FROM EDITOR
The fourth chapter presents V. N. Ipatiev's memoirs about the preparation and celebration of the 200th anniversary of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the next Mendeleev Congress. About repeated foreign business trip with commercial and scientific purposes. During this trip, Ipatiev managed to visit a large number of familiar chemists, heads of chemical faculties of German, French, Belgian universities and laboratories of leading chemical departments. His scientific activity during the final period of his life in Russia, before emigrating to Germany, and later to the USA, is described.
EVENTS
Experts discussed current opportunities for pharmaceutical development in our country, discussed actual difficulties and the ways for overcoming it.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF NEW DRUG PRODUCTS
Introduction. The emerging resistance of bacteria to drugs is one of the serious problems of medicine, which stimulates the constant search for new antimicrobial drugs, also of natural origin. Researchers widely address representatives of various families and genus of the plant world, using various morphological groups of plant raw materials, studying the effect of both the sum of extracted substances and individual compounds.
Aim. Investigation of antimicrobial activity of water-alcohol extracts of some representatives of the genus Potentilla in the search for new antimicrobial medicines of plant origin.
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were extracts on 40 and 70 % ethyl alcohol from the aboveground part of Potentilla anserinа L., P. erecta (L.) Raeusch, P. argentea L., P. paradoxa Nutt. ex Torr. et Gray, P. goldbachii Rupr., P. approximate Bunge, P. chrysantha Trevir. Antimicrobial activity was determined by diffusion into agar using paper disks. Collection strains of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and 29 strains of MSSA isolated from biomaterial from patients were used as test cultures. The sensitivity of MSSA strains to antibiotics was characterized by an antibioticogram.
Results and discussion. The strain of Escherichia coli turned out to be insensitive to all extracts of the paws. The strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is minimally sensitive to extracts of 40 % ethyl alcohol of P. anserinа and P. argentea, to 40 and 70 % extracts of P. approximata. All strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) are sensitive to all extracts of the paws to varying degrees. Among 40 % of the extracts, the most active are P. anserinа, P. paradoxa and P. erecta extracts, among 70 % of the extracts are P. paradoxa and P. argentea extracts.
Conclusion. The studied extracts of seven Potentilla species showed antimicrobial activity against both sensitive and insensitive to antibiotic strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) to a close or comparable degree, while extracts on 40 % ethyl alcohol are slightly more active compared toextracts on 70 % ethyl alcohol. The results indicate that the studied Potentilla species are promising for further research.
Introduction. The review is dedicated to the scientific analysis of the composition, properties and features of the biological effects on the man's organism of the Lycium Fruit as a prospective plant raw material for the production of innovative drugs.
Text. The most important aspects related to plant raw materials of various types of Lycium are considered, such as, the worldwide prevalence of plants and the unification of raw materials numerous synonymous names, the generalization of pharmacopoeia data, the qualitative and quantitative composition of Lycium components, their structural features, biological effects on vital body systems. The review also presents the problem of the absence of general pharmacopoeia monographs on Lycium raw materials in Russia, despite the cultivation of Lyceum ruthenicum M. plants in Russia. This fact opens up significant opportunities to develop the Russian regulatory document for Lycium, as a promising pharmaceutical raw material.
Conclusion. The obtained results demonstrate the potential of introducing into pharmacy a new type of pharmaceutical raw material and a new finished products based on them, as well as predicting the biological activity of the substances of Lycium fruit and mechanisms of alkaloids, flavonoids, polysaccharides and Lycium carotenoids action.
Introduction. Cultivation of biomass of plant cells as a method of obtaining raw materials has existed for quite a long time. Plant cells cultivated in vitro act as a source of valuable secondary metabolites such as phenols, alkaloids, phytosteroids, glycosides, etc. It is important to create conditions under which the accumulation of valuable biologically active substances will be observed in the strains. Cultivation involves the use of complex multicomponent nutrient media containing a certain set of macro-, microelements, vitamins, growth stimulants. Salvia officinalis has a wide spectrum of pharmacological action. Due to the limited growing area of medicinal sage, as well as the deterioration of the ecological situation in the growing regions, the use of a phytobiotechnological method for obtaining raw materials is relevant.
Aim. The aim of the study is to obtain a viable callus culture of salvia officinalis (Salvia officinalis L.).
Materials and methods. Leaves of an intact plant sage medicinal, of the Lamiaceae family (Salvia officinalis, Lamiaceae) were used as explants. The explants were pre-sterilized with 6 % sodium hypochlorite solution for 20 minutes and 70 % ethanol for 1 minute. It was cultivated on a nutrient medium according to the Murasig – Skoog recipe. Determination of cell viability using vital dyes was assessed using microscopy (digital microscope Bresser LCD 50x-2000x, Germany). High performance thin layer chromatography was performed using a HPTLC PRO SYSTEM (CAMAG AG, Switzerland).
Results and discussion. After two weeks of cultivation, the formation of primary callus was observed on the surface of the explants. Visually, it was a thin layer of intensely dividing undifferentiated light yellow cells. During cultivation, the biomass of the resulting callus increased, it became looser and acquired a darker shade, and the nutrient medium also began to darken. The detected cells during microscopy can be divided into two types: the first type is cells of the meristematic type, the second type is cells of the parenchymal type. Microscopy showed that more than 95 % of all visualized cells are alive. In the following passages, no significant changes in the morphotype of the culture were noted. In the eleventh passage, a study of the growth activity of the strain was carried out. The maximum specific growth rate of 0.42 day-1 is observed on the 14–18th day of growth, while the biomass doubling time is the smallest and corresponds to the value of 1.66 days. During one cultivation cycle, the amount of biomass increases by 7.73 times. The results of a qualitative analysis by the method of high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HTPLC) show that the qualitative composition of the biomass of medicinal sage is generally close to that of intact plants.
Conclusion. A viable stable strain of plant cells of salvia officinalis was obtained on a nutrient medium according to the Murasig – Skoog recipe with a half content of micro- and macrosols and phytohormones 2,4-D (6 mg/ml) and kinetin (1 mg/ml). For the following passages, it is recommended to use a nutrient medium according to the Murasig – Skoog recipe with a full content of micro and macrosols and phytohormones naphthylacetic acid (1 mg/ml) and kinetin (1 mg/ml). The bulk of the obtained heterogeneous callus is made up of cells of the meristematic and parenchymal type. The qualitative composition of BAS biomass of medicinal sage is generally close to that of intact plants.
Introduction. Intensive anthropogenic impact leads to a sharp reduction in natural reserves of many valuable plants. In this regard, previously obtained data on stocks quickly become obsolete. Therefore, the inventory of stocks of medicinal plants in the Russian Federation as a whole and the Middle Urals, in particular, remains an urgent problem. Unfortunately, modern technologies are not being implemented intensively enough in the domestic pharmacy. In our opinion, the reasons for this are expensive software, insufficient theoretical and practical skills to work on personal computers, as well as the specifics of the industry. Despite this, the use of geographic information systems (GIS) in pharmacy is quite promising [7–9]. The use of geographical information systems as a methodological basis will make it possible to map the areas of medicinal plants, to analyze plant communities not only for the territory of the Middle Urals at a high scientific level [1, 4].
Aim. Development of predictive models for the distribution of medicinal plants based on a comprehensive assessment of the state of populations of wild medicinal plants of the Middle Urals.
Materials and methods. The determination of raw material reserves of the studied species of medicinal plants was carried out on specific thickets according to the generally accepted methodology. The authenticity of raw materials was established by the macroscopic method when collecting samples of raw materials. In the course of the study, stocks of 4652 populations of 27 species of medicinal plants growing in the Middle Urals were studied. The collection of the material was carried out in the period from 2006 to 2019 during the survey of the administrative districts of the Perm Krai and the Sverdlovsk region. A comparative comprehensive assessment of resource and phytochemical indicators was studied using the example of 6 species of wild medicinal plants: Origanum vulgare L., Lamiaceae, Hypericum perforatum L., Hypericaceae and Hypericum maculatum Crantz, Hypericaceae, Tanacetum vulgare L., Asteraceae, Artemisia absinthium L., Asteraceae, Leonurus quinquelobatus Gilib., Lamiaceae, Achillea millefolium L., Asteraceae.
Results and discussion. In the course of resource and phytochemical studies of representatives of the medicinal flora of the Middle Urals, a comprehensive assessment of the state of populations of wild medicinal plants – sources of medicinal plant raw materials (herba Origani vulgaris, herba Hyperici, flores Tanaceti vulgaris, herba Artemisiae absinthii, herba Achilleae millefolii and herba Leonuri) was carried out. A geospatial analysis of the distribution of medicinal plant populations by soil types within the regions of the Middle Urals was carried out. An algorithm for constructing predictive models of the distribution of populations of wild medicinal plants of the Middle Urals has been worked out. A set of maps of the "occurrence" of medicinal plants in the study area has been developed.
Conclusion. The conducted complex of studies will allow updating information about the medicinal flora of the Middle Urals. Developed on the example of a number of representatives of the medicinal flora of the Middle Urals, the algorithm for constructing forecast maps can be used for any regions in the presence of appropriate topos.
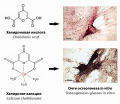
Introduction. The development and implementation of new effective and safe drugs with osteogenic activity is an urgent problem of modern medical and pharmaceutical sciences. This is due to the wide prevalence and complexity of the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which entails significant economic costs for the treatment and recovery of this group of patients. Recently, standard therapy regimens are increasingly being supplemented with drugs derived from medicinal plants, which is associated with their rather pronounced therapeutic effect and the absence or mild side effects compared to more expensive modern medical analogues. In this regard, the development of new directions in the strategy for the development of pharmacological agents from plant sources becomes relevant. The study of plant secondary metabolites is one such area that has already yielded good results in relation to the development of such drugs, and holds great promise. The review provides information on the biological properties of chelidonic acid and its possible derivatives in order to demonstrate the prospects for the use of these objects for the development of drugs, including those with osteogenic activity.
Text. Chelidonic acid is a substance present in many medicinal plants and has a wide range of pharmacological effects – analgesic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, oncostatic and sedative. At the moment, methods have been developed for obtaining chelidonic acid and its derivatives from natural sources. In addition, chelidonic acid belongs to the so-called “small” molecules with osteogenic properties, which makes it promising in the creation of drugs for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system caused by impaired formation and regeneration of bone tissue. Native chelidonic acid has a low osteogenic activity, but given its ability to form complex compounds, it can act as a delivery system for osteoprotective micro- and macroelements. So, calcium chelidonate in experiments in vitro and in vivo shows a pronounced osteogenic activity: it stimulates the viability, adhesion and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells, enhances the mineralization of the extracellular matrix.
Conclusion. Taking into account the wide range of biological activity of chelidonic acid, its use in the complex therapy of allergies, depression, diabetes mellitus, inflammatory diseases, malignant neoplasms and other pathological conditions seems relevant. Calcium chelidonate is a promising drug candidate that can be used to accelerate regeneration processes and in bone tissue engineering.
PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
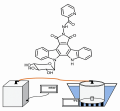
Introduction. N. N. Blokhin National Medical Research Center of Oncology of the Ministry of Health of Russia synthesized an original derivative of indolocarbazole with the carbohydrate residue xylose, which has a pronounced cytotoxic and anti-angiogenic activity. The substance LCS-1269 is an amorphous powder that is almost insoluble in water, which causes difficulties in the development of an injectable dosage form (IDP). To solve this problem, a technological approach to obtain a solid dispersion (SD) of LCS-1269 has been proposed.
Aim. To develop a model of IDP of the indolocarbazole derivative LCS-1269 based on SD.
Materials and methods. We used a substance LCS-1269 synthesized in the Chemical Synthesis Laboratory of the N. N. Blokhin National Medical Research Center of Oncology. Emuxol 268, Kolliphor® P 188, Soluplus®, Lutrol® F68, Kollidon® 12 and Kollidon® 17, soybean phosphatidylcholine unsaturated S PC and saturated S PC-3 were investigated as carriers of the active substance. SD LCS-1269 was obtained by solvent removal: the active substance was dissolved in acetone, the carrier − in chloroform, the obtained solutions were mixed, transferred into a bottle and evaporated under vacuum (50 ± 5 mbar) in the desiccator at water bath temperature 65 ± 2 °С. To obtain aqueous solution of LCS-1269 dry mass was dissolved using different auxiliary substances or their mixtures: water for injection, ethanol 95 %, benzyl alcohol, Kollisolv® PEG 400, MONTANOX™ 80. To increase stability, the aqueous solution of LCS-1269 was lyophilized in an Edwards Minifast DO.2 freeze dryer.
Results and discussion. Kollidon® 17 was chosen as the carrier material for the SD active substance. It was found that a clear solution of LCS-1269 with the concentration of the active substance 0.5 % was formed by dissolving the SD in ethanol 95 % and then gradually diluting the alcohol mixture with water for injection. In this case, the mass ratio of the components of the developed model IDF LCS : Kollidon® 17 : ethanol : water is 1 : 40 : 32 : 127. As a result of freeze-drying of the water-ethanol solution of LCS-1269 the IDF in the form of lyophilizate easily soluble in a 10 % solution of ethanol was obtained.
Conclusion. An IDF model of the hydrophobic derivative of indolocarbazole LCS-1269 based on SD was developed and submitted for biological studies to evaluate its effectiveness.
Introduction. Nowadays deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are the object of close attention of the scientific community in various fields, such as chemistry, biology, pharmacy, biotechnology. The areas of application of DESs vary widely, and one of them is the extraction of biologically active substances from plant raw materials.
Aim. The aim of this work was to study the possibility of extraction of flavonoids from plant raw materials with using of deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride, as well as to compare the efficiency of their extraction with traditional solvents.
Materials and methods. The extraction of flavonoids was carried out from the collection of a plant composition consisting of the herb of motherwort cordial (common motherwort) (Leonurus cardiaca L.), the herb of St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.), the herb of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) and the herb of creeping thyme (thyme) (Thymus serpyllum L.) in a ratio of 4 : 2.5 : 2.5 : 1, crushed to a particle size of 2–3 mm. DESs based on choline chloride as hydrogen bond acceptor were used as extractants.
Results and discussion. In this article, DESs based on choline chloride were investigated for the ability to extract flavonoids from the medicinal collection of a plant composition based on leonurus grass, hypericum grass, melissa grass and thyme grass, which has a sedative effect. The influence of the water content in DES solutions on the properties of the extractant was also studied. Quantitative determination of flavonoids in terms of rutin was carried out by differential spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 410 ± 2 nm. The maximum yield of flavonoids was achieved by using a 50 % aqueous solution of DES based on choline chloride, glucose and water in a molar ratio of 2 : 1 : 1 at an extraction temperature of 60 °C.
Conclusion. The extracting ability of the obtained DES in terms of the efficiency of flavonoid extraction exceeds the extracting characteristics of the classical extractant for the composition under study – 70 % ethanol. Further study of the properties of the obtained extractant, its physical, chemical, and toxicological characteristics is the task of future experiments.
Introduction. Rhenium-188 has found wide application in nuclear medicine for the treatment of metastatic lesions of the skeletal system and joint diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and synovitis. Also, 188Re-radiopharmaceuticals are being developed for the palliative treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and others. Immediately after the first clinical trials of 188Re-radiopharmaceuticals, when information on clinically effective administered doses for radionuclide activity was obtained, the use of sodium perrenate, 188Re solutions with high volume activity for radiopharmaceutical synthesis and, consequently, additional concentration of obtained from the generator solutions became extremely relevant.
Aim. Development of the technique for concentration of sodium perrenate, 188Re solution, obtained from the 188W/188Re generator "GREN-1" (State Research Center of the Russian Federation IPPE named after Leipunsky, Obninsk, Russia) under laboratory conditions, and comparison of the quality indicators of the resulting product and Na188ReO4 solution obtained from the generator with an automatic concentration module NEPTIS-TH (IRE, Belgium).
Materials and method. The objects of this study were eluates from the 188W/188Re generator "GREN-1" manufactured by the IPPE JSC (Obninsk, Russia) and the materials used in the production and quality control of these generators, as well as the generator produced by the National Institute of Radioelements (IRE, Belgium) with an automatic concentration module NEPTIS-TH. The following methods were used to control the quality of sodium perrhenate, 188Re solutions: radiometry, thin layer chromatography, potentiometry, potentiometric titration, atomic absorption spectroscopy.
Results and discussion. The efficiency of concentration of the eluate from the "GREN-1" generator using cartridges filled with cation exchanger Dowex® 50WX8 (100–200 mesh) (Sigma-Aldrich, USA, Cat. No. 217506) and Al2O3 with pH 4 (100–200 mesh), and the IRE generator using the automatic NEPTIS-TH module was studied. The yield of rhenium-188 after concentration was 75–85 %. As a result of the concentration process, there is no proportional increase in the content of chemical impurities, and it is possible to obtain cleaner solutions for the content of metals such as Fe, Zn, Cu and others. It was found that in the routine use of generators, the value of the volume radioactivity of the obtained concentrated sodium perrhenate, 188Re solution should not exceed 7.4–8.0 GBq/ml.
Conclusion. The conducted studies have shown that the task of concentration of sodium perrenate, 188Re solutions with high volume activity of appropriate quality for the preparation of radiopharmaceuticals for radionuclide therapy can be solved using quite affordable materials, namely a sequence of cartridges. The use of an automatic module is more preferable than the use of manual assembly of a sequence of cartridges, based on the guaranteed quality assurance of the resulting sodium perrenate, 188Re solution and reducing the dose burden on personnel. However, the conducted studies have shown that the tested concentration module is incompatible with the domestic generator, so the system proposed for the study was not registered in Russia. The results obtained in this work will be used to organize the industrial production of domestic modules and cassettes in complete set with "GREN-1" generator.
Introduction. For the last decade, nanotechnology has been studied extensively in the pharmaceutical field. Among all the nanotechnology formulation areas, nanostructured lipid carrier is enormously researched by formulation scientists as it is one of the focused areas of lipid carrier for the effective formulation.
Materials and methods. The nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) consists of solid lipid, liquid lipid & surfactant for fabrication of formulation. Methods such as high energy methods, low energy methods and organic solvent-based methods are used for the preparation of NLC. As per literature study the High pressure homogenization is the most efficient method for fabrication of formulation.
Results and discussion. This carrier system has significant advantages such as high drug entrapment, improved bioavailability, stability during storage, and targeting the site with a better-controlled release making it a prominent area for the formulator to emphasize on it. Although many drugs are formulated with a nanostructured lipid carrier, it is a concern for researchers to find out the effectiveness of formulation by studying the process parameter and safety.
Conclusion. The present review was focused to study the impact of various parameters such as Lipid, surfactant, homogenization rate, preservative, Crystallinity, and surface charge on the formulation. The study also extended towards toxicity and biocompatibility, topical targeting & cancer treatment of the Nanostructured lipid carrier.
Introduction. The solubility of an active pharmaceutical ingredient plays a major role in drug absorption. Hot melt extrusion is a batch or continuous process that allows creating solid dispersion systems based on various carriers in order to increase solubility and bioavailability of active substances. Development of effective and safe analgesics is one of the most vital tasks of organic and medicinal chemistry. An innovative non-opioid analgesic with very low toxicity and low dosage, but practically insoluble in water, was used in this work. It was suggested to obtain a solid dispersion by hot melt extrusion in order to increase bioavailability.
Aim. Development a hot melt extrusion technology for production of a solid dispersion system of PAV-0056 as an active substance and Plasdone™ S-630 as a polymeric carrier to increase the solubility.
Materials and methods. PAV-0056 (methyl-2-(7-nitro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-3-propoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-1-yl)acetate) (JSC "Organica", Russia) Figure 1; Plasdone™ S-630 (Boai NKY Pharmaceuticals Ltd., China); PEG-1500 (Clariant, Switzerland); acetonitrile for chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany). Extrudates were obtained using a HAAKE™ MiniCTW co-rotating twin-screw laboratory extruder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany). Extrudates were examined by optical microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry, and time of water solution stability was determined. The quantitative content of the active substance and related impurities in the 2.5 % solid dispersion of PAV-0056 was determined by HPLC-UV.
Results and discussion. Hot melt extrusion process conditions were established for a mixture of 2.5 % PAV-0056 and Plasdone™ S-630. Stability of the extrudate solution in water was studied, the content of the active substance and impurities in the extrudates was determined. Based on the binary mixture, a composition containing 10 % of PEG-1500 was developed. The optimal conditions for the extrusion process were chosen for obtaining a solid dispersion system that meets the requirements of the regulatory documentation for the content of the active substance and impurities.
Conclusion. The binary mixture proved to be unsuccessful for the creation of SDS by hot melt extrusion due to significant accumulation of impurities during the extrusion process. By adding PEG-1500 to the composition, it was possible to considerably lower the operating temperature of the process, reduce the impurity content in the extrudate, and maintain satisfactory stability of the PAV-0056 solution in water.
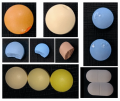
Introduction. In modern practice, suppositories are prepared by hand rolling method or fusion. 3D printing can overcome the disadvantages of traditional suppository manufacturing methods and solve the problems of personalization. 3D printing makes it possible to manufacture drug-loaded suppositories without the use of molds or other physical support. The current studies have a number of limitations, and the printing of one suppository requires a long time. This report proposes a method of 3D modeling and 3D printing to produce personalized suppositories by fusion.
Aim. Various sizes and shapes suppositories silicone molds development by molding method from hydrophilic, lipophilic and amphiphilic bases.
Materials and methods. Suppository bases: cocoa butter (Luker, Colombia), polyethylene glycol (PEG) 1500 (Merck KGaA, Germany), PEG-400 (Merck KGaA, Germany), Witepsol H-15 (Chimmed Group, Russia); pharmaceutical substance: paracetamol (Hebei Jiheng (Group) Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, China); filaments for 3D printing: polyethylene terephthalate (PET-G natural, LLC "PrintProdakt", Russia); silicone two-component platinum, hardness Shore 30A (China); solvents: Acetonitrile Grade HPLC (Merck KGaA, Germany). The design of the both casting and master molds of suppositories was carried out using the KOMPAS-3D version 17.1. Master molds were printed by Picaso PRO 250 and Picaso X Pro 3D printers. Mold segments were obtained by filling master molds with a mixture of two-component silicone. Suppositories were obtained by molding method. Their average weight and standard deviation were determined. Paracetamol concentration in suppositories was carried out by UV spectrophotometry on a UV-1240 mini spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Япония). Silicone molds were soaked and washed in hot water with surfactants. Washouts from the molds were taken by soaking the mold.
Results and discussion. The torpedo-shaped form was chosen as the model form of suppositories. For the chosen form, three volumes of suppositories were designed: 3.32 ml; 1.5 ml and 0.25 ml. Silicone molds were designed and manufactured for all volumes. The cast suppositories were examined for compliance with the regulatory documentation for the dosage form, the average weight and mass uniformity were evaluated. Suppositories with paracetamol were made. A procedure for cleaning the obtained silicone molds has been developed.
Conclusion. The resulting silicone molds make it possible to obtain suppositories in accordance with the regulatory documentation for the suppositories. Silicone molds have significant advantages compared to analogues of metal or polymeric molds.
Introduction. Actual use of plant raw materials in the production of medicines is caused by a variety of bioactive substance complexes in their composition. These drugs have a wide range of therapeutic effects and in this regard, the properties and compositions of various plant materials are currently being actively studied. Aronia melanocarpa (chokeberry) has been the focus of scientific research for many years to identify various healing properties, and in 2015 its fresh and dried fruits are presented as a plant raw material in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XIV edition. The variety of biologically active substance complexes of Aronia melanocarpa fruit allows its use in different fields (food and pharmaceutical industries). For this reason, the development of the composition and technology of effervescent tablets containing a complex of biologically active substances and possessing the following advantages: rapid release of active ingredients, high rate of BAS assimilation, usability and pleasant flavor are of interest.
Aim. The aim of the present study is to develop the composition and technology of effervescent tablets with a biologically active complex from dried Аronia melanocarpa fruits.
Materials and methods. Extracts enriched with anthocyanins were obtained from dried chokeberry fruits. As excipients in the technology of effervescent tablets, sodium carbonate, tartaric acid, lactose monohydrate, povidone (Plasdone™ K-29/32), polyethylene glycol 6000 and aspartame were used. Under laboratory conditions, granules (acidic and basic) were obtained by the method of punching wet masses, where extract (granulate 1) and ethyl alcohol 96 % (granulate 2) were used as a moisturizer. Numerical indicators of medicinal plant raw materials, technological properties of granulate and tableting mass, as well as quality indicators of effervescent tablets were determined according to the methods described in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XIV edition.
Results and discussion. Numerical indicators of dry fruits of Aronia melanocarpa (crushing of raw materials and the content of foreign impurities, total ash in plant raw materials and ash insoluble in hydrochloric acid, content of extractives) were determined, and the good quality of the raw materials used in the subsequent stages of drug development was confirmed. An extract enriched with anthocyanins has been developed. The composition and technology of effervescent tablets with separate granulation of acidic and basic components has been developed. Extract and ethyl alcohol 96 % were used as moisturizers, and aspartame was used to improve taste characteristics. A draft specification for the quality indicators of effervescent tablets based on enriched extraction has been proposed.
Conclusion. In the course of the research work, the numerical indicators of medicinal plant raw materials were determined and its quality was confirmed, which enabled its use for further extraction. Extraction conditions were chosen, extracts were obtained. Excipients have been selected, the composition and technology of effervescent tablets based on the extracts of Aronia melanocarpa fruits have been developed, a draft specification for effervescent tablets has been proposed in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation, XIV edition.
Introduction. The article presents the results of the development of the composition and technology of orally dispersed tablets of ethylthiobenzimidazole fumarate – a new actoprotective and adaptogenic agent.
Aim. Development and substantiation of the composition and technology of orally dispersed tablets based on ethylthiobenzimidazole fumarate.
Materials and methods. The technological properties of tablet samples were studied according to the methods of the State Pharmacopoeia of the XIV edition using the PGR-10 tablet press (LLC "LabTools", Russia), TBH 125 TDP tablet hardness tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany), ZT 322 m tablet disintegration tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany), TAR 220 abrasion tester (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany).
Results and discussion. As a result of the study, the composition of orally dispersed tablets based on a new substance – ethylthiobenzimidazole fumarate was developed and justified. As a justification, the data of the analysis of the technological properties of the substance and excipients, the results of a multifactorial experiment planned using the Minitab 17 program, as well as data on the strength characteristics of the tablets obtained and the dependence of the disintegration time of the tablets and their strength characteristics on the pressing pressure are given.
Conclusion. Based on the results of the study, the optimal composition of orally dispersed tablets based on ethylthiobenzimidazole fumarate is proposed.
Introduction. One of the modern remedies used to treat vaginal infections are suppositories "Depantol", which have an antiseptic, regenerating effect due to the combination of chlorhexidine and dexpanthenol. The initial stage in the life cycle of any medicinal product (MP) is pharmaceutical development, a systematic approach to which implies the principle of Quality-by-Design (QbD), which is based on obtaining reliable scientific data and risk management for quality. With this approach, pharmaceutical development begins with a preliminary determination of significant factors in the creation of a drug.
Aim. Aim of study was to design Quality Target Product Profile, Critical Quality Attributes, Critical Material Attributes – the initial data necessary for the development of composition and technology of a generic drug in accordance with the QbD methodology of ICH Guidance Q8 "Pharmaceutical Development".
Materials and methods. Objects of study: chlorhexidine bigluconate, dexpanthenol, PEG-400 and PEG-1500, pharmaceutical development documents. Methods of study: content analysis, system analysis; FMECA method (Failure Modes, Effects and Criticality Analysis).
Results and discussion. In order to implement the QbD for the production of a drug of good quality, initial data for the development of the composition and technology of two-component suppositories were obtained. Quality Target Product Profile (QTPP) was compiled taking into account the data of the original drug was used as reference. Based on the compiled QTPP, Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) were identified. The determination of CQAs from QTPP parameters was based on the strength of the potential harm to the product. Due to the fact that we developed a well-known dosage form, quality indicators were chosen that are standard for hydrophilic suppositories. In order to determine the parameters of the drug components that affect the Critical Quality Attributes, for each of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) suppositories contain, the Critical Material Attributes (CMAs) were determined. For example, for liquid ingredients, according to the specification of the substance manufacturer, these are pH, viscosity, impurities, identification, assay, refraction index. For the initial risk assessment, risk assessment matrices of the influence of the Сritical Material Attributes of the components on the Critical Quality Attributes were compiled. When evaluating the effect of chlorhexidine bigluconate on the critical characteristics of the final product, attention was paid to all parameters from the manufacturer's specification, since any deviations in pH, density, presence of related substances and extraneous impurities, assay and identification of the substance may signal the chemical unsuitability of the component. The weight uniformity of suppositories is affected only by the parameters of the technological process. The influence of CMAs of dexpanthenol on the Critical Quality Attributes of the finished product is generally similar to the influence of the parameters of chlorhexidine bigluconate. The difference in the influence of pH and water content on the microbial limits: unlike chlorhexidine bigluconate, which has antiseptic properties, dexpanthenol is more susceptible to microbial contamination. The effect of base CMAs on identification, content uniformity, and assay is not critical. Whereas the pH, assay and identification of PEG-400 and PEG-1500 have a significant impact on the dissolution profile of the active ingredients from the finished dosage form.
Conclusion. The data required for the pharmaceutical development of a generic drug, two-component suppositories, was obtained: Quality Target Product Profile, Critical Quality Attributes, Critical Material Parameters. The impact of the critical characteristics of the raw materials on the critical quality attributes of the developed suppositories was assessed.
Introduction. Technology transfer is an integral part of the life cycle of any drug. The coating is a critical step in the production of coated tablets. The transfer of the film coating application process is often accompanied by the rejection of a part of the drug series due to various defects in the target surface.
Aim. To classify the types of defects formed at the stage of “Application of the film shell” in the devices of the “Coater” drum type, to identify the causes of occurrence, to develop ways to eliminate these defects.
Materials and methods. Film-coated tablets with INN diosmin, sildenafil, dipyridamole, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin as the object of the study were selected. The samples were obtained on a single-punch tablet press EP-1 (ERWEKA GmbH, Germany) and coated with a film shell in a coating unit of the type "copper" BGB-1 (Chongqing Jinggong Pharmaceutical Machinery Co., Ltd., China).
Results and discussion. Appearance defects are classified according to the degree of criticality: critical (influx, chipping, recess, rupture, delamination, breaking, rubbing, sticking, pigmentation, discoloration, scratches, crack), significant (build-up, inclusion), minor defect. The main causes of the defect have been established: the property of the core tablet (for example, poor adhesive properties, hydrophobicity), technological parameters of the process (the speed of rotation of the drum, the speed of spraying, the pressure on the spray, the pressure on the formation of the torch, the temperature of the incoming air. The main consequences of the occurrence of each type of defect are considered, among which are insignificant (not affecting the quality) and critical (affecting the quality indicators of "dissolution").
Conclusion. In the course of the study, the types of critical and significant defects, the causes of occurrence and ways to eliminate these defects are considered.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
Introduction. An increasing number of studies conducted in various countries in the field of biopharmacy convincingly show the differences in the physiological effects on the human body of stereoisomers of pharmaceutical substances. As a rule, one of the enantiomers has the necessary pharmacological effect, the other enantiomer is either inert or has a negative side effect. Currently, it is important to obtain enantiomerically pure pharmacological substances from their racemic mixtures.
Aim. Obtaining the R-isomer of salbutamol from a racemic mixture of salbutamol and developing a preparative procedure for chiral separation by supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) with a yield of the target product sufficient for the production process.
Materials and Methods. Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is widely used for analytical and preparative separations of enantiomers of pharmaceutical substances. The relevance of the use of supercritical fluid chromatography SFC is largely due to the fact that it uses sub- or supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) as the main component of the mobile phase (MP). Studies were carried out on semi-preparative Investigator SFC (Waters Corporation, USA) and preparative Prep 200 qSFC (Waters Corporation, USA) supercritical fluid chromatographs with PDA detectors. Samples were weighed to the nearest 0.0001 g on a XPE206DR balance (Mettler Toledo, USA).
Results and discussion. The process of chiral separation of salbutamol sulfate by the SFC method on Prep 200 qSFC (Waters Corporation, USA) was studied. It was revealed that in the chromatographic system under supercritical conditions, the salt is separated into acidic and basic residues, which significantly reduces productivity and shortens the duration of continuous operation of the chromatograph. Conditions for the preparative chiral separation of the racemic mixture of salbutamol base into R- and S-isomers with high enantioselectivity and productivity have been developed. The resulting R-isomer of salbutamol base can be converted into the pharmaceutical substance in the form of sulfate or other salt without loss of enantiomeric purity, the S-isomer can be subjected to racemization and subsequent use.
Conclusion. A preparative method has been developed for the chiral separation of a racemic mixture of salbutamol by supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) with a yield of the target product (R-isomer) of 5.5 g per shift (8 hours).
Introduction. Natural sources, especially plants, have been used in folk medicine of various countries for many centuries and appears as rich sources of natural compounds. One of the interesting plants for study is the yellow loosestrife (Lysimachia vulgaris L.), the information on the chemical composition of which is scarce.
Aim. Carry out a phytochemical research of the L. vulgaris aerial part, by isolation of individual secondary metabolites and elucidation of their structure.
Material and methods. Aerial part of L. vulgaris, was collected in the Leningrad region (Vsevolozhsk district, Morozov village, the shore of Lake Ladoga) in July 2021. Fraction analysis was performed through analytical high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a LC-20 Prominence (Shimadzu corp., Japan) equipped with a SPD-M20A diode-array detector. The isolation of compounds was carried out by open column chromatography using sorbent Dianion HP-20, as well as by preparative HPLC using a Smartline system (Knauer, Germany) equipped with a spectrophotometric detector. The structures of the isolated compounds were established by NMR experiments (Bruker Avance III 400 MHz, Germany).
Results and discussion. As a result of L. vulgaris aerial part phytochemical research, the structures of seven individual compounds (1–7) were elucidated. Compounds 1 and 2 are luteolin and quercetin, respectively, while compounds 3–7 are glycosides of quercetin, myricitin and kaempferol, namely myricetin-3-O-β-D-rutinoside (3), myricetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (4), quercetin-3-O-β-D-rutinoside (rutin) (5), quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), kaempferol-3-O-β-D-rutinoside (7).
Conclusion. As a result of L. vulgaris aerial part phytochemical research, seven individual compounds were isolated. Compounds 1 and 4 have been found in the aerial part of L. vulgaris for the first time, and all compounds (1–7) have been isolated for the first time from the yellow loosestrife herb.
Introduction. Medicinal plants are a rich, almost inexhaustible source of medicinal substances, and due to their large chemical diversity of metabolites available for isolation their research is always an important task. One of the promising medicinal plants for research is marsh cinquefoil (Comarum palustre L.), widely used in folk medicine for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Aim. Isolation of individual secondary metabolites from the aerial part of C. palustre and their subsequent structural elucidation by NMR experiments.
Materials and methods. The aerial parts of the marsh cinquefoil, were collected next to the Saint Petersburg State Chemical-Pharmaceutical University Nursery Garden of Medicinal Plants (Leningrad region, Vsevolozhsky district, Priozerskoe highway, 38 km) in July 2021. Fraction analysis was performed through analytical high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a LC-20 Prominence (Shimadzu corp., Japan) equipped with a SPD-M20A diode-array detector. The isolation of compounds was carried out by open column chromatography using sorbents with different selectivity, as well as by preparative HPLC using a Smartline system (Knauer, Germany) equipped with a spectrophotometric detector. The structures of the isolated compounds were established by 1D NMR experiments (Bruker Avance III 400 MHz, Germany).
Results and discussion. Seven individual compounds (1–7) were isolated and their structures elucidated. Two compounds (1 and 2) are derivatives of ellagic acid, namely 4-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside ellagic acid (1) and 4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside ellagic acid (2), while the other five compounds are derivatives of flavonoids: kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucuronide (3), quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide (4), quercetin-3-O-β-D-(6’’-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-glucopyranoside (5), quercetin-3-O-β-D-(2’’-galloyl)-glucopyranoside (6) and (+)-catechin (7).
Conclusion. As a result of the current research, seven individual compounds were isolated from the aerial part of the marsh cinquefoil and their structure were elucidated. Compounds 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6 were found and isolated from the aerial part of C. palustre L. for the first time.
Introduction. Medicinal plant raw materials, containing a wide range of various biologically active compounds, are of considerable interest as a likely source of new, pharmacologically active biologically active substances. One of the promising plants is Rhodiola quadrifida (Pall.) Fisch. & C.A. Mey, since the raw materials contain phenolic compounds and their derivatives, which cause anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anticarcinogenic effects. In addition, this plant has considerable popularity in folk medicine as a dietary supplement.
Aim. Isolation of individual compounds from rhizomes and roots of Rhodiola quadrifida and subsequent determination of their structure by NMR and mass spectrometry for phytochemical profiling.
Materials and methods. Rhizomes and roots of Rhodiola quadrifida, purchased in the pharmacy of St. Petersburg (place and time of procurement according to the information on the package – Altai (near Barnaul), in March 2019. The ethanol extract fractions (ethanol, hexane, butanol, and water) obtained during sequential liquid-liquid extraction were examined on a LC-20 Prominence instrument (Shimadzu, Japan) with an SPD-M20A diode array detector to determine the chromatographic profile. The most promising ethyl acetate fraction was purified by column chromatography on open glass columns with sorbents of different selectivity and preparative chromatography [Smartlina (Knauer, Germany)] with a spectrophotometric detector. The structure of the obtained individual compounds was determined by NMR (Bruker Avance III 400 MHz, Germany) and confirmed by low-resolution mass spectrometry [Flexar FX-15 (PerkinElmer, USA)].
Results and discussion. During the study, 7 individual compounds were isolated from the rhizomes and roots of Rhodiola quadrifida, namely 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, caffeic acid, ethyl gallate, catechin, epicatechin and tyrosol. These compounds were isolated for the first time from the raw materials of Rhodiola quadrifida. They are the major compounds and can characterize the phytochemical profile of raw materials, as well as determine the direction of pharmacological activity.
Conclusion. For the first time, Rhodiola quadrifida was isolated from raw materials and the structure of 7 majority compounds was proved by NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, which can serve as a foundation for further study of this species of Rhodiola and targeted study of its pharmacological activity in vitro and in vivo, considering the individual phytochemical profile.
Introduction. An urgent trend in pharmacy is the development of application dosage forms with high bioavailability and long-term effect for use in dentistry. Medicinal preparations in the form of gels have a number of advantages over other traditionally used dosage forms for the prevention and treatment of caries. Acyzol, containing zinc in an ionized state, which is part of such preparations, reduces the risk of caries by suppressing the aggressive properties of soft dental deposits.
Aim. On the basis of a step-by-step complex of studies, to develop a dental gel with acisol.
Materials and methods. For the study, we used gels with an active pharmaceutical substance – acisol-bis – (1 – vinylimidazole) zinc diacetate (FC 000286-191211.2011, LLC "Makiz-Pharma", Moscow, Russia, series 101218, shelf life 3 years); basic and gel-forming components – Na-KMC C75 (TU 2231-002-50277563-2000, Base of chemical products "Yugreaktiv", Russia, series 151118, shelf life 3 years), methylcellulose – 35 (TU 2231-107-57684455-2003, JSC "UZPH", Russia, series 221218, shelf life 3 years), sodium alginate (TU 15-02-544-83, Base of chemical products "Yugreaktiv", Russia, series 151018, shelf life 3 years) glycerol (FS.2.2.0006.15 "Glycerin", JSC "Kupavnareaktiv", Russia, series 082018, shelf life 3 years), purified water (FS.2.2.0020.18 "Purified water"). During the research, technological, chemical, physicochemical, physical and biopharmaceutical methods were used.
Results and discussion. As a result of a complex of experimental studies, a composition was developed, a rational technology was proposed, quality indicators were determined, standardization was carried out and a preliminary shelf life of a new dental gel with acisol was established. In the process of gel standardization, methods have been modified and tested, which can be used to establish the good quality of the gel during its manufacture and storage. The degree of release of acyzol from the gel was determined by the conductometric method, informative, fast and easy to perform. The stability of the gel during storage was investigated and a packaging material was selected that allows keeping the quality indicators within the normal range.
Conclusion. The studies carried out have shown the prospects for the development of a gel with acisol. The proposed methods of analysis can be recommended for use to assess the good quality of the gel in the process of manufacturing and storage, as well as for inclusion in regulatory documents.
Introduction. One of the priority directions in the development of modern pharmacy is the search for new highly effective pharmaceutical substances with a high spectrum of pharmacological action and low toxicity. As a result of studies conducted by a number of authors, positive results have been shown for the use of genistein for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases and osteoporosis in menopausal women. It exhibits hypocholesterolemic and antidiabetic effects, as well as radioprotective properties. A comparative evaluation of genistein from soybean seed cake [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] and synthesized by SPC "Pharmzashchita" and the department of chemical technology of medicinal substances, SPCPU was carried out. Studies of natural genistein by GC-MS showed the presence of an admixture of a related isoflavone, daidzein, in the sample. The synthesized genistein was assessed in terms of qualitative analysis.
Aim. The aim of our study was to develop a method for the quantitative determination of genistein for its certification as a CRM.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was 96 % genistein (abcr. Gute Chemie, Германия). Quantitative determination by non-aqueous titration was carried out on a laboratory pH meter F20 (METTLER TOLEDO, USA) in a reagent grade DMFA medium (JSC "EKOS-1", Russia). The HPLC study was carried out on an Agilent 1200 Series high-performance liquid chromatograph LC-20 Prominence (Shimadzu, Japan).
Results and discussion. The method of non-aqueous titration in DMFA medium which recommended by the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XIV edition, titrant 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution, was used as the basis for the development of a method for the quantitative determination of genistein. The end point of the titration was set using thymol blue indicator. However, the difficulty in visual fixation by changing the color of the indicator was noted. It has been proposed to use a potentiometric end-point determination. For the quantitative determination of genistein in dietary supplements and drugs containing this substance a HPLC method was proposed.
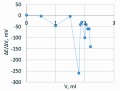
Conclusion. A method for non-aqueous titration of genistein with potentiometric end-point determination in DMFA medium has been developed. The integral curve is not very informative for a clear definition of the titration end point. It is recommended to use a differential curve. The validation evaluation of the obtained results showed that the method is trueness (RSD, % = 1.25), precision (RSD, % = 1.21) and intermediate precision (on the first day of RSD, % = 1.21, on the second day of RSD, % = 1.41).
Introduction. 3D printing has shown its usefulness as a drug manufacturing technology over the past decade. However, the lack of regulated methods for quality control of finished printed drugs imposes a limitation on the widespread use of 3D printing methods in pharmaceutical practice. Thus, the development of methods for the analysis of printed dosage forms is of interest in pharmaceutical development.
Aim. To develop a specific method for the determination of ramipril in filaments and printlets by HPLC.
Materials and methods. Substance: ramipril. Excipients: Kollidon® VA 64, Kollidon® CL-F, PEG-1500, sodium carbonate anhydrous, Poloxamer-188, sodium stearyl fumarate. Reagents: hydrochloric acid, acetonitrile for ultra-HPLC, sodium octanesulfonate for HPLC, orthophosphoric acid 85 %, sodium perchlorate analytical grade, triethylamine. Standard: ramipril USP (No 1598303).
Results and discussion. A special HPLC method in accordance with an ion-pair reagent (sodium octanesulfonate) for the determination of ramipril in the composition of filaments and printets was proposed.
Conclusion. The developed chromatographic method should be adapted for ramipril release determination. This method can be used to quantify ramipril in further studies.
Introduction. The creation of new highly effective drugs requires a thorough study of the metabolome of plant raw materials and a comparative phytochemical study of the underground organs of closely related species of Rumex, such as: R. crispus, R. obtusifolius and R. aquaticus, ubiquitous in Russia. It was noted that they have a metabolome like the official R. confertus, which in turn confirms the potential for studying these species. Of scientific and practical interest is the study of the dynamics of accumulation of the leading group of biologically active substances – anthracene derivatives, depending on the phenological phases of plant development.
Aim. Identify and quantify anthracene derivatives in the underground organs of R. confertus, R. crispus, R. obtusifolius and R. aquaticus harvested in three different phases of vegetation.
Materials and methods. Extracts from the underground organs of the studied plants obtained according to the method from the pharmacopoeial article on R. confertus were used as the analyzed solutions. The solutions were analyzed on a Nexera-i LC-2040 chromatograph (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan) equipped with a column and sample thermostat, a degasser, and an autosampler using an individually selected mobile phase elution gradient (0.1 % phosphoric acid/acetonitrile solution). Primary data were processed using LabSolutions Single LC software (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). Compounds from the group of anthracene derivatives were identified by retention times. Detection was carried out using a UV detector with a dynamic change in the absorption wavelength during analysis from 365 ± 2 nm to 254 ± 2 nm.
Results and discussion. Alcohol-water extracts were obtained from the underground organs of Rumex. An elution gradient was selected for the simultaneous determination of 5 anthracene derivatives with a single analysis time of 40 minutes. These chromatographic conditions made it possible to identify and quantify the content of emodin, 8-O-β-D-glucoside of emodin, and chrysophanol in the underground organs of R. confertus, R. crispus, R. obtusifolius and R. aquaticus in three different vegetations. Glycosides of anthracene derivatives: glucofrangulin A and frangulin A were not found in the studied objects.
Conclusion. Anthracene derivatives were isolated from the underground organs of different vegetations, a method for the quantitative determination of anthracene derivatives in alcohol-water extracts was developed, emodin, 8-O-β-D-glucoside of emodin and chrysophanol were found and quantified.
PRECLINICAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES
Introduction. "Eltrombopag" is a thrombopoietin receptor agonist (TPO-RA) that is approved for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). According to the literature, very few analytical methods for determining eltrombopag in biological samples have been reported. To study the pharmacokinetics of new formulations of eltrombopag, a sensitive and specific method is required that allows one to accurately determine the concentration of eltrombopag in human blood plasma. Normally, HPLC methods should provide time, accuracy, and sensitivity as a result, it is necessary to develop fast or ultra-fast methods such as LC-MS/MS without any loss in sensitivity or separation efficiency.
Aim. We aimed to develop and validate a method for the quantitative determination of eltrombopag levels in human plasma by using HPLC with mass spectrometric detection for performing the analytical part of pharmacokinetic studies.
Materials and methods. Eltrombopag levels were determined in human plasma by HPLC with mass spectrometric detection. The samples were prepared using protein deposition.
Results and discussion. The method was validated for selectivity, matrix effect, calibration curve, accuracy, precision, the limit of quantification, carry-over effect, and sample stability.
Conclusion. The method for the determination of eltrombopag levels in human plasma has been developed and validated by HPLC-MS. The analytical range of eltrombopag levels in human plasma was 10–6750 ng/ml. This method could be used to determine eltrombopag levels in plasma for PK and BE studies.
Introduction. For the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatoprotective drugs are actively used. The existing models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease used to study the effectiveness of medicinal products are characterized by a long duration of recovery and high mortality of test systems, in connection with which, the actual task is to test the screening model of this pathology. A number of studies have shown the hepatotoxic activity of orotic acid (OK), species-specific for rats, leading to the development of NAFLD.
Aim. Approbation of the NAFLD model induced by orotic acid on 2 rodent species (mice and rats), research of the reversibility of pathology under the action of a reference drug (ursodeoxycholic acid – UDCA).
Materials and methods. The reseacrh was conducted on outbred male rats weighing 260–265 g (n = 21) and inbred male mice of the C57BL/6 line weighing 16–18 g (n = 30). By randomization, the rats were divided into 3 groups (7 rats each): group 1 – intact animals; group 2 – NAFLD model; group 3 – NAFLD + UDCA model, mice were divided into 2 groups (10 and 20 mice, respectively): group 1 – intact animals; group 2 – NAFLD model. NAFLD was modeled by a high-carbohydrate diet with orotic acid (75 % standard feed, 24 % fructose and 1 % potassium orotate). UDCA was administered after the first control point 1 time a day through a probe in terms of 150 mg/kg. Biochemical and histological examination was carried out.
Results and discussion. It was revealed that a high-carbohydrate diet with the addition of 1 % potassium orotate for 4 weeks causes moderate balloon dystrophy, mild hepatitis and an increase in the content of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase in the blood of rats and less significant changes in mice. Low animal mortality was also noted. The use of UDCA on the claimed model causes a decrease in the severity of liver dystrophy and a decrease in the level of liver enzymes in the blood.
Conclusion. Based on the conducted experiments, rats turned out to be the optimal test system on the reproduced model, and a high-fat diet with the addition of orotic acid allows screening studies of drugs with hepatotropic activity.
Introduction. In modern oncology, the identification of sentinel lymph nodes (SLN), the first nodes that stand on the way of malignant tumor metastasis, is of increasing interest. Detection of SLN followed by morphological examination allows personalizing the surgical intervention for early breast cancer, melanoma, head and neck tumors, neoplasms of the cervix and endometrium. Currently, there is an active development of specific radiopharmaceuticals for SLN imaging. Within the framework of the grant from the Federal Target Program "Pharma-2020", an original radiopharmaceutical using gamma aluminum oxide – [99mТс]-Al2O3 was developed. Preclinical studies have been demonstrated its effectiveness and safety. Pharmacokinetic studies of [99mTc]-Al2O3 showed that 24 hours after its subcutaneous administration, about 12 % of the administered dose is accumulated in the SLN, which gives possibility for its detection.
Aim. To study the possibility of clinical [99mTc]-Al2O3 using for visualization of SLN in breast, larynx and laryngopharyngeal cancer.
Materials and methods. The definition of SLN was carried out in 55 patients with breast cancer and 30 patients with malignant tumors of the larynx and laryngopharynx. The study included peritumoral radiopharmaceutical injection, single-photon emission computed tomography with qualitative and quantitative analysis of the images and radioguided surgery detection of lymph nodes with their subsequent morphological examination.
Results and discussion. Clinical studies have shown that radionuclide imaging of SLN using [99mTc]-Al2O3 is characterized by high sensitivity in breast cancer, larynx and laryngopharyngeal cancer patients (94.5 and 90 %, respectively), due to the high-intensity accumulation of this radiopharmaceutical in the lymph nodes. The optimal time point for SPECT and radioguided examination is an interval of 18–20 hours after injection of [99mTc]-Al2O3, which allows visualizing the maximum possible number of lymph nodes with the most optimal level of radioactivity for their detection.
Conclusion. Application of radionuclide imaging of SLN with the use of [99mTc]-Al2O3 as a radiopharmaceutical is useful in planning surgical treatment of patients with tumors of the breast, larynx and laryngopharynx to determine the extent of surgery.
Introduction. To date, one of the reasons for the ineffectiveness of chemotherapy in various malignant neoplasms, including lung cancer, is the formation of the multidrug resistance (MDR) phenotype in tumor cells, which is caused by the expression of ABC transporter genes.
Aim. The aim of this work was to assess the expression of ABC-transporter genes during chemotherapy and to analyze the relationship with the effectiveness of chemotherapy and prognosis of the disease.
Materials and methods. We used biopsy and surgical material from 91 patients with stage IIB–IIIA non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The treatment regimen included: 2 courses of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), surgery and 3 courses of adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT) with platinum doublets. RNA was isolated from the samples, followed by quantitative PCR to assess the expression of genes ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2, ABCC5, ABCG1, ABCG2.
Results and discussion. It was shown that the level of expression of the studied genes was not associated with the effect of NAC in patients with lung cancer, except for the ABCC5 gene, which showed a relationship at the level of a pronounced trend (p = 0.07). It was also shown that in the group of patients with an objective response to chemotherapy, the frequency of decreased expression of the ABCC1 (p = 0.01) and ABCC5 (p = 0.004) genes was statistically significantly higher than in the group of patients with stabilization. Further, using the Kaplan – Meier method, it was found that a decrease in expression is associated with high rates of metastatic-free survival (MFS). The highest rates of 5-year MFS (more than 85 %) are observed in patients with a decrease in the expression of the ABCB1 and ABCG2 genes, log-rank test p = 0.0007 and p = 0.002, respectively.
Conclusion. Thus, it has been shown that changes in the expression of ABC transporter genes are associated with the effectiveness of chemotherapy and the prognosis of the disease. The data obtained can be used as a basis for the detection of potential drug targets.
ANNIVERSARY
ISSN 2658-5049 (Online)