements were quantified. The content of the total elemental complex in the studied types of LRs varies from 1.91 to 7.68 % in terms of dry raw materials. The studied raw materials accumulate macroelements to the greatest extent (more than 84 %). Essential trace elements accumulate most in dioecious nettle leaves (more than 9 mg/g). Of the essential trace elements, silicon and iron accumulate most of all the studied raw materials. Content of regulated toxic trace elements does not exceed requirements of pharmacopoeia.
Conclusion. The results of the study showed a complex macro- and microelement composition of the studied medicinal vegetal raw materials, which can be used in the medical and pharmaceutical practice of creating phytopreparations and biologically active additives for correcting physiological norms of the content of elements in the human body. The most quantitatively rich elemental composition is noted for the grass of five-lobed dumplings, nettle leaves of dioecious and large plantain (more than 50 mg/g).
Introduction. The question of the possibility of recovery of postischemic myocardium remains relevant.
Aim. The aim of the study was to study the effect of dispersed decellularized allogeneic extracellular matrix (allogeneic biomaterial, DAB) on the developed fibrous degeneration of the myocardium, as well as to reveal the possible mechanisms of cellular regeneration.
Materials and methods. The muscular wall of the heart of rats was subjected to cryodestruction. After 45 days, the rats of the main group were intramyocardially injected with a suspension of allogeneic biomaterialinto the area of the affected myocardium, and the rats of the control group were injected with saline.
Results and discussions. In the experimental group, there was a regression of the formed fibrous connective tissue, chemoattraction of progenitor cells, their differentiation and integration into the myocardium. The thickness of the muscular part of the wall of the left ventricle was three orders of magnitude higher than in the control group.
Conclusion. Analysis of the results of the study indicates that the heart in adult mammals has a powerful regenerative reserve. It is likely that, based on the use of DAB, a protocol can be developed that allows the restoration of the heart muscle even in conditions of already developed fibrous degeneration.
Introduction. Pharmacotherapy of cardiac arrhythmias is one of the urgent problems of modern medicine. The presence of serious side effects, in particular proarrhythmic action, limits the use of known antiarrhythmics in clinical practice. One way to reduce the toxicity of pharmacological agents is to use them as complex compounds with amino acids.
Aim. Studying the effect of nibentan derivatives containing magnesium salt of L-aspartic acid and glycine as anions on the course of early occlusive and reperfusion arrhythmias.
Materials and methods. Aminоacid derivatives of nibentan have been studied in models of occlusive and reperfusion arrhythmias in rats. The activity of the drugs was assessed by the incidence of ventricular extrasystoles (VEC), ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), by the latent period and duration of arrhythmias, the average duration of VT, and by the number of VEC per 1 animal.
Results and discussion. Nibentan derivatives in models of early occlusive and reperfusion arrhythmias were not inferior in antiarrhythmic activity to lidocaine and nibentan in their ability to prevent cardiac arrhythmias. The nibentan derivative containing the magnesium salt of L-aspartic acid (compound LHT-53-91) in the model of occlusive arrhythmias at a dose of 2 % LD50 completely prevented cardiac arrhythmias in experimental animals. A nibentan derivative containing glycine (compound LHT-20-92) at a dose of 1 % LD50 significantly reduced the number of cases of PVCs, prevented the occurrence of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation in 100 % of cases. In the model of reperfusion arrhythmias, LHT-53-91 at a dose of 1 % LD50 prevented the development of ventricular fibrillation and paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia and reduced the risk of developing ventricular extrasystole (p < 0.05). Increasing the dose to 2 % LD50 led to an increase in the activity of the substance, which was expressed in the prevention of cardiac arrhythmias in 100 % of the animals. LHT-20-92 at a dose of 1 % LD50 in this model of cardiac arrhythmias statistically significantly reduced the occurrence of VES and VT paroxysms and completely prevented the occurrence of VF (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. The inclusion of nibenthan amino acids in the structure, which shielded genotic grouping and reduced potential teratogenicity and mutagenicity, had not led to a reduction in the antiarrhythmic and antifibril-torn activity on the studied models of rhythm disorders.
Introduction. Citicoline is an endogenous nucleoside consisting of cytidine and choline linked by a diphosphate bridge that is involved in the synthesis of membrane phospholipids. Drugs containing citicoline have neuroprotective and neurometabolic effects and are used for the treatment of a wide range of neurological disorders. In its turn, bioequivalence study is a pathway to register a generic citicoline drug in Russian Federation.
Aim. The aim of the study was to investigate the comparative pharmacokinetics (PK) and bioequivalence of two citicoline-containing drugs GP30121 and Ceraxon® in healthy male volunteers when taken on an empty stomach.
Materials and methods. We evaluated the pharmacokinetics of citicoline-containing drugs corrected for endogenous analyte (uridine) level using an adaptive design. We determined uridine concentration by high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. We used R Project software, version 3.6.3. for performing statistical analysis for the study.
Results and discussion. GP30121 and Ceraxon® exhibited similar PK profiles. It was shown that the values of 94.12 % confidence interval (CI) at α = 0.0294 for the geometric mean ratios for the primary PK parameters of the main metabolite of the active ingredient of the investigated drugs were fully contained within the predefined equivalence limits of 80.00–125.00 %.
Conclusion. The study demonstrates bioequivalence of GP30121 and Ceraxon® proving the approach with the correction for endogenous analyte could be considered in studies of other drugs.
Introduction. Favipiravir is one of the most well-known broad-spectrum drugs against many RNA viruses, including the severe acute respiratory syndrome virus 2 [severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)]. Due to its structure, favipiravir is embedded in the RNA of the virus and blocks its further replication in the cell of the human body. Favipiravir is also included in the list of vital and essential medicines, which confirms the importance for Russian healthcare of this drug in the fight against common RNA viruses. We have already published bioanalytical methods for determining favipiravir in human blood plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with an ultraviolet detector (HPLC–UV) in order to study the pharmacokinetics of favipiravir with parenteral administration (the analytical range of the technique was 0.25–200.00 µg/ ml for the dosage of favipiravir 400 mg in 1 vial of lyophilizate for the preparation of concentrate for the preparation of solution for infusions) and by HPLC with tandem mass-selective detection (HPLC-MS/MS) in order to study the pharmacokinetics of β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine and favipiravir in their joint determination in blood plasma with oral administration (the analytical range of the technique was 250.00–20000.00 ng/ml for the dosage of favipiravir 400 mg in 1 tablet). The expectation of low favipiravir’s concentrations (the dosage of favipiravir in the drugs in question is 200 mg in 1 tablet in this study) and, in this regard, the expansion of the range by reducing the value of the lower limit of quantitative determination (LLOQ) used in this study necessitates the development of another method. Therefore, this study is given the development and validation of a method for determining favipiravir in human blood plasma by HPLC-MS/MS with an analytical range of 50.00–15000.00 ng/ml.
Aim. The aim of this study is to develop a method for quantitative determination of favipiravir in human blood plasma by HPLC-MS/MS for further for further researches of pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of drugs.
Materials and methods. In the process of sample preparation, a method of proteins precipitation with methanol was used. A solution labeled with stable isotopes of favipiravir-13C3 was used as an internal standard, the mobile phase was a 0.1 % solution of formic acid in water (eluent A) and methanol (eluent B). Chromatographic column – Phenomenex Kinetex C18, 100×3.0 mm. The determination of favipiravir in human blood plasma was carried out by HPLC using a tandem mass spectrometric detector with a triple quadrupole. The analytical range for favipiravir is 50.00– 15000.00 ng/ml in human blood plasma.
Results and discussion. This method was validated by selectivity, calibration curve, accuracy, precision, matrix effect, spike recovery, carry-over effect, the lower limit of quantification and stability.
Conclusion. A method of quantitative favipiravir’s determination in human blood plasma by HPLC-MS/MS with a confirmed analytical range of 50.00–15000.00 ng/ml in human blood plasma has been developed and validated. This method allows using it for the analytical part of pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence studies of drugs containing favipiravir in order to expand their range in the domestic pharmaceutical market.
Introduction. Trastuzumab is the first drug based on the monoclonal antibodies’ technology targeted to the neu oncogene expression product discovered in the middle 80-s – human epidermal growth receptor, HER2. After being approved trastuzumab had become the drug of choice for combine therapy of metastatic breast cancer (BC). This therapy had also allowed to improve patients’ 5-year survival rate dramatically, almost up to 90 % in some cases. Despite the fact that more than 10 biosimilars of trastuzumab are now in the pipeline around the world, including Russia, the development and registration of trastuzumab biosimilars still remain relevant.
Aim. Aim of the study was to conduct the analytical part of the double-blind randomized comparative clinical trial for trastuzumab pharmacokinetics and safety assessment in healthy volunteers with subsequent biosimilarity evaluation of "Trastuzumab" (LLC "Mabscale", Russia) and Herceptin® (F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Switzerland).
Materials and methods. 92 healthy volunteers, who fulfilled the inclusion/exclusion criteria, were enrolled to the study. Trastuzumab quantitation and anti-trastuzumab antibodies detection was performed using ELISA method with photometric detection. To support the clinical trial two different independent bioanalytical methods were validated.
Results and discussion. Trastuzumab quantitation method in human blood serum was validated for selectivity, calibration curve and regression model, sensitivity (LLOQ), accuracy and precision, MRD, dilution linearity and stability. The method for anti-trastuzumab antibodies detection, that was previously described by the authors, was validated for cut-point, selectivity, sensitivity, prozone effect, drug tolerance, precision and stability (short-term and long-term). The validated methods were successfully applied to the study samples assay to perform the analytical part of the comparative study for trastuzumab pharmacokinetics and immunogenicity assessment. The obtained drug concentrations were used for PK-parameters and confidence interval calculations to estimate the biosimilarity of test and reference drug.
Conclusion. The study results showed that test and reference drug are biosimilar, and moreover immunogenicity assessment showed no anti-trastuzumab antibodies in any samples of healthy volunteers.
REGULATORY ISSUES
Introduction. Advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) rely on recent advances in medical science, but alongside with potential benefits they may also bring safety concerns for patients. The inherent complexity of the ATMP production and use calls for special approaches to risk management throughout their lifecycle, from obtaining the raw materials to administration to the patient.
Aim. The aim of the present study was to develop approaches to risk management for ATMPs, using the example of CAR T-cell therapy.
Materials and methods. The study analysed the relevant regulatory frameworks currently in force in the European Union and the United States of America, namely the regulations and guidelines adopted by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency.
Results and discussion. The paper provides a classification of patient risks, which was developed based on the European risk-based approach. It formulates the principles of risk management for each of the risks, depending on the stage of the product life cycle. Each type of risk was considered separately. The following risk minimization strategies were determined: compliance with the good practices, ensuring the necessary qualifications or expertise of all parties involved in the product life cycle. The main element of risk control is the detailed description of the medicinal product use in the summary of product characteristics and patient information leaflet.
Conclusion. The study identified the main stages at which ATMP risks may occur, and each type of risk was considered separately. The following requirements should be put in place in order to manage the ATMP risks: requirements for distributors on how to perform the product transportation and storage and to keep records for the marketing authorisation holder; requirements for healthcare facilities on how to perform the product storage, its preparation for use, advising and informing the patients on the treatment risks, symptoms of adverse events, preparatory and follow-up medical procedures, and on how to keep records for the marketing authorisation holder; requirements for the qualifications of healthcare professionals who are in charge of the product storage, its preparation for use, treatment procedures, advising and informing the patients on the treatment risks, symptoms of adverse events, and follow-up medical procedures. The data obtained will be used in the preparation of recommendations for ATMP developers.
ERRATUMS
Drug development & registration. 2023;12(2):62–72. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.33380/2305-2066-2023-12-2-62-72. Published: 25.05.2023.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)