FROM EDITOR
This year congress was devoted to the 10th anniversary of the "Drug development and registration magazine". We have changed and supplemented the program of the Congress in comparison with the events of previous years, and also added an online format. During the congress we have discussed such themes as drug development, non-clinical and clinical trials, drug production and registration.
This section contains appendices to the previous 4 parts of the article. These applications are important because they document every step taken by the leadership of the young Soviet Republic, and then the USSR, to restore the domestic chemical industry destroyed during the First World War and the revolution. The contents of the appendices, as well as clarify names of the responsible employees who signed the resolutions and decrees, it becomes clear the consistency and consistency of all actions of government members, as well as the relevance of the events held in the country.
Labconcept Ltd. company is the official distributor of the world`s leading analytical and laboratory equipment producing companies. In addition to that, Labconcept company has developed its own analytical equipment OEM-brand SILab. Various instruments under that trademark are already available on the Russian market: atomic absorption spectrophotometers, FTIR and UV-Vis spectrophotometers, TOC analyzers and ion-exchange liquid chromatography systems. LicArt 62 is a new product of Labconcept company. It is an HPLC system with modular design and with a wide range of detectors and several pump modifications available. Main blocks of LicArt 62 HPLC systems are assembled and tuned-up in Saint-Petersburg . After that all assembled instruments are thoroughly tested at the company`s Technical Control Department. Technical parameters of LicArt 62 HPLC systems perform technical parameters comparable or even superior to those of the world`s leading HPLC systems that are no longer available on the Russian market.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
Introduction. Recently, the anticancer activity of representatives of the genus Artemisia L. has been actively studied, and most studies are devoted to Artemisia annua L., which has been used since ancient times in the folk medicine of several countries as an antimalarial and anticancer agent. The similarity of the chemical composition predetermines the study of the anticancer activity of other species of the genus Artemisia L. The information about this is still not fully presented in scientific publications, is very diverse and sometimes even contradictory. Review of modern studies of anticancer activity of species of the genus Artemisia L., generalization of available data and providing information for future research is relevant.
Text. The article presents a review of experimental data on the study of anticancer activity of representatives of the genus Artemisia L. It is noted that the main mechanism of such activity is apoptosis. Apoptosis is triggered by the increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inside cancer cells, reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential, activation of pro-apoptotic and, on the contrary, inhibition of anti-apoptotic proteins, as well as by formation of membrane bubbles, cell compression and by activation caspase.
Conclusion. In the presented review, about 30 species of the genus Artemisia L. With the presented degree of study of this area, a number of questions remain unresolved. The most studied with respect to cytotoxic activity are Artemisia absinthium L. and Artemisia vulgaris L. In this aspect, the study of other closely related species of the genus Artemisia L. Also relevant is the study of cytotoxicity of representatives of the genus Artemisia L. on normal cell cultures and in comparison with positive control. In addition, a detailed study of the pool of secondary metabolites of different species of the genus Artemisia L. remains significant in order to reliably determine the components responsible for the manifestation of anticancer action. The pronounced effectiveness against cancer cells and, at the same time, a weak effect on healthy cells of the body of representatives of the genus Artemisia L. opens up the prospect of their use as sources of partner drugs with a synergistic effect and means of augmentation of antitumor therapy.
Introduction. Chemotherapy with Cabazitaxel (CBZ) is a typical first-line treatment option for naïive castration-resistant prostate cancer resistant to docetaxel. On the other hand, Cabazitaxel's therapeutic success is constrained by chemoresistance and side effects.
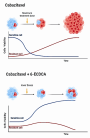
Aim. To assess whether 6 alpha-ethylchenodeoxycholic acid (6-ECDCA), a selective agonist for bile acid receptors will enhance the efficacy of CBZ in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells.
Materials and methods. The 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) viability assay was used to assess the cytotoxicity of 6-ECDCA and CBZ medicines or their combinations against the human prostate cancer cell line (PC-3). The combination outcome suggested by Chou TC et al. was then evaluated using the combination index (CI) to find out the nature of synergism, antagonism, and additive effect of the drug’s combination. Furthermore, the Dose-Reduction Index (DRI) was determined to measure how many times the dose could be reduced for each drug in a synergistic combination.
Results and discussion. Analysis of the dose-effect curve showed that the treatment of PC-3 cells with CBZ alone or combined with 6-ECDCA for 48 h led to 50 % cytotoxicity of 20.5 nM and 4.7 nM, respectively. 6-ECDCA at 1.77 µM had an additive effect based on the CI value, which was 1.02, while at 21.02 µM, the CI was 0.54 which designates a strong synergistic effect. The combination of CBZ and 6-ECDCA at a submaximal lower dose by 6-folds of each one produced a 95 % cell death than treatment with either agent alone.
Conclusion. The Combination index plot showed CI ≤ l for all combinations used in this study, which indicates additive and synergistic interactions between CBZ and 6-ECDCA. The significant impact of 6-ECDCA in combination with CBZ for treating androgen-independent prostate cancer cells was confirmed by this study to be preferred to the treatment with a single drug.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Introduction. Marine-derived polysaccharides are promising candidates for the development of innovative drugs. One of such compounds is the polysaccharide fucoidan from brown seaweeds, which shows anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory activity. The development of topical transdermal formulation for the treatment of chronic venous diseases is of particular interest, because with targeted delivery, the active compound in high concentration comes directly to the site where the drug is required, while the risk of side effects is minimal.
Aim. Experimental and theoretical justification of the methodological scheme for the development of a transdermal delivery system with fucoidan for local therapy using the Quality by Design (QbD) approach.
Materials and methods. Fucoidan was isolated from the thalli of Fucus vesiculosus L. from the Barents Sea according to the original technology of the MMBI RAS. All excipients were approved for medical use. The experiments for rational selection of the excipients for the transdermal delivery system (TSD) were planned using the Greek-Latin square 4 × 4 with repeated observations. The colloidal and thermal stability and pH were evaluated as physicochemical parameters of TSD Structural and mechanical properties of TSD were deter-mined with rotational viscometer. The dissolution rate of fucoidan in vitro was evaluated using the paddle-over-disk method at a temperature of 32 ± 0.5 °C.
Results and discussion. The composition and technology of topical TSD цwith fucoidan were developed using the QbD concept. The composition and technology of topical TSD with 15 % of fucoidan as active ingredient were developed. TSD has thermo- and colloidal stability, and has a pH value close to the pH of human skin. Poloxamer 407 was used as a gel base; olive oil was used as a hydrophobic phase. It was found that the ratio of poloxamer 407 to the aqueous phase should be no less than 0.1 and no more than 0.37; the ratio of water to the aqueous phase should not be less than 0.56 and not more than 0.69; and the ratio of polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil to the oil phase must be at least 0.34. It was found that 9 % poloxamer 407 provides the necessary structural and mechanical properties of TSD. It has been established that the developed TSD of fucoidan with poloxamer 407 belongs to non-Newtonian flow types with plastic properties and has thixotropy.
Conclusion. The complex of studies based on QbD approach led to the experimental and theoretical justification of the methodological scheme for the development of a transdermal delivery system with marine polysaccharide fucoidan. The methodological scheme takes into account the physicochemical and technological features of fucoidan and allows you to create a high-quality TSD that ensures stability and complete release of the active substance.
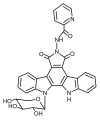
Introduction. LHS-1269 is an indolocarbazole derivative with high antitumor activity. Due to the hydrophobic properties of the active substance, the use of organic co-solvents – dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and ethanol – is required to obtain an injectable dosage form (DP). However, the inclusion of organic solvents in the composition of the DF carries a potential risk of side effects as a result of the use of the drug.
Aim. Selection of auxiliary substances for obtaining an aqueous solution of hydrophobic indolecarbazole derivative, which allows minimizing the concentration of organic solvents in the composition of DF.
Materials and methods. The object of the study is the active substance LHS-1269 series 010320, produced in the Chemical Synthesis Laboratory of the N. N. Blokhin National Medical Research Center of Oncology. The following auxiliary substances were used to obtain model compositions: Kollidon® 17 PF, Kollisolv® PEG-400, Kolliphor® P 188, Montanox™ 20, DMSO (p.a.), ethanol 95 % (standardized according to pharmacopoeia quality standard ФС.2.2.0019.18 of The State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation). Analytical scales OHAUS Analytical Plus AP 100S and laboratory scales AND DL-120 were used for weighing LHS-1269 and auxiliary substances. The dissolution and mixing of the components was carried out on an IKA® C-MAG HS 4 magnetic stirrer.
Results and discussion. In the course of the study, 2 groups of model compositions were obtained and estimated, comprising a complex of two or more auxiliary substances as a solubilizer. The first group of formulations contained DMSO at a concentration of 5 % and ethanol at concentrations from 0 to 15 %. The compositions of the second group included DMSO from 0 to 4 %. As a result, it was found that the addition of 5 % Kolliphor® P 188 to the composition of the solution reduces the content of ethanol to 5 %. In this case, with further decrease in ethanol, turbidity of the solution and precipitation are observed. Reducing the concentration of DMSO in the DF to 2 % was achieved by using a combination of 20 % ethanol and solubilizer complex – Kollidon® 17 (20 %), Kollisolv® PEG-400 (20 %) and Kolliphor® P 188 (5 %). In this case, the total dissolution of the active substance without DMSO was observed when compensating for the organic solvent by introducing additional auxiliary substances – Montanox™ 20 (5 %) and benzene (2 %).
Conclusion. As a result of the research, the compositions of the auxiliary substances of solubilizers are selected, allowing to obtain an aqueous solution of the hydrophobic compound LHS-1269 with a minimum concentration of organic solvents.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. Enoxaparin sodium-containing drugs are included in relevant protocols for COVID-19 therapy. An increase in the production volume of such drugs leads to a demand for available and precise methods of identification and quantitative measurement of the active ingredient in the preparations. Considering the fact that pharmacopoeial methods require significant amount of expensive standards and reagents that are unavailable for numerous laboratories, it is relevant to develop a more available method that will accelerate and make cheaper the process of quality control for enoxaparin sodium-containing preparations.
Aim. To develop and validate a simple, economic, and precise method of gel-permeation HPLC with the application of a refractive index detector for the evaluation of enoxaparin sodium in preparations for injection.
Materials and methods. Samples of enoxaparin sodium-containing substances and commercial preparations were studied. The identification and quantitative content of the active ingredient were performed by the method of gel-permeation HPLC using a 1260 Infinity (Agilent Technologies, USA) chromatograph equipped with a refractive index detector.
Results and discussion. The authors analyzed standard validation characteristics: specificity, linearity, precision, and accuracy of the method. The analysis revealed high specificity and suitability of the proposed method to chromatographic symmetrical multiprocessing systems. The method is recommended for routine control of finished and semi-finished pharmaceutical preparations containing from 25 to 200 mg/ml of enoxaparin sodium-containing.
Conclusion. The proposed method can be used for routine quality control of enoxaparin sodium-containing preparations for injection.
Introduction. The chemical composition of plants is a combination of all primary and secondary metabolites and can be considered as the result of the implementation of genetic information, a «link» between the genotype and phenotype. The complex of biologically active substances (BAS) of most medicinal plants and medicinal herbal preparations derived from them is a multicomponent system that is in interaction, the composition of which is not always fully known. Sea buckthorn is one of the valuable plants with a wide distribution area. Sea buckthorn fruits contain a large number of classes of various BAS. The study of the variability of the chemical composition depending on the climatic conditions of growth, harvesting and drying in order to accumulate and generalize information for the development of unified scientifically based standards for raw material quality indicators is an important area for study.
Aim. The purpose of this work was to study the chemical composition of the fruits of sea buckthorn, which grows in the Central Chernozem region.
Materials and methods. The raw materials for the analysis were whole fresh fruits of sea buckthorn, harvested in the territory of the Central black earth region of the Russian Federation (Voronezh region). In the work, the TLC method was used to study the composition of various groups of BAS and their identification in extracts from the studied raw materials. In the process of a comprehensive study of the chemical composition of fruits, the determination of carotenoids, flavonoids, tannins, amino acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, anthocyanins, organic acids, sugars, some macroelements and vitamins was carried out.
Results and discussion. The fruits of sea buckthorn, growing in the conditions of the Central black earth region, accumulate free amino acids, tannins, organic acids and polysaccharides in significant quantities. The composition of free water-soluble simple sugars, organic acids, B vitamins, as well as the complete amino acid composition was studied in the fruits of sea buckthorn using capillary electrophoresis. A significant content of riboflavin and choline, as well as malic and succinic acids has been established. The results of HPLC analysis showed that flavonoids in the fruits of sea buckthorn growing in the conditions of the Central black earth region are represented by flavonol glycosides – derivatives of quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin. Minor flavolglycosides 3-rutinoside-7-rhamnosides of isorhamnetin, quercetin and kaempferol, 3-sophoroside-7-rhamnosides of quercetin and kaempferol, rutin, 3-glucoside and 3-rhamnoside of isorhamnetin can be used as chemomarkers.
Conclusion. The obtained data on the component composition of the phenolic fraction of the fruits of the studied samples of sea buckthorn are similar to the literature data on sea buckthorn of the same species of various varieties harvested in the conditions of the Central zone of the Russian Federation (Moscow region).
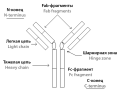
Introduction. Highly glycosylated proteins are the most abundant class of modern biopharmaceuticals. A majority of such therapeuticals produced by Russian biopharmaceutical companies is biosimilars. The foundation of biosimilar manufacturing is analytical assessment of structure equivalence to an original molecule. Fc-fusions present a challenge due to their structural properties. The only biosimilar of this kind registered in Russia is etanercept – a fusion of tumor necrosis factor receptor α and Fc-fragment of IgG1. Existing approaches widely used in protein analysis do not allow accurate and reliable description of glycoylation of these proteins. Development of new approaches and principles of such analysis is necessary, as the changes in biosimilar’s molecular structure can seriously affect its efficacy and safety.
Aim. Development of double proteolysis approaches for glycopeptide mapping of Fc-fusion protein etanercept using Arg-C protease.
Materials and methods. Etanercept was subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis using trypsin in combination with Arg-C or Asp-N. The resulting peptides were analyzed using HPLC-MS system Xevo G2-XS QTOF (Waters Corporation, USA). The conformation of glycan structure was performed via analysis of fragment spectra of glycopeptides, acquired with high collision energy mode (MS E ). UNIFI (version 1.8) with biopharmasuetical assessment setting (Waters Corporation, USA) was used to analyze the peptide maps.
Results and discussion. It was found that using the combination of trypsin with protease Arg-C leads to reliable results Using the developed approach we successfully determined the majority of O-glycosylation sites and types of O-glycans. It was shown that for an effective O-glycopeptide maping N-deglycosylation stage is required. Most abundant N-glycan structures were identified for each of three N-glycosylation sites (N149, N171, N317). It was determined, that the combination of trypsin with Arg-C allows identification of three-antenna forms despite the presence of O-glycosylation site on the analyzed peptide. General N-glycosylation profile shows comparability of results for both approaches.
Conclusion. As a result of this research we developed glycopeptide mapping approaches in which a combination of proteases is used. Using these methods sites of N- and O-glycosilation and glycofoms of etanercept were accurately and reproducibly determined. Developed procedures can be applied to other types of Fc-fusion proteins, making it of broader appeal and benefit to the overall biopharmaceutical industry. These approaches provide comprehensive information useful for structure-function studies and of potential value for product comparability measurements and possibly even future manufacturing control strategies.
Introduction. Promising sources of biologically active compounds (BAS) are extracts obtained from various morphological parts of plants of the numerous genus Astragalus L. One of the main groups of BAS isolated from plants of this genus are flavonoids, saponins, and polysaccharides. Sufficiently studied are Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge) and Astragalus mongholicus Bge., whose extracts have a wide range of pharmacological activity. Expansion of the nomenclature of medicinal plant materials and the study of BAS groups that determine the main pharmacological effects are topical studies in pharmacognosy. From this point of view, little-studied species of Astragalus (Astragalus henningii (Stev.) Klok., Astragalus testiculatus Pall., Astragalus varius S.G. Gmel., Astragalus dasyanthus Pall.), massively growing in the Volga region, are of interest.
Aim. Isolation and identification of 5 aglycones of flavonoids in hydrolysates of water-alcohol extracts from Astragalus herb: A. henningii, A. testiculatus, A.varius, A. dasyanthus by HPLC/UV.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were the herb of four types of Astragalus (A. henningii, A. testiculatus, A.varius, A. dasyanthus), harvested during the period of mass flowering in the Saratov region and dried to an air-dry state. To study the composition of phenolic compounds, extraction was carried out with 70 % ethanol in the ratio of raw material : extracting agent 1 : 10 by infusion for 7 days. Acid hydrolysis was carried out with hydrochloric acid 37 % with heating for 40 min. The resulting hydrolysates were analyzed on an Agilent 1260 chromatograph (Agilent Technologies, USA) with a diode array detector, manual sample injection (Agilent G1328C manual injector, Agilent Technologies, USA) and an Agilent OpenLab CDS chromatographic data collection and processing system using an individually selected elution gradient of the mobile phase (0.1 % solution of orthophosphoric acids/acetonitrile). Compounds in the hydrolysates were identified by the retention times and UV spectra of a mixture of reference standards (RS) of quercetin, isorhamnetin, luteolin, kaempferol, and apigenin.
Results and discussion. An elution gradient was selected for one time determination of 5 aglycones of flavonoids with a single analysis time of 13 minutes. These conditions made it possible to identify compounds in the hydrolyzates of water-alcohol extracts of four types of Astragalus. Luteolin, quercetin and apigenin were found in hydrolyzates of A. henningii, A. testiculatus and A. varius; isorhamnetin and kaempferol were found in A. henningii and A. varius. None of the analyzed aglycones was found in the A. dasyanthus hydrolyzate.
Conclusion. After preliminary selection of the optimal conditions for the chromatographic separation of a mixture of 5 aglycones of flavonoids, hydrolysates of four types of Astragalus were analyzed. The data obtained indicate the prospects for further study of the chemical composition of Astragalus and confirm the expediency of their use for obtaining of new herbal remedies.
Introduction. The Laboratory of Drug Formulation Development at the N. N. National Medical Research Center of Oncology developed a liposomal dosage form of FS tetra-3-phenylthio-pthalocyanine hydroxyluminide (TPHA) for which a simple, accurate and easily reproducible method of quantitative determination of the main active substance and excipients in the drug product was needed. High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) was chosen as such a technique.
Aim. The aim of this work was to develop chromatographic methods for the quantitative determination of excipients in a liposomal dosage form of a tetra-3-phenylthiophthalocyanine hydroxyaluminium (TPHA).
Materials and methods. Determination of substances was carried out by the method of high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) followed by TLC-densitometry. Substance TPHA 98 % (Federal State Unitary Enterprise "SSC "NIOPIK", Russia), placebo lyophilized liposomal form without TFHA in the composition (FSBI "National Medical Research Center of Oncology. N. N. Blokhin" of the Ministry of Health of Russia), egg phosphatidylcholine (96 %, CAS № 97281-44-2, EPC Lipoid, Germany), cholesterol (≥99 %, CAS № C8667, Sigma-Aldrich, Japan), sucrose analytical grade (CHIMMED, Russia) and various organic solvents.
Results and discussion. The selected mobile phase for HPTLC analysis: isopropanol: ammonia 25 % aqueous 80 : 20, separation time was 20–25 min (l = 75mm), t = 20 °С. To visualize the spots of sucrose, phosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol, a 5 % solution of phosphomolybdic acid was chosen. The stability of the standard samples was confirmed on a series of prevalidation studies. Validation of the methodology was carried out.
Conclusion. For quantitative determination of sucrose, phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol in a new liposomal dosage form, the method of HPTLC with TLC-densitometry was chosen, which allows identifying all three components in the dosage form simultaneously. The method was validated.
Introduction. A reliable assessment of the quality and safety of medical products (MP) by biological indicators is directly related to the use of culture media (CM) that meet the established requirements. However, when conducting trial, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of culture media due to the presence in their composition of components of biological origin. In particular, a high degree of variability and unstable stability of raw materials, as well as possible mistakes in producing and storage of media, create the prerequisites for deviations. The use of industrial culture media also does not guarantee their suitability for the appropriate test. Therefore to obtain reliable results, the compliance of each batch CM with the specified criteria be confirmed must be confirmed by standard methods using the full range of meaningful indicators. The current lack of a state standard in the Russian Federation regulating the requirements for the use of culture media when confirming the quality of medical products makes it much more difficult to assess the suitability, comparability and reliability of the analysis results, both themselves CM and drugs.
Text. The article discusses the draft General Pharmacopoeia Article (GPM) "Culture media", which presents the general requirements for of culture media when used in pharmacopoeia analysis. The standard is intended for specialists involved in the development, improvement and application of methods and / or techniques necessary for confirming the properties of medical products for the purpose of registration, entry into civil circulation, as well as in their production. The document was drawn up taking into account modern domestic and international approaches of good pharmaceutical practices to the assessment of the drugs that involve the use of culture media. The project identifies the key factors that most affect the quality of culture media. Based on the principle of continuity, compiled and described in detail a set of standardized control methods, including tests on physical-chemical and biological indicators. For exploring of specific properties, there are requirements for test cultures have been established. Governs special requirements for culture media used to obtain biological medical products are regulated. The procedure for storage and disposal of culture media unsuitable for use is described.
Conclusion. The introduction of the GPM "Culture media" into the practice of domestic pharmacopoeic analysis will increase the reliability of the results of the evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of drugs, and as a result will lead to a reduction in production risks and risks of harm to health patients during in pharmacotherapy and immunoprophylaxis. The proposed approaches can also be used in other branches of science and industry.
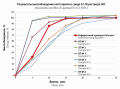
Introduction. As part of a comparative assessment of drugs quality available on the Russian market a dissolution profile studies and uniformity of dosage units test was conducted for various manufacturers of "Captopril" drugs. Drug release studies in three dissolution media (0.1 M hydrochloric acid, acetate buffer pH 4.5, phosphate buffer pH 6.8) with sampling at 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30 min and analysis using UV/Vis spectrophotometer at 212 nm were conducted. Dissolution kinetics was compared based on calculation of the similarity factor f2 and the values of relative standard deviations. Uniformity of dosage units test of scored tablets were evaluated based on HPLC-UV analysis and AV factor calculation.
Aim. The purpose of this study was a comparative evaluation of "Captopril" drugs from various manufacturers on the Russian market based on dissolution profile studies and uniformity of dosage units test of scored tablets in order to assess the quality of the tablets.
Materials and methods. To prove the dissolution profile studies DT 827/1000 tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany) was applied. Each drug in three dissolution media in 12 replicates for each dissolution medium was analyzed. The selected samples were analyzed on a UV 1800 UV spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan) at a of 212 nm. In uniformity of dosage units test of scored tablets each tablet was divided according to the applied mark. Sample preparation was carried out in accordance with a validated method and samples were analyzed by HPLC-UV using Agilent 1260 (Agilent Technologies, США).
Results and discussion. Based on the results of dissolution profile studies and calculations of the similarity factors and values of the relative standard deviation it can be concluded that the dissolution kinetics for drug no. 4, drug no. 5, drug no. 6 are not equivalent in comparison with the reference drug. During the uniformity of dosage units test of scored tablets, no deviations were found in accordance with the requirements of the RF Pharmacopoeia OFS.1.4.2.0008.18 "Uniformity of dosing" and the EAEU Pharmacopoeia OFS.2.1.9.14 "Uniformity of Dosed Units".
Conclusion. The conducted dissolution profile studies and uniformity of dosage for scored tablets of Captopril drugs show the example of possibility to identify potential problems with drugs quality presented on the Russian market and as a result improve and maintain quality assurance of drugs for the national healthcare system.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
Introduction. As a part of the registration of the drug product a bioequivalence study of the fixed-dose combination "Ezetimibe + rosuvastatin" (JSC "Sanofi-aventis group", Russia) compared with coadministered Ezetrol® (ezetimibe) and Crestor® (rosuvastatin) was conducted with 76 healthy volunteers. Enzymatic hydrolysis was used to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of total ezetimibe. This was the reason for the inclusion of the additional monitored parameters in the validation and analysis.
Aim. The purpose of the bioequivalence trial was a comparative study of the pharmacokinetics and evidence of the bioequivalence of the fixed-dose combination "Ezetimibe + rosuvastatin" (ezetimibe + rosuvastatin,tablets, 10 + 40 mg, JSC "Sanofi-aventis group", Russia) compared with coadministrated monocomponent drugs ezetimibe and rosuvastatin in fasting healthy volunteers after a single administration using the described additional parameters for controlling the enzymatic hydrolysis of ezetimibe-glucuronide during the analysis of samples.
Materials and methods. To prove bioequivalence, an open label, comparative, randomized, crossover two-period clinical trial was conducted. During the study, blood plasma samples were taken from volunteers, the concentrations of ezetimibe (unconjugated) and total ezetimibe (ezetimibe + ezetimibe-glucuronide) and rosuvastatin in plasma samples were determined by validated HPLC-MS/MS methods. Based on the received data pharmacokinetic and statistical analysis was performed and confidence intervals (CI) for the pharmacokinetic parameters Cmax and AUC0-72 were calculated.
Results and discussion. It can be concluded that the studied formulations are bioequivalent in terms of pharmacokinetic parameters of ezetimibe (free) and rosuvastatin. Pharmacokinetic parameters of total ezetimibe were considered as secondary and were not required for the conclusion on bioequivalence. While HPLC-MS/MS analysis of incurred samples, additional control parameters for the enzymatic hydrolysis of ezetimibe-glucuronide made it possible to legitimately reject the results of inaccurate analytical batches.
Conclusion. Thus, according to the criteria used in the study, the drugs are proved to be bioequivalent. The described additional parameters for controlling the enzymatic hydrolysis of ezetimibe-glucuronide have been shown to be effective.
Introduction. Using of immunoglobulins containing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies may be an effective and safe tool for COVID-19 treatment. An intravenous immunoglobulin COVID-globulin from donor blood plasma containing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies was developed at Joint-Stock Company Nacimbio.
Aim. A pilot study of the safety of the "COVID-globulin".
Materials and methods. When studying the safety of the preparation in animals the following parameters were evaluated: general toxicity, thrombogenic potential, influence on hematological and biochemical parameters, blood clotting and hemolytic activity, determination of local irritant action, pyrogenic properties, bacterial endotoxins, allergic effect of the drug preparation and its physicochemical characteristics.
Results and discussion. Safety studies of "COVID-globulin" in animals showed no signs of intoxication, local irritant action and thrombogenic properties. Macroscopic and histological examination of the organs of rats treated with COVID-globulin showed no signs of necrosis, inflammation, atypia, or any significant pathological changes. Hematological and biochemical parameters of the blood of laboratory animals after the administration of "COVID-globulin" corresponded to the reference values. Administration of COVID-globulin to rabbits did not activate blood clot formation. The IgG subclasses distribution in the preparation corresponded to that in human plasma. The activity of the Fc-function of the immunoglobulin molecule was more than 130 % compared to the reference standard preparation, the concentration of the prekallikrein activator in the COVID-globulin ranged from 4.2 to 4.8 IU/ml, anticomplementary activity was less than 1 unit complement per 1 mg of protein.
Conclusion. The results of all studies have demonstrated a high level of safety of the developed COVID-globulin preparation, which meets the safety requirements for human immunoglobulins for intravenous administration by national regulatory documents and the European Pharmacopoeia.
Introduction. Behavioral methods on laboratory animals are recognized as the main approach in studying the activity of potential psychotropic drugs and allow us to evaluate the main effects of new compounds, increase the possibility of predicting a successful outcome of future clinical trials.
Text. This review article analyzes the main modern behavioral models in rodents that are widely used for screening and studying the pharmacological activity of potential psychotropic drugs. The advantages and disadvantages of each test are highlighted and complexes of behavioral methods are demonstrated that most conclusively confirm the reproducibility of the results obtained in clinical trials. The description and evaluation of behavioral methods that characterize the state of anxiety, which are used to screen for new compounds with anxiolytic activity (tests «Open field», «Dark-light chamber», «Elevated plus maze», «Sequence of rays»). The range of tests used to study cognitive functions and memory processes is widely presented (various mazes – T-shaped, U-shaped, radial maze, Barnes maze, E-maze; water mazes – Morris, T-maze) with a description of a comparative analysis and necessary conditions that ensure the reliability of information. An important direction in the field of behavioral pharmacology is the modeling of violations of social behavior and the study of approaches for its correction – the main methods necessary for the study of social behavior are presented in the review by the tests «Three-chamber social test», «Open field» extended test, etc.
Conclusion. Behavioral pharmacology dictates the need for close interaction between preclinical and clinical stages of research in the framework of the development of translational medicine and the development of approaches that provide evidence for the reproducibility of the results obtained in clinical trials. It is also necessary to improve existing and develop new behavioral models of mental disorders and to search for new ways to study the mechanisms of formation of behavioral disorders.
Introduction. The drug can be used in the treatment of one disease and for the prevention and treatment of another pathological process. This is possible due to the repurposing of medicines. Creating drugs from scratch takes a long time to develop and implement, which leads to large financial costs, and also has a high dropout rate of candidate substances and requires significant financial costs. The main advantage of repurposing instead of creating new drug is relatively low financial costs and a significant reduction in the first two phases of clinical trials.
Text. Drug repurposing is based on pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, pharmaceuticals and clinical trials, where the first two phases are significantly reduced compared to the creation of a completely new. There are examples of successful repurposing and negative side effects with off-label drug use, which is unsafe but the best solution for orphan diseases. A targeted search for the possibility of repurposing drugs using an automatic procedure is being carried out, where a large number of chemical compounds are tested for activity or affinity for receptors and enzymes – high-throughput screening. Computer design has become widespread, which or repurposing "in silico", where information about the drug is used: targets, chemical structures, metabolic pathways, side effects, followed by the construction of appropriate models. Machine learning (ML) algorithms: Bayes classifier, logistic regression, support vector machine, decision tree, random forest and others are successfully used in biochemical pharmaceutical, toxicological research. But the most promising development of reprofiling is associated with the use of deep neural networks (DNN). Using deep learning, DNN were found to outperform other algorithms for drug development and toxicity prediction.
Conclusion. Currently, interest in drug repurposing has grown markedly. A search for the keywords «drug repurposing» showed 2,422 articles on the problem of new uses for drugs that already exist in medicine.
Introduction. As the first approved drug for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) treatment, riluzole is known as a glutamatergic neurotransmission inhibitor administrated in 50 mg tablets twice daily. For this reason, a generic product of riluzole has been developed at a lower price by Hogar-Daroo, Iran, which would benefit patients.
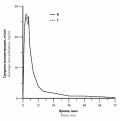
Aim. The objective of this study is to develop and validate a novel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method for the analysis of riluzole in human plasma samples and its application in the bioequivalence study of riluzole tablet.
Materials and methods. The chromatography was performed by using a C18 column (100 mm, 4.6 mm, 5 mm), 0.1 % formic acid and acetonitrile (60 : 40, v/v) as the mobile phase, at a flow rate of 0.90 ml/min in the gradient program. Carbamazepine was used as an internal standard (IS). The method employed only 100 µL of human plasma for quantification by a liquid-liquid extraction technique. The multiple reaction monitoring modes (MRM) was used for quantification of ion transitions m/z 235.0/165.9 and m/z 137.6/110.0 for riluzole and the m/z 236.9/194.0 for the IS. Dwell time was set at 200 ms.
Results and discussion. The calibration curve was linear over the concentration range 0.5–300 ng/mL. The lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) was obtained at 0.5 ng/mL. The intra-day and inter-day accuracy ranged from 93.21 % to 101.34 % and 91.77 % to 104.88 % respectively. The intra-day and inter-day precision values ranged from 2.19 % to 5.69 % and 1.67 % to 5.31 % respectively, all within the FDA acceptable ±15 %.
Conclusion. The validated method was applied in Iranian healthy subjects under fasting condition with a 50 mg riluzole tablet successfully.
Introduction. The genus Astragalus L. is one of the largest genera of flowering plants and includes at least 3,270 species. Individual species of this genus have long been used in traditional and scientific medicine. In recent years, species of the genus Astragalus L. have attracted attention because of the detection of a wide range of neurobiological effects in its representatives. The review presents an analysis of the literature data on experimental and partly clinical studies of various neurobiological effects of extracts and chemical compounds of species of this genus and the prospects for their use in medicine.
Text. A variety of neuroprotective effects of these compounds has been established. In many cases, inhibition of oxidative stress, which plays an important role in the development of a number of neurodegenerative diseases, has been noted as a neuroprotective mechanism. Chemical compounds contained in representatives of this genus protect brain neurons from ischemic damage, the effects of neurotoxins and glutamate, and beta-amyloid deposition. These substances have been found to inhibit increased acetylcholinesterase activity and dimyelination processes. These compounds also improve cognitive functions, including memory and learning. Their anticonvulsant effect has been established. Of particular interest is the data indicating the possibility of using some chemical compounds contained in representatives of the genus Astragalus L. in therapy of mental diseases, particularly schizophrenia.
Conclusion. The analysis of experimental works for the last ten years shows that extracts and chemical compounds of species of the genus Astragalus L. have a very heterogeneous spectrum of neurobiological action and, probably, may find application in the future as therapeutic agents in neurological and psychiatric practice. Unfortunately, in contrast to a large number of preclinical experiments, clinical trials of these compounds are sporadic. It is also noteworthy that less than one percent of the species of this genus have been investigated to date with respect to neurobiological activity. Thus, more extensive research, clinical trials, studies to standardize and establish therapeutic doses for humans of extracts and chemical compounds of species of the genus Astragalus L. are needed.
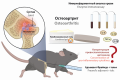
Introduction. Osteoarthritis is now considered to be a slowly progressive inflammatory disease that completely affects the joint. An important role in the development of this pathology is played by inflammation of the synovial membrane and ligaments (synovitis), supplemented by constant mechanical stress. Normally, a balance of anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory mediators is observed in cartilage, however, under the influence of risk factors, this balance shifts towards the latter.
Aim. Evaluation of the effect of a previously developed soft dosage form containing meloxicam, a purine derivative and an immunomodulator M on the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines: IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in osteoarthritis.
Materials and methods. The experiment included 25 animals, which were divided into 5 groups by simple randomization: 1 – test (gel 0.5 %), 2 –test (gel 1 %), 3 – reference (Amelotex®, gel 1 %), 4 – control (gel base); 5 – intact. Preclinical modeling of the pathology was carried out by combined injection of 0.1 ml of a mixture of complete Freund's adjuvant with a 10 % suspension of talc in isotonic sodium chloride solution in a ratio of 1 : 10 into the cavity of the hock (tarsal) joint of Brown Norvay Catholic Rats male rats. Enzyme immunoassay of animal blood serum on the 28th day of the experiment was performed using standard ELISA plate kits (Cloud-Clone Corp., USA). Statistical data processing was performed using GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 software (GraphPad Software Inc., USA), differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results and discussion. The developed compositions contributed to a decrease in the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1α, IL-6 and TNF-α) compared with the main and reference gel preparation. At the same time, differences were found between the effect observed from the use of the test agents (gel 0.5 %, gel 1 %) and the reference drug in terms of the effect on the level of IL-1α and TNF-α, which indicates a greater effectiveness of the selected combination of active substances, because, unlike the single-component gel Amelotex®, the compositions developed by us additionally included a purine derivative and an immunomodulator M. The data obtained are important from the point of view of understanding the mechanism of action of a soft dosage form.
Conclusion. Based on the results of previous and present studies, it is assumed that the combined composition of the soft dosage form with a half (0.5 %) concentration of meloxicam is of greatest interest for clinical practice, since its use at a high level of effectiveness additionally reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions from the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, which is important in the case of long-term therapy of osteoarthritis.
Introduction. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus (severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2). COVID-19 is now expected to stay with us for many years as a recurring disease. Molnupiravir and favipiravir are oral antiviral drugs with anti-RNA polymerase activity. The Russian Health Ministry has approved molnupiravir and favipiravir for the treatment of COVID-19. The study describes development and validation of high-performance liquid chromatography – tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) method for the simultaneous determination of β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine and favipiravir in human blood plasma. The method could be applied in pharmacokinetic study of molnupiravir and favipiravir.
Aim. The aim of this study is to develop and validate a HPLC-MS/MS bioanalytical method for the determination of β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine and favipiravir in human plasma.
Materials and methods. The determination of β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine and favipiravir in human plasma by HPLC-MS/MS. The samples were processed by 0.1 % formic acid in acetonitrile. Internal standard: promethazine. Mobile phase: 0.01 mol/L Ammonium formate buffer solution (Eluent A), 0.1 % formic acid and 0.08 % aqueous ammonia in water/acetonitrile 10 : 90 (Eluent B). Column: Shim-pack GWS C18, 150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm. Analytical range: 50.00–10000.00 ng/mL for β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine, 250.00–20000.00 ng/mL for favipiravir in human plasma. Ionization source: electrospray ionization. Detection conditions: 260.00 m/z → 82.10 m/z, 260.00 m/z → 111.00 m/z, 260.00 m/z → 127.95 m/z (β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine); 156.15 m/z → 65.95 m/z, 156.15 m/z → 85.00 m/z, 156.15 m/z → 113.10 m/z (favipiravir); 285.05 m/z → 198.05 m/z (promethazine).
Results and discussion. This method was validated by selectivity, suitability of reference standard, matrix effect, calibration curve, accuracy, precision, spike recovery, the lower limit of quantification, carry-over effect and stability.
Conclusion. The HPLC-MS/MS method for quantitative determination of β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine and favipiravir in human plasma was developed and validated. The analytical range was 50.00–10000.00 ng/mL for β-D-N4-Hydroxycytidine, 250.00–20000.00 ng/mL for favipiravir in human plasma. This method was applied to investigate the pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir and favipiravir.
REGULATORY ISSUES
Introduction. Out of specification (OOS) results represent a major challenge in the development, validation and use of the Assay and Dissolution methods. The topic is relevant, which is confirmed by Internet search data for the phrase "Out-of-Specification" + "HPLC" – about 35,300 results were found.
Text. The analytical and technological reasons (factors) that can lead to underestimated or overestimated test results are considered and systematized in the form of a summary table important for practice. These are the following factors. Factors associated with the calculation formula. Factors related to the preparation of samples. Factors related to the sample solvent and ratio of the pH the sample solution and the mobile phase. Factors associated with chromatograms and their processing. The main technological factors.
Conclusion. Data and recommendations are presented to search for analytical and technological reasons for obtaining Out-of-Specification results in the case of tests Assay and Dissolution.
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)